Obsessive-compulsive disorder, called impulse (obsessive) compulsive disorder capable of largely worsen the quality of life of the patient suffering them.
Many patients mistakenly postpone visits to the doctor, not realizing that timely access to specialist reduce the risk of chronic disease and help get rid of obsessive thoughts and panic forever.
The content of the article:
- 1 Description of the disease
- 2 As the disease begins
- 3 Main reasons
- 4 biological
- 5 Social and psychological
- 6 symptoms
- 7 methods of diagnosis
- 8 Can people help themselves?
- 9 methods of psychotherapy
- 10 Medication: lists of drugs
- 11 Home Treatment
- 12 Rehabilitation
- 13 complications
- 14 The forecast for recovery
- 15 Video of the syndrome OCD
Description of the disease
Impulsively (obsessive) compulsive disorder - a violation of human mental activity, manifested by elevated anxiety, the emergence of involuntary and compulsive thoughts that contribute to the development of phobias and hinder normal life patient.
Violation of mental health is characterized by the presence of obsessions and compulsions. Obsessions are thoughts, arising spontaneously in the human mind that lead to the emergence of compulsions - special rituals, repetitive actions that allow to get rid of obsessive thoughts.
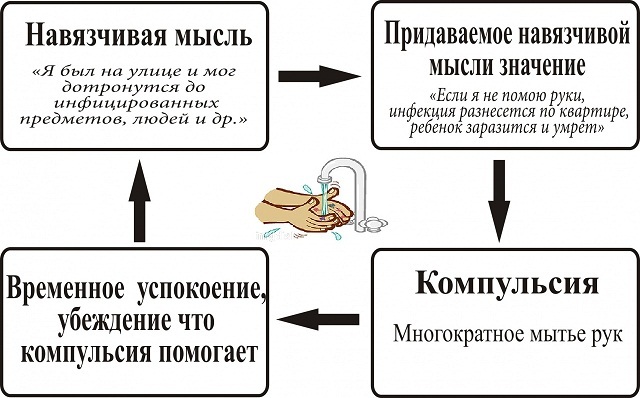
In modern psychology, violation of mental health belongs to the species of psychosis.
The disease can:
- be in an advanced stage;
- be episodic in nature;
- flow chronically.
As the disease begins
Obsessive-compulsive disorder is generated in people aged 10-30 years. Despite the fairly wide age range, patients were treated to a psychiatrist about aged 25-35 years, which indicates the duration of the disease before the first consultation doctor.
Disease are more prone to middle-aged people, children and adolescents disorder symptoms are detected less frequently.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder at the beginning of the formation is accompanied by:
- increased anxiety;
- the emergence of fears;
- obsessions and the need to get rid of them through specific rituals.
The patient at this stage may not be aware of the illogicality and the compulsion of his behavior.
Over time, the deviation begins to deteriorate and flows into active progressive form of the patient:
- can not adequately perceive their own actions;
- He feels severe anxiety;
- unable to cope with phobias and panic attacks;
- require hospitalization and medication.
Main reasons
Despite the large number of studies can not determine the main cause of the formation of obsessive-compulsive disorder. This process may occur as a result of psychological and sociological and biological reasons, which can be classified in tabular form:
| Biological causes of disease | Psychological and social causes of disease |
| Disease and functional and anatomical features of the brain | Violations of the human psyche as a result of the occurrence of neuroses |
| Features of the functioning of the autonomic nervous system | Increased susceptibility to certain psychogenic effects due to the strengthening of individual character traits and personality |
| Abnormalities in metabolism, often accompanied by a change in hormone levels of serotonin and dopamine | The negative influence of the family on the formation of a healthy psyche of the child (overprotection, physical and emotional abuse, manipulation) |
| genetic factors | The problem in the perception of sexuality and the emergence of sexual deviations (deviations) |
| Complications after infectious diseases | Production factors, often associated with long-term work, accompanied by nervous overloads |
biological
Among the biological causes of obsessive-compulsive disorder, scholars have identified genetic factors. Investigation of occurrence of the disorder by studying adult twins led scientists to the conclusion of the moderate hereditary disease.
State of mental deviation is not generated by a particular gene, but researchers have found a link between the formation of the disorder and the functioning of the genes SLC1A1 and hSERT.
People with the disorder, it is possible to observe a mutation of these genes, which are responsible for the transmission of impulses in neurons and the collection of the hormone serotonin in the nerve fibers.
There are cases of early occurrence of illness in a child due to complications after suffering childhood infectious diseases.
As a result of the first study investigating the biological link between the disorder and an autoimmune response of the body, scientists We came to the conclusion that the deviation occurs in children infected with streptococcal infection that causes inflammation of the nerve clusters cells.
The second study looked for the cause of mental deviations in action prophylactic antibiotics taken for the treatment of infectious diseases. Also, the state of the disorder may be due to other reactions to infectious agents.
As for the causes of neurological disease, then using brain imaging methods and its activity scientists were able to establish the biological relationship between obsessive-compulsive disorder and brain parts patient.
The manifestation of symptoms of mental abnormalities of the active part of the brain was activated governing:
- human behavior;
- emotional manifestations of the patient;
- bodily reactions individual.
Excitation of the individual parts of the brain produces in humans a desire to perform some action, for example, to wash their hands after contact with something unpleasant.
This reaction is normal and the urge arose after one treatment is reduced. Patients with the disorder have problems with the termination of these desires, so they are forced to carry out the ritual of washing hands frequently normal, receiving only temporary satisfaction requirements.
Social and psychological
In terms of behavioral theories in psychology obsessive-compulsive disorder it is explained on the basis of the behavioral approach. Here the disease is perceived as a repetition of reactions, which facilitates the reproduction of their subsequent implementation in the future.
Patients spend a lot of energy, constantly trying to avoid situations where there may be panic. As protective reactions patients perform repetitive tasks that can be executed both physically (handwashing checking electric devices) and mentally (prayers).
Their exercise temporarily reduces anxiety, but it also increases the likelihood of recurrence of intrusive action in the near future again.
In such a state often fall people with unstable mentality that subject to frequent stress or are experiencing difficult life periods:
- a break up;

- loss of employment;
- conflict situations;
- exacerbation of mental disorders.
From the perspective of cognitive psychology, the disorder is explained as the inability of the patient to understand themselves, a violation of human connection with his own thoughts. Suffering from obsessive-compulsive disorder are often not aware of the deceitfulness of the value they attach to their fear.
Patients because of fear of their own ideas are trying to get rid of them as soon as possible, using a protective reaction. Reason intrusive thoughts is a false interpretation of them, giving them great value and a catastrophic sense.
Such distorted perception arises from the plant, formed in childhood:
- basal anxietyArising from the violation of a sense of security in childhood (ridicule, overprotective parents, manipulation).
- perfectionism, is to try to achieve an ideal, non-acceptance of their own mistakes.
- exaggerated sense the person responsible for has an impact on society and environment safety.
- hypercontrol mental processes conviction materialization of thoughts and their negative impact on themselves and others.
Also, obsessive-compulsive disorder can cause injuries in childhood or more conscious age and constant stress.
In most cases, the formation of the disease, patients succumbed to the negative influence of the environment:
- They were ridiculed and humiliated;
- clashed;
- experienced over the death of loved ones;
- We could not solve the problems in relationships with people.
symptoms
Impulsively (obsessive) compulsive disorder is characterized by certain signs and symptoms. The main feature of mental deviations can be called a strong worsening in crowded areas.
This is associated with a high probability of occurrence of panic attacks that occur because of fear:
- pollution;
- pickpocketing;
- sudden and loud noises;
- strange and unknown odors.
The main symptoms of the disease can be divided into specific types:
- obsessions;
- images and memories of the intrusive nature;
- obsessive impulses and thoughts;
- obsessional dubiousness of acts;
- aggressive obsessions;
- phobias and fears;
- compulsions;
- movement disorders.

Obsesii - the thoughts of a negative character, which can be represented as:
- words;
- individual phrases;
- meaningful dialogue;
- offers.
These thoughts are intrusive in nature and cause a very unpleasant emotions in the individual.
Repeated human mind images often presented scenes of violence, perversion and other negative situations. Intrusive memories - a pop-up in the memory of the moments of life events, where the individual felt shame, anger, regret or remorse.
Pulses of obsessive-compulsive disorder - a motivation to commit acts of a negative character (in conflict or to use physical force against others).
The patient fears that such pulses can be realized, because of what he feels shame and regret. Obsessive thoughts are characterized by constant disputes patient with himself, in which he treats everyday situations and argues (counter) to solve them.
Obsessive dubiousness of acts and actions with regard to certain doubts as to their correctness or incorrectness. Often, this symptom is associated with the fear of violation of certain regulations and harm to others.
Aggressive obsession - compulsive representations associated with prohibited acts, often with a sexual nature (violence, sexual perversion). Often such thoughts are combined with hatred of the loved ones or popular personalities.
By phobias and fears, which are most frequently encountered can be attributed to an exacerbation of obsessive-compulsive disorder:
- nozofobiya (fear incurable disease);
- thanatophobia (fear of death);
- filth-dread (fear of infection);

- harpaxophobia (fear of being the victim of a robbery);
- phobophobia (fear fear of occurrence);
- ohlofobiya (fear of crowds).
Often phobias may contribute to compulsions - protective reactions that reduce anxiety. Rituals include a repetition of thought processes and the manifestation of physical activities.
Often among the symptoms of the disorder may be noted movement disorders, in the event that the patient is not aware of the groundlessness of obsessions and reproducible movements.
Symptoms of rejection include:
- tics;
- certain gestures and movements;
- Play abnormal repetitive behaviors (biting cube spitting).
methods of diagnosis
Mental disorder may be diagnosed using several tools and methods to identify the disease.

When referring to methods of research on impulse (obsessive) compulsive syndrome mainly isolated deviation diagnostic criteria:
1. Repeated occurrence of intrusive thoughts in the patient, accompanied by the manifestation of compulsions in two weeks.
2. The thoughts and actions of the patient have special features:
- they are, in the opinion of the patient, considered not his own thoughts imposed by external circumstances;
- they repeated long enough and cause negative emotions in a patient;
- man trying to resist the obsessive thoughts and actions.
3. Patients feel that the obsessions and compulsions arising limit their lives, hinder productivity.
4. Formation of the disorder is not associated with such diseases as schizophrenia, personality disorders.
Often used to detect disease screening questionnaire compulsive disorders. It consists of questions that a patient may respond positively or negatively. As a result of the test revealed a tendency of an individual to obsessive compulsive disorder prevalence of positive responses over negative ones.
No less important for the diagnosis of the disease symptoms of the disorder are the consequences:
- a high degree of anxiety and suffering of the patient;

- sense of restraint of liberty, a waste of energy resources to the alarm suppression;
- negative impact on the status of the professional sphere of life;
- the patient's problems in relationships, social isolation;
- behavioral disorders in society.
Additional diagnostic methods obsessive-compulsive disorder great importance is the analysis of the patient's body by a computer and positron emission tomography. As a result of examination of the patient may experience symptoms inner brain atrophy (brain death of neural cells and its compounds) and increased cerebral blood flow.
Can people help themselves?
In the event of obsessive-compulsive disorder symptoms of the patient should be carefully evaluated his condition and contact a qualified technician.
If the patient is temporarily not possible to visit the doctor, you should try ease symptoms yourself using the following guidelines:
- Examine their mental disorder by examining the scientific and educational literature. You must be aware of the main symptoms of the disorder, its causes and symptoms.
- Compare studied materials with its own state. Understanding the internal mental processes is a big step in the treatment of disease.
- Write down the symptoms of mental deviations on a piece of paper and a number of them to describe their own experiences and fears arising from the manifestation of the disease. You must be aware of the invalidity of obsession and anxiety, and think about it every time during acute illness.

- Awareness does not mean getting rid of the disorder, so at this point you can not blame yourself for not being able to resist fear. It is necessary to reward and praise yourself for small steps toward recovery, and success in daily life. During the development of the disease there is a risk to aggravate the mental health self-incrimination, and the depreciation of their own feelings, so tolerance, understanding, caring and loving to her, despite the difficulties, makes it easier to go through the aggravation of the symptoms, to consult specialist.
methods of psychotherapy
Psychotherapy is the most effective way to treat obsessive-compulsive disorder. In contrast to the medical method of suppressing symptoms, therapy helps to understand yourself his challenge and weaken the disease long enough, depending on the mental state patient.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is recognized as the most suitable for the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder. At the beginning of the sessions, the patient meets with the general concepts and principles of therapy, and after a while study of patient's problem is divided into several sections:
- the essence of the situation that causes negative psychological reaction;
- the content of obsessions and rituals of the patient;
- intermediate and deep beliefs of the patient;
- fallacy of core beliefs, search for life situations that provoked the appearance of obsessions in a patient;
- are compensatory (protective) patient strategies.
After analyzing the patient therapy plan formed during the learning disorder who suffer:
- to use certain techniques of self-control;
- analyze their own condition;
- monitor their symptoms.
Special attention is paid to work with the patient's automatic thoughts. Therapy consists of four stages:
-
identification stage. Here the patient learns to find and analyze obsessive thoughts, trained technicians filtering and neglect. For example, the doctor may suggest the patient to master the technique of "stop thinking", which is to stop the memories of the brightest situations manifesting obsessive-compulsive disorder. After a thorough analysis of stressful events the patient learns to control his fear.

- Step distancing. At this stage, the patient learns to separate the automatic thoughts of his personality.
- Test phase of negative thoughts on the validity. During logical analysis is checked truth obsessions.
- A step of replacing negative beliefs on adaptive. Here, the patient's underlying beliefs are replaced with more adaptive. With this technique, the patient is trying to act in accordance with his new conviction, feeling no doubt of its truth. Working with thought-attitudes and actions lead to what suffering from the disorder develops self-confidence, no longer feel anxious and begins to feel more at ease.
Psychotherapy is developing patient awareness and understanding of their own state, it has no negative impact on the the body of the patient, and generally shows a very beneficial effect on the process of treating obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Medication: lists of drugs
Impulsively (obsessive) compulsive disorder often requires medical treatment by application of certain drugs. Conducting therapy requires a strictly individual approach that takes into account the patient's symptoms, age and the presence of other diseases.
The following medications are used only on doctor's prescription and taking into account special factors:
- features of display disorder;
- age, sex of the patient;
- presence in the patient burdeness other diseases.

| antidepressants | Luvox, Zoloft, clomipramine, amitriptyline |
| anxiolytics | Phenazepamum, clonazepam |
| antipsychotics | etaperazin, haloperidol |
| mood stabilizers | carbamazepine, Depakine |
| nootropics | Phenibut, Pantogamum |
Home Treatment
It is impossible to pinpoint a universal method of getting rid of the disease, because each patient suffering from a disorder, an individual approach and special treatments.
Specific instructions for self-healing of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the home does not exist, but it is possible to allocate the general tips that can help to ease symptoms of the disease symptoms and avoid deterioration of mental health:
- it is your responsibility to try to neutralize the negative thoughts and doubts, do not let them bring yourself to anxiety and panic attacks;
- it is desirable to monitor the state of mind and do not give yourself quibble over minor details and events where perfectionism requires perfect execution of tasks;
- do not try to drown a serious condition of alcohol, tobacco and other psychoactive substances. Their use will only aggravate the disease will cause addiction and eliminate the possibility of self-maintain the normal functioning of the body;
- should follow the normal sleep mode, to avoid lack of sleep;

- you must try to give the body enough time to rest;
- it is desirable during the illness to try to distract themselves in any activity - sports, painting or music. Depending on individual preferences, you need to find something that will distract from the obsessive thoughts and allow to relax;
- when a problem occurs, it is worth trying to look at it from the side to examine their feelings and relieve tension in physical labor or leisure. It is important not to blame yourself for the manifestation of fear, and recognize the presence of the disease, which is a big step towards his treatment.
Rehabilitation
Obsessive-compulsive disorder is characterized by irregularly changing the character, so, regardless of the type of treatment, any patient can feel an improvement after some time.
After maintaining conversations, inspiring confidence and hope for recovery, and psychotherapy, which are produced by methods of protection from intrusive thoughts and fears, the patient feels much better.
After the recovery phase begins social rehabilitation, which includes determining the ability of training programs needed for a comfortable self-awareness in the society.
These programs include:
- development of communication skills with others;
- learning the rules of communication in the professional sphere;
- the formation of understanding of everyday communication;
- development of proper behavior in everyday situations.
rehabilitation process aimed at forming a stable psyche and building personal patient boundaries, finding them faith in their own strength.
complications
Far not all patients can be cured of obsessive-compulsive disorder and undergo a full rehabilitation.
Experience has shown that patients with disease which are in the stage of recovery, are prone to relapse (resumption and exacerbation of disease) so only as a result of successful therapy and independent work on a possible to get rid of symptoms of the disorder for a long time.
The most probable complications of OCD include:
- depression;
- increased anxiety;
- suicidal tendencies;
- substance use;
- eating disorders;
- inability to communicate with people;

- increased aggression, inability to control themselves;
- isolation and social exclusion.
The forecast for recovery
Impulsively (obsessive) compulsive disorder - a disease that often takes place in the chronic form. Full recovery for this mental disorder is rare.
In the mild form of the disease results from the treatment start to occur no earlier than 1 year of regular therapy and possible adoption by the drugs. Even after five years after the detection of disorders the patient may feel some anxiety and symptoms of the disease in their daily lives.
A severe form of the disease is more resistant to treatment, so patients with this degree of disorder are prone to relapse, resumption of the disease after an apparent complete recovery. This is possible due to the stress and exhaustion of the patient.
Statistics show that the vast majority of patients improve mental states appear after one year of treatment. By behavioral therapy a significant reduction of symptoms by 70%.
In severe cases of the disease possible negative outlook disorder that manifests itself in the appearance of:
- negativism (behavior when a person speaks or behaves demonstratively oppositely expected);
- obsessions;
- major depressive state;
- social exclusion.
Modern medicine does not emit a single treatment impulsively (obsessive) compulsive disorder who have guaranteed to relieve the patient from negative symptoms forever. To regain the mental health of the patient should be promptly see a doctor and be prepared to overcome internal resistance on the way to a successful recovery.
Author: Anna Fleyman
Registration of the article: Vladimir the Great
Video of the syndrome OCD
The doctor will tell about obsessive-compulsive disorder:




