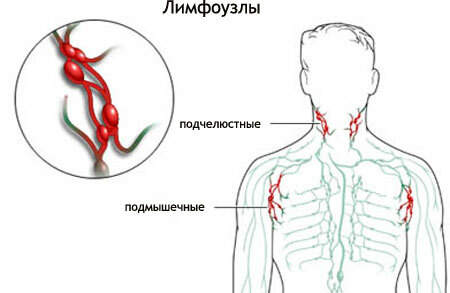
What is it?
Lymphadenitis is a consequence of the developing inflammatory process, which manifests itself as a lesion of the lymph nodes. It occurs as a result of getting into the lymph node with lymph or blood of pathogenic microorganisms and toxic substances, products of tissue decay.
It can be both an independent disease, and a signal about the presence of a pathological process in a particular organ. It is considered as a manifestation of the barrier function of the lymphatic system, a restrictor of infection.
About the causes of
The most common causes of lymphadenitis are acute, subacute and chronic inflammatory processes( furuncle, phlegmon, ulcers).Very rarely, with direct infection of the lymph node or trauma, primary lymphadenitis occurs.
The leading role in the etiology belongs to staphylococcus, less frequent pathogens are streptococci, mycobacteria, toxoplasma, protozoa. A generalized increase in lymph nodes is observed with toxoplasmosis, AIDS, mononucleosis, tuberculosis.
Regional lymphadenitis occurs against the background of genital herpes, tularemia, syphilis. The enlargement of the lymph nodes can be provoked by their infiltration by metastatic malignant cells in cancer diseases.
Content
- 1 Types lymphadenitis, photo
- 2 Symptoms lymphadenitis
- 3 Diagnostics lymphadenitis
- 4 Treatment lymphadenitis, antibiotics
- 5 Lymphadenitis in children - especially
- 6 Complications lymphadenitis
Types lymphadenitis, photo
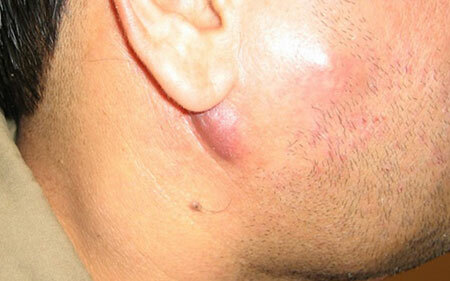
lymphadenitis under the ear, photo
Depending on the localization of inflammatory processes lymphadenitis is cervical,submaxillary, inguinal.
Cervical lymphadenitis is associated with various inflammatory and tumor processes. Through the neck area completely or partially passes the lymph from all parts of the body.
Acute streptococcal pharyngitis, paratonzillitis, tonsillitis, dental and oral diseases, respiratory viral infections can be accompanied by acute or chronic lymphadenitis.
In the diagnosis, the localization of inflamed lymph nodes is important. Nodes located behind the neck can vary in size for rubella and toxoplasmosis, and parotid nodes increase when infection of the conjunctival membrane.
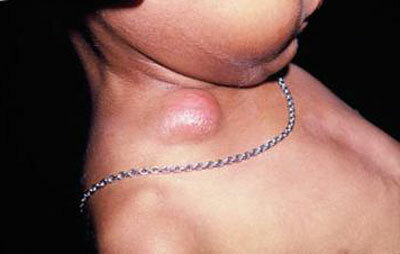
photo of lymphadenitis in a child
Submandibular lymphadenitis occurs more frequently and is observed in most cases in childhood and adolescence. The development of lymphadenitis is complicated by inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils.
Submandibular lymph nodes increase with dental inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis. This lymphadenitis passes with the cure of the underlying disease.
inguinal lymphadenitis - most often it is caused by inflammatory diseases of the external and internal genital organs, which are of an infectious nature. To cause an increase in inguinal lymph nodes may purulent processes of the lower part of the trunk and extremities.
Such processes include purulent wounds, furuncles, panaritsia, trophic ulcers.
Symptoms of lymphadenitis
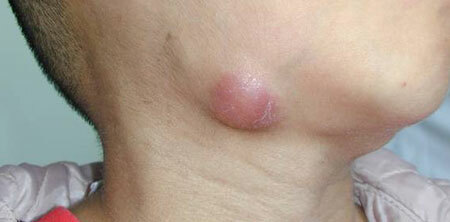
submandibular lymphadenitis, photo
Clinical symptoms of lymphadenitis are the same. To start the disease is characterized by a rise in temperature, enlarging and tightening of lymph nodes, their soreness. With palpation, you can find that they are not welded to each other and covering the skin.
With the progression of the inflammatory process, a dense and very painful infiltrate is formed. Later the skin over this area becomes red, still, hot, thinned.
If lymphadenitis does not go into a purulent process, then after a while the lymph nodes decrease and acquire their normal form, respectively, with the effectiveness of therapy of the underlying pathology.
In case of an unfavorable course of inflammation, it can go into purulent. At the same time, the body temperature rises to 39 ° C. The general state is often violated. There is malaise, sweating, headache and loss of appetite.
Within a few days the lymph node melts and the pus breaks out. As the abscess clears, intense pain with lymphadenitis passes, regress and other symptoms - recovery comes. If the disease is not treated in time, the inflammatory process can lead to complications( see below).
As a result of the stifling of the acute process, chronic lymphadenitis often develops, in which there are enlarged lymph nodes of different sizes with limited mobility. They are painless, but dense enough.
The enlarged dimensions can last a long time, but then the nodes decrease due to the proliferation of connective tissues. The general condition of a person with chronic lymphadenitis is not violated, the body temperature is normal.
Diagnosis of lymphadenitis
Superficial lymphadenitis is diagnosed easily, especially if a foci of infection is detected. The doctor is guided by clinical symptoms and anamnestic data. If the clinical diagnosis is unclear, an additional examination is necessary. For patients with lymphadenitis, it should be comprehensive, including:
- clinical blood test;
- serological and microbiological examination;
- ultrasound;
- X-ray examination;
- puncture biopsy according to indications;
- computed tomography.
Recently, progress has been made in the diagnosis of lesions of the lymphatic system by radiocontrast lymphography, remote infrared thermography, and scanning.
Treatment of lymphadenitis, antibiotics
Sanitation should begin with the elimination of an infectious inflammatory focus( treatment of carious teeth, tonsillitis, infected wounds).Treatment of lymphadenitis depends on its stage.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes after a flu or sore throat does not require medication, as in most cases the symptoms go away on their own.
With lymphadenitis, antibiotics are prescribed if a suppuration occurs in the affected area. Antibiotic therapy and sulfonamide drugs are used depending on the sensitivity of the flora( it is determined in the diagnosis).
The duration of therapy depends on the presence of general and local symptoms, the timing of normalization of laboratory indicators. Any therapeutic scheme provides, in parallel with antibiotics, the reception of fortifying agents and vitamins that increase immunity and improve the overall condition of the patient.
Physiotherapy( electrophoresis, ultrasound) gives a positive result. Physiotherapeutic therapeutic methods have a stimulating effect on nerve and humoral processes, increase the reactivity of the body and its tissues, act resorptively, cause an increase in local phagocytosis.
In the absence of the effect of conservative treatment of lymphadenitis, surgical intervention is possible, resulting in the removal of purulent masses from the body, by opening the focus of accumulation. Suppurated lymph nodes can be removed and then sent to a histological study( to exclude oncology, cancer).
Lymphadenitis in children -
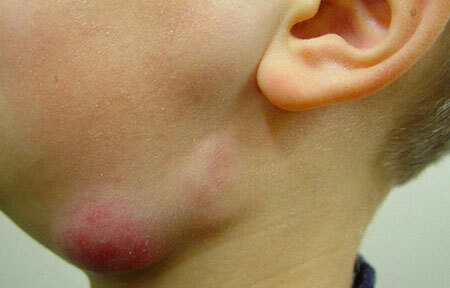
features of submandibular lymphadenitis in a child, photo
In a child, inflammatory processes in the lymph nodes are promoted by acute respiratory viral infection with nasopharyngeal involvement. Acute lymphadenitis in children occurs violently - local symptoms and general reaction are pronounced. On the foreground is general weakness, fever, headache and decreased appetite.
Children of pre-school age are more often ill. In most cases, the inflammatory process affects the submaxillary group of lymph nodes.
The smaller the child, the stronger the clinical symptoms of lymphadenitis and the more serious the treatment. It consists in revealing and eliminating the main cause of the disease and complex therapy in the pediatrician, dentist and ENT doctor.
Complications of lymphadenitis
Of the local complications of lymphadenitis, one should remember the possibility of developing suppuration( usually in childhood).Progressing inflammation of the lymph nodes without proper treatment often entails:
- abscessing;
- tissue necrosis;
- blood poisoning;
- fistula formation;
- thrombophlebitis of adjacent veins.
Purulent lymphadenitis can be complicated by the development of phlegmon, the erosion of the walls of blood vessels with bleeding. Currently, such processes are very rare in severe septic and toxic-septic forms. With antibiotic therapy, the outlook is favorable.
Thus, the increase in lymph nodes is observed in many diseases, both infectious and non-infectious nature. Treatment of lymphadenitis begins with the elimination of the primary focus of infection, in the initial stage the disease can be cured by conservative methods.