The human musculoskeletal system undergoes various static and dynamic loads. At the same time, various diseases can develop which are the result of the spinal reaction to this load.
So, the impact on intervertebral disks, consisting of cartilaginous tissue, leads to the development of osteochondrosis of intervertebral discs in various departments. This is the name of the degenerative degenerative process that occurs in the cartilage.
What will happen if this process does not arise in the cartilaginous tissue, but in the ligaments of the intervertebral joints?- Spondyloarthrosis will develop.
Contents of
- 1 What is spondylarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine?
- 2 Causes of development of spondylarthrosis
- 3 Symptoms of spondylarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine
- 4 About diagnosis of spondylarthrosis
- 5 Treatment of spondylarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine
- 6 Prophylaxis of spondylarthrosis
What is spondylarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine?
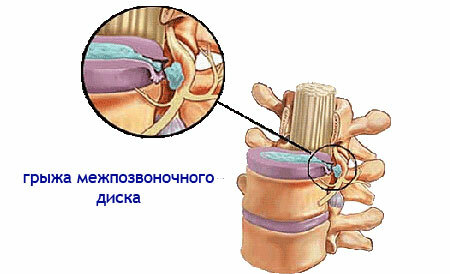
It is known that the mobility of the spine in all its departments, mainly depends on the elasticity of the intervertebral discs. This is true. But between the vertebrae there are other joints that are not equipped with discs. They are called faceted.
They received their name from a small size of articular surfaces, which are quite numerous, and the ligaments in the spine are strong. Therefore, they are inactive, and can be degenerated. Now we come close to answering the question "What is this?"
In fact, the spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine is a common arthrosis, only developing in the small joints of the spine, which is chronic, and leading to a restriction of mobility, in this case - inlumbosacral spine.
In addition to the term "spondyloarthrosis" there may be a name for spondylosis. The difference between these concepts is that spondylosis affects the anterior longitudinal ligament, which undergoes calcification, and the joints of the spine are less affected, and degeneration is less pronounced in them.
Features of the lumbosacral section are more massive vertebrae, a high load on them, greater mobility, as well as the presence of a single sacral bone into which five vertebrae have fused.
Therefore, all manifestations of arthrosis( the appearance of osteophytes, the development of stiffness) is possible only in the overlying department, or in the lumbar.
It is clear that only moving surfaces can experience pressure against each other, and in the sacral bone these phenomena are absent. Only arthrosis of the sacroiliac joints is possible, as well as their inflammation - sacroiliitis.
Causes of development of spondylarthrosis
 Spondylarthrosis, like any involutionary disease, depends on age and metabolic disorders. It has much in common with other causes of arthrosis, which are localized in other places, for example, in knee or shoulder joints. The most common causes of spondylarthrosis are as follows:
Spondylarthrosis, like any involutionary disease, depends on age and metabolic disorders. It has much in common with other causes of arthrosis, which are localized in other places, for example, in knee or shoulder joints. The most common causes of spondylarthrosis are as follows:
- Disturbance of phosphoric-calcium metabolism;
- Osteoporosis, especially in postmenopausal women;
- Diabetes mellitus and thyroid disorders;
- Spinal Injuries and Consequences of Fractures;
- Sacralization of the lumbar vertebra or lumbalization of the sacral. So called congenital anomalies, in which either the last, the fifth lumbar vertebra "grows" to the sacral bone, or the first sacral vertebra is separated from the sacral bone. In this case, 6 vertebrae arise in the lumbar region, and their excessive mobility provokes the development of the load;
- Occupation of professional sports, leading to increased workload;
- Office work and sedentary lifestyle;
- Disturbance of posture and deformation of the spinal column( kyphosis, kyphoscoliosis of the overlying divisions);
But, of course, the main reason for the development of spondylarthrosis is osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. Intervertebral discs, devoid of elasticity, become thinner, and the articular surfaces, together with the ligament apparatus of the arcuate joints, begin to experience significant loads.
Symptoms of spondylarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine
 Because of the chronic joint disease, the main symptom is back pain.
Because of the chronic joint disease, the main symptom is back pain.
As a rule - this aching pain of low intensity, which is given( irradiated) from the waist in the pelvis or in the leg. Irradiation never falls below the knee, and pain can only be given up to the middle of the thigh or higher.
Characteristic of pain and discomfort in case of prolonged sitting and immobility, but also, on the contrary, with severe physical exertion on the lumbar spine, for example, when carrying a heavy backpack.
In case the disease continues to progress, then soon such a symptom of spondyloarthrosis as stiffness joins pains. Most often it appears in the morning, and lasts for several minutes to an hour. Then it passes. Then the stiffness can last several hours, and become a constant companion.
This symptom of spondylarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine indicates a significant decrease in the elasticity of the ligamentous apparatus and pronounced osteophytes in the vertebrae.
In addition, stiffness may have a secondary nature, when muscle tone increases due to the development of subluxations in small joints. In this case, the distance between the articular surfaces increases, and the muscles experience a strong stretching. This causes pain reflex spasm with the accumulation of lactic acid.
This results in increased pain. In addition, muscle spasm can cause secondary disorders, as there is compression of the nerve roots, joint pain increases.
About diagnosis of spondylarthrosis
Since both osteochondrosis and spondyloarthrosis are very related to each other and anatomical localization, and risk factors, these processes can occur simultaneously. Differences between them can only be established with the help of visualizing techniques, for example, radiology.
In the event that after an MRI is performed, it makes it possible to examine long spine ligaments that are often involved in the pathological process.
Treatment of spondylarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine
The disease, like any chronic, long-term ongoing process, has exacerbations that alternate with periods of remission. As a rule, exacerbations occur twice a year - in the spring and in the autumn, and are often associated with hypothermia and physical exertion.
Spondyloarthrosis can be treated by a doctor - rheumatologist, vertebrologist( specialist in spinal diseases), or a neurologist.
Treatment of spondylarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine in the period of exacerbation is reduced to drug-induced pain relief, possible signs of inflammation, improvement of motor activity. For this, standard medicines are used:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, both inwards and in injections, as well as for local application to the lumbar region: ketoprofen, meloxicam, lornoxicam, ibuprofen. Commercial names for these drugs are Ketonal, Movalis, Xsefokam, Nalgezin. To improve the tolerability of these drugs are taken together with the proton pump blocker - omeprazole. It is the reception of omeprazole that allows you to minimize the manifestations of ulceration in the gastrointestinal tract, which are called "ulcerogenic effect of NSAIDs."
- Muscle relaxants of central action. Spondylarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine: treatment, injections will be effective in reducing muscle tone. This will release the nerve endings from the tightened muscles, and also reduce stiffness in the back. These drugs include tolperisone( "Midokalm") and tizanidine( "Sirdalud").
- Local treatment consists of lozenges of ointments, gels and creams containing anti-inflammatory components( Ketonal-Cream, Fastum-gel), or derivatives of snake and bee venom( Nayatox, Viprosal, Apizarthron).A good effect is warming and irritating ointments, which are created on the basis of an extract of cayenne pepper, for example, ointment "Capsicum", containing capsaicin.
- Chondroprotectors have some effect. These drugs are a "donor" of chondroitin-sulfate and mucopolysaccharides( glucosamine), which form a cartilaginous tissue. These preparations can be used, both in the tablet form of "Artra", "Teraflex", and in the form of solutions for intramuscular injection of "Alflutop".
- The reception of multivitamins and mineral complexes enriched with calcium and magnesium.
- Wearing a semi-rigid corset.
- Using an applicator Kuznetsova or Lyapko( applying to the waist area 2 to 3 times a day for 15 to 20 minutes
- Using an orthopedic mattress and pillow Moreover, this should become the norm for every person even in the absence of back problems,that in a dream we spend a third of life, and the state of stress on the spine caused by improper selection of a sofa and a mattress can cause pain and various disorders
After the acute stage of spondyloarthrosis treatment begins,th degree depends on non-medicinal factors. The most popular species are
- exercise therapy in the presence of an instructor
- Swimming The load on the muscles of the back in the horizontal state allows to increase blood flow in the muscles of the back, normalize the outflow of metabolites from muscles to the venous channel and prevent exacerbation
- Physiotherapeutic proceduresIn spondyloarthrosis, such instrumental techniques as CMT( sinusoidal modulated currents), magnetotherapy, galvanization, electrophoresis on the lumbar region with vitaminthiamine, with hormones( hydrocortisone).At the first sessions, electrophoresis with local anesthetics( novocain) is shown for the relief of pain syndrome.
- Sessions of osteopathy and manual therapy.
- Acupuncture.
- Hand massage. It allows to reduce the level of muscle tone, to normalize blood circulation in the deep muscles of the back.
Prevention of spondylarthrosis
In the treatment of spondylarthrosis and osteochondrosis, prevention plays a very large role. With age, you need to monitor your weight, the level of hormones, try to lead an active lifestyle, do gymnastics.
It should be remembered that the small joints of the spine, due to its large number, can be a source of severe back pain, even if the intervertebral disc is preserved.
If you do not pay enough attention to the problem of small joints, then as a result, not only stiffness in the back, but also ankylosis of the spine, in which all movements in the waist will be impossible, since the spine simply "ossifies" can develop.
In addition to this disability factor, patients are concerned about persistent pains that significantly reduce the quality of life.
- In order not to miss the changes in the small joints of the vertebrae, it is necessary to perform radiography of the lumbar department in 2 projections at the appearance of low back pain, and to consult a specialist.