
Contents of the page
- 1 Unco-vertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine - what provokes development?
- 2 The main symptoms of
- 3 How does uncovertebral arthrosis develop in the cervical spine?
- 4 Diagnosis
- 5 Methods of therapy Uncoarthrosis
Unco-vertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine is a chronic degenerative process that leads to the destruction of cartilages in the vertebrae. Symptoms of this disease are similar in many respects to osteochondrosis, but differ from it by the appearance of osteophytes( bony outgrowths in the form of spines).Simply put, the deposition of salts and the deformation of the vertebrae occur in the region of the cervical vertebrae, which can lead to the jamming of the nervous and vascular bundles located inside the spine. This threatens a violation of sensitivity and may be accompanied by intense pain, which prevents the free tilt or turn of the head.
The vertebral column is the most important organ, which at the same time is the most vulnerable part of the human body. Constant workloads, lifestyle characteristics, previous physical traumas and illnesses - all this has the most negative impact on the spine and can provoke its deformation. Arthrosis of the spine causes wear of the intraarticular cartilage, which leads to impaired mobility, working capacity and well-being of the patient. What causes lead to the appearance of the disease, what changes you need to pay attention to and how to deal with uncoarthrosis of the cervical department, learn from our article.
Unco-vertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine - what provokes development?
 The defeat of the cervical vertebrae can be caused by a number of reasons related to the state of human health, the peculiarities of its physique, the nature of professional activity or the habitual way of life. Pathological changes in most cases start under the influence of the following factors:
The defeat of the cervical vertebrae can be caused by a number of reasons related to the state of human health, the peculiarities of its physique, the nature of professional activity or the habitual way of life. Pathological changes in most cases start under the influence of the following factors:
- Intensive loads of , which are of a permanent nature and are accompanied by frequent, repetitive, monotonous movements.
- Seated work , limitation of motor activity, creating a static load on the cervical spine.
- Overweight , excessive fullness, in which the fat deposits are localized in the cervical region, as well as in the area of the forearms and shoulder blades.
- Diseases of the stagnant system ( for example dysplasia), in which there is an incorrect jointing of the articular surfaces, leading to abnormal pressure on the cartilaginous tissue.
- Diseases of the endocrine system , disruptions in the thyroid gland, leading to metabolic disorders.
- spinal cord injuries.
- Congenital diseases associated with cervical vertebral lesions,( poliomyelitis).
In general, uncoarthritis of the cervical vertebrae has the same causes as most arthrosis. But this form of the disease is considered to be the heaviest, as extra bone growths are formed on the posterior surfaces of the cervical vertebrae, which provoke serious neurological diseases( neuritis).
The main symptoms of
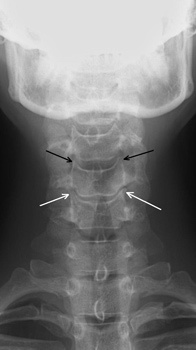 In the initial stages, the disease runs unnoticed. Sharp pain in the neck can appear when lifting weights or turning the head, but it is of a short-term, local nature, that is, it is felt only in one or two vertebrae. If you consult a doctor at this stage and start treatment in time, then the process can be stopped pathologically in just two weeks.
In the initial stages, the disease runs unnoticed. Sharp pain in the neck can appear when lifting weights or turning the head, but it is of a short-term, local nature, that is, it is felt only in one or two vertebrae. If you consult a doctor at this stage and start treatment in time, then the process can be stopped pathologically in just two weeks.
But, usually on such anxious "bells" few people pay attention, so as the disease progresses further the symptoms become more pronounced. The pain in the cervical region acquires a permanent character and intensifies under the most insignificant load, appearing under hypothermia or the onset of raw and windy weather. As a result, a rainy, autumn time with temperature drops becomes a real test for a sick person.
With the further development of the pathological process, the pain syndrome is supplemented by a feeling of stiffness and limited mobility, the patient has difficulty in turning the head, tilting and moving the arms in the shoulder joint. At later stages, pain does not release even in a state of complete rest and causes insomnia and chronic fatigue. At this time, when you turn your head, you can hear a characteristic crunch. In the future, painful sensations spread to all parts of the spinal column.
In advanced stages, the pathological process affects the nerve plexus, which leads to dizziness, nausea, imbalance, visual impairment, gait instability and increased blood pressure.
Any changes in the cervical spine require timely and adequate treatment, otherwise the destructive process can affect the nerve endings of the spinal cord and cause serious neurological syndromes leading to disability.
How does unco-vertebral arthrosis develop in the cervical spine?
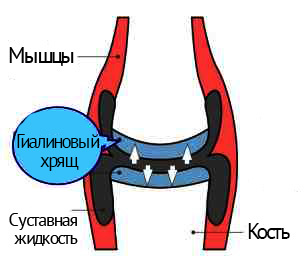 Like other varieties of arthrosis, the pathological process in the cervical spine is first of all affected by the structure of the hyaline cartilage. It is an intervertebral disc, the purpose of which is to soften the friction of the joints and to protect the nerve endings and vessels adjacent to the vertebra. Osteoarthritis, which affects the cartilaginous tissue, leads to its cracking, as a result, the hyaline layer of cartilage begins to dry out, losing the synovial fluid that feeds it.
Like other varieties of arthrosis, the pathological process in the cervical spine is first of all affected by the structure of the hyaline cartilage. It is an intervertebral disc, the purpose of which is to soften the friction of the joints and to protect the nerve endings and vessels adjacent to the vertebra. Osteoarthritis, which affects the cartilaginous tissue, leads to its cracking, as a result, the hyaline layer of cartilage begins to dry out, losing the synovial fluid that feeds it.
At the same time, osteophytes( bone growths) begin to grow, they block the movement of the cervical vertebrae and cause painful sensations. In the vertebrae, the deposition of salts begins, which leads to a loss of elasticity and flexibility of the cartilage, the dystrophy of the neck muscles gradually develops. Muscular ligaments cease to hold the intervertebral disc, which protrudes beyond the vertebrae in the posterior and forward directions, which causes permanent pain. Deformation of the vertical structure of intervertebral discs threatens the formation of hernias, squeezing blood vessels and worsening the general condition of the patient.
Diagnosis
 Seek medical attention when the first symptoms appear. To make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment, the specialist will inspect and send for a special diagnostic examination.
Seek medical attention when the first symptoms appear. To make a correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment, the specialist will inspect and send for a special diagnostic examination.
When collecting anamnesis and visual examination of the patient, the doctor can already notice an increase in the vertebrae, and during palpation, the presence of stagnant growths is determined. To clarify the diagnosis, the patient is directed to hardware research:
 The X-ray of the of the cervical spine allows confirming the presence of pathological changes. The images are taken in several projections, which helps to identify the presence of bone growths and to determine the degree of damage to the cervical vertebrae.
The X-ray of the of the cervical spine allows confirming the presence of pathological changes. The images are taken in several projections, which helps to identify the presence of bone growths and to determine the degree of damage to the cervical vertebrae.
MRI( magnetic resonance imaging) - is the most modern and informative diagnostic method. With his help, clarify the picture of the disease, determine the stage of the disease and precise localization of damage.
CT( computed tomography) - allows you to confirm the results of other studies, to detect hernias, the initial stages of tumors and other pathological changes in the cervical spine.
In addition, the patient is referred for a biochemical blood test and, as necessary, conducts a number of additional consultations with other specialists( neuropathologist, vascular surgeon).Only after conducting a full-fledged examination the doctor can put the correct diagnosis and choose the necessary treatment regimen.
Methods of treatment of uncoarthrosis
 Treatment of unco-vertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine involves the following methods:
Treatment of unco-vertebral arthrosis of the cervical spine involves the following methods:
- Medical treatment
- Physiotherapy and therapeutic gymnastics
- Chondroprotective drugs
- Manual therapy
- Vascular treatment.
Anti-inflammatory drugs . Therapy of the disease begins with the appointment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that eliminate swelling, pain and muscle spasms. Such drugs are used in the form of tablets, injections, or as external agents( ointments, gels, creams), intended for rubbing the affected area. The dosage of the drugs and the duration of the course of treatment are set by the doctor. The patient should strictly adhere to all the recommendations, since unsystematic and prolonged use of NSAIDs can lead to undesirable side effects.
 Chondroprotectors - are drugs that repair cartilaginous tissue. Such means are not able to heal from arthrosis, but they significantly slow down the process of destruction of intervertebral disks and prevent further progression of the disease. In such preparations, the main active ingredients are chondroitin and glucosamine, which are a kind of building material necessary for the restoration of cartilage tissue cells.
Chondroprotectors - are drugs that repair cartilaginous tissue. Such means are not able to heal from arthrosis, but they significantly slow down the process of destruction of intervertebral disks and prevent further progression of the disease. In such preparations, the main active ingredients are chondroitin and glucosamine, which are a kind of building material necessary for the restoration of cartilage tissue cells.
Muscle relaxants - medicines that help to relieve muscle spasm and increase joint mobility( Midokalm, Sirdalud).
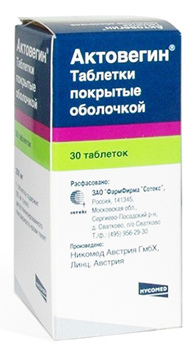 Preparations that restore blood supply .Because of the displacement of the vertebrae and the destruction of the cartilaginous tissue, there is a deterioration in the supply of intervertebral discs and a disturbance of blood flow in the region of the vertebral patients. To restore normal blood circulation, prescribe such drugs as Actovegin, Kurantil, Prodectin.
Preparations that restore blood supply .Because of the displacement of the vertebrae and the destruction of the cartilaginous tissue, there is a deterioration in the supply of intervertebral discs and a disturbance of blood flow in the region of the vertebral patients. To restore normal blood circulation, prescribe such drugs as Actovegin, Kurantil, Prodectin.
Vitamin and mineral complexes .The doctor will choose special means that will help improve the nutrition of the joints and provide them with the necessary vitamins and microelements.
In the period of exacerbation of the disease it is important to immobilize the cervical section. Therefore, the patient is recommended to wear a special orthopedic collar of Shantz, which relieves the load from the diseased area of the spine and provides gentle traction of the cervical region.
In advanced cases, in the last stages of the disease, only the surgical intervention can help the patient. During surgery, the surgeon removes osteophytes( bone spines) and restores the damaged vertebral disc with the help of artificial implants.
Physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy
 Therapeutic physical training( LFK) as part of complex treatment is designed to strengthen the neck muscles, eliminate dystrophic changes and pain, normalize blood microcirculation. Exercises for the cervical spine are selected by the attending physician. The patient should learn to perform them correctly, without making sudden movements, otherwise you can aggravate the situation and worsen the condition.
Therapeutic physical training( LFK) as part of complex treatment is designed to strengthen the neck muscles, eliminate dystrophic changes and pain, normalize blood microcirculation. Exercises for the cervical spine are selected by the attending physician. The patient should learn to perform them correctly, without making sudden movements, otherwise you can aggravate the situation and worsen the condition.
Manual therapy with uncoarthrosis consists of massage procedures that are performed during the remission period. Massage should be done by an experienced specialist with medical education. The procedure will help improve blood circulation in the affected area, eliminate muscle spasms and restore joint mobility.
Of the physiotherapeutic procedures the most popular and effective are:
-
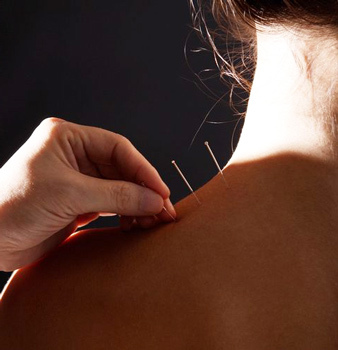 Electrophoresis and phonophoresis( with solutions of analgesics)
Electrophoresis and phonophoresis( with solutions of analgesics) - Acupuncture
- Darsonvalization
- Magnetotherapy
- Applied barothermia
Unco-vertebral arthrosis of the cervical department is treated on an outpatient basis, in a hospital patient is placed only in complex and neglected cases. During the period of remission, the patient is recommended to undergo sanatorium-resort treatment and apply folk remedies that complement the basic methods of therapy.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers the use of grindings and compresses based on animal fat, propolis or natural vegetable oils.
 Compress from sea buckthorn oil. Sea buckthorn oil can be purchased in a specialized department of the pharmacy. Before the procedure, the oil composition is slightly warmed up, the gauze cloth is moistened in it and applied to the sore spot for 15-20 minutes.
Compress from sea buckthorn oil. Sea buckthorn oil can be purchased in a specialized department of the pharmacy. Before the procedure, the oil composition is slightly warmed up, the gauze cloth is moistened in it and applied to the sore spot for 15-20 minutes.
Oil rubbing. For the preparation of the composition take 4 parts of flax oil and 1 part propolis and turpentine. All components are mixed, slightly heated and used to rub the diseased area.
All folk recipes are completely safe, but before using them, consult a doctor. This will help to avoid unwanted complications.



