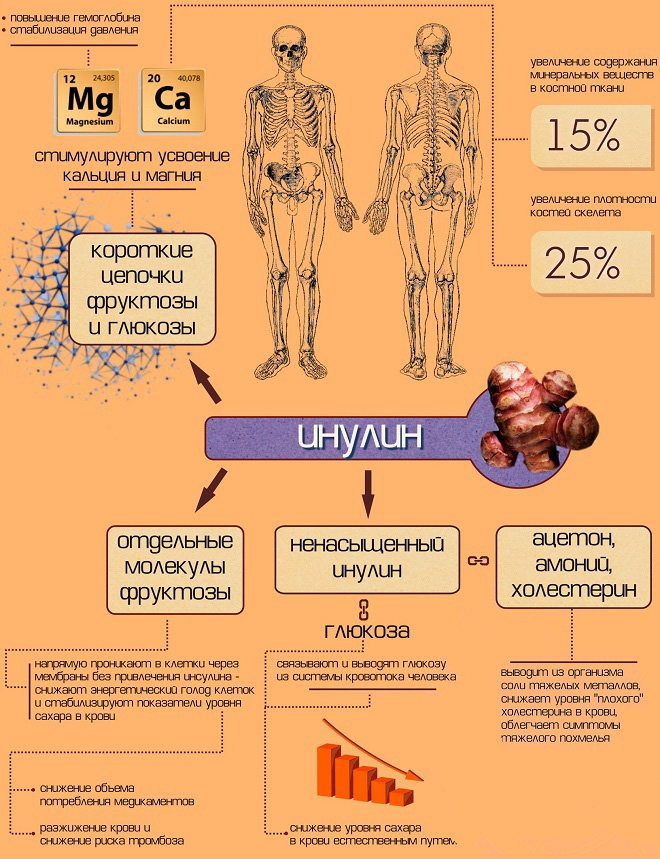
But in 10% of cases they are formed in the paraganglia (organs of the neuroendocrine system), the sympathetic ganglia and other organs. Cells which are located in the adrenal medulla produce noradrenaline and adrenaline. Those that are located in other organs, produce only norepinephrine.

What it is?
Pheochromocytoma - hormonally active tumor chromaffin cells sympathoadrenal system or adrenal extraadrenal localization secreting large amounts of catecholamines. Disease refers to tumors (benign or malignant) APUD-system and often is one of the components of the syndrome of multiple endocrine neoplasia (usually in this case is pheochromocytoma two-sided).
Causes of
The exact causes of pheochromocytoma progression has not yet been established. But scientists have several theories on this subject:
- Gorlin syndrome and Sipple syndrome. This two hereditary disease, which is characteristic of uncontrolled cell proliferation endocrine glands. In this case, not only affects the adrenal glands, but also thyroid, muscle and bone structure and so on.
- Hereditary predisposition. During the research it was found that 10% of patients who have been diagnosed pathology, there were direct relatives with the same diagnosis. Therefore, scientists have suggested that the development of the disease is directly linked to a mutation of the gene responsible for the proper functioning of the adrenal glands. As a result, brain cells begin to grow rapidly substance.
In most clinical situations, clinicians fail to identify the true cause of tumor formation.
The role of catecholamines in the body
Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted continuously in the human body. Their concentration increases sharply after the load of any kind. Catecholamines rightly called "stress hormones." Any active work, especially physical work, contribute to the release of norepinephrine and epinephrine. A manifestation of this reaction can be regarded as an increase in body temperature, increased heart rate, blood flow redistribution.
Adrenaline is considered a hormone of "fear". adrenaline occurs under strong agitation, fear, intense physical activity. Epinephrine increases blood pressure, increases the utilization of carbohydrates and fats. Physiological response to stress by the action of adrenaline is to increase endurance.
Norepinephrine is a hormone of the "struggle." Under its action significantly increases muscle strength, there is an aggressive reaction. Norepinephrine produced when bleeding, physical activity, stress. Excessive formation of catecholamines may chronic stress.
Classification
Chromaffin cells are present not only in the adrenal cortex, but also in the sympathetic ganglia, and therefore pheochromocytoma can be located in the adrenal gland and other organs and tissues. Extraadrenal localization characteristic of hereditary tumors.
Distinguish between benign and malignant pheochromocytoma. Recent occur in no more than 10% of cases. They are usually located outside the adrenal glands and predominantly produce dopamine. At diagnosis using clinical classification according to which the disease are divided into 3 groups.
With characteristic clinical picture, divided into:
- Persisting - manifest stable increase in blood pressure.
- Paroxysmal - pressure and other symptoms caused by an excess of adrenaline, appear only during an attack in the attack-free period no symptoms.
With uncharacteristic pheochromocytoma clinical symptoms that are similar to symptoms of other diseases. Can manifest as cardiovascular, psihoneyrovegetativnogo, abdominal and endocrine and metabolic syndrome.
Nemyepriznaki pheochromocytoma, without clear evidence giperkateholaminemii. They, in turn, are divided into:
- Hidden (exchange) of pheochromocytoma symptoms only under very heavy stress conditions, when the normal rhythm of life has been a slight increase in metabolism and in rare cases, emotional lability.
- Asymptomatic in which clinical symptoms are completely absent during the entire life of the patient and the tumor can not be diagnosed; in this case, along with the hormone, tumor cells produce an enzyme that transforms it into an inactive metabolite, therefore, have no symptoms.
Symptoms of adrenal pheochromocytoma
One of the main symptoms of pheochromocytoma is hypertension. High blood pressure in a patient can be episodic or chronic. In the first case of hypertension attacks provoke emotional distress, excessive exercise or overeating.
The symptoms of pheochromocytoma during an attack of hypertension include:
- pale skin,
- sweating,
- discomfort in the chest and abdomen,
- headache, pulsating character,
- nausea,
- vomiting,
- cramps leg muscles.
After an attack, the patient has a complete disappearance of all symptoms of pheochromocytoma, a sharp decrease in blood pressure up to the radically opposite state - hypotension.
Among the symptoms of pheochromocytoma complicated forms distinguish signs of neuropsychiatric, cardiovascular, endokrinno- metabolic, hematologic and gastrointestinal disorders:
- psychoses,
- renal vascular lesion and the fundus,
- hyperglycemia (elevated blood glucose),
- hypogonadism (deficit-androgen hormones in the body)
- neurasthenia,
- heart failure,
- increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate or blood,
- drooling, etc.
Pheochromocytoma, patients look like: photo
The photo below shows how the disease manifests itself in humans.

Diagnostics
During the general survey of patients identified rapid heartbeat, pale skin of face, neck and chest, high blood pressure. Also characteristic of orthostatic hypotension (when a person stands up, the pressure is sharply reduced).
One of the most important diagnostic criteria is to increase levels of catecholamines in the urine and blood of the subject. The serum levels determined as chromogranin A (universal transport protein), adrenocorticotropic hormone, calcitonin and trace elements - calcium and phosphorus.
The differential diagnosis of pheochromocytoma should be performed in individuals with complaints:
- anxiety attacks,
- hyperventilation syndrome,
- hot flashes during menopause,
- an increased need for caffeine,
- convulsions,
- brief loss of consciousness.
Non-specific changes in the electrocardiogram, as a rule, be determined only during the crisis.
When pheochromocytoma are often associated pathology - gallstone disease, neurofibromatosis, disorders of blood circulation in the extremities (Raynaud's syndrome), and hypercortisolism with the development of the syndrome Cushing's.
A significant portion of subjects detected due to hypertensive retinal vascular damage (retinopathy). All patients suspected of having pheochromocytoma need to pass an additional examination by a specialist ophthalmologist.
treatment of pheochromocytoma
During the crisis the patient requires strict bed rest. Head of the bed should be elevated. If you are unable to normalize the pressure, then you need to call an ambulance. To establish the diagnosis and selection of treatment of patients admitted to hospital.
Drug treatment of pheochromocytoma:
| Category drugs | instruction | Mechanism of action |
| Alpha-blockers | Tropafen or Phentolamine. 1 ml of a 1% solution diluted in 10 ml of isotonic NaC solution. Administered intravenously every 5 minutes until relief crisis. | Blocks adrenergic receptors, making them insensitive to the high content of adrenaline. It reduces the negative impact of hormones on the internal organs. |
| Calcium channel blockers | Nifedipine. Is the inside of 10 mg 3-4 times a day. | Blocks calcium entry into smooth muscle cells and myocardium prevents vasospasm. It decreases heart rate and lowers blood pressure. |
| Beta-blockers | Propranolol. For removal kriza intravenously administered 1-2 mg every 5-10 minutes. Inside of 20 mg 3-4 times a day. If necessary, the dose is gradually increased up to 320-480 mg per day. | Reduces sensitivity to adrenaline. It eliminates irregular heartbeat and lowers blood pressure. |
| Catecholamine synthesis inhibitor | Metyrosine. Taken orally. The initial dose of 250 mg four times a day. Subsequently, it increased to 500-2000 mg per day. | Suppresses the production of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Reduce the disease symptoms by 80%. |
Operation
Different methods of surgery can be used to remove the pheochromocytoma. These include both transbryushinnoe, extraperitoneal, transthoracic and combined.
Sometimes after the operation did not occur the positive dynamics, that is, blood pressure remains high. This may be the reasons associated with the wrong surgery. You may also receive and hypotension as a result of bleeding or inflammation of the BCC.
Deleting multiple forms of pheochromocytomas is carried out in several stages.
If you can not resection of a malignant tumor, its recurrence, or when it has a multicentric growth may surgical removal of only part of it, to reduce the functioning tissue and thereby reduce the level of circulating catecholamines.
Radical treatment of pheochromocytoma almost always gives absolute cure many patients. But as a result of prolonged giperkateholaminemii, there are changes in SSS and kidney, indicating that the preservation of the many symptoms that were before the operation. But the appointment of necessary medicines regulate blood pressure.
The most important outcome for patients remains after surgery, which may make available or missing, at the moment, metastases. Because signs that refer to a malignant tumor, for example, capsules or germination angioinvaziya give little chance for recovery. Thus, the only operative surgical treatment of pheochromocytoma can help patients, but about 8% of cases, this disease gives relapses. A mostly favorable prognosis, if not detected during the operation metastases distant character.
All patients who underwent surgery to remove the pheochromocytoma was performed, are on permanent medical observation.