According to statistics, the disease occurs in about 20 people per 1 million per year. In this limited form mainly diagnosed in children and female adolescents. The approximate ratio of women to men with scleroderma is 6: 1.

What it is?
Scleroderma - autoimmune disease of the connective tissue, with a characteristic skin lesions, vascular, musculoskeletal system and internal organs (lung, heart, digestive tract, kidneys), which is based on a violation of microcirculation, inflammation and generalized fibrosis.
Causes of
So far, the consensus among scientists about the cause of scleroderma is not, therefore, more appropriate to speak about the provoking factors studied. These include:
- frostbite;
- vibration;
- transferred malaria;
- malfunction of the endocrine system;
- trauma;
- hereditary predisposition and identified genetic alterations;
- virus infection, particularly cytomegalovirus;
- quartz dust and from coal;
- Contact with organic solvents;
- vinyl chloride polymeric material;
- Some potent cytotoxic drugs used in cancer chemotherapy.
Studying the composition of the blood of patients with scleroderma revealed increased content of coagulation factor VIII, enzymes (granzyme-A), which may damage the inner shell of the vascular wall.
classification of scleroderma
Depending on the prevalence of pathologic process distinguish the following forms of the disease:
- diffuse (a common skin lesion, the early development of pathology of the internal organs);
- scleroderma without scleroderma (Raynaud's phenomenon; seal on the skin are absent; there are signs of internal organ);
- limited or restricted (for a long time preserved only Raynaud's syndrome, which was later added to skin lesions in the hands, feet and face, and behind him, and internal organs);
- cross shape (combination of signs of systemic sclerosis with other connective tissue diseases);
- presklerodermiya (isolated Raynaud's syndrome plus characteristic systemic scleroderma capillaries change)
- juvenile scleroderma (debut at the age of 16 years earlier, the type of skin lesion localized scleroderma, education contractures, loss of internal organs is not manifested clinically, and is detected only during Survey).
It should be noted that each of these forms of the disease and further characterized by certain vascular changes detected by Capillaroscopy, as well as some features blood test. However, since this article is intended for a wide range of readers, we decided not to burden you much specific data.

Common symptoms of scleroderma
Symptomatology differs depending on the form of scleroderma. Some symptoms can behave as separate diseases, and even amenable to topical treatment. However, there are some common manifestations of scleroderma for all forms:
- Raynaud's syndrome - loss of limbs in response to cold weather or stress. Small blood vessels become hypersensitive to the temperature and the momentum of the nervous system, so the fingers or palm numb amid vasospasm (decrease in vessel diameter). Against the background of chronic course of changing the color of the hands and feet may occur pain in the extremities, tingling and itching.
- Modification of the skin. The most common lesions of the limbs and face. The skin is stretched excessively, because of this characteristic luster appears. There is swelling on the phalanges and between the toes. Changes in skin and swelling appear around the wrists and around the lips. Movements can become painful and difficult.
- GERD - gastroesophageal reflux diseaseAssociated with dysfunction and thickening of the walls of the esophagus and defeat its sphincter muscle. There wall damage due to increased acidity and regurgitation. gastric peristalsis is broken, so digestion becomes difficult. There are problems with the absorption of minerals and vitamins through the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. Because of GERD may appear beriberi, and minor hormonal disruptions.
What is Scleroderma: photo
The photo below shows how the disease manifests itself in humans.

Diagnostics
After attending physician, the patient is sent to a rheumatologist who evaluates symptoms and decides how to treat the disease. By inspection, which is estimated:
- Skin changes on the limbs, and carpal, metacarpophalangeal joints;
- Pathology tips on the fingers;
- Characteristic changes of skin integument and face.
Laboratory tests make it possible to identify the main disturbances in the body - structural, metabolic and functional:
- biochemistry of blood - high levels of urea, creatinine indicates kidney failure, high bilirubin speaks about defeat bile ducts;
- CBC - detect anemia, thrombocytopenia (platelet lowering), an unfavorable course of the disease - increase in ESR;
- blood test to determine the level CXCL4 and NT-proBNP - bioactive substances, which increase in output indicative of pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension;
- clinical analysis of urine - discovered protein and red blood cells suggests functional renal insufficiency;
- assays for autoantibodies (rheumatoid factor) - is carried out for detection of an autoimmune disease;
- Analysis for C-reactive protein reveals an acute stage of inflammation in the body.
Also, the patient is carried out:
- ECG for the detection of disorders of the heart;
- US of internal organs to estimate their structure and function;
- transthoracic echography for determining the pressure in the pulmonary artery;
- Capillaroscopy nail bed to examine the state of peripheral capillaries;
- measurement of the living lung volume to determine the degree of organ involvement sclerotic process;
- measurement of the living lung volume to determine the degree of organ involvement sclerotic process;
- histological examination (biopsy) of the skin and the lungs to detect sclerotic tissue changes.
In addition to laboratory, radiology applied research methods: computed tomography X-rays, which are necessary for the detection of osteomyelitis, pulmonary fibrosis, foci of calcification, formed under the skin.
complications
Scleroderma affects almost all organs and systems. Therefore, the disease is considered to be intractable.
Originally from scleroderma, of course, the skin suffers. On this basis, and diagnose the disease. Standard picture - this is swollen and reddened skin on the head and hands. In addition, these areas are often in disturbed blood circulation, there are blisters, changing the shape of the nail, the hair falls out. Changing facial features, wrinkles appear. The skin loses its quality. It happens that the disease involves not only the head and hands, but also other areas of the body. In this case, the disease is called diffuse scleroderma, if struck only certain areas of the body, it is limited scleroderma.
It happens that the disease affects the muscular system. From this muscle fibers are deformed, dying a few fragments, the amount of muscle tissue becomes less and ligaments, on the contrary, become more. If the disease gives a complication in the human skeleton, the deformed fingers on all the limbs. This is also one of the symptoms of scleroderma.
Approximately 50% of scleroderma patients suffer and organs of the digestive tract. If we carry out ultrasound of these bodies and their changes show up, it will also be a sign of scleroderma. In addition, almost two-thirds of the patients suffer from problems with the heart and lungs.
Methods of treating Scleroderma
How to treat scleroderma disease depends on the shape, extent and depth of the pathological process diseased organs and systems. Main therapeutic methods comprise administering to the following medicines:
- Vascular antifibrotic drugs whose action is designed to prevent spasm of blood vessels. The most effective means of vascular expansion are considered calcium channel blockers. These include: the dihydropyridines (amlodipine, nifedipine, nicardipine), phenylalkylamines (gallopamil, verapamil) and piperazine derivatives (flunarizine, cinnarizine).
- Antiplatelet drugs that prevent blood clots. Drugs such as acetylsalicylic acid, ticlopidine, dipyridamole increase the effectiveness of vasodilator drugs.
- Antifibrotic therapy. Doctors often prescribe in scleroderma patient penicillamine, which inhibits the formation of collagen. Thus, there is a blocking excessive formation of connective tissue.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy with diclofenac, ketoprofen, ibuprofen, nimesulide in standard dosages eliminates disruption of the musculoskeletal system.
- Symptomatic treatment which is aimed at eliminating certain disease symptoms. Thus, inflammation of the lower esophagus, doctors recommend to follow the rules of fractional power and take the course as a prokinetic meklozin, domperidone or ondansetron. Intestinal lesions require the use of antibacterial agents (amoxicillin, metronidazole and erythromycin). Manifestations of pulmonary fibrosis cropped low-dose prednisone.
Therapy limited form of scleroderma is individual. The purpose of this treatment - is a stop progress sclerosing inflammation of the skin.

Physiotherapy
Patients with scleroderma are shown:
- massage;
- enzyme electrophoresis, absorbable, anti-inflammatory drugs;
- laser therapy;
- light therapy - PUVA therapy (treatment with ultraviolet light).
It has a good effect of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide baths. Patients with systemic form of the disease acupuncture sessions are assigned (acupuncture).
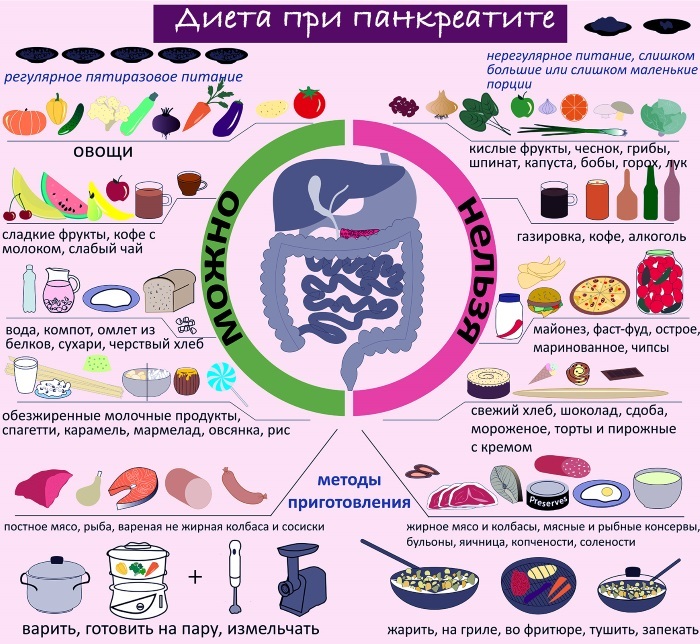
Nutrition and diet
Scleroderma is not a disease in which the need any specific diet. However, the correct nutrition to reduce the discomfort and ease the patient's general condition.
In scleroderma it is recommended to adhere to the following principles of nutrition:
- esophageal lesion avoid solid food;
- you must eat enough calories;
- avoid large doses of vitamin C (1000 mg / day), because it promotes the formation of connective tissue;
- bowel lesions should eat foods rich in dietary fibers;
- should eat plenty of vitamins and minerals, as often their absorption in the intestine is broken;
- with kidney disease expedient is reducing the amount of dietary salt and water.
Forecast
In scleroderma remains the most unfavorable prognosis among systemic connective tissue disease, and largely depends on the shape and course of the disease. According to the results of 11 studies, five-year survival of patients with scleroderma ranges from 34 to 73% and an average of 68%.
Poor prognosis factors are:
- male gender;
- rasprostranennnaya form;
- age of onset of the disease over 45 years;
- anemia, high ESR, urinary protein excretion in the onset of disease;
- pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, arrhythmia and renal injury in the first 3 years of the disease.
All patients with scleroderma are subject to dispensary observation. Medical examination is carried out every 3-6 months depending on the disease and the presence and severity of visceral lesions. At the same time hold general and biochemical blood and urine tests. Recommended study of respiratory function and echocardiography.
Patients taking warfarin should be monitored prothrombin index and the international normalized ratio, and in the treatment of cyclophosphamide - explore common blood and urine tests every 1 1-3 months.