Severe pain, shortness of breath and weakness in the body, as well as fever are serious reasons to go to the hospital. Haemophilus influenzae is accompanied by just such symptoms. As it progresses infectious inflammatory process complications appear in the absence of timely and correct therapy.
Record content:
- 1 What is Haemophilus influenza?
- 2 Reasons for the appearance
- 3 How does the infection take place?
- 4 What diseases does it cause?
- 5 Risk group
- 6 Symptoms for various diseases
- 7 Diagnostics and analyzes
- 8 In what cases is a hemophilic bacillus culture with an antibiotic susceptibility test prescribed?
- 9 Vaccination
- 10 How to treat Haemophilus influenzae?
- 11 Treatment for complications
- 12 Possible complications, why infection is dangerous
- 13 Haemophilus influenza vaccine video
What is Haemophilus influenza?
Hemophilus influenzae in medicine is called influenza infection. The disease often affects the organs of the respiratory system, provoking a strong infectious inflammatory process. In some situations, other internal organs also suffer, purulent foci are formed in them.
The causative agents are pathogenic bacteria of the hemoflux class. The source of infection is a person. The disease is accompanied by characteristic signs, with which it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
The initial examination will help the specialist to make a preliminary diagnosis and send the patient to the most informative research. The results obtained are taken into account when choosing a treatment regimen.
Reasons for the appearance
There are numerous factors that create favorable conditions for the development of hemophilic infection after it enters the human body:
- bad habits (abuse of alcoholic beverages, tobacco products, drugs);
- long-term treatment with certain antibacterial drugs;
- poor living conditions;
- prolonged stress, nervous tension, emotional outbursts;
- unfavorable ecological environment.
Overcooling of the body or high temperature are also provoking factors.
How does the infection take place?
Haemophilus influenzae is an infection, mainly by airborne transmission. Infection occurs when the patient sneezes, coughs or talks, with the release of mucus, phlegm.
In some situations, the pathogenic pathogenic flora enters the human body through contact and everyday life. We are talking about a towel, toys or dishes. A person is a source of infection from the moment of infection until complete recovery.
Hemophilic infection enters the human body through the nasopharynx. This is a latent stage when the pathogenic flora develops within the ENT organs. Further, the body's resistance decreases, the growth of pathogenic bacteria occurs. This stage is manifest, when a viral infection joins.
Throughout the body, Haemophilus influenzae spreads through the blood or lymph, getting into various internal organs and provoking an inflammatory process. In difficult situations, even bones and joints are affected. Once in the central nervous system, Haemophilus influenzae affects the meninges, provoking the development of meningitis.
What diseases does it cause?
Hemophilic bacillus, penetrating into the human body, causes certain pathological diseases:
- purulent arthritis;
- acute pneumonia;
- purulent meningitis;
- epiglottitis (a disease that is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the epiglottis region);
- osteomyelitis;
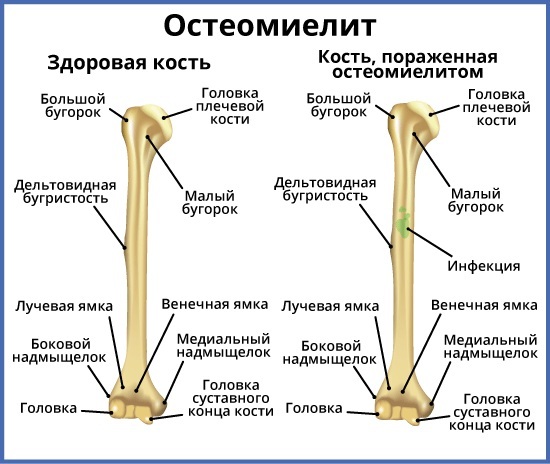
- septicemia (a pathological condition in which blood is infected, weakness appears as a result of a developing inflammatory process);
- cellulite (subcutaneous fatty tissue becomes inflamed).
Otitis media, sinusitis, pericarditis, pleurisy are also a consequence of the development of Haemophilus influenzae in the human body. Each disease is accompanied by characteristic clinical symptoms.
There are also carriers of haemophilus influenzae. The person feels well, there are no clinical signs, but he is dangerous to those around him. The carrier constantly releases pathogens into the environment.
Risk group
Conditionally pathogenic microorganisms are always present in the body of a healthy person. They are harmless as long as, for example, a person's immunity is strong. Against the background of its decrease, favorable conditions are created for the development of infection, therefore, pathogens begin to multiply, thereby provoking the development of the inflammatory process.
Haemophilus influenzae is a serious and dangerous infection that often occurs in the following segments of the population:
- newborns;
- elderly people;
- persons who live in unfavorable living conditions;
- people with congenital or acquired immunodeficiency pathological conditions;
- children who attend kindergarten;
- persons suffering from chronic alcohol dependence.
Infection with Haemophilus influenzae also threatens patients who take cytostatics and formula-fed children. The same applies to premature babies, preschool workers, and cancer patients. Children from orphanages are also at risk.
Symptoms for various diseases
The clinical picture of Haemophilus influenzae infection depends on the type of disease, which was provoked by pathogenic microorganisms:
- Purulent meningitis. The lining of the brain becomes inflamed. Pathology is more often diagnosed in children under 5 years of age. Purulent meningitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the temperature rises sharply, which is accompanied by chills;
- a severe headache appears;
- a person is worried about excruciating nausea;
- muscles and joints hurt;
- psychomotor agitation appears;
- human consciousness is disturbed;
- there is a stiffness of the muscles in the back of the head;
- the upper eyelid drops;
- squint appears.
- Pneumonia. The disease is characterized by pneumonia and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- body temperature rises;
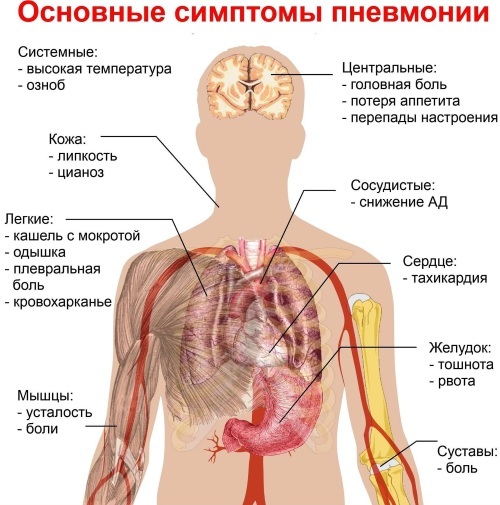
- sore throat;
- sweating increases;
- a person is worried about general weakness, weakness;
- appetite worsens;
- a small amount of sputum is separated;
- shortness of breath appears after minor physical exertion and at rest;
- worried about intense cough;
- worried about severe pain in the chest area when inhaling.
- Hemophilic sepsis. It is more often diagnosed in newborns, in particular, in those who are on artificial feeding. The symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- body temperature rises sharply;
- there is a strong chill;
- the body is covered with maroon rashes;
- appetite worsens;
- stool is disturbed;
- sleep problems appear, insomnia worries;
- internal organs affect purulent foci;
- septic shock develops, which is fatal.
- Hemophilic cellulite. The disease often manifests itself on the face, rarely affecting the lower or upper extremities. The pathological condition is characterized by the following symptoms:
- slight weakness appears;
- body temperature rises;
- headache occurs;
- sore throat worries;
- stuffy nose;
- swelling of the eye and cheek;
- the skin first acquires a red tint, then cyanotic.
- Epiglottitis. A strong inflammatory process affects the epiglottis cartilage. The disease is characterized by the following clinical symptoms:
- signs of severe intoxication of the body appear;
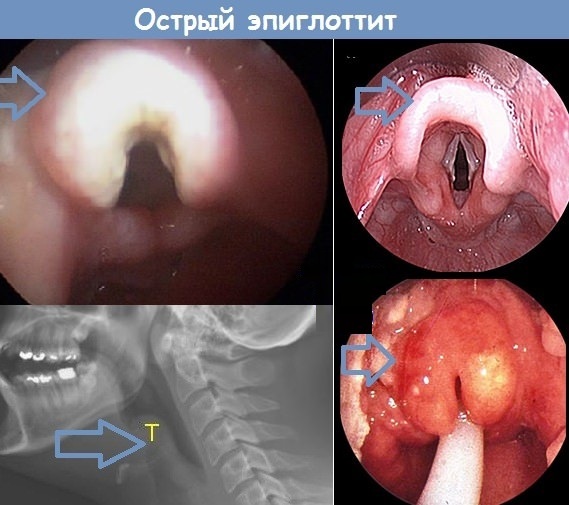
- body temperature rises;
- fever occurs;
- apathy appears to the world around;
- breathing becomes noisy;
- the upper and lower limbs are warm, but the skin becomes bluish;
- respiratory failure intensifies.
- Purulent arthritis. Pathology is characterized by a strong inflammatory process, which is provoked by pyogenic microorganisms. The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- fever appears;
- there is a general weakness in the body;
- worried about muscle and headache;
- the skin is swollen;
- the local temperature rises;
- limited mobility in the affected joint.
The incubation period is different in each case, depending on the person's immunity, but more often 2-4 days pass between the infection of the body and the appearance of the first signs.
Diagnostics and analyzes
Haemophilus influenzae is a dangerous disease, the main and most informative diagnostic method of which is bacteriological culture. The taken material is colonized in a suitable environment and the development of pathogenic bacteria is monitored.
Taking into account the pathologies that arise during infection with a hemophilic bacillus, experts take the following types of material for research:
- sputum from the lungs (with the development of bronchitis, pneumonia);
- joint fluid (with the development of arthritis);
- CSF (with the development of meningitis);
- purulent discharge (with the development of pneumonia, purulent infectious diseases);
- mucus (with damage to the upper respiratory tract).
Patients with suspected infection with Haemophilus influenzae are also prescribed additional diagnostic tests:
- Blood analysis. Plasma is examined, in which specialists identify the DNA of the causative agents of the disease.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A diagnostic method that allows you to determine the DNA of pathogenic microflora in the patient's blood.
-
Serological tests. The blood is examined for antibodies to the causative agents of hemophilic infection.
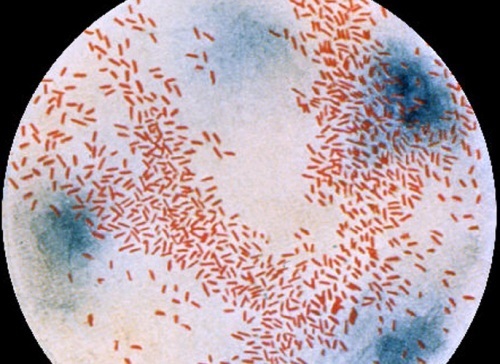
Haemophilus influenzae under a microscope
Instrumental diagnostic methods help to determine the complications of an infectious lesion of the body. (X-ray, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography). It is important to differentiate infection with Haemophilus influenzae, as many of the symptoms are similar to other manifestations of numerous diseases.
In what cases is a hemophilic bacillus culture with an antibiotic susceptibility test prescribed?
Bacteriological culture is a diagnostic method by which experts determine the type of pathogen and its resistance to antibacterial drugs.
The taken pathogenic flora is placed in a favorable environment with a certain temperature regime. Specialists monitor the development of pathogens. The information received after laboratory tests will allow you to choose the most effective and adequate treatment for patients.
Bacteriological culture has certain advantages and disadvantages:
| Positive sides | Negative sides |
|
|
In medical practice, bacteriological inoculation is widely used.
Laboratory research is indicated in the following situations:
- infectious diseases;
- gynecological pathologies;
- urological lesions;
- oncological diseases;
- otolaryngological pathologies.
Without fail, bacteriological culture is prescribed to patients with suspicion of a strong inflammatory process that has affected the internal organs or systems of the body. The same goes for sepsis.
Vaccination
Vaccination is the prevention of influenza infection. It is better to prevent the disease with a vaccine than to cure it. Haemophilus influenzae is difficult to treat, in most cases leads to serious complications.
Various vaccines are used for prevention: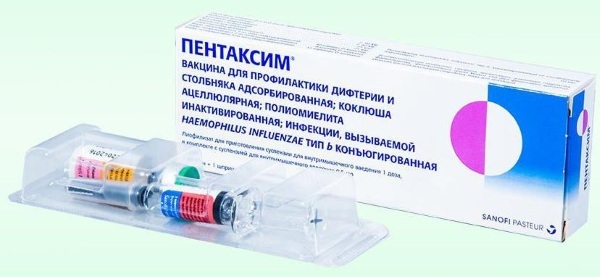
| Name | Description |
| Act-HIB | French-made vaccination. It contains the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type B. To develop immunity, it is allowed to enter a person from 2 months of age. |
| Pentaxim | Vaccine for the prevention of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, poliomyelitis, infection caused by Haemophilus influenzae type B. |
| Infanrix Hexa | Belgian vaccination. Infanrix Hexa vaccine is indicated for primary and booster immunization of children in order to prevent diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, polio. |
Haemophilus influenzae has a specific prophylaxis - this is vaccination. It helps to reduce not only the incidence rate, but also the carriage of pathogens.
Vaccination is carried out in several stages:
- The first vaccination is given to a child at 3 months.
- The second injection is given at 5 months of age.
- The next vaccination is done after six months.
- The last time a child is vaccinated is 1.5 years.
A pediatrician will help you choose the vaccine, taking into account the condition of the little patient and the individual characteristics of his body.
How to treat Haemophilus influenzae?
Therapy for the disease provoked by the Haemophilus influenzae is selected by the doctor after a comprehensive medical diagnosis. The patient is prescribed medications, taking into account the results of the study, the degree of development of pathological processes and the individual characteristics of the organism. The patient is shown bed rest, proper nutrition.
The treatment regimen involves the use of the following drugs: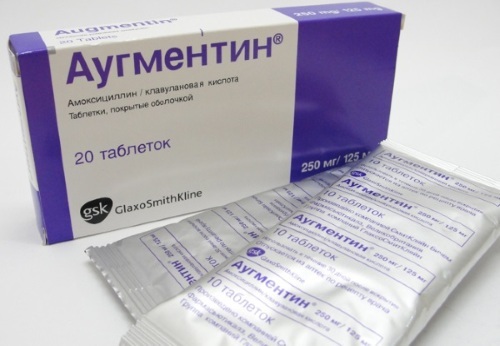
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Antibacterial agents | Augmentin, Emoxilav | The drugs act directly on the causative agents of the disease. The dosage of the drug depends on the patient's body weight and the degree of development of pathological processes. Adults are prescribed 1 tablet (125, 500, 875/125 mg) 2-3 times a day. The course of therapy lasts 5-14 days. |
| Antipyretic drugs | Nurofen, Paracetamol | The medicine reduces the inflammatory process. The drug should be taken orally with plenty of water. The adult dosage is 1 capsule. A certain time interval must be observed between doses, at least 4 hours. The maximum daily dosage is 1200 mg. |
| Expectorants | Ambroxol, ACC | The medicine is taken orally after meals with a little water. Adults are prescribed to take 30 mg 3 times a day for the first 3 days. On day 4, it is recommended to take 30 mg 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 4-5 days without consulting a doctor. |
| Immunomodulators | Likopid, Imunorix | The medicine is taken orally before meals for 30 minutes. The standard dosage for adults is 1-2 mg once a day. The course of treatment lasts 10 days. |
| Diuretics | Furosemide, Hypothiazide | The drug has a diuretic effect, eliminates edema, which can provoke serious consequences (cerebral edema, arterial hypertension). Adults are advised to take 40 mg 1 time per day. |
| Antihistamines | Zyrtek, Zodak | The dosage and treatment regimen with the drug depends on the patient's condition. Adults are prescribed 5-10 mg once a day. The course of therapy is determined by the doctor, taking into account the disease. |
In emergency situations with severe intoxication of the body, detoxification solutions are administered to the patient. Additionally, vitamin complexes are prescribed to increase and strengthen the defenses.
Treatment for complications
Haemophilus influenzae is a serious infection that entails dangerous complications, and they also require specially selected therapy.
Treatment in most cases is carried out with antibacterial agents:
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| Rifampicin | The medicine is recommended to be taken 30 minutes before meals. The adult dosage is 0.45-0.6 g per day. The capsules can be taken in the morning and in the evening. |
|
| Cefuroxime | The medicine is administered intramuscularly or intravenously. Adults are prescribed 0.75 g 3 times a day. |
|
It is important not only to eliminate the underlying disease, but also the complications after it. Medicines are selected by an infectious disease doctor, taking into account the patient's condition.
Possible complications, why infection is dangerous
The lack of timely diagnostics and correctly selected therapy entails the occurrence of serious consequences, up to and including death.
| Name | Description |
| Cerebral edema | Complication in the development of meningitis. In most cases, it is fatal. |
| Acute respiratory failure | A serious consequence of hemophilic infection, against the background of which the risk of developing pneumonia increases. |
| Asphyxia | The pathological condition is characterized by obstruction of the airways. It is a consequence of the defeat of the ENT organs. Provokes acute respiratory failure, as a result of which the patient dies. |
Complications of Haemophilus influenzae are also infectious-toxic shock, osteomyelitis and mental disorders. The same goes for persistent visual acuity, sepsis, and hearing loss. In pregnant women, the presence of pathogenic bacteria provokes spontaneous miscarriage, the development of defects that are dangerous for the child.
The main defense against Haemophilus influenzae is the vaccine. This is a dangerous infection that is more often diagnosed in children at an early age. Therefore, it is important to vaccinate the child in order to protect his body from serious pathologies that develop during infection.
Haemophilus influenza vaccine video
Vaccinations for children against pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae: