Brucellosis is an infectious diseasecaused by small ellipsoid gram-negative bacteria.
People get sick after contact with infected animals or eating meat, unpasteurized milk from infected animals. As a rule, a person infected with brucellosis is not a spread of the infection. The disease, the symptoms of which are very diverse, is more common in young people and middle-aged people.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Brucellosis video
Views
The development of the disease is influenced by various types of brucella.
In nature, 6 species are known, but 4 species are most active:
- Brucella melitensis, a gram-negative bacterium transmitted by sheep and goats, most often infects humans and causes the most severe forms of the disease in humans.
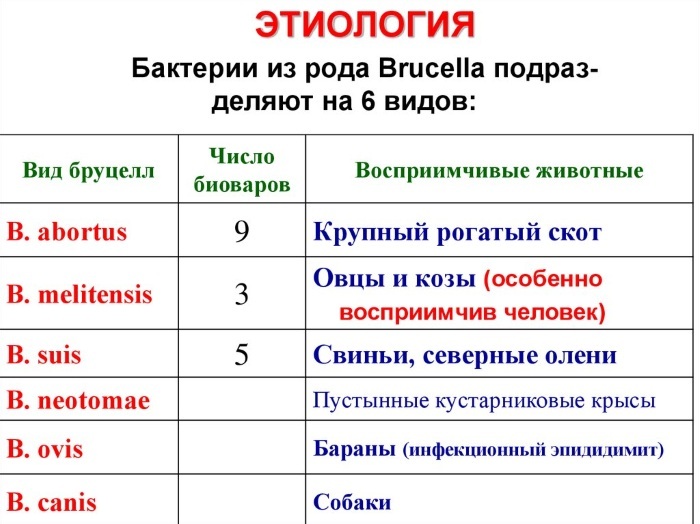
- Brucella abortus, a livestock-borne bacterium.
- Brucella suis, a bacterium carried by pigs.
- Brucella canis, which spreads through domestic animals, particularly dogs.
Stages and degrees
Brucellosis in humans (symptoms in children and adults are the same) has several clinical forms:
- Acute malignant. Symptoms of this stage of acute brucellosis are similar to those of the flu and include sudden onset of fever, chills, prostration, and physical pain. Perhaps the development of lymphadenopathy, a condition in which the lymph nodes are enlarged. The spleen and liver become palpable. Sudden death may occur at this stage, a few days after the onset or after several weeks of delirium and coma.
- Recurrent brucellosis (fever). Comes after 2 months after the initial episode of the disease. It is characterized by flu-like symptoms that recur with undulating relapses. The cycles can last for several weeks, gradually decreasing the severity of the disease.
- Chronic (intermittent). The duration of the disease can be up to 1 year or more. This form is caused by the bacillus B. abortus. The onset may be acute or there is a gradual increase in malaise, weakness, weight loss, and vague physical pain. Fever is usually mild, but weakness can be severe.
Acute brucellosis takes three forms:
- light severity;
- medium;
- heavy.
Symptoms
The incubation period for brucellosis varies from 5 days to several months and averages 2 weeks.
Acute brucellosis is characterized by the rapid development of the disease with chills, fever, severe headache, joint pain, back pain, and a sharp rise in temperature. Diarrhea is often present.
In the recurrent and chronic type, the onset can be insidious, asymptomatic. At the same time, in the prodromal period, a person may feel a slight malaise, headache, muscle pain, especially in the back of the neck, and a subsequent increase in the evening temperature.
As the disease progresses, the temperature rises to 40–41 ° C, then gradually decreases to normal with profuse sweating in the morning.
Intermittent fever persists for 1-5 weeks, after which remission occurs within 2-14 days, when symptoms are significantly reduced or absent. In some patients, the fever may be transient. In others, the febrile phase (temperature rise) repeats in waves, remission may occur within several months, or the disease manifests itself as a fever of unknown origin.
Constipation, moderate swelling of the lymph nodes is often pronounced. Up to 50% of patients have symptoms of hepatomegaly (abnormal enlargement of the liver).
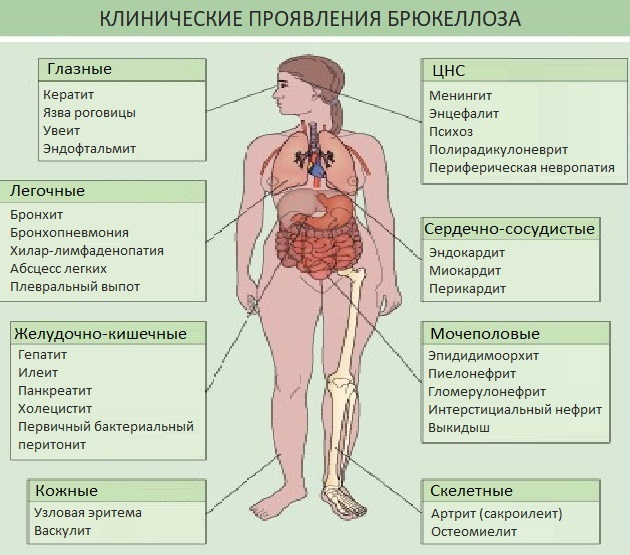
Brucellosis is dangerous because various organs are involved in the pathological process:
- Soft tissues are affected. Perhaps the development of subsequently cellulite, myositis, inflammation of fibrous tissue.
- Articular syndromes appear. The appearance of pain syndromes in the area of the joints of varying severity is likely. This subsequently leads to the development of contractures, articular deformity.
- Skin rashes are possible. They are transient and appear in the form of papules, erythema.
- There is a violation of the lymphatic system. Tonsils and lymph nodes are enlarged.
- Cardiovascular diseases develop: infective endocarditis, septic aneurysm, myocarditis.
- The activity of the digestive tract is disrupted. Loss of appetite occurs, pains in the stomach appear, the liver and spleen enlarge, and jaundice may develop.
- The respiratory system is impaired. A dry cough may appear, pneumonia may develop.
- Promotes the development of nervous disorders. These symptoms are rare, but abscesses of the brain tissue, damage to the cranial nerves are possible.
- The disease affects the eyes. The appearance of keratitis, uveitis, retinal detachment is possible.
Almost all patients who have undergone brucellosis suffer from functional nervous disorders: irritability, excessive sweating.
Reasons for the appearance
Brucellosis in humans (the symptoms of the disease are very diverse) develops under the influence of the bacteria Brucella, which enters the body along with dairy and meat products.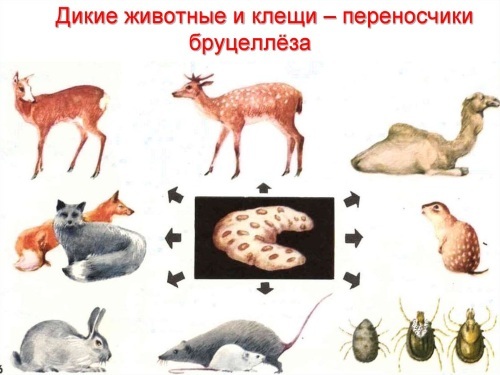
Most infections come from the consumption of contaminated food, especially improperly pasteurized milk, cheese or raw meat. Animals can carry bacteria without showing any symptoms, contaminating dairy and meat products. The bacterium is found in cattle, goats, pigs, sheep, camels, deer, elk and pigs.
Infection occurs through direct contact when the infection is transmitted through an open wound to slaughterhouse workers, veterinarians, farmers and others who have had access to infected animals. Hunters are at risk of infection because they come into contact with infected animals.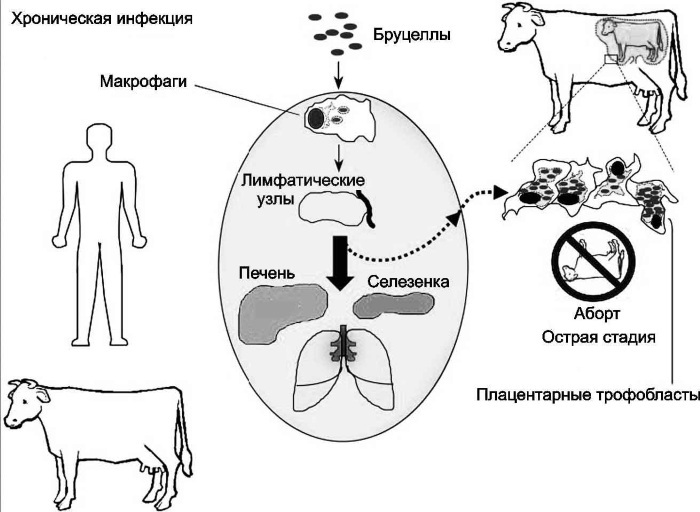
Often, sick animals bring brucella into the soil, grass, water, and feed. There have been registered cases of human injury when caring for animals, cleaning manure. Another way of infection is when shearing sheep, combing out the fluff from animals, at the time of inhalation of an air-dust mixture.
Diagnostics
The initial stage involves a physical examination of a patient with a symptom of brucellosis by an infectious disease specialist. This takes into account the presence of fever, pain in the joints, and clarifies the conditions for contact with animals or contaminated products. The next stage is laboratory diagnostics.
| Diagnostics type | What do they reveal | Price |
| General blood analysis | Hemoglobin concentration, number of leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets, their sedimentation rate | From 100 rubles. |
| PCR | Latently existing forms of microorganisms are checked | From 3 thousand rub. |
| Blood chemistry | Uric acid, albumin, C-reactive and total protein | From 1 thousand rub. |
| Bacteriological research | Bacterial inoculation on nutrient media | 1 thous. rub. 3 thous. rub. |
| Instrumental diagnostics | ||
| X-ray | Examination of the joints and spine | From 1 thousand 500 rubles. |
| Ultrasound | Examination of the liver and spleen | From 2 thousand rub. |


Blood cultures should be performed; growth may take> 7 days and subcultures using special media may require aging for 3-4 weeks, therefore the laboratory should be notified of suspicion of brucellosis.
Serums should be taken from a patient in the acute phase and during the recovery period, with an interval of 3 weeks. For PCR analysis, blood or any tissue of the body is suitable. The test result can be positive as early as 10 days after the pathogen has entered the human body.
When to see a doctor
The disease is more common in men than in women. Children's brucellosis accounts for 3-10% of the total number of cases. The disease becomes chronic in older people.
Brucellosis in humans (symptoms are often pronounced) is fatal in 2%. This occurs as a result of endocarditis or severe complications of the central nervous system.
The diagnosis and treatment of the disease is carried out by an infectious disease doctor. You should consult a doctor when the first signs of the disease appear, especially if there were epidemiological prerequisites.
Prophylaxis
Brucellosis is not spread from person to person, but in some cases, women transmit the disease to their babies during childbirth or through breast milk. In rare cases, brucellosis can spread through sexual activity or through blood or bone marrow transfusions.
It is recommended to register a person who has had brucellosis, regardless of the form of the disease. Symptoms and changing health conditions should be monitored for 3 years.
The International Association for Infection Specialists has recommended the vaccination of people at risk.
The national vaccination calendar contains a column that indicates the timing of preventive vaccinations. They are not carried out for persons under the age of 18, for women during pregnancy.
To prevent the disease, you should remember about preventive measures:
- It is necessary to vaccinate pets.
- Do not buy meat products that have not passed the control of inspection bodies.
- Farm unprocessed milk should be consumed after heat treatment.

- To avoid contamination, it is best to use pasteurized foods.
Treatment methods
Treatment for brucellosis is aimed at relieving symptoms, preventing recurrence of the disease, and avoiding complications.
Stages of therapy:
- Detoxification. It is carried out in the form of infusion therapy. Treatment is aimed at removing toxins from the body.
- Combined treatment with two or more antibacterial drugs.
- Immunomodulatory therapy. It is carried out to increase the reactivity of the immune system, to help the body fight infection.
- Treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are used to stop the inflammatory processes caused by infection, to lower the temperature.
- Prescribing painkillers. Used to relieve joint pain and neuritis.
- Vitamin therapy. They are used to maintain the cardiovascular system, boost immunity.
- Antihistamine therapy. It is carried out to reduce the allergic status.
- Physiotherapy procedures. They are performed to restore body functions after an illness.
If the terms of treatment are not followed, the disease can return and become chronic. In acute brucellosis, vital activity is limited, bed rest is recommended for the entire duration of treatment. Brucellosis endocarditis requires surgery in addition to antibiotic therapy.
Medications
Severe musculoskeletal pain, especially in the spine, may require pain relief. In the case of antibiotics, combination therapy is preferable, since the frequency of relapses is high with monotherapy.
For optimal treatment, 2 antibiotics are usually required:
- doxycycline or trimethoprim / sulfamethoxazole;
- gentamicin or streptomycin / rifampicin.
Antibacterial agents:
| A drug | Doses | Price |
| Doxycycline (oral) | 100 mg twice a day for 6 weeks | RUB 400 |
| Gentamicin (oral) | 3 mg / kg once a day for 14 days | RUB 50 |
| Uncomplicated cases | ||
| Rifampicin (oral) | 600 to 900 mg twice daily, 6 weeks | RUB 400 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 500 mg 2 times / day for 14–42 days | RUB 50 |
| Children's doses | ||
| Trimethoprine / Sulfamethoxazole | Within 4-6 weeks | RUB 400 |
| Rifampicin |
Additional drugs for the treatment of brucellosis: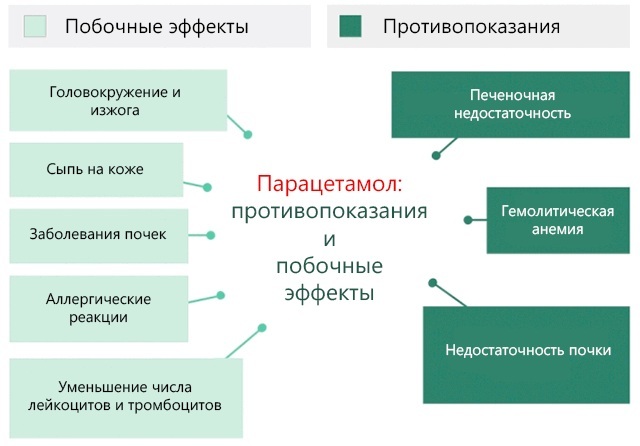
| Group of drugs | Name | Price in rub. |
| Immunostimulants | Dibazol | 20 |
| Timalin | 380 | |
| Pentoxil | 350 | |
| Detoxifying agents | Atoxil | 2 800 |
| Enterosgel | 380 | |
| Methionine | 40 | |
| Polysorb | 50 | |
| NSAIDs | Nimesil | 300 |
| Paracetamol | 30 | |
| Ibuprofen | 20 | |
| Indomethacin | 20 | |
| Nurofen | 80 | |
| Pain relievers | Dexamethasone | 30 |
| Hydrocortisone | 25 | |
| Prednisolone | 25 | |
| Antihistamines | Claritin | 200 |
| Loratadin | 25 | |
| Suprastin | 120 | |
| Vitamins | Group C | 100–800 |
| Group B |
In mild forms of the disease, treatment with fluoroquinolones is carried out, they are used as monotherapy. When treated with antibiotics, 5–15% of patients have relapses, therefore it is necessary to carry out treatment with repeated serological titers within 1 year.
Recovery takes weeks to months. And it depends on the timing of the start of treatment, the severity of the course of the disease. Death from brucellosis is rare, occurs in no more than 2% of cases.
Traditional methods
Brucellosis in a person whose symptoms have already been stopped can be treated with folk remedies. They are used as an additional treatment, as well as during the period of remission of the disease.
Joint Pain Relief Baths:
- Take 1 tbsp. l. coconut oil, add 4 drops of sandalwood essential oil or fennel oil. Stir, add to warm bath water. Take a water treatment for 15–20 min.
- Take 5-10 drops of peppermint oil, -5-10 drops of eucalyptus oil, 1-2 tbsp. l. tablespoons of carrier oil (olive, almond, grape). Mix everything, add to warm water. Take a bath for 20-25 minutes.
Healthy herbal drinks consist of dried herbs, berries and boiled water added to them. All ingredients are taken in equal parts, mixed, poured with boiling water, infused. After straining, they should be taken warm throughout the day. It is recommended to drink 2-3 times / day for 1-2 weeks.
Composition of 1 collection:
- Juniper berries.
- Honey.
- Water
Composition 2 collection:
- Stinging nettle leaves.
- Dried parsley roots.
- Black elderberry flowers.
- Dried willow bark.

Composition 3 collection:
- Black elderberry leaves.
- Stinging nettle leaves.
- Dried willow bark.
- Field horsetail, flowers and leaves.
- Dried bark of warty birch.
A drink based on pectin is useful, especially for those who suffer from arthrosis.
- Ingredients: 1 tbsp. l. liquid pectin, 200 ml of grape juice, mix everything. Drink 1-2 times a day for 1-2 weeks.
Other methods
Various methods of physiotherapeutic treatment are used during the period of persistent remission in the chronic form of the disease:
- Therapeutic physical education.
- Balneotherapy.
- Radon baths.
- Irradiation with ultraviolet radiation.
- UHF therapy.
- Electrophoresis sessions.
Many people who have had an illness benefit from spa treatment.
In case of complications after the disease, surgical treatment is used. It is necessary to eliminate defects in the musculoskeletal system or in case of serious damage to internal organs.
Possible complications
The long-term outlook for most people with brucellosis is positive. With early treatment, within the first few months after the onset of the disease, the disease is curable and has a low risk of returning or becoming chronic.
Failure to adhere to the treatment regimen leads to relapses, developing into a chronic form, which can progress in the absence of treatment. People who have not been treated or who are not receiving adequate treatment are more likely to come back. However, relapse is also possible in those who followed the treatment regimen.
Mortality in this disease is due to a rare case of associated endocarditis or severe neurological impairment The prognosis is known to be poor for people with brucellosis who have congestive heart disease. failure. In these cases, the mortality rate is close to 85%.
Brucellosis affects many body systems, introducing dissonance into their work. Chronic brucellosis causes complications in one organ or throughout the body.
What disorders in the work of the body occur as a result of the disease:
-
Development of endocarditis. Inflammation of the inner lining of the heart occurs. Heart valves are damaged or destroyed without proper treatment. Endocarditis is one of the causes of death in brucellosis.
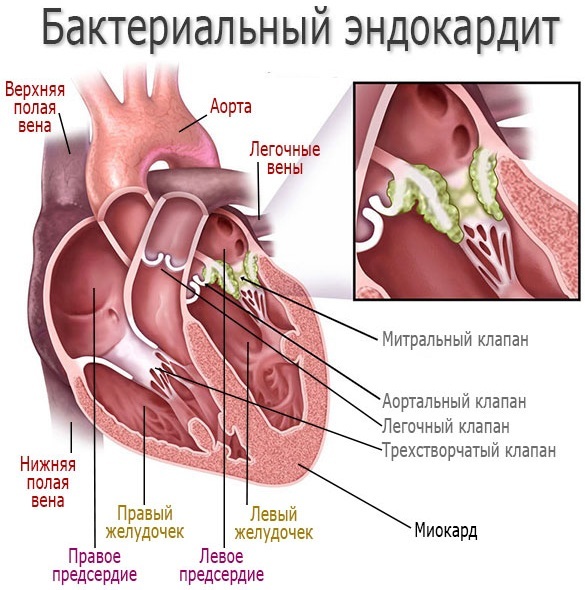
- Arthritis. Joint damage occurs under the direct influence of infection and is characterized by pain, stiffness and swelling. The most common sites of injury: knees, ankles, wrists, thighs, spine.
- Spondylitis. Inflammatory lesion of the joints between the spine and the pelvis. The disease is difficult to treat and often leads to long-term damage.
- Epididymo-orchitis. Inflammatory and infectious disease of the epididymis. The bacteria that cause brucellosis infect the epididymis, the coiled tube that connects the testicle and the vas deferens. With the disease, edema occurs in the scrotum. Untreated infection leads to the chronic form of the disease.
- Hepatosplenomegaly. The overgrowth in the volume of the spleen and liver simultaneously occurs under the influence of brucella, which enter these organs.
- Central nervous system infections. The causative agents of meningitis, encephalitis in this case will be brucella. Infection can lead to inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord.
Persistent residual effects, improper and untimely treatment leads to disability.
Brucellosis is an insidious disease that affects many body systems. A week is enough for the development of the disease, and then a person will feel the consequences of his dangerous symptoms for years. Do not neglect preventive measures, this will help reduce the risk of infection.
Author: Belyaeva Anna
Brucellosis video
Signs and symptoms of brucellosis: