Non-diabetes mellitus, or diabetes is a fairly rare chronic disease, occurs in about 3 people out of 100,000. This pathology develops most often at the age of 18-20 years, very rarely the disease is congenital.
The cause of diabetes insipidus is a lack of vasopressin production by the hypothalamus, or a violation of absorption of this hormone in the renal tubules.
The mechanism of water absorption in the kidneys
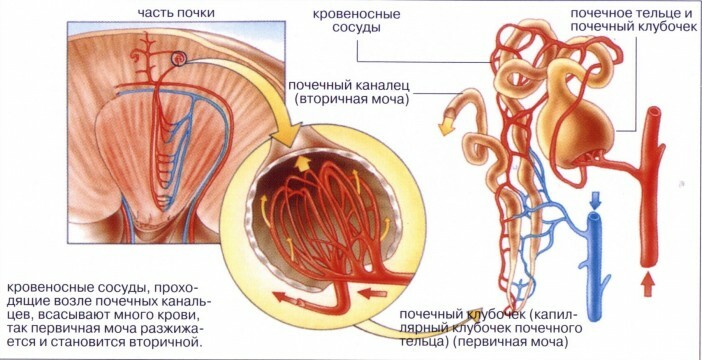
Kidney are the organs of excretion. Dissolved in the blood allergens, toxins, tissue metabolism products( creatinine, uric acid, bilirubin and others) are filtered out and along with excess water are eliminated from the body. Urine formation takes place in two stages:
- Primary filtration. Due to the fact that the lumen of the renal arteries is larger than the diameter of the vascular glomeruli of the kidney, the liquid part of the blood with the tissue exchange products dissolved in it enters the lumen of the Shumlyansky-Bowman capsule( a special cavity for collecting primary urine) and then into the urinary tubules. Primary urine forms.
- In the urinary canals of the nephron, water and substances dissolved in it( amino acids, vitamins, glucose and others) are absorbed back into the bloodstream. Those substances that must be removed from the body( creatinine, drugs, toxins, allergens) are collected by the tubule system in the kidney pelvis and enter the ureter, then into the bladder. Secondary urine forms.
Causes and types of diabetes insipidus
The mechanism of reverse absorption of water and nutrients from the primary urine is regulated by the hormone vasopressin. It is formed in the hypothalamus and accumulates in the neurohypophysis, from where it enters the blood, if necessary. There are several types of diabetes insipidus:
- Neurogenic( central) - when the formation of vasopressin in the hypothalamus or its release from the neurohypophysis is disrupted.
- Nephrogenic( renal) - when the renal tubular receptors are not susceptible to vasopressin.
- Non-diabetes mellitus in pregnant women - is temporary and occurs immediately after childbirth.
- Non-diabetes mellitus of nervous origin. It is the result of the psychological upheavals suffered.

Signs of development of diabetes insipidus are:
- craniocerebral trauma;
- tumors of the hypothalamus or pituitary gland;
- meningitis or encephalitis;
- kidney disease, leading to a violation of vasopressin receptors;
- hereditary pathology.
Symptoms of diabetes insipidus
The disease can start suddenly or develop gradually. Primary symptoms of diabetes insipidus are increased thirst and frequent urination. The amount of daily urine in severe cases exceeds 10 liters( polyuria).In this regard, increased fluid intake, patients experience constant thirst( polydipsia).
And then diabetes insipid symptoms manifests the following character:
- due to lack of fluid in the body, signs of dehydration increase: weight loss, dryness of mucous membranes and skin;
- increases body temperature;
- decreases blood pressure and tachycardia( rapid heartbeat) occurs.
- decreases the separation of sweat;
- increases fatigue;
- due to the arrival of a large amount of fluid stretch the walls of the stomach, there is spontaneous vomiting;
- digestion processes are broken, constipation occurs.
- stretch the walls of the bladder, often patients suffer from enuresis( urinary incontinence);
- because of the constant abundant discharge of urine there is insomnia;
- is broken psycho-emotional state: patients become irritable, suffer from headaches. In severe cases, mental activity decreases;
- in women, in addition to the above symptoms of diabetes insipidus, the menstrual cycle is violated and infertility is often detected. If pregnancy occurs, in most cases it ends in a spontaneous abortion;
- in men decreases potency.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of diabetes insipidus is based on anamnesis and clinical laboratory studies.
When a patient is questioned, attention is drawn to the daily amount of fluid and urine output. With this disease, the average daily diuresis exceeds 3 liters. Frequent nocturnal urge for toilet and thirst is evidence for diabetes insipidus.
Find out what causes the appearance of unusual thirst and frequent urination. If the patient has suffered a craniocerebral injury, has a history of endocrine system disease or is oncology for a brain tumor - it is more likely that in this case polydipsia and polyuria are symptoms of diabetes insipidus.
If the symptoms of the disease disappear under certain circumstances, accompanied by positive emotions( for example, when a person is occupied with a favorite thing or attends a performance, an exhibition) - this indicates a psychogenic form of the disease.
Laboratory diagnosis of diabetes insipidus includes the following:
- Zimnitsky sample - accurate counting of daily drunk and secreted fluid;
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys;
- radiographic examination of the skull;
- computed tomography of the brain;
- echoencephalography;
- excretory urography;
- detailed biochemical blood test: determination of the amount of sodium, potassium, creatinine, urea, glucose.
The diagnosis of diabetes insipidus is confirmed on the basis of laboratory data:
- low urinary osmolality;
- high blood plasma osmolarity;
- low relative density of urine;
- high sodium content in the blood.
The "dryness" test( restriction of fluid intake) is performed when symptoms of diabetes insipidus are expressed, and laboratory diagnostic data do not differ from normal parameters. With the help of this study, it is determined which origin of diabetes insipidus is neurogenic or nephrogenic.
The patient's initial weight is determined, laboratory tests of urine and blood are carried out. The patient stops drinking for as long as he can withstand. At the same intervals, new measurements of body weight are made and the biochemical indices of blood and urine are repeatedly examined. The test is completed if the patient has lost 5% of body weight or has a strong thirst for , his condition has worsened dramatically or laboratory changes have exceeded the norm.
If, as a result of this test, the patient has decreased the amount of excreted urine with the stored body weight and normal sodium content in the blood - a diagnosis of diabetes insipid diabetes is made.
In the case of an increase in the degree of osmolarity of blood and sodium level with a decrease in body weight, a diagnosis is made of diabetes insipidus of central genesis( neurogenic).
Treatment of diabetes insipidus
Therapy begins with the elimination of the causes of the disease. With renal pathology appropriate treatment of diabetes insipidus is carried out, with brain tumors - surgical intervention and subsequent therapy.
Treatment of the disease of the central genesis
After eliminating the reasons, the need for drug therapy is determined. It is indicated when the amount of liquid drunk per day is increased by 4 liters. If less - it is enough for a patient to follow a diet and replenish fluid losses in time.
Drug treatment is performed by analogues of vasopressin( Minirin) and stimulators of the production of this hormone( carbamazepine and Chlorpropamide).Dosages for each patient are selected for several days under laboratory control.
Treatment of renal disease
At a reduced or elevated level, the water-salt balance is restored - intravenous saline solutions and a decrease in the amount of urine. To do this, diuretics are prescribed with thiazides. Their action is to reduce the reverse absorption of chloride ions from the primary urine. As a result, the sodium content of blood decreases and the absorption of water increases. The amount of secondary urine decreases.
Diet for diabetes insipidus
The objectives of therapeutic nutrition for this disease are to fill the deficiency of nutrients lost in the urine, reduce urine output and, accordingly, reduce thirst. Nutrition is recommended in small portions 5-6 times a day, with the following principles:
- Food is practically excluded from salt. Dishes are prepared without salt, the patient receives no more than 5 g of sodium chloride.
- The diet includes potassium-containing dried fruits. They make up the deficiency of the element, which stimulates the synthesis of vasopressin.
- In the daily diet include foods rich in protein - meat, eggs and dairy products. However, the amount of protein should not be more than 60 g per day to reduce the burden on the renal tubules.
- Sweet foods are excluded from the diet, as they increase thirst. It is forbidden to drink alcoholic beverages.
- Recommended daily intake of fresh and boiled vegetables, sweet and sour fruits and berries.
- Loss of liquid and trace elements is well replenished by sour milk drinks, citrus juices, milk and compotes.



