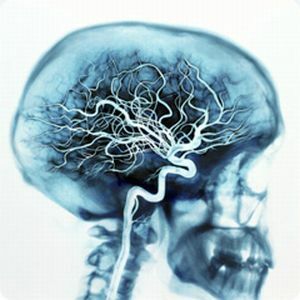
 Moya - Moya disease is a rare disease characterized by a progressive nature of bilateral nature, leading to a narrowing of the intracranial arteries, which eventually leads to a malfunction in the bloodstream of the brain. The disease itself can ultimately lead to the development in acute form of a malfunction in the cerebral circulation - stroke, insufficient supply of gray matter with oxygen and nutrients.
Moya - Moya disease is a rare disease characterized by a progressive nature of bilateral nature, leading to a narrowing of the intracranial arteries, which eventually leads to a malfunction in the bloodstream of the brain. The disease itself can ultimately lead to the development in acute form of a malfunction in the cerebral circulation - stroke, insufficient supply of gray matter with oxygen and nutrients.
A characteristic feature of the pathology is the formation of a network of collateral vessels in the base of the brain - when examined in photographs, they create the effect of light darkening, haze. It was this characteristic feature that was discovered in 1967, which gave the modern name of the pathology - in translation from Japanese my - my translate as a ball of smoke.
In accordance with the classification of ICD-10, the disease is enrolled in the category of cerebrovascular pathologies. Most pathology affects patients under 10 years old or in the age range from 30 to 49 years, while women are 1.5-2 times more susceptible to disease than men.
Where lies the cause of the disease?
The main reasons for the development of this disease by scientists have not been established for certain - many scientists are inclined to consider it a hereditary pathology, with an autosomal dominant type of inheritance characteristic for it. Not so long ago, doctors and scientists made a discovery - loci were discovered in the human body responsible for the development of the Moya-Moya disease. But this assumption has not yet been scientifically substantiated.
According to other assumptions - the disease is a nonspecific form, the result of an autoimmune reaction, provoked by the inflammatory process. So in some scientific publications statistics are shown that in 7 out of 10 cases the pathology is associated with the previously transferred sinusitis and otitis.
Features of the development of
The leading pathogenetic process of the development of the disease is a progressive occlusion of the vessels through which the
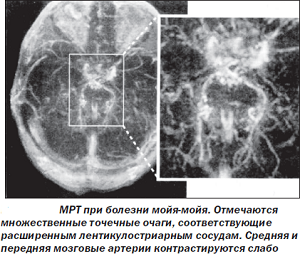
MRI brain diagnoses Moya-moya
disease receives oxygen and nutrients and most often affects primarily the level of bifurcation of the internal carotid artery.
In this case, the blood flows through the vertebrobasilar system of blood vessels and arteries and as a consequence - the formation of a collateral vascular network on the base of the brain. In the case of progression of the disturbance, the external carotid artery may be involved in the pathological process, as a consequence the patient develops a second anastomosis network in orbit. At this stage, the formation of ischemic foci in the brain.
In practice, physicians identify 2 possible ways of developing aneurysms:
- in a typical artery and aortic artery, which can lead to profuse internal bleeding;
- formation of multiple, small in size, miliary aneurysms, subject to thrombosis.
With untimely diagnosis of pathology and its intensive development, the disease can cause a cerebral infarction.
Symptoms of the disease
Moya-Moya disease is marked by a specific set of characteristic features. Among these, physicians distinguish the following:
- is chronic by nature, disturbing the patient constantly attacks of headache - especially such attacks disturb the patient in the morning and at night;
- attacks of weakness in the arms and legs of , gradually turning into paralysis of the limbs, the inability of the patient to independently move them;
- loss of nerve endings on a particular part of the body of sensitivity - the patient feels neither cold nor
 heat, no injections;
heat, no injections; - disturbances in speech activity - slurred speech, patient's inability to fully pronounce words and sentences, patient's misunderstanding of the meaning of words in his native language;
- vision problems , which can manifest themselves in the form of reduced sharpness, darkening in one or another field of view, the ability to see a limited area of space in front of you;
- disorders in the consciousness of , fainting and fainting, darkening before the eyes and tinnitus.
Diagnostic process
Diagnosis of pathology is simple enough, but due to the fact that the disease is rare and resembles many cerebrovascular diseases of the brain - it is not always possible to identify it in time.
The diagnostic process itself consists of the following items:
- Collecting an anamnesis of the course of the disease, interviewing the patient .At this stage, the doctor specifies the age at which the patient is concerned about headaches, if there is any weakness in the limbs and when the weakness began to appear, the vision problems.
- Conducting a neurological examination of - it is aimed at identifying and diagnosing the neurological nature of the disease. In particular, the doctor finds out whether the patient has paralysis, whether the level of sensitivity is broken on one or another part of the body.
- For the precise diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the brain - this diagnostic method allows you to study the gray matter thoroughly, by layers, to assess how narrow the vessels inside the skull are in the Moya-Moya disease.
- Assignment of angiography of cerebral vessels - in this case, an X-ray of the brain is performed using a contrast agent, which is injected into the vascular system and takes a series of pictures. A special sign, which will specifically point to this pathology, is the formation in pictures of such a picture resembling a cigarette smoke, frozen in the air.
- If necessary, the patient can be referred for counseling and examination from such narrowly specialized specialists as neurologist and neurosurgeon .
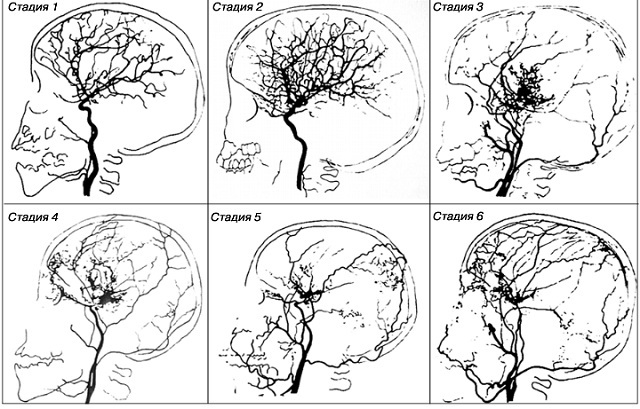
Stages of the development of the disease My-my
Complex of therapeutic measures
In the course of treatment of the Moya-Moya disease, doctors can prescribe both a conservative course of treatment and apply radical techniques.
 Regarding the appointment of a conservative method of treatment, doctors most often prescribe vascular therapy, prescribing the chicken admission of such drugs as Cavinton and Instenon, Sermion, Nifedipine.
Regarding the appointment of a conservative method of treatment, doctors most often prescribe vascular therapy, prescribing the chicken admission of such drugs as Cavinton and Instenon, Sermion, Nifedipine.
In addition, medics can be prescribed and neurometabolic therapy, prescribed drugs such as Aminalon, Piritinol, Nootropil. The appointment of such drugs will significantly improve the overall condition of the patient, the very clinical picture of the pathology, but still they can not stop the very progression of the disease.
When diagnosing a severe form and in case of a stroke, the patient is prescribed an intensive care course - it is continued until the patient's general condition is stabilized. In the case of development of an ischemic form of a stroke, the doctor prescribes a course of taking either anticoagulants or drugs classified as antiaggregants.
For surgical intervention, this method is more radical and in this case, physicians perform an operation that results in the formation of a separate vascular shunt that will supply blood to the brain, avoiding stenotic arteries.
Shunt can be performed as a direct method - in this case, the necessary level of blood supply is achieved immediately, and indirectly - in this case, the result of normalization of blood flow in the brain is achieved after a certain period of time, taking from six months to a year of time.
As the statistics show, the greatest effect is achieved with a direct shunting method, after which the problems with ischemic attacks are diagnosed only in 10 patients out of 100. In the case of indirect vascular withdrawal pathologies are diagnosed after operation in 56% of operated patients.
Consequences and prognosis of
If timely diagnosis of pathology and surgical intervention takes place, bypass surgery - doctors give very patient-friendly outcomes. So according to statistics in 84% of surgical intervention gives a positive dynamics of treatment.
In the absence of a course of treatment, the patient has an increase in the pathological pathology in a negative dynamics, cerebral hemodynamics is observed - as a consequence, the progression of neurologic deficit, ischemic stroke.
For the lethal outcome - in children the percentage is at 4.3, in adults - 10%.In the issue of preventive measures, doctors have not established what measures can serve as an obstacle in the development of this pathology, since the true reasons for its development in the patient have not been established for certain.
