Otitis relates to an ENT diseases which proceed with the development of inflammation in the ear canal. Pathology is dangerous not only hearing loss but also damage to adjacent tissues in both children and adults. Therefore, experts recommend passing the timely examination, suspected of the disease, and the appropriate treatment.
The content of the article:
- 1 What is otitis media?
- 2 Causes of
- 3 Types and symptoms of otitis media in adults
- 4 Can otitis pass itself?
- 5 Diagnostics
-
6 How to treat otitis media in adults?
- 6.1 First aid
- 6.2 antibiotic therapy
- 6.3 Ear drops
- 6.4 ointments
- 6.5 Homeopathy
- 6.6 Ultrahigh frequency therapy
- 6.7 Paracentesis or tympanotomy
- 6.8 Folk remedies
- 7 Than to treat otitis media in pregnant women?
- 8 Which is not desirable to do with otitis?
- 9 complications
- 10 Video of otitis
What is otitis media?
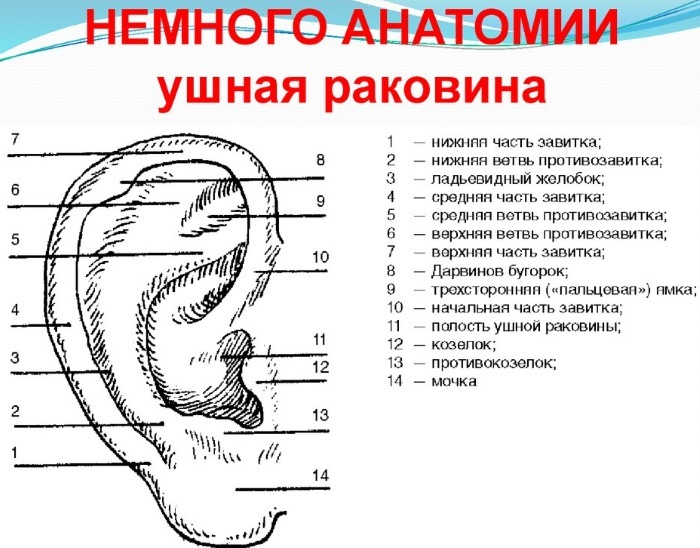
Otitis - a disease with inflammatory tissue damage in the ear canal. Depending on the source of inflammation localization pathology can develop in the outer, middle and inner ear.
When external otitis inflamed tissue of the auricle and the auditory meatus up to the tympanic membrane. When otitis media affected the cavity behind the eardrum, which consists of 3 auditory ossicles. When an internal otitis inflammation develops in a kind of labyrinth, which is located behind the middle ear in the temporal bone.

Depending on the nature of occurrence of the disease may be infectious (virus, fungus, bacteria) and noninfectious (trauma, allergies) character as well as otitis may be unilateral and bilateral.
Causes of
Otitis (treatment in adults depends on the cause of disease development) can be developed as a result of the impact of the following factors:
- prolonged exposure without headgear outdoors in cold weather or wind, and total body hypothermia;
- the presence of infection in the body. Most often, otitis media develops as a complication of acute respiratory infections, scarlet fever or flu;
- frequent irritation of the nasopharynx tobacco smoke, chemicals, or alcohol;
- work in hazardous work or reside in the contaminated area;
- chronic rhinitis, enlarged adenoids or curvature of the partition in the nose;
- weakened immunity or vitamin deficiency, as a result of the infection rapidly enters the body and begins to develop;
- Contaminated water entering the ear canal;
- frequent atmospheric pressure (when immersed in water, in aircraft flights);
- Prolonged stress, severe fatigue, physical exhaustion;
- caries. After a decayed tooth infection penetrates quickly into the ear canal;
- renal work;
- presence endocrine diseases;
- trauma pinna or meatus foreign body, a sound wave or a jet of hot / cold air;
- frequent allergic reactions accompanied by rhinitis;
- lack of hygiene in the ear canal or misuse its implementation;
- genetic predisposition due to the structural features of the auditory canal.
Also, Otitis can be a complication after the surgery ENT organs.
Types and symptoms of otitis media in adults
Before the appointment of the treatment it is important to determine the type of otitis media, which has a division of the following criteria; corresponding symptoms:
| Criteria separation disease | symptomatology | |
| The shape of the flow | Acute | Symptoms begin to appear in an acute form after 6-48 hours after the onset of the disease:
The most important symptom is constant pain in the ear, which is enhanced by pressing a finger on the area around the ear. |
| Chronic | It develops as a result of improper treatment of the acute form or in the case of regular exposure to precipitating factors of ENT organs (most often cigarette smoke). Characterized by the following symptoms:
Soreness in the ear canal is weak, but it is well felt by palpation the area behind the ears. |
|
| At the place of localization | Outer | The pathology is accompanied by the following features:
Often accompanied by visible reddening of the ear. |
| Average | symptoms:
Additionally, there may be a swollen lymph nodes behind the ear. |
|
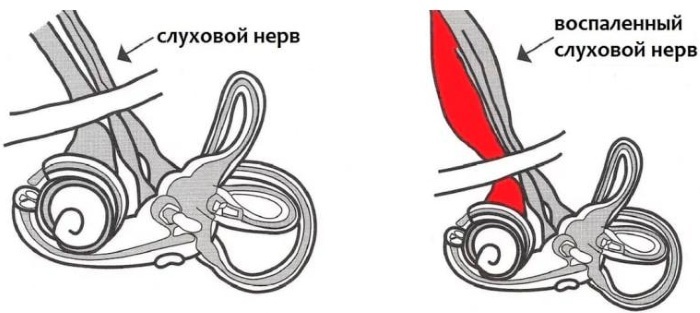
| Interior | Symptoms:
Perhaps incoordination. |
|
| By the presence of infection | Bacterial | Symptomatology of the disease is similar to acute otitis media flow. Additionally, itching may be present. |
| Viral | ||
| Fungal | ||
| noninfectious | Otitis media is characterized by redness and swelling of affected tissues, fever is rare. | |
| By the nature of discharge | without isolation | |
| exudative | Distinguished by the presence in the ear canal lymphatic fluid, which has a transparent, thick consistency. The patient may feel the gurgling in my ear. | |
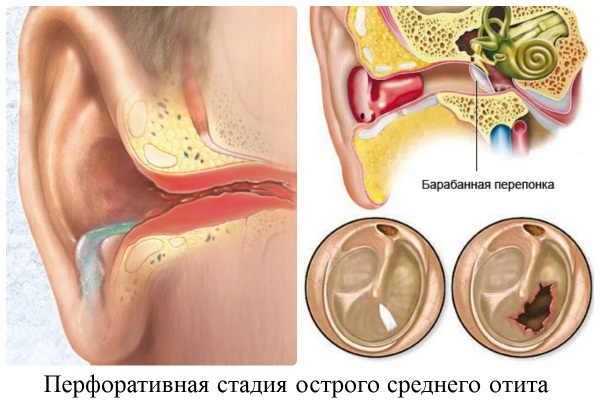
| Purulent | Expressed presence and purulent masses in the ear canal, which may leak out. |
Determine the type of otitis media and danger can only ENT after a complete patient examination.
Can otitis pass itself?
Otitis (treatment in adults is a mandatory procedure, as well as in children) is dangerous disease, since the absence of pathology therapy can result in not only the development of deafness.
The ear canal is close to the brain, as a result of the infection can affect the body, that the risk of developing more serious complications than hearing loss. Therefore, ignore the symptoms or pathology to self is extremely dangerous.
Otitis media can go on their own, if struck by the ear department in an easy manner, not in the presence of an infection in a patient and strong immunity. But for the production of the diagnosis requires a visit to Lore. Importantly, even in this case, the probability of complications (in the absence of treatment) may be 70%.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of otitis media is made in stages:
1. Medical history:
- detected predisposition to this disease by the presence of precipitating factors;
- ENT discovers that preceded the development of a pathology (allergy, infectious disease, or work in hazardous environments);
- how long the symptoms are present and how.
2. Visual inspection:
- doctor inspects ear canal using mirrors and otoscope;
- necessarily the method of palpation in the area of the ear, to identify the pain;
- examination of the nasal passages and throat to detect swelling and redness;
- hearing test quality;
- temperature measurement.
3. Delivery of urine and blood tests to detect the infection in the body and determine the overall condition of the patient.
4. In the presence of secretions from the ear is made fence material to determine the nature of mucus. Additionally, it may be taken from the throat swab and nasal passage to determine the type of pathogen.
5. If necessary or performed tympanometry reflectometry to detect the presence of fluid in the ear canal.
6. When internal otitis suspected lesion or tissue adjacent assigned MRI, X-ray or CT scan.
The diagnosis is made after the availability of the results of the survey, followed by the appointment of treatment.
How to treat otitis media in adults?
In adults, to eliminate disease therapy is based on test results, which may consist of antibiotics (as well as antiviral or antifungal agents), ear drops, and physiotherapy. It is important to undergo a course of treatment and is completely under the supervision of a physician. Self-medication or incompleteness rate risk of developing complications of otitis media in the background.
First aid
First aid for otitis is required when there is no opportunity to appeal urgently to LORu (evening or night, being away from the city).
In this case, it is allowed to use the following tools:
- drip into the auditory meatus 2 drops boron alcohol. Plug the ear with cotton wool. It is important that a means should be warm. Alcohol prevents the development of infection and eliminate swelling;
- in the presence of severe pain use 1-2 drops Otipaks ear drops into the passageway;
- to remove secretions from the nasal passages in the nasal drip vasoconstrictive drops (Rinonorm, Tizin, Xylene). Suffice 1-2 drops into each passage;
- in the presence of high temperature take antipyretics (Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen, Ibuklin;
- exclude the use of hot or cold food and beverages;
- if there is a chance of developing otitis media against the background of allergies, the recommended intake of antihistamines (Zyrtec, Aerius, Claritin).
These drugs will stabilize the state prior to the visit to the specialist. Other manipulations are not recommended (especially warming) as otitis of the cause is not identified. If the condition worsens, it is required to urgently call an ambulance.
antibiotic therapy
Antibiotics for otitis appointed if the causative agent of disease is bacteria.
For the recommended drugs include:

| The name of the drug, the release form and conditions of realization | The active substance and its effects | Rules of application and course | Contraindications and side effects |
| Amoxicillin (tablets, capsules and granules for suspension). It sold with a prescription. | Amoxicillin is active substance and refers to the broad-spectrum antibiotics penicillin. | Take 1-2 tablets / capsule 3 times daily for 5-12 days. Dosage granules for slurry preparation is carried out individually. treatment similar. | The drugs should not be taken during gastrointestinal pathologies, which are accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea, if you have a viral or fungal infections, as well as in violation of hematopoiesis process. The drug can cause a violation of stool (diarrhea or constipation), the development of allergic reactions in different manifestations (rash, pruritus, Quincke's edema) and deteriorating liver function. |
| Flemoxin Solutab (tablets). Prescription. | The active ingredients amoxycillin and clavulanic acid which softens and enhances the action of antibiotic. | The dosage is adjusted individually according to the weight. Duration of 7-15 days. | |
| Zinnat (tablet and granules). It sold with a prescription. | The main element (cefuroxime axetil) refers to a second generation cephalosporin antibiotic series. It destroys bacteria resistant to amoxicillin. | Take tablet 2 times a day for 5-10 days. |
Antibiotics are also prescribed if the temperature does not fall down and do not start to improve for 4-5 days.
Ear drops
Ear drops for any form of appointed otitis. Depending on the composition means can destroy the infection, to eliminate swelling of tissue and pain symptom. The advantage is speed drugs achieve a result, since the composition acts locally penetrate to the site of inflammation.
By effective dropwise with otitis include:
| Name of product and conditions of sale | The active substance and a description of its actions | Rules of application and course | Contraindications and possible backlash |
| Otipaks. Sold without a prescription. | Active substances (fenazol and lidocaine) have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. The facility has an alcohol base. | Otipaks required to bury 3-4 drops into the ear canal 2-3 times a day for 5-10 days. | Can not be used in case of hypersensitivity to the drug and violation of the integrity of the eardrum. When using small drops of possible irritation in the ear canal and an allergic reaction to components of development. It is important Otipaks allowed to use during the childbearing and lactation. |
| Otofa. Sold with a prescription. | The active ingredient (sodium rifamycin) has an antibacterial effect. | Otofa necessary to instill 5 drops of 2 times a day for 7 days. | Allergic reaction is possible contraindication and adverse reaction of the organism when using drops. It can be used during lactation and pregnancy. |
| Anuran. Prescription. | Basic elements (Naomi sulfate and lidocaine) have antibacterial and analgesic effect. |
In the appointment of ear drops is important to follow the instructions on the landfill:
- ear canal requires pre-clean cotton sticks;
- contents of the vial should be warm (about 38 degrees);
- with instillation slightly delay the ear to remedy penetrated deeper into the ear canal;
- after completion of the procedure to lie on its side for 15 minutes, the means is not leaked out immediately.
When selecting funds is required to take into account the integrity of the eardrum.
ointments
Upon confirmation of the diagnosis of otitis externa LORom therapy may be performed using gels or ointments which may have antihistaminic, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory composition.
The most commonly prescribed external assets include: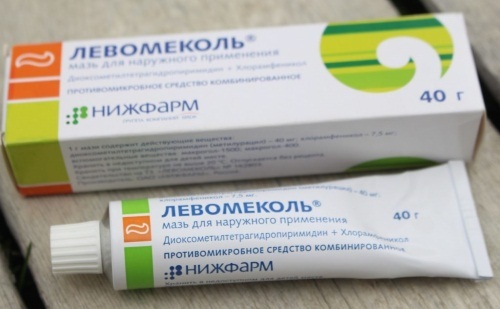
| The name of the drug, the release form and conditions of sale | The active substance and a description of its actions | Rules of application and course | Contraindications and possible backlash |
| Levomekol (ointment). Sold without a prescription. | Main components (dioksometiltetragidropirimidin and chloramphenicol) have regenerating, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect. |
Treat the ear canal with a cotton swab ointment composition 3 times a day for 5-7 days. You can insert into the ear canal soaked turunda ointment. |
It means you can not use in the presence of a fungal infection and hypersensitive to the components. For external use may develop allergic reactions such as itching, rash and swelling. |
| Methyluracyl ointment. Available without prescription. | The basic substance methyluracil, anti-inflammatory, healing and immunomodulatory activities. | Process ear canal ointment 2 times a day till recovery. |
Ointment is not indicated for the presence of cancers and in case of hypersensitivity to the components. For external use may develop an allergic reaction. |
| Flutsinar (ointment, gel). Sold without a prescription. | Fluocinolone acetonide (active element) possesses antihistaminic, antipruritic and antiinflammatory action, also helps to eliminate swelling of tissues. | Treating ear canal means 2 times a day for 7-14 days. |
Ointment / gel is not assigned with infectious otitis and hypersensitivity to the components. Use of the drug can cause the development of allergies. |
Before processing ointment ear passes them require pre-cleaned of impurities and sulfur.
Homeopathy
The use of homeopathy with otitis is possible only with the permission of Lore. The drugs mostly directed not to destroy the infection, and strengthening the immune system so the body alone struggled with pathogen pathology.
the following types of drugs recommended for otitis media:
-
Belladonna. The granules have a relaxing effect on the nervous system by blocking the pain symptom. Means required to take on 1-5 pellets 3 times a day for 7-15 days;

- Aconite. Granules eliminate the symptoms of intoxication. Accept required to 7 pellets 3 times a day for 14-28 days;
- Hepar Sulfur-GF. Ointment possesses wound-healing and anti-inflammatory action. Treat the ear canal, 2 times a day for 7-14 days.
These funds are allowed to use during pregnancy and lactation, as well as in the elderly and children.
Ultrahigh frequency therapy
UHF treatment (exposure to magnetic waves tissue) allows with otitis:
- eliminate swelling and inflammation in the ear passage;
- reduce painful symptom;
- terminate the bacterial growth;
- increases the effects of drugs;
- It accelerates the healing process;
- It prevents the development of complications of otitis media.
Procedure is assigned in the step of recovery and recommended in complex combination with the use of medicines.
Importantly, the presence of cancerous and benign tumors of the pacemaker and psychological pathologies method is contraindicated.
Paracentesis or tympanotomy
Procedures are as piercing or sectional eardrum to extract purulent masses of lymphoid or aural passage. Next, the surgeon handles the auditory meatus antibiotic and disinfecting agent.
If done correctly, manipulations at the injury site, in the eardrum, formed a small scar, which does not affect the quality of hearing. Methods used only in the absence of effect of drug treatment.
Folk remedies
Traditional recipes can be combined with the use of medicines, as well as an independent agent for the development of otitis media in an easy manner and infectious nature.
The following compounds are the most effective:
- heat the salt in a pan and put it in a soft cloth. Applying to the affected ear canal. Hold until the salt has cooled. Compress pulls fluid, relieves pain and reduces swelling. The number of procedures is not limited. Hot salt thereof is contraindicated in the presence of infection and elevated temperature;

- minced garlic clove and squeeze out the juice. Treating the ear with a cotton swab juice 3 times a day for 5-7 days. Do not use if damage to the eardrum;
- treating the ear canal 3-5 times a day turundy soaked in hydrogen peroxide. It removes germs and removes puffiness. Use caution when damaged tissue integrity in the ear canal;
- use decoctions of herbs (plantain, chamomile or bay leaf). Requires 10 g steamed plants in 200 ml of boiling water, simmer for 20 minutes. Strain. Moisten turunda warm broth and placed in the auditory canal 15 min. The procedure is done 3-5 times a day for 1 week. Plants will eliminate swelling and inflammation, and will prevent the development of infection.
Importantly, data recipes recommended to apply only after the permission of Laura and elimination of allergic reactions.
Than to treat otitis media in pregnant women?
Otitis (treatment of adults, including pregnant women, held under the strict supervision of a specialist) in the period of gestation of the child, is dangerous not only for the health of the mother but also the fetus. Therefore pathology recommended to remove the first sign of its manifestation.
During this period, after consultation with LORom and gynecologist, a leading pregnancy, permitted the use of the following drugs:
- Augmentin antibiotics and Amoxiclav;
- saline lavage of the nasal passages, or by means of sea water;
- nasal vasoconstrictor (Nazivin or Otrivin);
- ear drops (or Otipaks otinum);
- antipyretics based on ibuprofen.
Be sure to take additional vitamin complexes for immunity.
Which is not desirable to do with otitis?
If you suspect that the development of otitis media can not start treatment yourself (only if a doctor's visit is not possible), so both depending on the nature of the disease, the type of agent and the form of the disease depends on the flow and type of dosage medicines.
It is important strictly prohibited warming of the ear canal, to the diagnosis, as well as the presence of a high temperature is required to call a specialist at home, especially in the winter.
complications
Otitis (treatment of adults with folk remedies or drugs, selected independently, can lead to the development of complications) is dangerous not only to the development of deafness or degeneration disease into a chronic form, It can also be seen:
- development meningitis (inflammation of the meninges);
- paralysis of the nerve cells, including the face;
- formation fluid in the cranium.
In the absence of further therapy, otitis media can result disabilities and deaths.
Otitis media is a dangerous disease in both children and adults. Pathology, ignoring symptoms or self-medication, can result in not only hearing impairment, but also the development of disability and even death. Therefore, it is crucial to be examined by Laura and completely take the prescribed treatment.
Author: Svetlana Kotlyachkova
Registration of the article: Vladimir the Great
Video of otitis
The doctor will talk about otitis media: