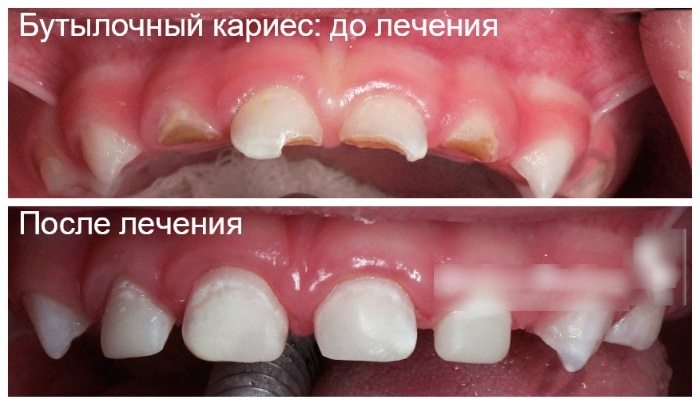
Stomatitis refers to one of the most frequent inflammations of the oral cavity. In children, aphthous stomatitis appears on the inside of the mouth mucous areas and develop as an independent disease. In adults, aphthae may also be a symptom associated disease, which did not receive adequate treatment.
The content of the article:
- 1 Aphthous stomatitis - especially diseases
-
2 forms of the disease
- 2.1 chronic recurrent
- 2.2 acute stomatitis
- 3 Where can appear aphthous stomatitis
- 4 diagnosis of the disease
-
5 Treatment of acute forms of aphthous stomatitis
- 5.1 adults
- 5.2 children
-
6 Therapy of chronic forms of the disease
- 6.1 In adult patients
- 6.2 children
- 7 The formulations with the fast action with aphthous stomatitis
- 8 Prognosis of the disease in children and adults
- 9 Videos about aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis - especially diseases
Stomatitis - protective adaptive process in the mouth that occurs in response to injury or the pathogenic effects of the stimulus. Inflammation of the oral cavity is more common in children of preschool age.
In medicine, there are several types of the disease:
- aphthous;
- allergic;
- vesicular;
- herpes;
- catarrhal;
- traumatic;
- Ulcerative.

If left untreated canker sores it can develop into necrotizing
Aphthous stomatitis is manifested in the form of fine white-yellow oval shaped formations on the mucosa, which is called aphthae. Aphthae differ from ulcers that have a lower degree of damage, which does not leave scars.
The disease accompanied by painful sensations at the site of damage, increased salivation and enlarged lymph nodes (submandibular). Inflammation occurs each in different ways, and held an average of 7-14 days, depending on the chosen method of treatment.
forms of the disease
Aphthous stomatitis (treatment in adults and children depending on the type and stage of the disease) has two types: acute and chronic.
chronic recurrent
The majority of patients experienced chronic disease that is recurrent in nature. Basically, this is due to lack of timely treatment of acute stomatitis or permanent availability of the allergen. The cause of the chronic type of disease may also be a blood disease, manifested in a lowering of neutrophil assays.
Aggravation observed in response to the slightest stimuli:
- cold;
- spicy and salty foods;

- weakening immunity against viral or bacterial diseases;
- constant tension and stress;
- the use of hot liquid;
- antibiotics.
With the development of chronic aphthous stomatitis exacerbation occur no more than 2-3 times in the first year. Failure of control measures provoking factors increases the number of recurrences.
Symptoms exacerbations coincide with symptoms of an acute form of the disease which is characterized mainly by itching and soreness of oral mucosa.
acute stomatitis
Acute stomatitis most susceptible to pre-school children, whose immune systems are at a formative stage.
Aphthous stomatitis has three steps:
- Elementary. The symptoms of aphthous stomatitis type reminiscent of the beginning of SARS: there is a malaise, loss of interest in food, the temperature rise (slightly in most cases). In this case, noted an increase in neck, jaw and cervical lymph nodes.
- Manifestation of the first external symptoms. The patient was observed for the formation of erosive mucosal entities within the oral cavity, which are accompanied by redness, severe pain at a contact tongue and itching. Pain is a response to any stimulus, e.g., during a meal or liquid. Aphthae may occur in different quantities: single or multiple small eruptions. The amount of such entities does not exceed 5 mm in diameter. Ignoring the symptom leads to its strengthening: erosion spread quickly on the inner surface of the mouth and in severe cases flow in the cheek, palate and tongue.
- Healing. Aphthae disappear within 1-2 weeks during the necessary treatment. In the process of healing damaged mucosa recovers without scarring because the formation of aphthous not affect the deeper layers of the inner membrane of the mouth.
Trigger the development of acute stomatitis of this type may different factors:
- mechanical stimuli - the sharp edge of the teeth, incorrect size fillings, biting the inside of the cheek or other trauma;

- products - citrus, spicy, nuts, chips and so on.
- bacteria, fungi and viruses.
Erosion also appear in the background of other diseases of the intestine or stomach, lack of vitamins and constant stress.
Where can appear aphthous stomatitis
Localization of canker sores depends on the severity of the disease, but most often aphthae appear in places like:
- the inner side of the cheeks;
- lip mucosa within the oral cavity;
- gums;
- sky;
- language;
- under the tongue.
- cheek (for acute and severe).
Stomatitis occurs because immune responses to foreign molecules: Protective cell lymphocytes react to new particles, resulting in the formation of ulcers and aphthae.
When you join a bacterial or viral infection, and the symptoms affecting the upper respiratory tract: the throat and nasal passages. It appears on the surface of the mucous erosion formation, redness and swelling. At the beginning of the disease, before the formation of the AFL, the manifestations of stomatitis can be confused with the development of acute respiratory viral infections or sore throats.
In babies thrush can occur due to trauma of the sky, in this case we speak about aftah Bednar.
In infants, the damage caused by the sky more often:
- large dimensions and excessive stiffness pacifiers;
- rough skin damaged nipple;
- mechanical trauma inside the oral cavity due to improper maintenance.
Causes sores on the mucous membrane of the lips and cheeks are also poor hygiene (dirty hands in your mouth, unwashed bottle, poor hygiene breast of the mother).
diagnosis of the disease
If the following symptoms should immediately consult your pediatrician (for children), physician or dentist:
- general depression, weakness;
- pain and itching in the mouth;
- aphthous education.
In infants, among other manifestations noted by other symptoms: crying, insomnia, not eating that occur against a background of strong pain or palate of the mouth. On examination, the doctor will conduct a thorough diagnosis of the oral cavity with a mirror and light.
On stomatitis also indicate:
- appearance plaque;
- swelling of the affected areas;
- temperature rise.

To clarify the cause of the doctor may prescribe laboratory tests, the results of which will determine the method of treatment. An important point in the process of diagnosis is considered dental check-state, in particular, fillings and veneers: their degree of fit and the possibility of traumatizing the mucous.
Treatment of acute forms of aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis, therapy in adults which runs considerably lighter, characterized by several approaches to therapy, and age-dependent form of the disease. The presence of one or a maximum of 2 erosive formations requires initiation of therapy, since in most cases they are alone.
However, when a large number of aphthae mouth doctor compulsorily assigns pharmacological treatment aimed at eliminating the symptoms and improving oral health.
adults
After the diagnosis the doctor, first of all, appoints conduct daily disinfection of the mouth antiseptic preparations:
- Miramistin as a spray: 3-4 puff per day.

- Chlorhexidine 0.2 - 0.5%: required mouthwash 1 tbsp. l. solution. Disinfection procedure no more than 30 seconds should be carried out. A solution of 0.5% is recommended to dilute 1-2 tbsp. l. water.
- Furatsilinom: 2 tablets are dissolved in 200 ml of warm water and treated in the mouth throughout the day for 30-60 seconds.
Rinse these agents prevent attachment of further infection and spread of the AFL. In the event of a strong burning sensation, especially after Chlorhexidine and Furacilinum, the concentration of drug necessary to reduce: chlorhexidine diluted in 1-2 tbsp water and Furatsilinom 250-300 ml of warm water. After the procedure, it is not recommended to eat and drink within 60 minutes.
To facilitate the ingestion and the general condition of prescribed painkillers:
| Title | Dose |
| Benzocaine tablets | Table 1-4. a day at regular intervals. |
| Lidocaine Asepta (spray) | 1 dose (puff) 3-4 times a day. |
| Geksoral Tabs | 1 tab. every 2 h. The maximum dose per day 8 pi. |
Most anesthetic drugs also have antiseptic and antibacterial properties. The latter are used in the presence of a bacterial infection caused by the weakening of local immunity. Antibacterial drugs prescribed in various forms: ointments, sprays, tablets.
The most popular means for the treatment of stomatitis are:
-
Geksoral solution - combining antiseptics, analgesics (a slight degree) and antimicrobial properties. 15 ml of a solution used for rinsing the mouth for 30 seconds. Do not swallow!

- Holisal gel. In addition to anesthetic and antibacterial properties, anti-inflammatory effect. A small amount of gel in a 1 cm length is applied massaging movements to the affected area two times daily after or before meals (for pain relief).
- Kameton. The antibacterial agent in the form of spray, the treatment must sputtering 2-3 3-4 times per day.
When you join a viral or fungal infection of nature apply in addition:
- Acyclovir or Zovirax (herpes) 1 tablet 5 times per day.
- Nystatin ointment Levorinum (1-2 times a day topically) from fungi.
Strengthening the immune system plays an important role in the treatment of canker sores.
lack of vitamins help to correct various mineral and vitamin complexes:
- Alphabet 3 tab. per day (each containing a different substance);
- Vitrum 1 tab. per day.
- Gendevit 1-2 pills a day.
During the last stage of healing are assigned keratoplasty - drugs which promote mucosal tissue regeneration processes:
- Solkoseril.
- Karatolin.
- Proposol.
Drugs applied topically 2 times a day. Before treatment is necessary to disinfect the affected area.
For successful treatment it is recommended to abstain from alcoholic beverages, spicy, salty, pickled foods, which can trigger the rapid spread of aphthous formations. At the same time, patients are changing toothbrushes, thoroughly disinfect the spoons and forks after eating.
children
Aphthous stomatitis (treatment in adults and children is different dosing regimen) in preschool children requires stricter hygiene rules and standards of care. 
Combined therapy of stomatitis moderate and severe stage often involves taking the following groups of products:
| drugs group | Title | The dose per day (b. - times) |
| Analgesics and antipyretics (with temperature). | Nurofen for children - suspension. | 3-6 months 2.5 mL of 3 r. Months 6-12: 2.5 ml of 3-4 p. 1-3 years: 5 mL of 3 r. 4-6 years: 7.5 mL of 3 r. 7-9 years: 10 mL of 3 r. 10-12 years: 15 mL of 3 r. |
| Panadol Junior bags. | From 3 to 6 years old: 1 bag up to 4 times. From 6 to 12 years: 1-2 bags of up to 8 times. |
|
| Antisepsis with antimicrobial effect. | Miramistin. | 3-6 years: 1 zilch 3-4 p. 7-14 years: 2 zilch 3-4 p. |
| Stomatidin. | 5 years and over: 10-15 ml rinse. | |
| Antiviral. | Viferon 150,000 IU. | children under 12 years: 1 supp. 2 r. every 12 hours. |
| Anaferon children. | 10 cap 3 on p. In the first receiving chasa 2: 10 cap. every 30 min. . | |
| Antibacterial. | Geksoral Tabs | 4-12 years: 1 tablet up to 4 p. |
| Holisal. | For children: to 0.5 cm gel strip smear on aftam. |
The most commonly prescribed disinfectants and antimicrobials, anti-pyretic and anti-viral drugs are normally used in the case of accession of symptoms of viral infection. diet change will play a positive role in the treatment, it is necessary to eliminate the acid and citrus products, which can trigger a burning sensation of affected areas.
Do not be amiss to spend chamomile mouthwash or other pharmacy decoction.
Rinse children under 3 years carried out as follows:
- Prepare a solution or broth.
- Tilt the child's head to the side so that one of the corners of the mouth at the top and the other - from the bottom.
- Mark needleless syringe, fill it with antiseptic and enter into the mouth to the upper cheek fluid should be poured back from the cavity bottom.
The procedure is best done in the bathroom over a basin, as some teas have coloring properties (oak bark).
It is also necessary to reconsider the objects of care for children's teeth: Change to a softer brush, excluding toothpaste with sodium lauryl sulphate. Should be possible to limit the sucking fingers or pacifiers, all feeding bottles should be carefully treated with antiseptics.
Therapy of chronic forms of the disease
The chronic form of the disease requires a comprehensive approach, which includes:
- Sanitation of the oral mucosa.
- Anesthesia.
- Disinfection.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Agents affecting skin;
- Vitamin therapy.
- Probiotics, enzymes.
- Immunomodulatory drugs.
- antihistamines
Treatment of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis is slightly different in adults and children.
In adult patients
Aphthous stomatitis treatment of the chronic form has the same principles of treatment as an acute form of the disease. In addition, analgesic, antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, keratoplasty funds used immunomodulatory drugs that stimulate the production of interferon (protection of cells against viruses):
- Imudon: 6 tab. a day for 20 days.

- Polyoxidonium: 1 tab. 2-3 times a day for 10 days.
- Galavit: 1 tab. 4 times a day. The course of treatment - 10 days.
Dosage shown is a treatment of chronic diseases of the oral cavity. In the presence of concomitant diseases and gastrointestinal digestive system prescribe drugs improving intestinal microflora (Normobakt, Lineks).
Depending on the cause of disease in remission doctors can also write:
- Antihistamines (Suprastin, hystoglobulin).
- Hormonal medications (Prednisone).
Because the nature of the development of chronic canker sores are not fully defined, the treatment of the disease should take place under the supervision of a doctor who at the slightest negative changes revise the treatment plan in favor of a more effective.
children
During exacerbations regimen did not differ from the treatment of acute stomatitis. Chronic diseases require constant readjustment of the oral cavity and removing the risk of mechanical irritation of the mucosa.
In addition, you should take immunomodulatory and anti-allergic drugs, the most popular of which are, respectively:
- Polioksidony: Table 0.5. 2 r. in a day.
- Suprastin: Table 0.5. 2-3 p. in a day.

The course of treatment determined by the physician based on the severity and number of disease recurrence. Children of preschool age stomatitis relapses occur more frequently than in adults, so do not delay the campaign to the doctor, even during remission.
The formulations with the fast action with aphthous stomatitis
Timely initiation of treatment reduces the risk of complications and chronic forms bolzeni.
At the first signs should:
- Immediately be disinfected with a solution of chlorhexidine, which is one of the most powerful antiseptic. Mouth rinse will suffice 10-15 ml. rinse time should be 30 seconds, but no longer, as may increase burning.
- Strong pain relieve local analgesics, which include Geksoral as a solution. It cleans the mucous and has a mild anesthetic effect. It is also possible to use tablets of the same name.
- Anti-inflammatory external preparations will help to quickly cope with the swelling and soreness of the AFL: Holisal or Vinylinum are the most popular tools in the treatment of stomatitis. Formulations inhibit the growth of bacteria and reduce the severity of inflammation.
- prescribe antibiotics (Sumamed, Azitroks) and antiviral drugs (Viferon, Anaferon) When joining a bacterial or viral infection.

During the entire course of treatment, and he is 7-14 days on average, the patient is strictly not recommended drink irritate the food: nuts, chips, sunflower seeds, pickles, citrus fruits. One of the treatment options available is excessive drinking and continuous rinsing the mouth and throat after ingestion of food.
After therapy is recommended to take a course of vitamin and mineral resources, which make up for the lack of nutrients and reduce the chances of relapse. During remissions pediatrician may also prescribe physiotherapy (phonophoresis, electrophoresis). In rare cases, the use of helium-neon laser.
Prognosis of the disease in children and adults
Aphthous stomatitis, therapy in adults does not result which can lead to the deterioration of health and development of the following diseases:
- rheumatism - joint pathology;
- cardiovascular disorders;
- Adamantiadis disease - inflammation of blood vessels in the mucous membrane of the eyes, mouth, skin and genitals.
Performing the doctor's recommendations and improve hygiene standards will allow to overcome the disease and stop it in time. Prognosis of the disease is favorable, Ata did not leave behind a scar and, in most cases, disappear after treatment.
Aphthous stomatitis treatment of nature in adults and children requires the involvement of a competent pediatrician or general practitioner. Often the cause of development is lack of hygiene of the oral cavity, digestive system diseases, viral infections, bacterial and fungal nature.
Author: Guriev Natalia
Registration of the article: Mila Friedan
Videos about aphthous stomatitis
Elena Malysheva tell about aphthous stomatitis: