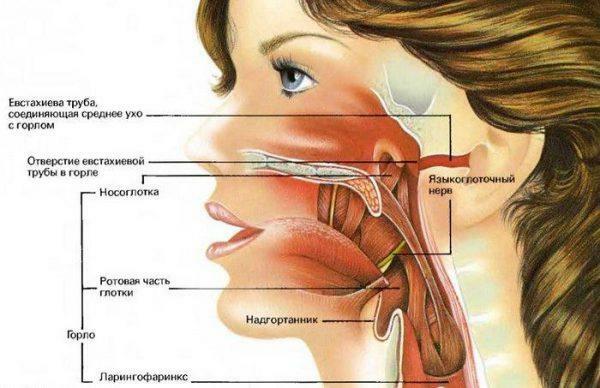
Due to the peculiarities of the anatomy of the human body, the throat and ear are a communicating system connected to each other by a number of formations. The main element of the throat is the pharynx - a wide canal, designed to transport food masses into the esophagus, and airways into the larynx. With the help of special drainage channels, which are called eustachian tubes, the pharynx connects to the ears and allows balancing air pressure on the eardrums.

The ear and throat aches on one side: the causes and treatment of
In various inflammatory processes, pathology quickly spreads through these channels, affecting the structure and organ of hearing, and pharynx. This is why patients with various otolaryngic diseases have unilateral pains in the throat and ear. Unpleasant sensations can be caused by a number of disorders:
- otitis media;
- pharyngitis;
- angina;
- laryngitis;
- sinusitis;
- lymphadenitis, etc.
Structure of the oropharynx
Attention! Discomfort in the ear and throat can also occur due to problems in the structure of the dentoalveolar apparatus. The most common cause of painful sensations is an abscess or phlegmon - a cluster of purulent exudate in the maxillofacial area.
Content of material
- 1 Otitis
- 2 Pharyngitis
- 3 Angina
- 4 Laryngitis
- 5 Lymphadenitis
- 6 Sinusitis
- 6.1 Video - What to do when "shoots" and hurts the ear?
Otitis
Otitis is an inflammatory process that affects various parts of the ear. The disease can be both acute and chronic. Depending on the extent of the disorder, the symptoms of the pathology are often somewhat different, but in most patients, otitis manifests itself by intense pain in the ear and throat from the affected side. Pain syndrome is acute, shooting character and is accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the person's well-being.
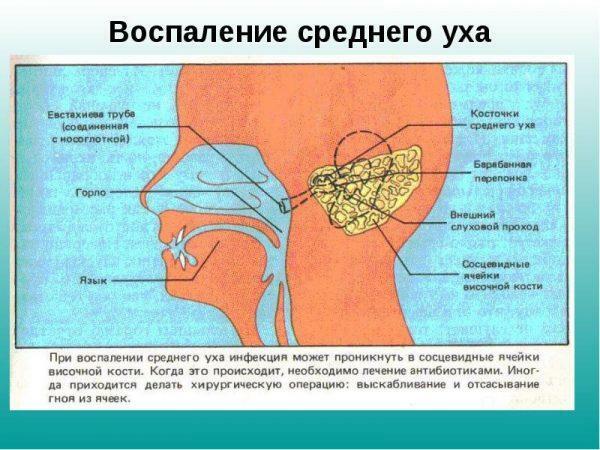
Inflammation of the middle ear
Attention! Otitis is a dangerous disease, as with improper treatment it can lead to a number of complications, including facial paresis, meningitis and abscess of brain structures.
When diagnosing otitis, three main types of this disease are identified:
- External otitis - affects external auditory structures, this form of pathology is more likely to affect middle-aged and elderly people.
- Average otitis media , in which the inflammatory process is localized in the middle ear and usually affects children under 5-7 years of age.
- Internal otitis media .It develops against a background of severe infection, for example, meningitis. With this pathology, the patient has a labyrinth - internal structure of the ear. The disease has an extremely high risk of complications.
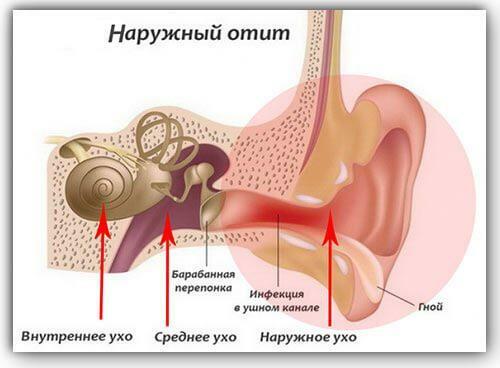
External otitis from within
The external form of the disease is divided into local and diffuse. In the first case, a patient develops a furuncle in his ear - purulent inflammation in soft tissues, which has clear boundaries. The doctor opens the pathological formation and drains the cavity.
Spilled otitis usually develops on a background of chronic otitis, when pathogenic microflora is retained in the ear canals for a long period. In this case, the inflammation spreads to the tissues of the structures of the ear, including the tympanic membrane.
In the absence of treatment, the pathological process passes to the middle ear. By eustachian tubes, the disease can spread to the throat. In this case, tubo-otitis or eustachiitis develops, a disorder in which the infection affects the mucosa of the auditory canals.
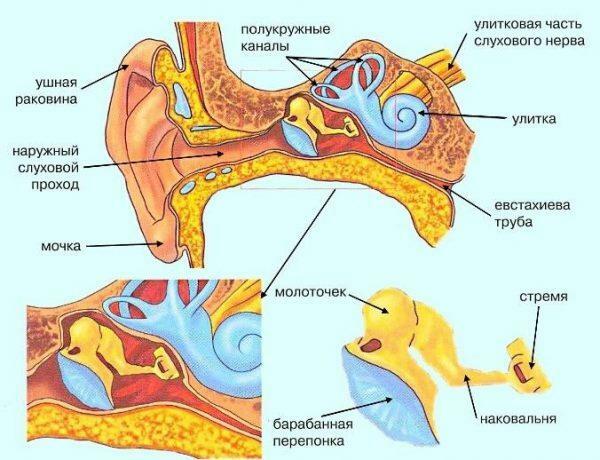
Ear structure
With otitis in the pathological process, nerves are drawn through the channels of the skull and connect the throat and ear. As a result, inflammation and compression of the ganglia occurs, which causes severe pain syndrome both in the area of the auditory canal and in the throat from the affected side. Also, when the patient is nursing, other symptoms are also worrisome:
- hyperemia of the epidermis of the ear with external otitis;
- sharp unpleasant sensations at a touch to an input or entrance in an acoustical canal;
- hearing loss, especially with the appearance of secretions;
- discharge from the ear canal, usually a greenish or yellowish hue;
- tinnitus;
- dizziness, cephalalgia;
- sore throat with the affected side, sometimes the pain syndrome can also affect the jaw;
- subfebrile or febrile fever.
Otorhinolaryngitis is treated by inserting into the ear canal turundum impregnated with alcohol or antiseptics: Otypax , Anauran .The patient is also shown physiotherapy, warming compresses and taking multivitamin complexes.
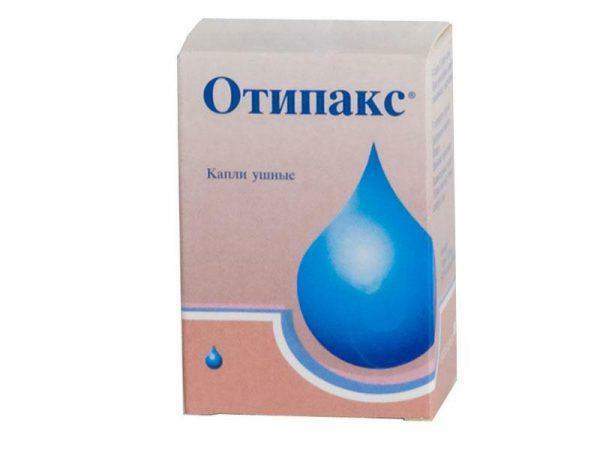

Ear drops Otypaks
In more severe forms of the disease, the otolaryngologist appoints antibacterial drugs: Ampicillin, Cefazolin, Augmentin , etc. Drops with anti-inflammatory effect are instilled in the ear: Otinum, Sofradex .
If conservative treatment does not work, then paracentesis is performed - a puncture of the tympanic membrane, which provides an outflow of purulent exudate. After the procedure, the patient should take antibacterial drugs, neuroprotectors and drugs to stimulate circulation. Treatment in this case is carried out in a hospital.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is a disease in which the epithelial membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall becomes inflamed. Pathology can be both non-infectious, bacterial or viral. The disease in most cases is combined with tonsillitis, accompanied by lacrimation and a feeling of stuffiness in the nose and ears.
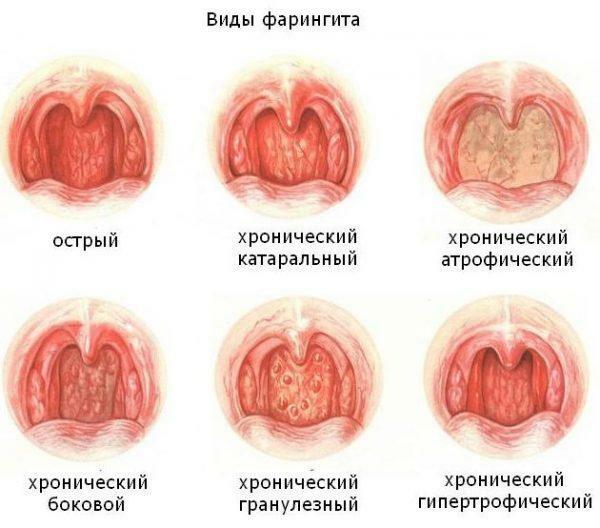
Types of pharyngitis
Non-infectious pharyngitis develops due to inhalation of excessively hot or cold air, toxic vapors, prolonged exposure to substances provoking mucosal irritations: charcoal, chalk, wood or rock dust, etc. Infectious form of the disease occurs when the human body develops streptococcal, staphylococcal, pneumococcal, fungal or viral infections. In this case, pharyngitis usually causes pathology that has spread beyond the inflammatory focus: sinusitis, otitis, etc.
Attention! When infectious pharyngitis is necessary to identify the nature of the causative agent of the disease. Otherwise, treatment may not be effective.
In patients with pharyngitis, the symptoms of the disease are noted:
- Pain .The pain syndrome is dull, localized in the throat. When swallowing discomfort increases, causing unilateral unpleasant sensations in the ear.
- Sore throat .The patient constantly has a desire to clear his throat, often patients complain of a painful dry cough.
- Hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membranes of the pharynx .In rare cases, when examined, you can note small papules or ulcers on the surface of the epithelium.
- Subfebrile fever with fever up to 37.5-38 ° C.
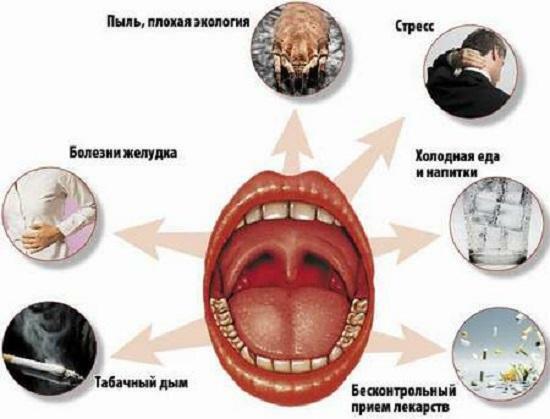
Causes of pharyngitis
Pharyngitis therapy is aimed at removing symptoms of pathology and eliminating the factor that caused the disease. The patient is prescribed antibacterial or antiviral agents: Doxycycline, Ampicillin, Acyclovir , etc. Reception of these drugs is necessary in the treatment of infectious pharyngitis. Sprays with a local anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect are also recommended: Hexoral, Strepsils, Chlorophyllipt .
For the treatment of a non-infectious disease, a patient should stop smoking, while working with irritants, use personal protective equipment, and avoid using acute or excessively hot food.
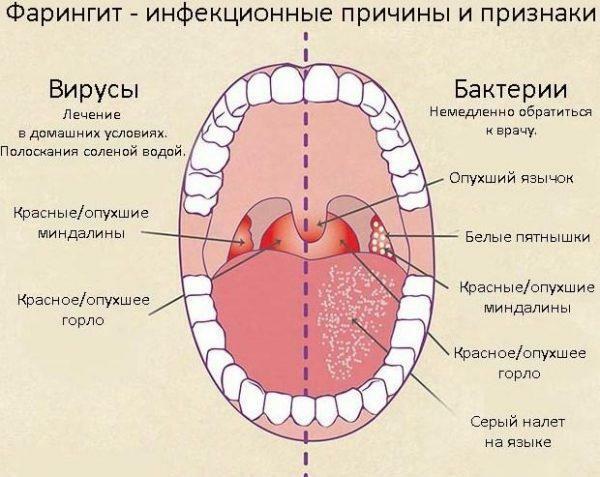
Causes and symptoms of pharyngitis
Angina
Angina is a group of acute diseases that arise due to the development of the infectious process on the tonsils of the pharyngeal ring. In this pathology can have both endogenous and exogenous nature. In the first case, the pathogen enters the throat from the sinuses of the nose, ear canals or caries destroyed by caries. When exogenous inflammation pathogens are transmitted by airborne or alimentary method.
Attention! In patients with immunodeficiency states, quinsy can cause opportunistic microorganisms that make up the microflora of the oral cavity and do not normally cause infectious processes.
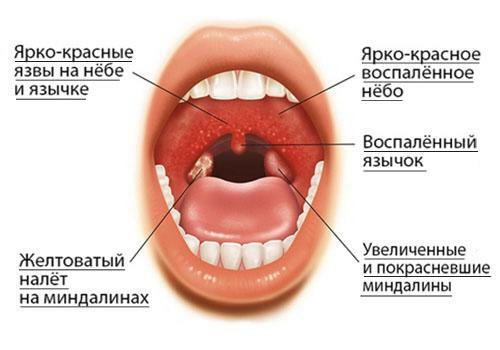
Symptoms of angina
In patients with angina, the characteristic symptomatology of the infectious process is concerned:
- Hyperthermia up to 38,5-39,5 ° C.
- Plaque on the tonsils, the appearance of ulcers.
- Intensive pain in the throat and ears, which increases with swallowing. In this case, pathology often affects the tonsils in only one half of the pharynx, in which case the pain syndrome is also unilateral.
- General deterioration of well-being.
- Acute hyperthermia of the palate, tonsils, tongue.
- Decreased appetite.
- Weakness, lethargy, drowsiness. Attacks of hyperhidrosis.
- Myalgia and arthralgia.
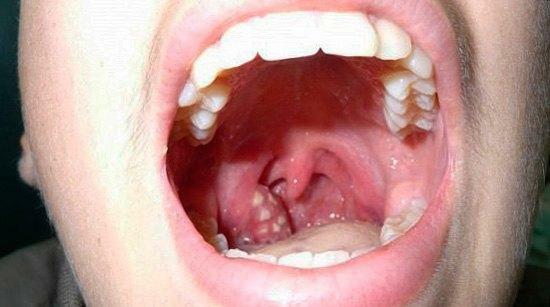
Throat with follicular angina
There are several main types of angina, each of which is characterized by specific manifestations.
Typical varieties of angina
| Symptomatic | Catarrhal - acute inflammation of the tonsils or acute catarrhal tonsillitis | Lacunar - involvement of tonsils in the pathological process of the lymph nodes | Follicular - purulent inflammatory process in which lesions are located as separate points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hyperthermia | Up to 38 °C | Up to 39 ° C | Up to 40 ° C |
| Patient condition | Fair | Median | Median |
| Enlarged lymph nodes | not expressed | Expressed | Expressed |
| Sore lymph nodes | Moderate | strongly expressed | strongly expressed |
| raid on the tonsils | No | Pronounced | No |
| pain when swallowing | Moderate | Expressed | strongly expressed |
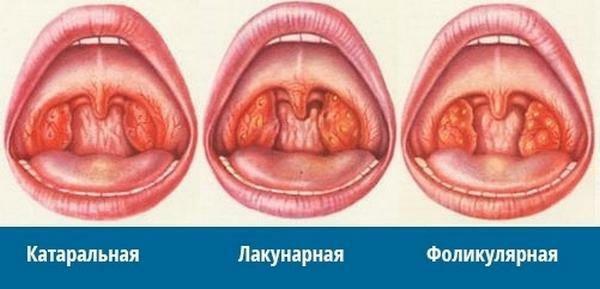
Types
angina In most cases, a sore throat is treated on an outpatient basis. The exception is severe or atypical forms of the disease. The patient shows the reception of local and general antibacterial agents: cephalosporins, macrolides and sulfonamides. The average course of treatment is about 7-8 days. The tonsils treat with Chlorophyllipt, Stopangin, Ambazone , etc. Possible irrigation with means containing chlorhexidine or streptocide. For the period of treatment and rehabilitation after illness the patient is recommended to maintain a sparing diet.
Laryngitis
Laryngitis is a disease in which the mucous membrane of the larynx becomes inflamed. In most cases, pathology is caused by various viruses, leading to hyperemia and swelling of the inner layer of the airways. In the absence of treatment, laryngitis, especially in preschool-age patients, can lead to the development of a false groin, a disease in which the movement of air masses in the larynx makes it difficult or impossible.
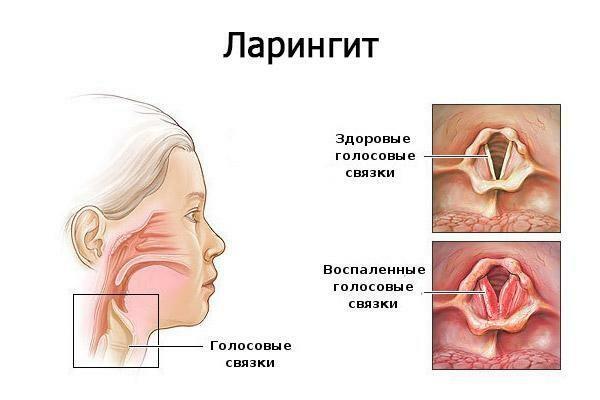
Ligament for laryngitis
Acute laryngitis rarely appears as an independent pathology, in most cases it develops against a background of severe form of SARS, measles, scarlet fever, etc. Chronic form of the disease is formed due to improper treatment of acute laryngitis or as a result of prolonged detrimental effects on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract of various pathogenic factors: dust, chemicals, smoke.
The disease manifests itself by dull pain and burning sensation in the throat, and discomfort can be localized on one side of the larynx. Often patients also complain of unpleasant sensations in the ears, difficulty in swallowing and dry mouth and throat. When diagnosing laryngitis, attention should be paid to other symptoms of the disease:
- hoarseness or hoarseness;
- sensation of foreign object in the throat;
- dry cough with acute laryngitis or moist with chronic.

Laryngitis medication
The patient with uncomplicated laryngitis does not need to be hospitalized, so treatment is done on an outpatient basis. In this case, bed rest is necessary only for patients with pathology developed against the background of ARVI.Other patients can lead a habitual way of life, but try not to talk or communicate in a whisper to reduce the burden on the vocal cords.
Patients are prescribed treatment with ultraviolet, magnetotherapy, quartz procedures, alkaline or oil inhalations. To stop the pain and stop coughing, a generous warm drink and the use of candies with an extract of eucalyptus, sage or chamomile are recommended.
Lymphadenitis
Lymphadenitis is an inflammatory process that affects the tissue of the lymph nodes. In most cases, there is a syndrome of various bacterial or viral pathologies, in some cases can be caused by exposure to the body of toxins, including the use of cytostatics. The defeat of lymph nodes in the neck or behind the ears leads to the appearance of a rather intense pain syndrome, which radiates into the throat and auditory canal.
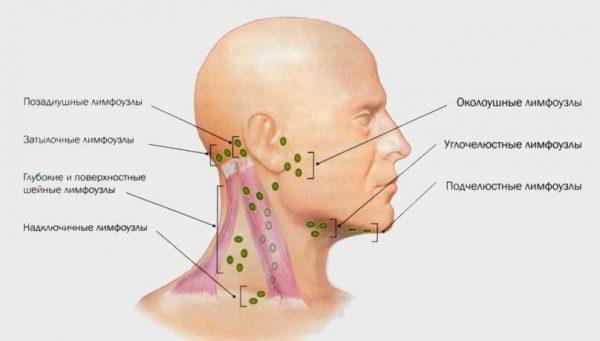
Location of
lymphadenitis In patients with lymphadenitis, the symptoms typical for the inflammatory process are:
- enlargement and soreness of the lymph node;
- possible hyperemia in the affected area;
- pain in the goal and ear on one side;
- increased discomfort when tilting or turning the head;
- it is possible to form an abscess at the site of the node;
- subfebrile fever, chills.
Attention! In children, lymphadenitis can occur in severe generalized form, in which the patient feels a sharp deterioration in health, he has a sharp hyperthermia to critical levels. If there is no timely treatment, there is a risk of developing sepsis.
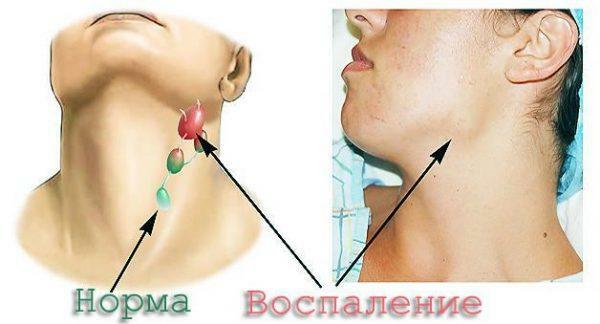
Inflammation of lymph nodes
Therapy of pathology includes the mandatory use of antibacterial drugs: Ampicillin, Doxycycline, Cefazolin , etc. The doctor prescribes a broad-spectrum antibiotic or chooses the most appropriate drug after determining the causative agent of the pathology. The patient is also shown UHF-therapy and vitamin-mineral complexes.
Sinusitis
A disease in which one or more sinuses become inflamed is called sinusitis. Pathology is inflammatory and develops as a complication in various bacterial or viral infections. Most often, this disorder is diagnosed in children and adolescents aged 4-15 years. Sinusitis is a whole group of diseases that are classified according to the site of inflammatory process localization:
- Maxillary sinusitis is an inflammation of the epithelium of the nasal sinuses of the upper jaw.
- Frontite-lesion of the frontal sinus mucosa.
- Ethmoiditis is a sinusitis of the cells of the latticed bone.
- Sphenoiditis is a pathological process in the sinuses of the sphenoid sinus.
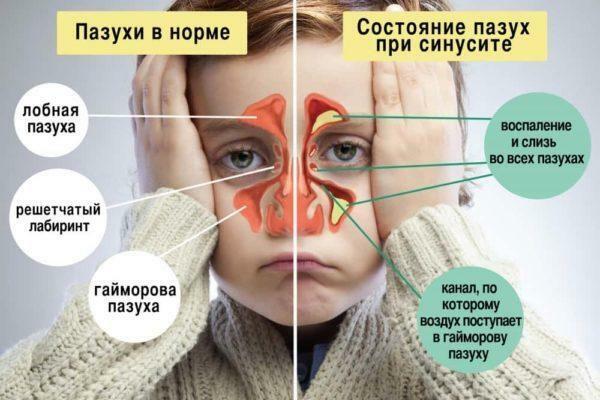
Maxillary sinuses with sinusitis
With sinusitis, the patient develops characteristic symptoms indicative of the development of inflammation in the paranasal sinuses:
- There are unpleasant sensations in the nose. Depending on the site of the lesion and the number of sinuses involved in the pathological process, the pain may be localized in the nose, above the eye or between the eyebrows. In this case, the discomfort is sharply increased when you press on the inflamed area or when the head is tilted.
- Cefalgia. The headache is dull or aching and intensifies in the evening.
- With sinusitis, there are often unpleasant sensations in the throat and ear area from the affected side.
- Nasal breathing disorder. Because of the stuffy nose, the patient's voice acquires a characteristic nasal.
- With a normal outflow of pus from the sinuses, the patient has yellowish-green or brownish discharge with an unpleasant putrefactive odor from the nose.
- Subfebrile or febrile fever, weakness, chills.
Treatment for sinusitis should be aimed at arresting the inflammatory process and ensuring free outflow of purulent exudate from the sinuses of the nose. For this, various antibacterial or antiviral drugs are used: Amoxicillin, Meropenem, Ceftriaxone , etc.

Drug Amoxicillin
If conservative treatment has no effect, then surgical drainage is performed. It is performed to purify the sinuses from pus and to take the material to detect the pathogen. After the analysis, a specialist can choose the most effective drug for the treatment of sinusitis.
Pain in the throat and ear on the one hand is a fairly common symptom that may indicate the development of various diseases of the upper respiratory tract, hearing organs or lymphoid system. When there are any signs of pathology, it is recommended to consult a specialist.