Immunoglobulin M is the body's defense cells that respond most quickly to disease-causing bacteria and infection. An excess of the normal amount of a substance in the blood shows the presence of pathogenic flora in any manifestation: from respiratory disease to inflammation of individual organs and tissues.
Immunoglobulin M is part of the immune system and, if there is a lack of such elements, it indicates a disorder in the immune system. Any deviation from the norm of immunoglobulins M in the blood can be the result of serious violations, therefore requires careful attention and excellent treatment with modern medications under control doctor.
Record content:
- 1 Functions in the body
- 2 How and under what conditions is it produced
- 3 Indicator table is normal
- 4 Reasons for promotion and demotion
- 5 Indications for research
- 6 How is it determined
- 7 Preparation and analysis
- 8 Decoding the results
- 9 When to see a doctor
- 10 How to bounce back
- 11 Medications
- 12 Traditional methods
- 13 Possible complications
- 14 Immunoglobulin video
Functions in the body
Immunoglobulins have a different structure and specificity. Immunoglobulin M is a class of antibodies that have not only the highest weight, but also a complex structure. They are the first to be synthesized when the antigen enters the body and neutralize the foreign substance as much as possible.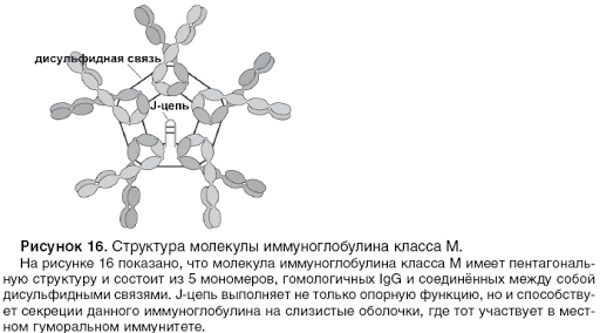
Such substances begin to be synthesized in the human body during the period of its formation in the womb, at about 26 weeks. By the age of 9 months, the level of immunoglobulin M in the blood of an unborn baby approaches the norm of production by an adult body. It is these antibodies that create the primary immunity of the child.
Besides:
- Due to the ability to interact with the polyimmunoglobulin receptor, immunoglobulin M passes into breast milk and helps to improve the immunity of a newborn baby at the age of 1 year of life.
- As a result of a reaction with a polyimmunoglobulin receptor, immunoglobulin M saturates the intestinal mucosa with antibodies, which creates a third of the body's immunity.
- During organ transplantation, the patient's body actively produces immunoglobulin M, which is most often does not participate in the process of rejection, but performs protective functions and promotes the fastest healing fabrics.
- Immunoglobulin M shows in a blood test for the presence of an initial stage of infection in the body. If the type of infection or bacteria is identified, already at the 1st stage of the disease, a diagnosis can be quickly made and treatment prescribed.
- The main function of immunoglobulins M is associated with the neutralization of harmful bacteria and sources of infections in the body, which actively bind and are excreted from the body. Most of all, antibodies of this group are active in creating anti-infectious immunity, which allows the body to protect against many diseases upon contact with the source.
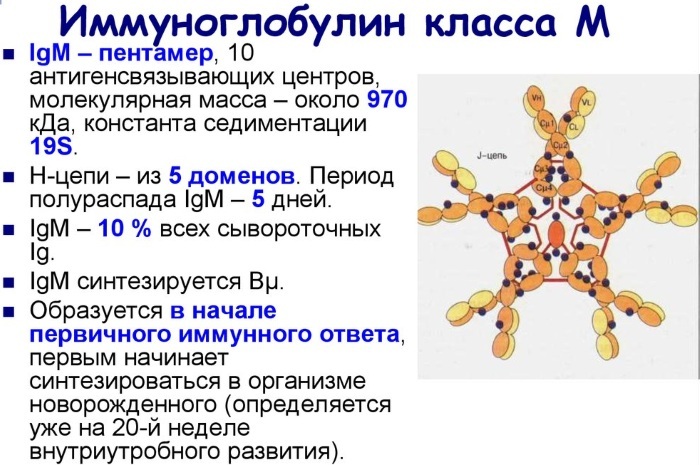
Together with other types of immunoglobulins, immunoglobulin M is part of a complex human immunity, allows you to cope with heavy loads and protects the body from infection.
How and under what conditions is it produced
Immunoglobulin M is a combination of protein and sugar (klicoprotetenoid) and is always present in small amounts in the blood and on the intestinal mucosa. The active substance begins to be produced in the body immediately after an infection or harmful bacteria enters the body.
Antibodies of this class are produced by the very first in an amount proportional to the volume of harmful substances. Immunoglobulins are actively produced by plastic blood cells within 1-2 hours after the penetration of harmful substances into the body.
They have the ability to penetrate into any tissues and parts of the body due to their structure and small size. Antibodies of this class easily detect "dangerous" elements for the body and block their action pointwise, sticking around them. By neutralizing the source of infection, antibodies are naturally excreted from the body.
In the normal state, class M immunoglobulins are always present in the blood of a person to locally eliminate harmful bacteria that a person encounters every day. But the level of M antibodies should not exceed 10% of the total amount of such substances.
Immunoglobulin M shows in a healthy state of a person the general state of the immune system. In the case of an increase in the level, inflammatory processes and certain diseases (rubella) are diagnosed, and with a decrease, problems with immunity.
Indicator table is normal
Already for 9 months. development of the child's immunoglobulins M are produced in the body in a standard amount. Throughout life, these substances are present in the blood and are involved in the formation of immunity. During physical exertion, in stressful situations, their level slightly increases in a natural way to create the desired level of protection.
Depending on age and health status, the level of immunoglobulin M may vary within normal limits. So for women, the rate of antibodies is considered to be 0.5 - 3.2 g / l. For men, this figure is 0.6 - 3.7 g / l. During or after respiratory diseases, the level of immunoglobulin increases slightly for up to 5 days.
| Floor | Immunoglobulin norm, g / l |
| Women | 0,5-3,2 |
| Men | 0,6-3,7 |
In children, immunoglobulins of this class are produced in smaller quantities in the normal state:
| Age, l | Immunoglobulin norm, g / l |
| 1 and earlier | Up to 1.4 |
| 2-4 | 0,19- 1,45 |
| 5-7 | 0,4-2,1 |
| 8-10 | 0,31-2,08 |
| 11-13 | 0,66-1,5 |
| 14-16 | 0,15-1,88 |
With a disease, the level of immunoglobulins in a child's body rises significantly in a short time and lasts up to 7 days. after complete recovery. Any deviation from the norm of immunoglobulin M is considered a pathology and requires medical examination and treatment.
Reasons for promotion and demotion
Immunoglobulin M shows in the blood in large quantities for the active work of the immune system. The increased production of antibodies helps a person to cope with infection and harmful bacteria.
The main reasons for an increase in the level of immunoglobulin M can be:
- the development of infectious diseases;
- inflammatory processes in the body or individual tissues.
Most often, immunoglobulin M increases in adults with the development of the following diseases:
- hepatitis;
- tumor;
- fungal infections;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
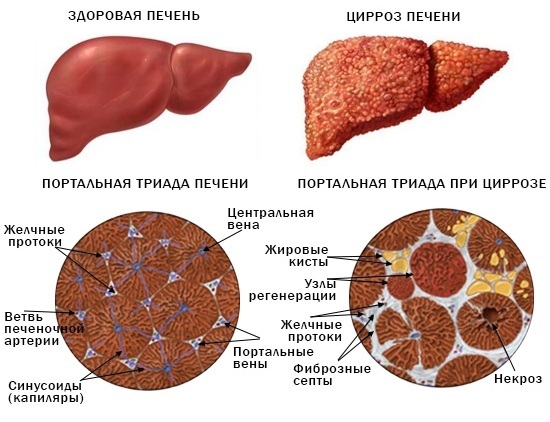
Cirrhosis of the liver - hyper-IgM syndrome, in which the system for the production of M. immunoglobulins is disrupted.
Any of these diseases causes serious complications and requires immediate treatment.
An increased level of immunoglobulin M in a healthy person occurs during the period of taking certain drugs (phenytoin, estrogen, chlorpromazine), the effect of which can last up to 6 months. At the same time, even minor intake of such drugs can cause a sharp increase in the production of class M immunoglobulins.
In rare cases, when taking tests, an increased level of IgM is found in athletes during the period of constant training, as well as in people with increased physical activity or in stressful situations.
Decreased production of immunoglobulin M indicates impaired immunity.
The reasons for the non-systemic production of antibodies can be:
- burns;
- lymphoma;
- the recovery period after removal of the spleen;
- radiation therapy;
- monoclonal gammopathy, in which immunoglobulin M is produced with a different chemical structure;
- Bruton's disease or congenital or acquired immunoglobulin deficiency;
- violations when taking certain drugs.
A slight decrease in the level of immunoglobulin appears after a long illness or several previous respiratory diseases. Gradually, the antibody index is restored to normal.
Indications for research
Immunoglobulin M shows abnormalities in the patient's body and, due to the similarity with the symptoms of other diseases, an analysis for the study of the level of antibodies assigned only if the following indications are present:
- severe otitis media or sore throats;
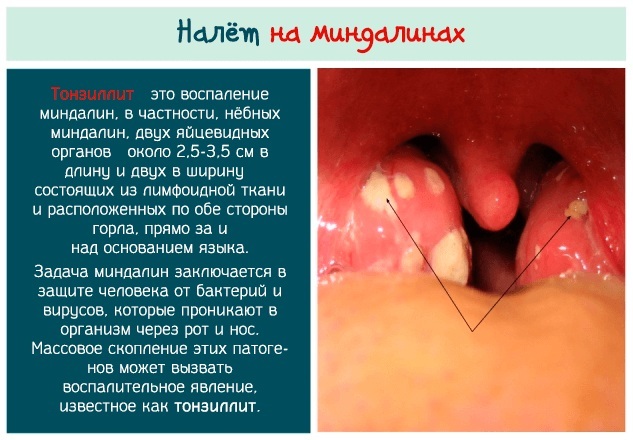
- systematic bacterial respiratory infectious diseases;
- tumors;
- suspicion of liver cirrhosis or hepatitis;
- chronic loose stools or malabsorption syndrome;
- suspicion of the presence of worms;
- allergic diseases or reactions, including taking medication;
- allergic dermatitis, eczema or hay fever;
- suspicion of an autoimmune disorder, rubella, or arthritis of various etymologies;
- HIV infection or a deficiency in the production of immunoglobulins.
A blood test for immunoglobulins is usually prescribed by an immunologist or allergist during the examination. In some cases, an analysis for immunoglobulins is prescribed by a therapist, gastroenterologist or dermatologist if there are clear indications for the analysis.
As a systemic examination, an analysis for globulins M is prescribed during a medication course restoration of the level of antibodies in the blood, as well as when undergoing treatment with hormonal drugs and cytostatics.
How is it determined
Immunoglobulins M are found in the blood and on the intestinal mucosa of a healthy person, the level of which indicates the state of the immune system at a given time.
There are only 3 types of immunoglobulin in the blood, 1 of which is immunoglobulin M, therefore, a blood test is prescribed to detect the level of type M antibodies. Only by the amount of the presence of a substance in the analysis sample can the level of immunoglobulin M. To obtain accurate results, you should eliminate all factors that may affect the outcome of the study.
Preparation and analysis
A blood test for immunoglobulins does not require special preparation.
However, prior to the analysis, it is recommended that you:
- do not drink alcohol for 2 days and do not smoke before undergoing the procedure;

- in the evening on the eve of the analysis, do not eat, since blood is donated only on an empty stomach. For children, a similar analysis can be carried out in 3-4 hours. after the last meal;
- exclude the intake of additional medicines and drugs per day;
- 1-2 days before the study, it is recommended to remove strong physical activity, intense sports and stress.
The analysis itself for immunoglobulins is carried out in the following order:
- The patient sits down in a special chair and opens his arm just above the elbow.
- Then the technician treats the inside of the elbow with disinfectant and fixes the tourniquet on the forearm.
- After that, a puncture of the vein is made with a syringe and the required amount of blood is taken from the vein.
- The needle is removed from the vein and the wound is clamped with sterile cotton wool soaked in disinfectant.
To exclude the formation of edema on the hand, it is recommended to squeeze the cotton wool with your elbow and hold for at least 20-30 minutes.
Decoding the results
After 8-24 hours. after passing the analysis, the patient can receive the results of the study, which are easily deciphered. In the document, in addition to the surname, initials and date of birth of the patient, the exact amount of immunoglobulins on the date of the study is indicated.
The IgM level is normally in the range of 0.2 to 3.6 g / l, with fluctuations depending on gender and health status. An immunoglobulin level of less than 0.2 g / L indicates a decreased level of antibodies.
An antibody index above 3.5 g / l indicates an increased level of the substance. The level of immunoglobulin M in the blood is influenced by the age of the patient and the intake of medications, therefore, it is better to consult a doctor to decipher the patient's analysis for further diagnosis.
When to see a doctor
In case of any deviation of the level of immunoglobulin M from the norm, it is necessary to consult a doctor for an accurate interpretation of the analysis and an additional examination.
It is recommended to consult a specialist in case of an increase in the level of immunoglobulin for flu and colds, as well as feeling unwell, since it is the immunoglobulin of this class that signals the initial stage of development of chronic diseases that have similar symptoms. When the disease is diagnosed even during the developmental period, the effectiveness of their treatment increases significantly.
With an increased level of immunoglobulins M of 3.5 g / l and higher, the therapist, together with a narrow specialist of the corresponding profile (gastroenterologist, oncologist or urologist), conducts the necessary treatment.
For the treatment of a low level (starting from 0.5 g / l) of immunoglobulins M in the blood, you will have to turn to immunologist or allergist who will diagnose and carry out a course of treatment with special drugs.
How to bounce back
Immunoglobulins M show, with their increased content in the blood, for the presence of an inflammatory process or diseases of internal organs. In this case, to normalize the level of immunoglobulin M, symptomatic and course specialized treatment of the disease or inflammatory process, including stationary, is required.
After elimination of the acute stage of the course of the disease, the level of immunoglobulin M decreases and, when the prescribed drug treatment is performed, gradually returns to normal.
A lowered level of immunoglobulins M in the absence of additional chronic diseases can be treated with a course vitamins and immunoglobulins prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the patient's health status and the body's response to the drugs.
Medications
Immunoglobulin M is increased by a course of vitamins and preparations containing an immunologically active fraction obtained from healthy donors. Blood samples are taken from 1000 and more donors who have been tested for hepatitis C and B and processed at a temperature of no more than 0 °.
At the heart of drugs are active antibodies of various classes and specificities in a concentrated state. When injected, antibodies from a donor are activated in the blood of a sick person and perform the functions of their own antibodies.
The most common and effective drug is normal human immunoglobulin, which is activated in human blood within 24 hours.
The drug is administered intramuscularly once or by 2-3 injections during the day. The dosage for adults contains 1 ml. for every 1 kg. body. After 1 month. the drug is re-administered. The course of treatment is 2-3 months, however, after the first receipt of the drug, a significant increase in immunity is observed. The cost of the medicine is 1000 rubles.
It is actively used to restore the level of immunoglobulins immunovenin, which has increased properties of reducing the number of infections with a reduced level of immunity. It is considered the best drug in the course of treatment of immunodeficiency and in the period after removal of the spleen.
The medicine is administered intravenously drip for 1-2 hours. A single dose is calculated as 0.1-0.4 g / kg. After 1 month. the medicine is re-administered. After 1 injection, the level of immunoglobulins is restored to normal, and infectious diseases disappear. The cost of the medicine is 3000 rubles. per packing.
Traditional methods
In addition to drug treatment, the level of immunity can be leveled using folk remedies.
Rosehip infusion effectively restores immunity:
- For this, 100 gr. rosehip berries are poured into a saucepan or thermos and poured into 0.5 liters. boiling water.
- Withstand the broth for 30-40 minutes. and drink strained like tea, adding lemon or honey to taste.

To increase the effectiveness of the rosehip tincture to the berries during brewing, you can add 1 tbsp. l. leaves of black currant, thyme or thyme.
The course of treatment is 14 days. After a 2-3 week break, the rosehip treatment can be repeated. After the first course of taking rosehip tincture, the immune system begins to activate.
A sweet medicine for raising immunity is prepared from nuts and dried apricots:
- 100 g walnuts need to be chopped in a meat grinder.
- Finely chop 100 gr. dried apricots and 50 gr. prunes.
- Wash 1 large lemon thoroughly with warm water and grind through a meat grinder.
- All the crushed ingredients are mixed.
- 3-4 tbsp are added to them. l. flower honey and mix thoroughly.
- The resulting jam is transferred to a jar and put into the refrigerator.
They eat a mixture of 1-2 tbsp. l. per day for 1 month. Then, after a break of 2 weeks. The treatment is repeated. Already after 2-3 weeks of taking a folk remedy, due to the vitamin-rich composition of the mixture, the body begins to actively restore immunity and in case of illness, colds pass gently and easily.
A honey-based drink helps to strengthen the immune system:
- For its preparation, 2-3 lemons are squeezed out.
- Add 250 gr. To the mixture. honey and the same amount of Cahors.
- Separately rub and squeeze the juice of 3 carrots and 1 radish.
- The mixture is combined with carrot and radish juice.
- The finished medicine is poured into a bottle and drunk 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day half an hour before meals.
The course of treatment is 20 days. After a break of 1 month. the treatment is repeated. With systematic use, immunity is significantly strengthened and the incidence of infectious diseases is reduced by half.
It is important to remember that folk remedies are in addition to and cannot replace the medication prescribed by your doctor.
Possible complications
In case of ignoring the increased level of immunoglobulin M, the acute stages of the current disease, about which signal antibodies, rapidly progressing, transforming into chronic forms or subsequently causing fatal outcome.
In the absence of treatment for a low level of immunoglobulin M in the blood, human immunity is gradually reduced to a minimum. The patient constantly suffers from viral respiratory diseases with various complications (rhinitis, otitis media, adenoids), headaches and poor health.
In the absence of proper therapy with special drugs, a patient with a low level of immunoglobulin can die from a cold or flu. In this case, the likelihood of contracting any infection, including fungal, is maximal even with short-term contact with the infection.
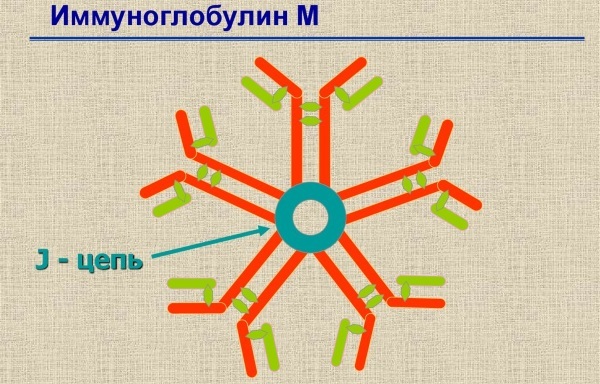
Immunoglobulin M is considered an antibody that provides a primary response and protection of the body against the presence of harmful substances. The level of a substance in the blood shows the state of the patient's immunity and the onset of a number of diseases and inflammatory processes.
When diagnosing such conditions in the early stages, the likelihood of restoration of immunity and full recovery completely depends only on the correct implementation of the doctor's recommendations and additional independent recovery.
Even in difficult cases, modern drugs of the latest generation make it possible to restore grade 1 and 2 immunodeficiency to normal and restore health for a long time.
Immunoglobulin video
Komarovsky about immunoglobulins:



