1 Conducting EGDs for adults and children
EGDS stands for esophagogastroduodenoscopy. In the process of this study, the mucosa of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum is assessed, and a piece of mucosa is taken for subsequent microscopy. This is necessary in order to exclude the malignant process. The first gastroscopy was invented in the beginning of the XIX century. For two centuries, the technology has been improved.
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method - write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;
Currently, flexible small diameter probes are used, which reduces the risk of esophageal injury and discomfort during the procedure. With the help of FGDS it is possible:
- to get a foreign object;
- remove the polyp;
- take a piece of tissue;
- enter the medicine;
- to stop bleeding;
- conduct electrocoagulation;
- apply ligation;
- determine the state of organs.
EGGS of the stomach is performed in a planned or urgent manner. The first option is much more common. Endoscopy with a diagnostic purpose is carried out within a few minutes.
2 When is recommended and what does the study reveal?
Such a study of the stomach is not done for every patient. There must be grounds for that. The direction to the EGDS is given if the patient has the following symptoms:
- pain in the epigastric region that occurs after eating;
- pain at night and on an empty stomach;
- weight reduction;
- vomiting;
- bloating( flatulence);
- decreased appetite;
- heartburn constant;
- belching sour or bitter;
- disturbed swallowing.
We recommend to read
- Preparing for gastric gastroscopy in the morning
- What is duodenitis of the stomach
- How is preparation for EGD
- effective for gastritis and gastric ulcer
Gastroscopy is organized with suspicion of gastric bleeding. In this situation, the procedure can be performed in an emergency. Fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy is a preparatory measure for operations on the heart, joints and other organs. The doctor who conducts the examination by examining the mucosa may suspect the following diseases:
- obstruction of the stomach and esophagus;
- narrowing of the esophagus;
- esophagitis( inflammation of the esophagus);
- acute gastritis;
- chronic atrophic gastritis;
- ulcer;
- hernia of the esophagus;
- reflux disease;
- neoplasms( tumors, polyps);
- diverticula( protrusion of the mucosa);
- developmental abnormalities;
- cardiospasm;
- duodenitis( total inflammation of the duodenum);
- bulbit( inflammation of the bulb of the 12th gut);
- gastroduodenitis.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
In most cases, a chronic gastritis or ulcer is detected. In the clinical picture, these diseases are very similar, therefore conducting EGDS is an indispensable measure. In the event that there is an ulcer or a tumor is detected, a biopsy is organized.
3 Contraindications to the appointment of a gastroscope
Not all patients are admitted to this study. There are a number of situations when the GHD is contraindicated. Contraindications are absolute and relative. Gastroscopy is not performed if the following conditions exist:
- enlargement of the thyroid gland;
- atherosclerosis of vessels;
- curvature of the vertebral column in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar region;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- coagulation disorder;
- acute myocardial infarction;
- narrowing of the esophagus;
- bronchial asthma in the exacerbation phase.

GDG of the stomach is not performed for people who have had a stroke in the recent past. These are absolute contraindications. Relative restrictions on gastroscopy include the presence of angina pectoris, grade 3 arterial hypertension, and lymphadenopathy in the neck. The study is not conducted in the presence of mental illness and acute pathology of the pharynx and larynx.
4 How to prepare for the procedure?
Preparation of the patient is of no small importance. If the stomach at the time of the study will be food, it will make it difficult to examine the mucosa. The doctor may not see a ulcer or tumor. Preparation for gastroscopy is not difficult. A few days before the EGDS should be followed a diet. It is recommended to abandon nuts, seeds, chocolate, carbonated water and spirits.
-
 Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;

Eating food should not be acute. In the case of narrowing of the esophagus, the training requirements are higher. On the day before the examination, do not need to eat too late. The last meal should be no later than 6 pm. Such a break between dinner and the procedure will completely empty the stomach.
Normally, evacuation of food from this organ occurs in 6-10 hours.
To the stomach was empty, in the morning before the examination you do not need to smoke, breakfast and brush your teeth.

You must skip the medication. Take a towel with the patient.
5 Conducting the
FGDS survey is carried out in the functional diagnostic room. Inspection of mucous is carried out by a doctor. The patient should be lying on the left side during the procedure. Legs should be bent at the knees and pressed slightly to the body. To the patient was not hurt, an anesthetic is used. A person drinks a liquid, and after a couple of minutes the throat becomes numb. The head is located on the pillow.
TIP FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read testimonials & gt; & gt;
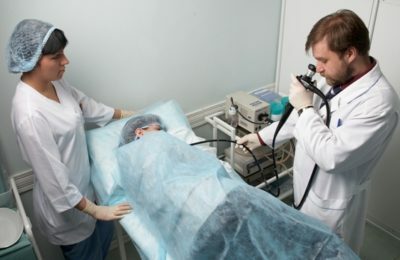
Place a towel under your face. Between the teeth is placed a mouthpiece made of plastic. This is necessary so that a person does not accidentally damage his pipe with his teeth. The doctor enters the probe to the root of the tongue, and then asks the patient to swallow saliva. During swallowing, the probe pushes further. When gastroscopy a patient is not recommended to talk.
After evaluation of the mucosal condition, the probe is removed. Do this slowly, so as not to induce a vomitive reflex. Conclusion is done immediately after the procedure. The doctor during a gastroscopy looks at the screen, where the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum is displayed. After EGDU 1-2 hours a person may have discomfort in the throat. Anesthesia departs slowly. During this period, you do not need to eat food.
6 Advantages and disadvantages of the
method EGDS is unquestionably the main method for diagnosing diseases of the stomach and esophagus. The benefits of this study include the following:
- the ability to visually inspect organs;
- informative;
- is easy to conduct;
- good portability;
- the possibility of exercising in childhood and during pregnancy without harm to the child;
- getting results in a very short time;
- no complicated preparation;
- security.
WE RECOMMEND!
For prevention and treatment of Digestive Diseases our readers advise Monastic tea. This unique remedy consists of 9 medicinal herbs useful for digestion, which not only supplement, but also strengthen each other's actions. Monastic tea will not only eliminate all symptoms of the gastrointestinal tract and digestive system, but will also permanently eliminate the cause of its occurrence.
Opinion of doctors. .. "
Complications after gastroscopy are very rare. Most often this happens when the doctor did not identify possible contraindications. Sometimes the wall of the esophagus is injured, and infection can also be infiltrated. Severe complications of EGDS include bleeding. When there is vomiting, fever, pain in the first days after the examination should visit a doctor.
Sometimes the probe is inserted in emergency situations( in the presence of a foreign body or bleeding).In this case, contraindications may not be taken into account, since there is a risk to life. Thus, the results of FGD are crucial in the diagnosis. In addition, computer tomography, ultrasound, sounding and other studies can be performed.
- 1 Carrying out EGDs for adults and children
- 2 When is recommended and what does the study reveal?
- 3 Contraindications to the appointment of a gastroscope
- 4 How to prepare for the procedure?
- 5 Survey of
- 6 Advantages and disadvantages of
Very often, if a stomach condition is suspected, a gastroscopy is prescribed. Not everyone knows how the EGDS is conducted, what it is and how to prepare for such a procedure. EGDS or FGDS is an instrumental, endoscopic method for examining the stomach, esophagus and the initial section of the small intestine. This is the most simple and informative way to identify pathology.