AIT most frequently detected in women aged 30-50 years and after pregnancy, and men - at the age of 40-65 years. The illness has no pronounced clinical symptoms. For many years, and sometimes decades, it can generally does not manifest itself.
Pain in this disease is absent. And often the only indication of the presence of low-intensity pathological changes in the thyroid gland can be increased titer of TPO.

What it is?
Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's thyroiditis) - is an inflammatory disease of the thyroid gland, arises due to the production of antibodies to the body's own thyroid (thyroid). They suffered 10 people out of a thousand.
Causes of
Regardless of the intended traditionally the main reason - a genetic predisposition, thyroiditis requires special conditions and the occurrence of other reasons for the development.
- Uncontrolled medication, especially hormonal or composition containing active iodine;
- The presence of foci of various types of chronic diseases in the acute form (carious teeth, inflammation of the tonsils or nasal sinuses);
- Harmful medium adverse effect ecology, surplus water and food chlorine, iodine, a second air oversaturated them;
- Hormonal instability - hormonal background of organism in view of other diseases due to trauma, pregnancy, after receiving the drugs in the other cases;
- The presence of radiation exposure during radiotherapy, or when working with radioactive substances, as active insolation;
- Trauma, stress, chemical and thermal burns, in general, and directly in the thyroid gland as well surgical intervention may negatively affect.
development of the disease is gradual, the basis for its acceleration or recurrence of active forms may be a number of factors in combination.
Classification
What is autoimmune thyroiditis, in terms of the classification of types? There are the following variants of the disease:
- Postpartum thyroiditis, which becomes a consequence of the excessive increase in the activity of the immune system after depression during pregnancy.
- Thyroiditis autoimmune origin, in which the developing primary hypothyroidism (deficiency of thyroid hormones).
- Cytokine-induced variant of the disease, which develops after prolonged interferon therapy.
- Silent (silent) thyroiditis, thyroid, postpartum similar to, but not caused by pregnancy.
By the nature of the flow recovered 3 major forms of autoimmune thyroiditis. It:
| The latent (hidden) | in which may be signs of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism but thyroid function are not violated. |
| hypertrophic | when iron is increased in volume (diffuse form) or in the nodules formed therein (nodular form) |
| atrophic | the most severe kind of disease in which iron is often reduced in volume |
Development of all types of autoimmune thyroiditis has 4 phases:
- euthyrosis - with preservation of pancreatic function;
- subclinical phase - partial violation of hormone synthesis;
- thyrotoxicosis - a characteristic feature of which is the high level of the hormone T4;
- hypothyroid phase - when reduced below a critical threshold during further goiter number of its cells.

Symptoms of autoimmune thyroiditis
Of various forms of the disease have certain characteristics.
Since pathological significance of chronic autoimmune thyroiditis organism is practically limited to developing at the final stage hypothyroid, euthyroid neither phase nor phase subclinical hypothyroidism clinical manifestations not have.
The clinical picture of chronic thyroiditis is formed, in fact, following polisistemny symptoms of hypothyroidism (thyroid suppression functions):
- intolerant of habitual physical activities;
- Slow response to external stimuli;
- depression;
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- feeling unmotivated fatigue;
- loss of memory and concentration;
- "Myxedema" appearance (puffiness of the face, puffiness around the eyes, skin pallor jaundiced, weakening mimicry);
- slowing of heart rate;
- loss of appetite;
- tendency to constipation;
- dull and brittle hair, their increased loss;
- decreased libido;
- dry skin;
- tendency to increase body weight;
- extremities chilliness;
- menstrual dysfunction in women (from intermenstrual uterine bleeding to complete amenorrhea).
The unifying characteristic for postpartum, silent and cytokine-induced thyroiditis - a succession of stages of the inflammatory process.
Symptoms characteristic of thyrotoxic phase:
- weight loss;
- intolerance of stuffy premises;
- tremor of limbs, trembling fingers;
- impaired concentration, memory loss;
- emotional lability (tearfulness, mood swings);
- tachycardia, increased blood pressure (blood pressure);
- feeling hot, hot flashes, sweating;
- decreased libido;
- fatigue, weakness, alternating with episodes of increased activity;
- menstrual dysfunction in women (from intermenstrual uterine bleeding to complete amenorrhea).
Manifestations hypothyroid phase similar to the manifestations of chronic autoimmune thyroiditis.
A characteristic feature of post-partum thyroiditis - the debut of hyperthyroidism symptoms to the 14th week, the signs of hypothyroidism - a 19 or 20-weeks postpartum.
Pain-free and cytokine-induced thyroiditis do not demonstrate, as a rule, stormy clinical picture, manifesting symptoms moderate severity, or are asymptomatic and detected during routine investigations thyroid hormone levels.
Diagnostics
In the case of suspicion of the presence of autoimmune thyroiditis following diagnosis should be carried out. Blood sampling on detection of hormones:
- TSH;
- T4 - free and overall;
- T3 is the free and total.
With an increase in TSH and normal T4 performance - we can talk about the presence of subclinical disease, if T4 with increasing TSH level is reduced - which means that the first symptoms of the disease on the way.
Diagnosis is established by combination of the following data:
- Reduced concentrations of T4 and T3, and TSH levels increased;
- on thyroid ultrasound determined hypoechogenicity tissue;
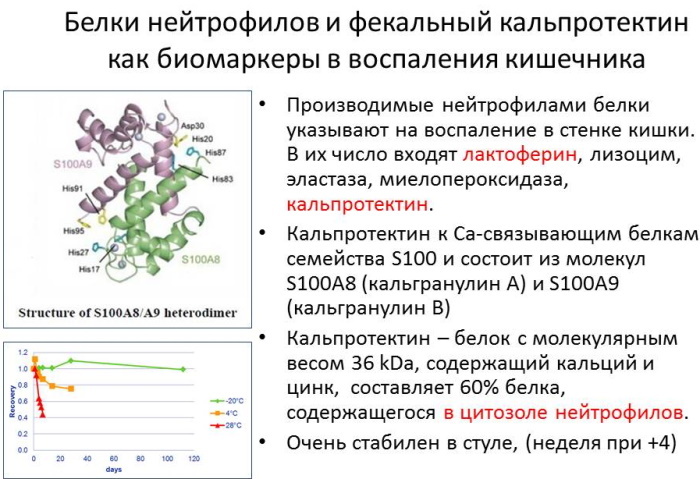
- increased levels of antibodies to an enzyme shchitovidki - thyroid peroxidase (TPO) in the venous blood.
If there are deviations of only one of the indicators of a diagnosis difficult. Even in the case of increasing the TPO can talk about the patient's susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid lesion.
In the presence of nodal thyroiditis node biopsy is performed to visualize the pathology as well as to eliminate cancer.

How to treat autoimmune thyroiditis?
Hitherto autoimmune thyroiditis no effective treatment methods have been developed. In case of thyrotoxic phase of the disease (appearance of blood thyroid hormones) Appointment tirostatikov, that is, drugs that suppress the activity of the thyroid gland (methimazole, carbimazole, propitsil), not recommended.
- If the patient has identified irregularities in the cardiovascular system, are appointed by beta-blockers. In identifying thyroid dysfunctions assigned thyroid preparation - levothyroxine (L-thyroxine) and treated carefully combined with regular monitoring of the clinical picture of the disease and the determination of the content of thyroid-stimulating hormone in serum blood.
- Often, in the autumn-winter period the patient AIT observed occurrence of subacute thyroiditis, ie, inflammation of the thyroid gland. In such cases, the appointed glucocorticoids (prednisolone). To combat the increasing number of antibodies in the patient's body are used such non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as voltaren, indomethacin, indomethacin.
In case of a sharp increase in the size recommended thyroid surgery.
Forecast
Autoimmune thyroiditis in most cases has a favorable prognosis. When diagnosing persistent hypothyroidism requires life-long therapy with levothyroxine. Autoimmune hyperthyroidism tends to slow the flow, in some cases, patients may be in a satisfactory condition about 18 years, in spite of minor remission.
Observation of the dynamics of the disease should be inspected at least once every 6-12 months.
In identifying the nodes at the time of thyroid ultrasound examination, the need for immediate consultation endocrinologist. If nodes have been identified with a diameter of more than 1 cm, and the dynamic observation comparison results of previous ultrasound, celebrated their growth, performance of needle biopsy of the thyroid gland to exclude malignancy process. Monitoring of thyroid sonography should be performed every 6 months. With a diameter of nodes less than 1 cm, reference ultrasound to be performed once every 6-12 months.
In attempts to impact on autoimmune processes (in particular on the humoral immunity) in the thyroid gland in over a long period of time glucocorticosteroids administered in high enough with this pathology doses. At the moment, clearly proved the ineffectiveness of this type of therapy in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis. Purpose of glucocorticoids (prednisolone) is expedient only in case of the combination of subacute thyroiditis and autoimmune thyroiditis, usually occurring in the autumn and winter.
In clinical practice, there were cases when patients with autoimmune thyroiditis with signs of hypothyroidism in pregnancy is spontaneous remission. Also, there were cases when patients with autoimmune thyroiditis, in which before and at the time of pregnancy manifested eutiroidnoe condition after giving birth, it was aggravated by hypothyroidism.