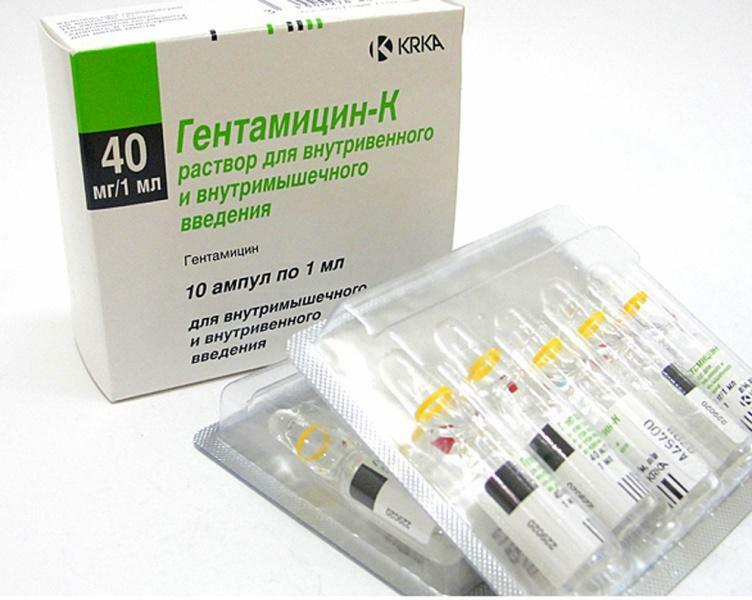
Cystitis is the inflammation of the inner( mucous) membrane of the bladder. Cystitis can be both an independent disease, and complication of a number of conditions, most often - diseases of the genitourinary system. In the vast majority of cases, cystitis is caused by bacteria.
Cystitis is the most common disease of the urinary system. The emergence of cystitis is the most frequent reason to call a urologist, especially among women!
Cystitis in pregnant women: what to treat?
Content of the material
- 1 Cystitis epidemiology
- 2 Cystitis pathogenesis
- 3 Cystitis of pregnant
- 3.1 Video - Cystitis in early and late pregnancy
- 4 Clinical manifestations of cystitis in pregnant women
- 5 Treatment of cystitis in pregnant women
- 5.1 Video - How to treat cystitis in pregnancy
Epidemiology of cystitis
Cystitis occurs in all age and sex groups, but the incidence of cystitis in female subjects is much higher than that of men: according to statistics, women are illistitom 3-6 times more often. This is due to the peculiarities of the anatomy of the lower urinary tract and the less extended urethra in women, which facilitates the penetration of bacteria into the bladder lumen ascending.
Among the individual population groups of cystia, the most vulnerable are women of reproductive age who have an active sex life. With age, the incidence of inflammation of the bladder becomes much less, and after 70 years it can be found with equal probability in both men and women. In addition, the frequency of occurrence of cystitis is affected by concomitant conditions and diseases, namely:
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Congenital malformations of the urinary system.
- Immunodeficiency.
- Pregnancy.

What is cystitis
Cystitis among the population is considered a kind of fast-paced disease that does not leave after itself the consequences, the treatment of which does not present particular difficulties. In fact, in addition to the extremely unpleasant and life-threatening symptomatology, cystitis can lead to a number of adverse consequences and complications. In itself, the presence of inflammation of the bladder is a sign of a violation of the body's defense mechanisms from the introduction of infection: after all, in a healthy person, the urinary system is sterile. Repeated cases of cystitis lead to a structural rearrangement of the bladder and ureters, which can subsequently be accompanied by the development of ascending infection, such as pyelonephritis, and this is an extremely dangerous condition. In addition, the relationship between the frequency of inflammation of the bladder and the likelihood of cancer of this organ is now proven!
Cystitis pathogenesis
There are a lot of reasons for the development of cystitis, and in principle they can be divided into two large groups: infectious and non-infectious( see table).
| Infectious factors | Noncommunicable factors |
|---|---|
| Bacteria | Chemicals |
| Viruses | Hypothermia |
| Mushrooms | Allergy |
| Chlamydia and Mycoplasma | endocrine and metabolic disorders |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Radiotherapy |
| Poor treponema | Drugs Parasitic infections |

Symptoms of acute cystitis
However, with all the variety of factors, the main cause of development of cystitis are bacteria living in a number of located organs: the rectum, the vagina, the large intestine, and also on the skin. Thus, the body's own flora - Escherichia coli, Proteus or Klebsiella - is the most likely culprit of cystitis. By what scenario does the disease develop?
The bladder is a hollow organ that communicates with the external environment through the urethra, or urethra. It is through the urethra in the vast majority of cases that microorganisms enter the bladder. Since the urethra is smaller in women than in men, the probability of infection of the bladder is much higher.
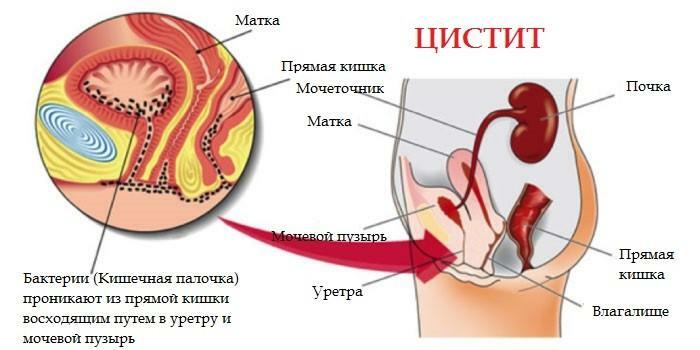
Cystitis in women
However, acute cystitis does not occur in every woman. The thing is that the inner surface of the urethra is normally very resistant to bacteria. The substances released by epithelial cells, called glycosaminoglycans( GAG), prevent the attachment of microorganisms to the walls of the urethra, and not fixing, the microbes are not able to divide and multiply.
Thus, for penetration into the urethra, bacteria need to overcome this protective barrier. This is possible in the following cases:
- The hormonal background of a woman is changed, resulting in a thinning, wilting of the mucous membrane of the urethra and a decrease in its protective properties. Such a mechanism underlies the so-called.postmenopausal cystitis - a chronic inflammation of the bladder that occurs in menopause and hard to treat.
- In the vagina, which is in the immediate vicinity of the outer part of the urethra, it may develop an uncharacteristic microflora. Normally, in women, vaginal microorganisms have a pronounced protective effect and do not allow the development of other, pathogenic microbes around themselves. However, in order to maintain the species composition of the flora at a satisfactory level, a good general condition of the organism is necessary, which creates conditions for the normal life of this very flora. In a number of cases, this equilibrium is violated.

Duration of clinical manifestations with acute cystitis
The most common reasons for this are as follows:
- Diabetes mellitus : Increased glucose in the tissues of the vagina creates excellent conditions for the development of fungal( yeast) flora and other pathogenic microbes. In diabetes mellitus, immunity and the ability of tissues to resist the excessive growth of opportunistic microorganisms are also impaired. Cystitis is a frequent companion of diabetes in women.
- Any immunodeficiency of , including acquired ones( HIV infection in AIDS stage, pronounced vitamin deficiency, treatment with hormones or cytostatics, severe operation, exhaustion).
- Anemia of any origin : reduces the body's resistance in general, so against the background of anemia, women often develop cystitis.
- Reception of antibiotics .It would seem a paradoxical situation: taking antibiotics can lead to the development of cystitis, for the treatment of which the same antibiotics are used! The fact is that taking antibacterial drugs to treat any infection is always accompanied by a systemic effect on the body. As a result, temporary dysbacteriosis may develop, incl.- and in the vagina. After some time after a course of antibiotics, a woman may have cystitis.
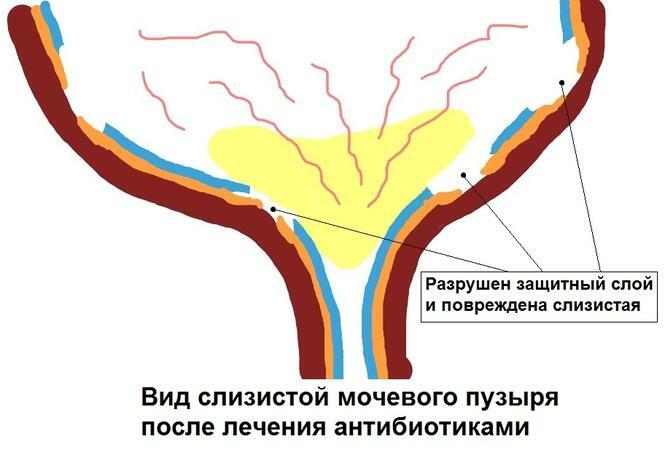
Kind of mucosa of the bladder after treatment with antibiotics
- Use of spermicides for contraception .The mechanism of development of cystitis is about the same: spermicides, acting on the flora of the vagina, violate its composition and thereby - the protective properties. It is proved that out of ten women who use diaphragms with spermicides, within a year seven times at least once they get cystitis.
- The younger or preschool age of girls .In this period, firstly, immunity has not yet been formed, and secondly, attention to hygiene of genital organs is reduced.
- Increased sexual activity : a very important factor in the development of cystitis. During intercourse, microtraumatism occurs not only the walls of the vagina, but also the entrance to the urethra. The inflammation developing there, not felt subjectively, nevertheless promotes the penetration of microorganisms into the bladder. For cystitis associated with sexual intercourse, there is a special name for "postcoital cystitis."With sexual intercourse, such states as defloration cystitis and cystitis of the first honeymoon are closely related, because it is during this time period that the sexual activity of the newlyweds is maximal.

What causes cystitis
In women, the occurrence of cystitis in the vast majority of cases is associated with cervical inflammation or bacterial vaginosis!
Separately it is necessary to consider a cystitis of pregnant women, clinic and which treatment has the distinctive features.
Cystitis of pregnant women
Of a hundred pregnant women, about two suffer from cystitis, which can be regarded as a fairly common phenomenon. In this category of women, cystitis is a multifactorial disease in which development matters:
- Hormonal restructuring.
- Mechanical compression of small pelvis vessels with a growing uterus.
- Systemic circulatory disorders.

Development of cystitis
In general, the mechanism of development of cystitis in pregnant women is as follows: a growing pregnant uterus presses on the bladder in such a way that the normal evacuation of urine from the bladder is disrupted;In addition, there is a stagnation of blood, which together dramatically reduces the protective properties of the urethral epithelium and promotes the development of infection. The hormonal background in pregnant women leads to the formation of soft tissue edema( which is visible to the naked eye and is one of the signs of pregnancy), including in the pelvic area. This supports broken blood circulation throughout pregnancy.
In addition, during pregnancy, there is a violation of another phenomenon: the closure of the ureters at the time of urination. Normally, during a urination attempt, a person contractes the ureters in the part in which they communicate with the bladder. This prevents reverse urine flow and infection of the kidneys.
In pregnant women due to mechanical reasons( compression by the uterus of the bladder), compression of the ureters does not occur. Therefore, urine, infected with various pathogens, can rise up the ureters to the kidney itself.
In pregnant women, the development of cystitis is dangerous with the addition of pyelonephritis, so cystitis should be rectified in a timely manner!
Video - Cystitis in early and late pregnancy
Clinical manifestations of cystitis in pregnant women
In general, the clinic of cystitis in pregnant women does not differ from that of non-pregnant women and consists of the following symptoms:
- Painful urination( dysuria).The pain is burning.
- The appearance of blood in the last portion of urine( it can be colored in brown color) - the so-called.terminal hematuria.
- Frequent urination( pollakiuria).
- The continuing urge to urinate, even against the background of an empty bladder. This symptom indicates the development of inflammation in the region of the cystic sphincter.
- Urination at night( nocturia).
This symptom complex is characteristic of any cystitis during its peak. Confirmation of the diagnosis is a general analysis of urine, in which a large number of leukocytes( pyuria), mucus, bacteria, altered and unchanged erythrocytes, as well as epithelial cells, are detected.
However, given the high likelihood of developing pyelonephritis during pregnancy, a modern strategy for treating pregnant women suggests an early diagnosis of the development of urinary tract infection, even before the development of clinical symptoms. To do this, all women during pregnancy should regularly take urine tests for the detection of bacteria( bacteriuria) in it.

Choice of medicines for pregnancy
If a pregnant woman has bacteriuria in more than 105 pathogens( even if there are no clinical manifestations of urinary tract infections), this condition is subject to compulsory treatment!
Asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women turns into pyelonephritis with a frequency of 20 to 40%, and pyelonephritis, unlike cystitis, can threaten the health of both mother and child and requires hospitalization in a therapeutic hospital. That is why early diagnosis of asymptomatic bacteriuria is so important.
Treatment of cystitis in pregnant women
When it comes to cystitis of bacterial origin, then the treatment of this disease is based on antibiotics. In this case, the treatment of cystitis in pregnant women has a number of features:
- The minimum duration of treatment for acute cystitis, according to current recommendations, should be 7 days.
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria also requires active antibacterial therapy lasting 3-5 days.
- It is necessary to take into account the negative effect of the drugs used on the fetus.

Treatment of cystitis in pregnancy
The choice of antibiotic in the treatment of cystitis is primarily determined by the safety of the drug for the fetus, and only then - its effectiveness for the mother.
Of the drugs currently used for pregnancy, the following are definitely recommended:
| Antibiotic | Image | Dosage | Indications | Application features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphomycin |  | 3 grams once | Asymptomatic bacteriuria( BB) | With sensitive flora |
| Amoxiclav, Augmentin |  | 0.5 g every 12 hours for 3-5-7 days | BB andcystitis | With sensitive flora |
| Cefalexin |  | 0.5 g every 12 hours for 3-5-7 days | BB and cystitis | With increased resistance |
| Trimethoprim |  | 200 mg every 12 hours for 3-5-7 days | BB andcentnersTruth | Contraindicated in the first trimester |
| Amoxicillin |  | 500 mg 3 times a day 3-5-7 days | BB and cystitis | With sensitive flora |
After the treatment all pregnant women should regularly( at least once a month!) take a general urine testfor the timely detection and treatment of recurrences of cystitis or bacteriuria.