What is it?
Polycystic ovary is a disorder of normal ovarian functions in combination with cystic degeneration. The disease can be found under a different name - polycystic ovary syndrome - a more capacious definition, because it unites several symptoms that form this pathology.
In the medical literature, there are other definitions: ovarian sclerosis( due to sclerotic changes in the ovary capsule) or Stein-Levintal syndrome( by the names of the authors who first described the syndrome).
Contents
- 1 Causes of development of polycystic ovary
- 2 Signs and symptoms of polycystic ovary
- 3 Can I get pregnant with polycystic ovaries?
- 4 Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome
- 5 Treatment of polycystic ovary, preparations
- 5.1 Complications of polycystic ovary
- 5.2 Prophylaxis
Causes of development of polycystic ovary
It is impossible to name the exact reasons contributing to the development of polycystic ovary. The disease is a syndrome in which changes are found in several organs of the endocrine system: the pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries, the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus.
The main value is given to the hormone - insulin, produced by the pancreas. Often, women with polycystic ovary obesity is male. Adipose tissue is insensitive to insulin and the pancreas is forced to produce a hormone in large quantities.
Insulin stimulates the ovaries to produce androgens, which leads to a disruption of the main function of the ovaries - to produce an egg that is capable of fertilization.
Also, the development of polycystic ovaries can occur in disorders in the hypothalamic-pituitary system. This system regulates the production of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones( FSH and LH), which promote the growth and development of follicles in the ovary and the onset of ovulation.
The concentration of hormones should be in a certain ratio, with an increase in the amount of LH, the ovaries produce male sex hormones, which inhibits ovulation.
During puberty hormonal failures can occur, then the adrenal glands of the girl begin to produce more androgens than necessary. This depresses the normal functioning of the ovaries.
Special attention is given to the hereditary factor. Although 100% of this is not certain, nevertheless, in families where the close relatives of a woman suffered from polycystosis, the risk of the disease is very high.
When family history is weighed, the family should carefully examine the girls who entered the period of puberty. With early diagnosis of the syndrome, the chances of recovery are much greater.
Symptoms and symptoms of polycystic ovary
The symptoms of polycystic ovary are very diverse and may resemble manifestations of other diseases. The peculiarity is that the presence of all the symptoms at once is not necessary for one woman. The signs of polycystic ovary can be invisible for many years. Most often a woman learns about her diagnosis only when she plans to become a mother.
The main symptom of polycystic ovary causing to consult a doctor is the inability to become pregnant.
The most common causes and additional symptoms of polycystic ovary:
1. The menstrual cycle is unstable. Disturbances begin to appear from the moment of onset of menstruation: an irregular cycle with scanty menstruation or vice versa, with prolonged bleeding.
Often menstruation may be absent for several months at all. Because of hormonal imbalance, the endometrium of the uterus increases in thickness, but monthly rejection does not occur or occurs with delay.
2. Tenderness in the abdomen. The pain symptom may be permanent. This is explained by the increase in ovaries and pressure on the pelvic organs.
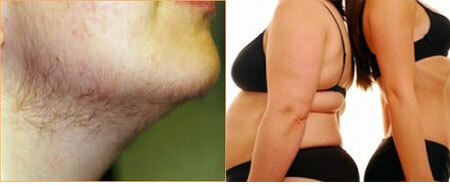
3. Weight gain. The symptom is unstable, but it is noted in many women. Characteristic obesity by the type of "apple" - the bulk of fat is located in the abdomen and waist.
Obesity is associated with excessive formation of insulin - insulin increases appetite, a constant feeling of hunger does not leave the woman. Due to a sharp increase in weight on the skin of the body appear stretch marks( striae).
4. The appearance changes. There is an appearance of acne on the skin, hair and skin have a fat type, often reveals fatty dandruff. Girls and women show increased hairiness on the body in the genital area, on the legs.
The so-called female tendrils break above the upper lip. On the head, on the contrary, focal hair loss( alopecia) can occur with the formation of bald patches. These changes indicate an increased production of male hormones.
5. It is noted by the increased pigmentation of the skin on the back, in the armpits.
6. From the nervous system side, irritability, drowsiness, mood swings, i.e., signs resembling PMS may be observed.
Can I get pregnant with polycystic ovaries?
Polycystic ovary and pregnancy, at first glance, the phenomenon is not feasible. But this is not so. With timely treatment and observance of preventive measures, a long-awaited pregnancy may occur.
A woman needs to learn to be patient, not to violate the plan of action prescribed by the doctor. This can take months and even years, but the result is worth it.
Treatment is aimed at maturation of a full egg and its release to meet spermatozoa for the long-awaited meeting and the birth of a new life.
The whole pregnancy and at the time of delivery the woman is under the close attention of physicians. It should be remembered that the very fact of pregnancy is not the result yet. In polycystic ovaries, pregnancy can end badly - the risk of miscarriages, fetal fetal and premature birth in women with this diagnosis is several times higher.
The risk of exacerbation of extragenital diseases is also high. Especially often in pregnant women with polycystic disease develops diabetes.
Diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome
Diagnosis of polycystic ovaries is a complex process. This is a whole complex of studies on the basis of which the diagnosis is put or refuted.
- The main criterion is infertility, due to rare ovulation or complete absence. Women unsuccessfully attempt to become pregnant, the years go by, and there is no pregnancy.
- The second important indicator is the quantitative determination of female and male sex hormones in the blood serum. Clinically, signs of an increase in androgens may not always appear, whereas a laboratory test may show an increase. It is also necessary to take tests for glucose and cholesterol.
- With a two-handed study, a gynecologist can grope enlarged ovaries that are dense to the touch.
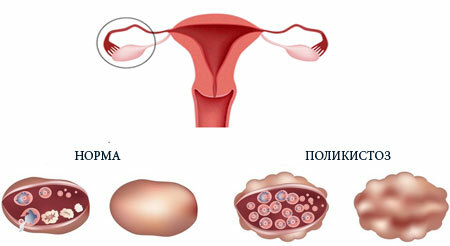
- Ultrasound examination will help to examine the structure of the ovaries. The doctor reveals the following ultrasound signs: the ovaries are enlarged, small follicles are visualized on the periphery of each, in the number of more than 10 pieces.
- Laparoscopy may sometimes be performed. This study is performed using a laparoscope instrument, which is inserted through a small hole on the abdominal wall. The laparoscope is able to look at the appearance of the ovaries: they are enlarged, their surface is covered with a white capsule, there are no signs of egg release on the surface of the capsule( dotted ruptures).Laparoscopy allows during the study to take a piece of tissue for histological examination, and is also one of the methods for treating polycystic ovaries.
The diagnosis is made only on the totality of several symptoms( the main ones are infertility, androgen and related symptoms).
None of the symptoms in a single manifestation can confirm the disease.
Treatment of polycystic ovary, preparations

Treatment of polycystic ovaries can take place with the involvement of several specialists at once: gynecologist( and better narrow specialist gynecologist-endocrinologist), endocrinologist and nutritionist.
Conservative treatment methods:
- Hormonal contraceptives. Help restore the cycle and avoid the development of endometriosis. Some drugs have anti-androgenic effect( they are fighting with pimples and excess hair on the body).This method is not suitable for women who are dreaming of becoming pregnant.
- Preparations that stimulate ovulation.
- Antiandrogenic drugs. This is a group of drugs that reduces the number of male hormones.
- Drugs aimed at the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Usually, this role is metformin drug, which, in addition to regulation of insulin production, contributes to weight loss.
- Diet. Some women just need to lose weight so that insulin levels come back to normal and ovulation occurs. Therefore, diet therapy plays an important role in the treatment of polycystic-altered ovaries. The diet for polycystic ovaries is aimed at eliminating a large number of fats and carbohydrates. It is necessary to combine diet with exercise.
Operative treatment:
- Minimally invasive surgery - laparoscopy. Using a laparoscope, a thick capsule of the modified ovaries is cut to facilitate the release of the oocytes.
- Sometimes an operation is performed to remove a part of the affected ovary. This is the most extreme measure and has recently been less and less common.
Complications of polycystic ovary
In addition to being unable to conceive, polycystic ovary has long-term complications.
- Uterine cancer. Irregular, monthly or prolonged absence contribute to the fact that the inner lining of the uterus( endometrium) gradually thickens, since its monthly desquamation does not occur. Endometrial cells first change their size and shape( hyperplasia), and then can degenerate into malignant ones.
- Development of obesity and diabetes due to insulin resistance of the body.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels due to elevated cholesterol( heart attacks and strokes).
Prevention
Prevention of recurrence of the disease is reduced to constant maintenance of weight in the norm. Even after successful treatment, which ended with the birth of a child, it is necessary to maintain a diet all your life. At any time, polycystic ovary can reappear.