Splenomegaly - pathology affecting the spleen. It occurs in people regardless of gender and age. This article is devoted to the question of what this disorder is and how to cope with it.
Record content:
- 1 What is splenomegaly?
- 2 Types of pathology
- 3 Reasons for the development of splenomegaly in adults and children, during pregnancy
- 4 Symptoms of the disease
- 5 Complications
- 6 When and to whom to seek medical help?
- 7 Diagnosis of splenomegaly
- 8 Drug treatment of the disease
- 9 Folk remedies
- 10 Diet
- 11 Surgical intervention
- 12 What is the threat of spleen removal?
- 13 Rehabilitation period
- 14 Forecast
- 15 Splenomegaly video
What is splenomegaly?
Splenomegaly (what it is, how to treat this condition is described later in the article) is an accompanying disease (syndrome). It develops as a result of an already existing pathological process. A hypertrophied spleen is an indicator of serious problems existing in the body. Therefore, this syndrome is called secondary.
Splenomegaly is a syndrome in which the spleen is larger than normal. In a normal state, the organ weighs no more than 150 g. It does not go beyond the rib cage and cannot be felt during examination.
Types of pathology
According to the criterion of etiology and pathogenesis, splenomegaly is divided into inflammatory and non-inflammatory.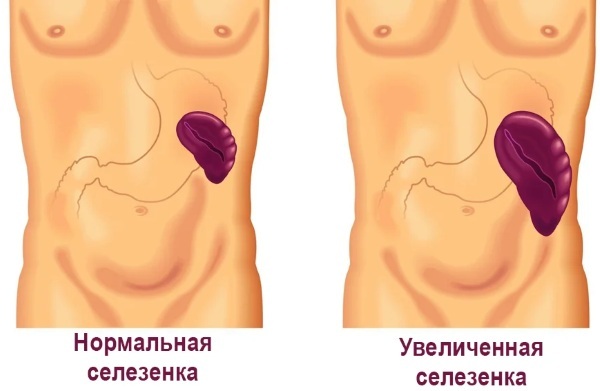
| Inflammatory | Non-inflammatory |
|
|
Reasons for the development of splenomegaly in adults and children, during pregnancy
The spleen is an important link in maintaining the normal functioning of the immune system.
Among the causes of splenomegaly are:
- various metabolic disorders. The development of the disease is associated with the colonization of spleen cells with lipids, macrophages and other metabolic products substances (metabolites) against the background of acquired or congenital pathologies of the metabolic system (glycogenosis, phenylketonuria).
- Myeloproliferative diseases. The formation of malignant cells occurs in the bone marrow. They begin to actively share. This process prevents the formation of blood cells: platelets, erythrocytes, leukocytes.

- Diseases that are infectious in nature. The spleen is hypertrophied due to the workload of the body's defense system.
- Disorders of the hematological system. Diseases of the blood (hereditary and acquired) additionally load the spleen.
- Any neoplasms (malignant and benign tumors).
- Autoimmune pathologies. The spleen acquires a hypertrophied size due to its enhanced performance of its filtration function. In an enhanced mode, the reticular tissue begins to work. It lines and supports the spleen. This happens with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Impaired blood circulation. Due to the obstructed movement of blood through the veins, congestion is formed. They provoke vascular proliferation, an increase in the number of red blood cells and an increased level of pressure in the venous system in which the veins end and begin with capillaries. Therefore, the spleen becomes hypertrophied. As a result of this process, thrombosis of the splenic vein may develop, and the vascular pedicle of the organ may twist.
In childhood, this syndrome can accompany even healthy children. In this case, it indicates a problem with the immune system.
In pregnant women, an enlarged spleen can occur when:
- helminthiasis;
- tumors;
- viral hepatitis;
- purulent process in the spleen;
- injuries;
- sepsis;
- spleen infarction;
- anemia (in hemolytic form);
- diseases of a viral and bacterial nature.
Symptoms of the disease
Splenomegaly (what is it, how to treat a disease, patients often find out only after an accidental diagnosis) symptomatically manifests itself depending on several factors:
- a kind of primary pathology that provoked an enlargement of the spleen;
- the cause of her hypertrophy;
- the degree of enlargement of the organ.
| Inflammatory | Non-inflammatory |
|
|
An enlarged spleen is often accompanied by an enlarged liver. This condition is called hepatosplenomegaly.
Complications
The lack of timely assistance to a sick organ can provoke the following consequences:
- ruptured spleen. As a result, severe bleeding occurs, hemorrhagic shock develops and the person dies (if medical assistance was not provided in a timely manner).
- Destruction of blood cells inside the spleen. A condition occurs in which the number of cells within the bone marrow increases, and their concentration in the peripheral blood decreases - hypersplenism. It is accompanied by anemia, leukopenia and thrombocytopenia. Further - a violation of blood clotting, a decrease in the protective function of the body, the development of hypoxia. The result is bleeding and shock - life-threatening conditions.
When and to whom to seek medical help?
Splenomegaly (what is it, how to treat hypertrophied spleen syndrome - such knowledge about the disease is best mastered by a specialist with a narrow focus - a gastroenterologist) is diagnosed several methods.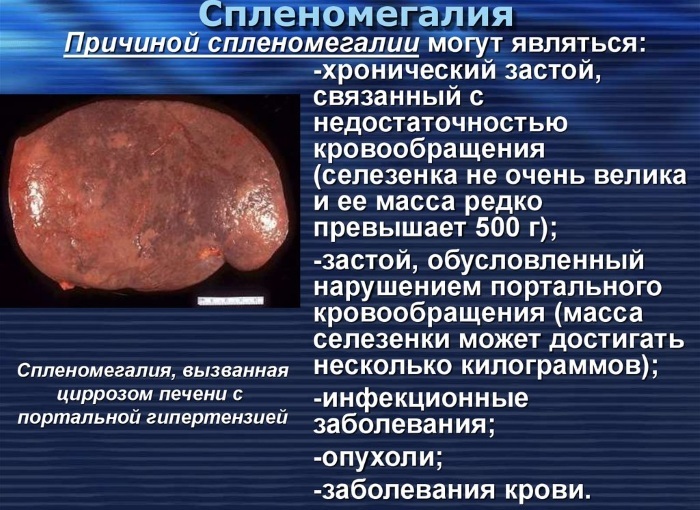
At the initial appointment, the doctor will probe and tap the spleen. Such a technique will help determine the degree of organ enlargement and changes in splenic dullness.
But it is not sufficient for a definitive diagnosis for two reasons:
- in some people (usually thin), the enlarged organ is not palpable;
- a palpable formation in the left hypochondrium may be a symptom of another pathology.
Also, the doctor will interview the patient about the diseases that he has suffered. To clarify the diagnosis, the patient is sent for additional research.
Diagnosis of splenomegaly
Signs of splenomegaly are similar to those of cancer. Therefore, careful research is needed.
Diagnostic methods to help establish the presence of changes in the spleen:
- scintigraphy(radioisotope research). Helps to assess the functional status of the spleen and pathological foci of the parenchyma.
-
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound). With its help, you can identify external changes in the organ - size and shape. It also shows well the presence of injuries, abnormal signs of development, inflammation and tumors.
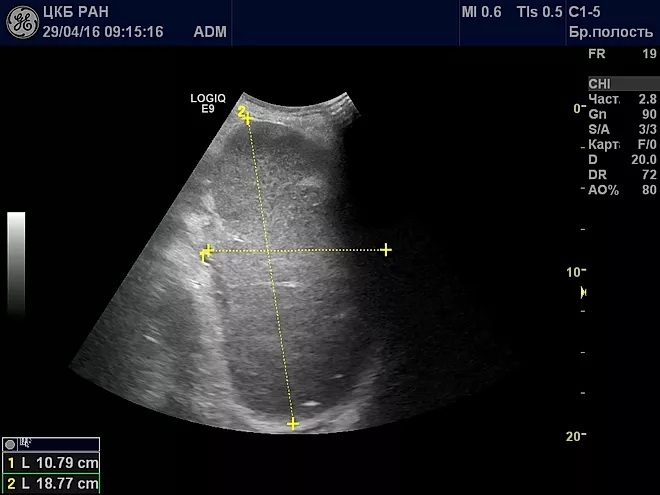
- MSCT (multilayer computed tomography) of organs located within the abdominal cavity. With this modern method, organs can be examined in detail. The cause of spleen hypertrophy is easily determined if the primary pathology is located in the abdominal cavity.
- X-ray abdominal organs of a general nature. During the study, the mobility of the spleen is preserved. You can see the degree of enlargement of the spleen and the displacement of adjacent organs - the intestines and stomach.
- Laboratory research methods: blood test (general and biochemical), general urine analysis. Deviation of indicators from the norm will help to identify the underlying disease.
Drug treatment of the disease
It is necessary to eliminate the cause of the syndrome, so the doctor makes a choice in favor of etiotropic therapy.
Based on the underlying disease, appoint:
- in oncology - antineoplastic drugs;
- for autoimmune disorders - hormonal drugs;
- with obvious symptoms of intoxication - anti-inflammatory and detoxification therapy.
Folk remedies
In addition to conservative treatment, folk remedies can be used to help with an increase in the spleen:
- ointment. Ghee, honey and grated ginger root are mixed in equal parts. Apply the mixture to the skin in the area of the left hypochondrium and leave overnight.
-
Infusion. 10 g of dry and chopped grass of shepherd's purse is poured into a glass of boiling water. Allow to stand for 30 minutes, then filter. Take 5 times a day for 1 tbsp. l.

- Infusion. Pour a spoonful of dried wormwood with a glass of boiling water, cover and let stand for 30 minutes. Then open the container and add 200 ml of freshly boiled water, stir and filter. Take the medicine before meals (30 minutes) for 1/3 cup. The infusion is bitter, you can sweeten it with sugar, honey or syrup.
- Tincture. Chopped hops are poured into a jar (500 ml) so that the container is a quarter full. The space remaining in the jar is poured with vodka. Leave to infuse for 10 days, then filter. The hop cones need to be squeezed out. Take a tincture of 40 drops 3 times a day. Treatment continues until it ends.
Diet
Splenomegaly is a medical condition that can be treated with dietary restrictions.
In this condition, it is necessary:
- exclude everything fried, canned and smoked;
- give up alcohol;

- significantly reduce the amount of sugary foods and drinks consumed;
- try not to consume mushrooms;
- choose dietary meats;
- eat vegetables rich in vitamins (cabbage, beets, peppers), cereals, berries, fruits;
- make a choice in favor of homemade drinks (fruit drinks, compotes), weak tea.
Surgical intervention
Reasons for splenectomy - spleen removal surgery:
- significant organ hypertrophy;
- irreversible changes;
- hypersplenism;
- lack of a positive effect from drug therapy;
- trauma;
- blockage of the splenic and portal veins (thrombosis);
- development of cumulative diseases (amyloidosis, Gaucher disease).
Before the operation, the patient takes all the tests and undergoes the necessary examinations. Vaccination against certain infections is a prerequisite. This is necessary for better protection of the body against harmful organisms, because without the spleen, it cannot effectively fight pathogenic microorganisms.
The operation is performed using general anesthesia.
The operation takes place as follows (with an open type of intervention):
- the surgeon cuts the skin over the diseased organ;
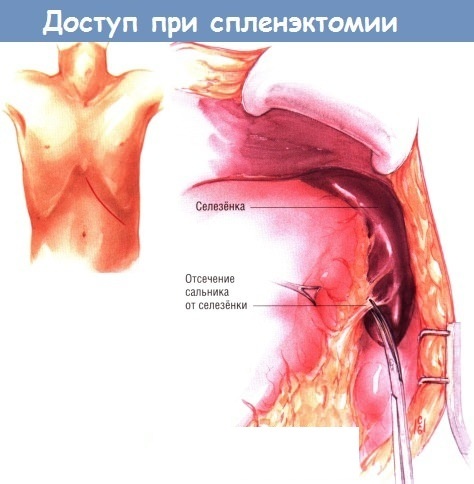
- the skin with muscles is pulled apart;
- the accumulation of blood vessels is cut off to release the spleen;
- special sponges are placed in the abdominal cavity that absorb blood and liquid;
- after removal of the organ, the sponges are also removed;
- cleansing the wound;
- fastening the skin and muscles with staples and sutures;
- the incision site is covered with a bandage.
Surgical intervention for laparoscopy is as follows:
- the doctor makes a small incision in the abdomen;
- a laparoscope is placed in the abdominal cavity (looks like a thin tube with a camera at the end);
- to increase the volume of the abdomen, carbon dioxide is pumped into the abdominal cavity;
- make 2-3 cuts on the abdomen through which special instruments are inserted;
- the blood vessels coming from the organ are tied up and cut off;
- the spleen is removed from any incision;
- in case of rupture of an organ, the doctor checks whether adjacent organs are not damaged;
- sutures are applied to the breaks.
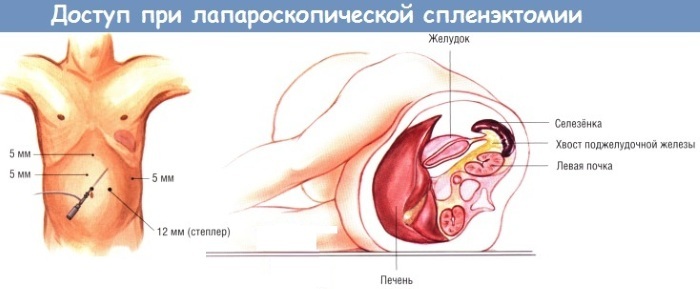
The operation takes no more than an hour. With a large blood loss, the patient needs a blood transfusion. The removed organ is sent for laboratory testing. The patient remains in the hospital for about 2 to 4 days. If complications arise, the length of stay is extended.
If the pancreas is affected, the surgeon removes only part of it, and the spleen completely.
Indications for distal hemipancreatectomy with splenectomy:
- damage to the parenchyma of an organic nature (destructive pancreatitis);
- neoplasms;
- damage to the gland due to trauma;
- complicated chronic pancreatitis;
- cysts;
- pathology of neighboring organs.
What is the threat of spleen removal?
Splenectomy is a complex surgical procedure.
As a result, the following health problems may appear:
- infections;
- bleeding;
- trauma to nearby organs;
- thickening of the blood;
- the altered blood structure will accompany the patient all his life (the fact is associated with the hematopoietic function of the spleen);
- thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery and cerebral vessels due to a high degree of blood coagulability and an increased concentration of platelets;
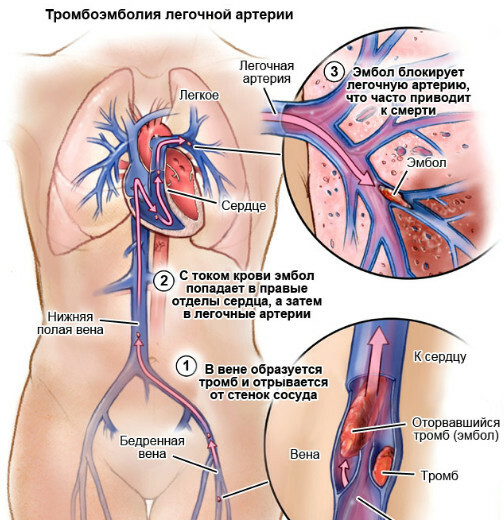
Pulmonary embolism - a weakened immune system causes frequent purulent-infectious disorders in a person, which can result in sepsis (blood poisoning) and death;
- a decrease in the concentration of protective proteins in the plasma, phagocytic function suffers, which increases the risk of illness in case of hypothermia (hepatitis, meningitis, pneumonia);
- the occurrence of a hernia or inflammation in the operated area;
- failure in the activity of all organs involved in digestion;
- due to the lack of functions that the spleen performed, leukocytosis (high concentration of leukocytes), thrombocytosis (high concentration of platelets) develop.
Rehabilitation period
Splenomegaly (what is it, how to treat the syndrome - these questions have been successfully studied and tested in the practical part of medicine) is treatable. One of the factors of the positive dynamics of therapy is the correct behavior of the patient during the rehabilitation period.
The recovery time depends on several factors:
- type of operation;
- complications arising during the operation or after it;
- the state of human health and internal reserves of his body.
After the operation, you need to ask the doctor when you can start washing, if you can wet the wound. For mild pain, the patient is prescribed pain relievers that do not contain aspirin.
Nutrition after splenectomy should be balanced and contain a sufficient amount of micronutrients. It is impossible for the body to enter food rich in cholesterol, extractive substances and fats with a high melting point.
Prohibited foods for operated patients:
- foods that contain sugar or a lot of salt;
- fatty meats, lard, butter, eggs;
- pickled and canned food;
- products made from white flour and yeast;
- coffee and alcoholic drinks;
- sour food;
- spicy dishes;
- offal;
- mushrooms, radish, spinach, horseradish, turnip, radish, sorrel.
Allowed Products:
- non-acidic fruits and berries, nuts, honey;
- milk and dairy products;
- homemade fruit and vegetable juices, herbal teas;
- liquid vegetable dishes (mashed potatoes, soups, broths);
- stale bread;
- porridge boiled in water;
- high protein foods (fish, poultry, pork, liver, beef).
General recommendations:
- eliminate stressful situations;
- massage on the left side of the abdomen to improve blood circulation;
- opt for loose clothing that does not interfere with normal blood circulation;
- establish a regimen of food intake, eat more foods rich in iron;
- lead an active lifestyle in order to prevent the development of stagnation (not earlier than 4 weeks after the operation), but contact sports should not be practiced.
Symptoms that may occur after discharge (if they occur, you should immediately seek help):
- discharge of blood or other fluid from the wound;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dyspnea;
- unbearable pain, severe chest pain;
- development of puffiness;
- signs that indicate the development of an infection (a sharp increase in temperature, chills, fever).
Forecast
The spleen is an important organ. It performs three vital functions: filtration, hematopoietic and protective (immune). Removing an organ affects the functioning of the entire body, which will take up to 3 months to adjust to new conditions.
Part of the functions of the spleen will now be performed by other organs - the liver and lymph nodes. 6 months after the removal of the spleen, the patient should undergo an examination to make sure that he can return to his normal life.
There are no special measures to prevent this pathology.
There are general guidelines that apply to the prevention of any disease:
- rejection of bad habits;
- sufficient sports load;
- the need to avoid strong emotions;
- balanced diet;
- well-established regimen of food intake and rest;
- timely vaccination;
- a positive outlook on life;
- regular examination by doctors (once a year), in which the emphasis is on existing health problems;
- timely seeking medical help for systematic pain and other unpleasant symptoms.
Splenomegaly (enlargement of the spleen) is a serious pathology that can lead to death if you do not seek help in a timely manner. This condition is amenable to drug therapy, but in case of failure, the doctor prescribes an operation to remove the diseased organ. With a good outcome of such treatment, the person returns to normal life, but with amendments to the diet and daily routine.
Author: Victoria Komarova
Splenomegaly video
How to treat splenomegaly:



