Mononuclear cells in most cases signal the development of a serious disease, when a thorough diagnosis and correctly selected therapy are needed. The treatment is carried out by a hematologist, but in some situations it may be necessary to consult another a specialized specialist, taking into account the provoking source of changes in the level of cells in the general analysis blood.
Record content:
- 1 What are mononuclear cells?
- 2 Role in the body
- 3 Views
- 4 Causes of the appearance of atypical cells in the blood
- 5 Norms of mononuclear cells in adults, children
- 6 Indications for examination
- 7 Infectious mononucleosis virus
- 8 Symptoms
- 9 Diagnostics for deviations from the norm
- 10 Preparation for the analysis of blood, urine
- 11 How are tests carried out and what do they show?
- 12 Decoding of the results. How are mononuclear cells designated?
- 13 Where to take the biomaterial and how long to wait for the result?
- 14 How are abnormal mononuclear cells treated?
- 15 Video about mononucleosis
What are mononuclear cells?
Mononuclear cells are blood cells with one nucleus. They support the normal functioning of the immune system. Cells belong to the category of phagocytes, since they absorb and neutralize pathogenic microorganisms. Due to the production of specific elements as a result of the penetration of the virus into the human body, their number increases.
Role in the body
Mononuclear cells are divided into monocytes and lymphocytes. The first cells absorb foreign microorganisms and bacteria, and also spread information throughout the human body that an invasion of infection has occurred. Lymphocytes are responsible for the production of antibodies that are needed to fight off pathogenic agents.

It is thanks to B-lymphocytes that a stable immunity to various infectious diseases is developed. Immune memory makes it easier to tolerate re-infection without complications. In most cases, mononuclear cells in the blood indicate the development of a serious pathology.
Views
Mononuclear cells have a simple non-segmented nucleus, they lack specific granularity. There are the following types of cells that allow us to talk about the deviation of mononuclear cells, the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of the therapy:
| Name | Description |
| Lymphocytes | Shaped elements, the responsibilities of which include cellular immunity. They produce antibodies to bind and kill pathogens. The same thing happens with the cells of your own body if they are infected. Lymphocytes also have the ability to distinguish between cancer cells in the blood and kill them. |
| Monocytes | Leukocyte cells, whose duties are the immune response and the synthesis of cytokines. They can distinguish between damaged cells, pathogenic flora or bacteria, and damaged tissue as a result of inflammation and render them harmless. |
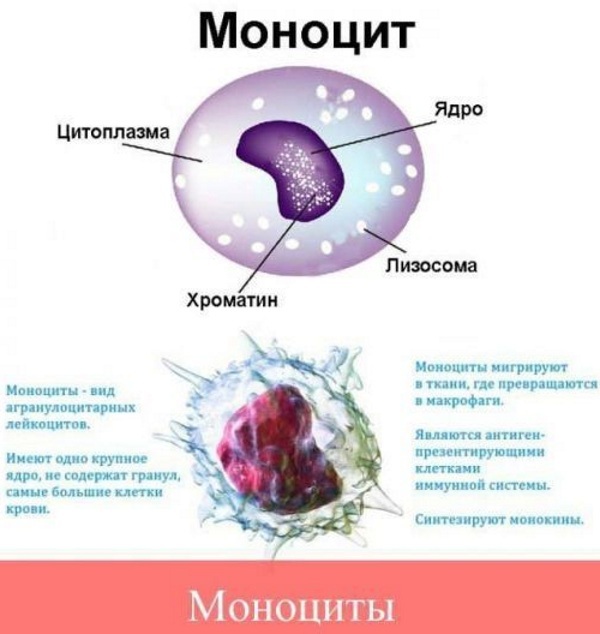
During a comprehensive examination, the level of these cells is determined, which help to identify changes in the level of mononuclear cells. The hematologist will help to decipher the diagnostic results and establish the disease.
Causes of the appearance of atypical cells in the blood
Mononuclear cells and other changes in the general blood test provoke numerous factors:
- infection with helminths;
- suspicion of systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis;
- mononucleosis caused by the Epstein-Barr virus;
- acute viral diseases;
- immune deficiency states;
- pathologies of bacterial origin (pneumonia, tuberculosis, endocarditis);
- individual sensitivity in relation to certain drugs;
- malignant or benign processes in the human body;
- anemia;
- diseases of the kidneys or liver, which are accompanied by severe intoxication;
- food poisoning;
- overdose of medications.
In a child's body, a change in the level of atypical cells occurs for the following reasons:
- autoimmune processes;
- oncological diseases;
- vaccination;
- severe intoxication of the body;
- pathological changes in the blood;
- long-term use of certain medications.
A hematologist will help to establish an accurate diagnosis and decipher the research results, as well as to choose the most effective treatment. The specialist deals with blood diseases. Given the provoking factor that caused the change in the level of mononuclear cells, the patient may need to consult other specialized doctors.
Norms of mononuclear cells in adults, children
Mononuclear cells in a general blood test, namely, their level depends on the person's age:
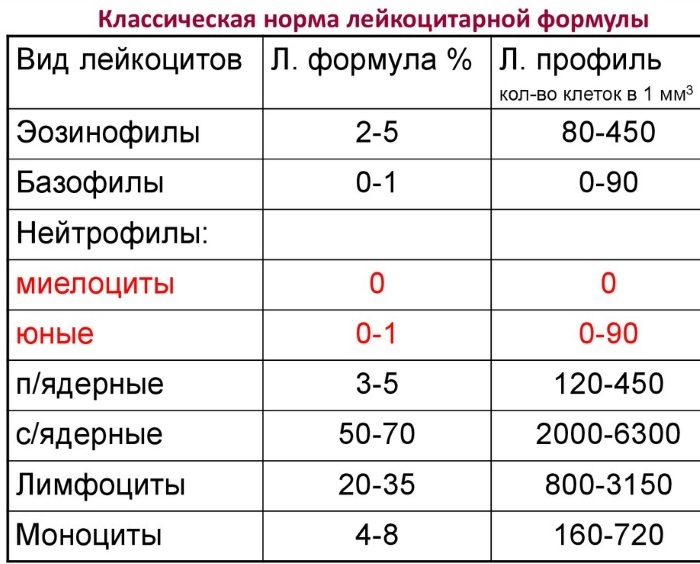
| Age | Monocyte count (%) | Lymphocyte count (%) |
| 0-5 years old | 4-10 | 16-32 |
| 5-10 years | 4-7 | 40-60 |
| 10-15 years old | 3-6 | 35-50 |
| 15-20 years old | 3-7 | 30-45 |
| 20-50 years old | 3-7 | 30-45 |
| over 50 years old | 4-8 | 35-50 |
Serious deviations from the established norms indicate the development of a certain disease. Ancillary complex diagnostics will help to clarify the diagnosis.
Indications for examination
The patient goes to the hospital with certain complaints and existing symptoms, taking into account which the pediatrician or therapist prescribes an examination.
There are the following indications for diagnostics:
- infectious and viral diseases;
- food or medication poisoning;
- blood disease;
- miliary tuberculosis;
- aplastic anemia;
- liver failure;
- treatment with cytostatics;
- pyogenic infections;
- state of shock.
During the period of gestation, the level of mononuclear cells may change. The same goes for vaccinations, tumors, autoimmune pathologies, HIV infection. A blood test for mononuclear cells is also prescribed to patients before surgery or before vaccination. Research will help make sure there is no hidden infection and control the treatment.
Infectious mononucleosis virus
In some situations, the change in the level of blood cells is due to the Epstein-Barr virus. Infection of the human body is carried out by airborne droplets during direct contact with a patient or a carrier of pathogens. There is also a risk of mother-to-child transmission (placental).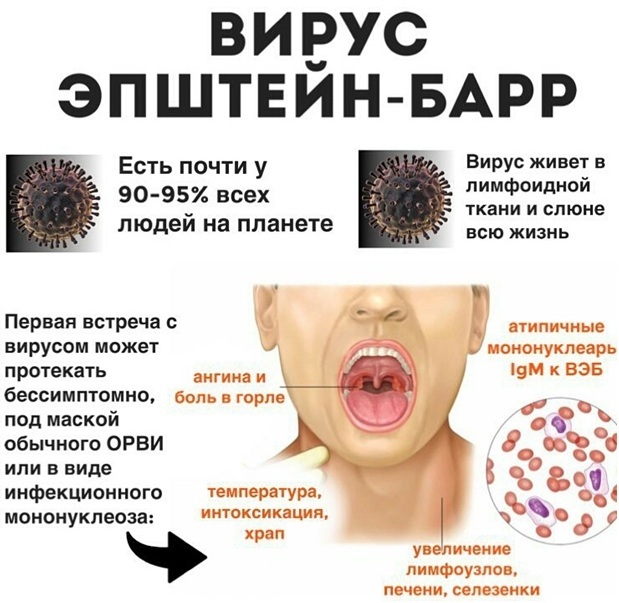
Infectious mononucleosis is more common among adolescents and young people (90%). The main feature of the disease is the defeat of all lymph nodes in the human body, tonsils, spleen and liver.
Mononuclear cells in a general blood test above the established norm cause characteristic symptoms:
- body temperature rises;
- pain syndrome appears during swallowing;
- a specific plaque forms on the tonsils;
- the patient is worried about the symptoms of intoxication (weakness, nausea);
- there is congestion in the nasal passages, against which the patient snores at night;
- cervical lymph nodes increase;
- sclera and skin turn yellow.
The time from infection to the appearance of the first signs of the disease is 5-60 days. In most cases, infectious mononucleosis resembles a sore throat, but a pediatrician or general practitioner must make an accurate diagnosis. If necessary, the specialist prescribes a comprehensive diagnosis, the results of which will help to make the correct diagnosis.
Symptoms
Diagnostic measures will help to determine accurately the abnormalities associated with mononuclear cells in the blood.
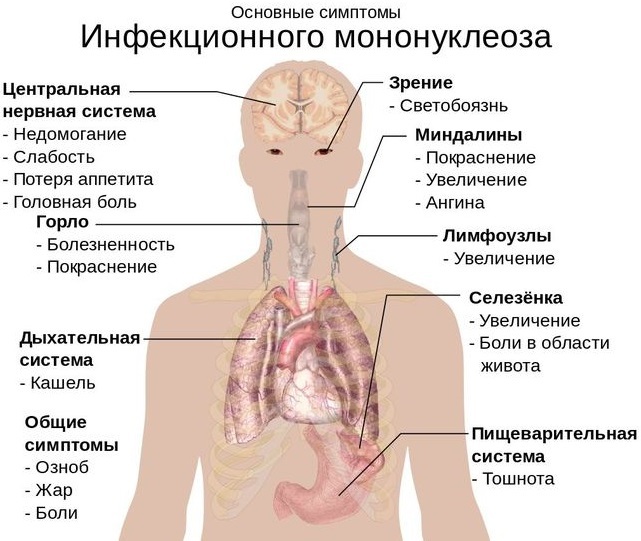
However, there are clinical signs that will allow you to suspect a problem and go to the hospital in a timely manner:
- a large amount of sweat is released;
- a person complains of general weakness and weakness;
- articular and muscle painful sensations occur;
- a sudden fever appears;
- working capacity decreases;
- the skin turns pale;
- cervical lymph nodes increase, soreness appears during palpation;
- a person breathes through his mouth more often;
- the voice becomes hoarse;
- shortness of breath appears;
- appetite worsens;
- sleep is disturbed, daytime sleepiness appears;
- mucous membranes and sclera turn yellow;
- hepatosplenomegaly develops.
In most cases, a change in the level of mononuclear cells in the blood occurs as a result of the development of a certain disease. Therefore, the patient will also have characteristic signs of concomitant pathology.
Diagnostics for deviations from the norm
The main method of diagnosis is general and biochemical blood tests. The examination is prescribed by a hematologist, taking into account the complaints of the person and his condition. It is important to differentiate the disease, since many of the symptoms of the disorder are similar to other pathologies (ARVI, diphtheria, viral hepatitis, acute leukemia).
In addition to laboratory tests, the patient is assigned additional methods. diagnostics, taking into account the results of a general blood test:
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity organs (ultrasound);
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- chest x-ray;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS).
To clarify the diagnosis, taking into account the provoking factor and concomitant disease, the patient may be assigned a biopsy.
Preparation for the analysis of blood, urine
The procedure for collecting biological material requires compliance with the minimum rules to obtain the most accurate results:
- On the day of the examination, the patient is not advised to eat.
- Before the analysis, it is necessary to completely exclude physical activity.
- The day before blood sampling, it is recommended to refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages, fatty and fried foods.
- A week before the delivery of the test material, it is necessary to stop taking medications.
- In the morning before the examination, it is not recommended to brush your teeth; it is enough to rinse the oral cavity.
- Hygiene procedures must be performed before urine collection begins.
Immediately before the blood test, patients should have a good rest and relaxation for 15-20 minutes.
How are tests carried out and what do they show?
Mononuclear cells in the general blood test and the viral infection that provoked their appearance will help determine the following diagnostic measures: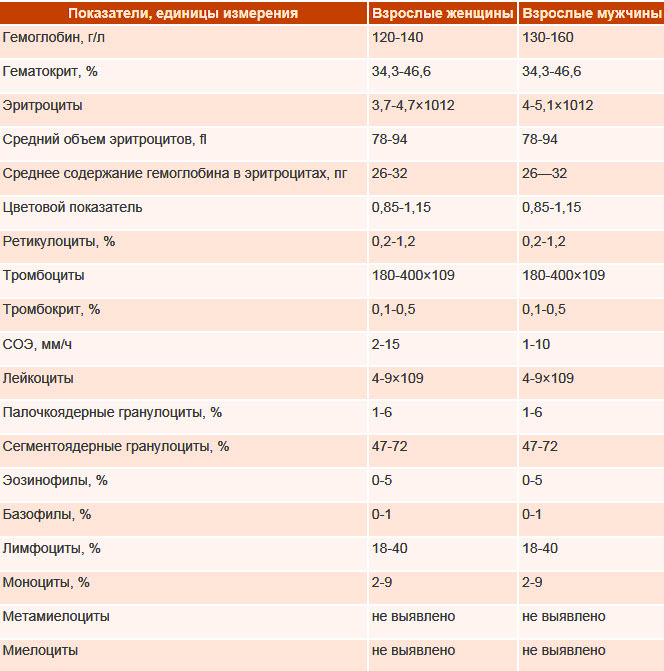
| Name | Description |
| General blood analysis | The test results show moderate leukocytosis. The leukocyte formula contains wide plasma lymphocytes (atypical mononuclear cells). |
| General urine analysis | The results of laboratory tests will help establish a complete picture of the inflammatory process, against the background of which the level of mononuclear cells has increased. |
| Biochemical analysis | The level of aldolase and alkaline phosphatase increases. Jaundice is indicated by an increase in bilirubin. |
| Linked immunosorbent assay | Specialists determine specific antibodies. The results allow to identify the Epstein-Barr virus and establish the degree of development of the disease. |
| Immunochemiluminescence analysis | The examination helps to confirm the presence of IgG antibodies. Doubtful results obtained require retesting after 5 days. |
| Polymerase chain reaction | The most informative diagnostic method that will show accurate results even with a minimum number of pathogenic cells. PCR also helps to identify the DNA of the causative agent of the disease and to draw up the most effective therapy regimen. |
| Monospot test | A diagnostic method that allows you to identify acute infectious mononucleosis in the first 2-3 months after infection of the human body. During the research, chemical reagents are used |
If necessary, the patient is assigned a consultation with other specialized specialists (endocrinologist, nephrologist, infectious disease specialist, immunologist, gastroenterologist).
Decoding of the results. How are mononuclear cells designated?
Only a pediatrician, general practitioner or hematologist can fully study the examination results. The specialist, guided by the data obtained, will make an accurate diagnosis.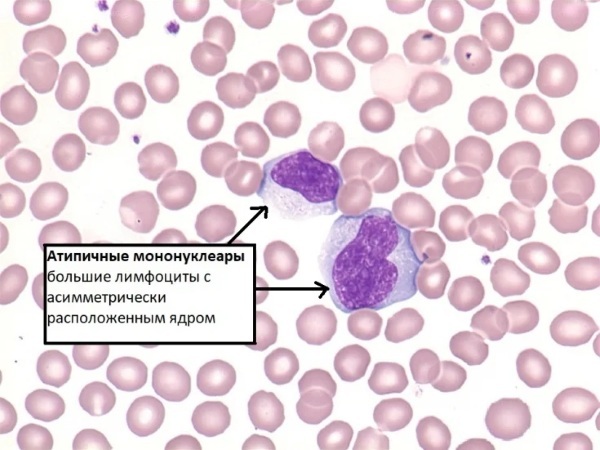
A complete blood count shows:
- an increase in atypical cells by 10%;
- an increase in monocytes by 40%;
- lymphocytes are increased by 10%;
- the total number of lymphocytes and monocytes is 80-90% when compared with the total number of leukocytes.
Leukocytes and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) will be slightly increased. The same goes for neutrophils (6%).
Where to take the biomaterial and how long to wait for the result?
Upon the referral of a doctor, the patient undergoes tests at a medical institution. A general blood test involves the collection of material from a finger. The biochemical method of examination is taking blood from a vein. The patient receives the finished test results the next day.
The monospot test also involves drawing blood from a vein, but the results will be ready in 5 minutes. The research requires special equipment, which is more often found in private medical institutions.
How are abnormal mononuclear cells treated?
Mononuclear cells in a general blood test more often indicate the development of a viral infection. In most cases, patients are treated in a complex and outpatient manner. The doctor prescribes medications, taking into account the results of the examination and the individual characteristics of the human body.
The main goal of therapy is to support the proper functioning of the immune system and eliminate the symptoms of an existing disease, as well as cope with the source of pathological processes.
Patients are prescribed the following medications:
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Antipyretic drugs | Ibuprofen, Paracetamol | Medicines help reduce high body temperature. The capsules should be taken orally, taking into account the time interval of 6-8 hours. The recommended dosage for an adult is 200-400 mg 3-4 times a day. The medicine is taken for a short time for 2-3 days. |
| Topical anti-inflammatory drugs | Strepsils, Faringosept | With infectious mononucleosis, a sore throat. Medication can help relieve discomfort and discomfort. It is recommended to dissolve 1 lozenge every 2-3 hours. The maximum daily dosage is 8 tablets. The therapy lasts 3 days. |
| Antibacterial drugs | Amoxicillin, Ciprofloxacin | Medicines are prescribed to patients in the event of a bacterial infection. The dosage is calculated based on the patient's weight and age. Adults and children from 2 years old are prescribed 125-500 mg once a day. For small patients, the dosage is calculated based on body weight. It is 20-100 mg / kg 2-3 times a day. |
| Choleretic drugs | Allochol, Hofitol | The drugs increase the production of bile and support the functioning of the liver. The adult dosage is 1-2 tablets 3-4 times a day. Children are prescribed 1 tablet 3 times a day for a month. |
| Antiviral drugs | Anaferon, Viferon | The medicine is taken orally before meals or after meals. The tablet should be kept in the mouth until it is completely dissolved. On the first day, the patient is prescribed 1 tablet every 30 minutes for 2 hours. Then you need to take 3 more tablets at regular intervals. Starting from the second day of treatment, you should take 1 tablet 3 times a day until complete recovery. |
| Immunomodulators | Immunal, Imudon | The medicine is recommended to be taken orally with plenty of water. The standard dosage for an adult is 1 tablet 3-4 times a day. The duration of treatment is 1-8 weeks. |
To strengthen the immune system, patients are prescribed vitamin complexes. Medicines have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Additionally, patients are advised to adhere to a strict diet, since the virus has a strong negative effect on the liver.
| Featured Products | Prohibited foods |
|
|
During therapy, the patient should also refrain from any physical activity, it is important to observe bed rest. For 1-2 weeks, eat right, adhere to a drinking regimen. After treatment, the patient should be observed by a doctor for another 6 months in order to prevent a recurrence of the disease.
It is impossible to avoid an increase in the level of mononuclear cells in human blood. There are only general recommendations of a hematologist.
In other situations, the main thing is to go to the hospital in a timely manner with alarming signs and undergo a full examination to make an accurate diagnosis. The results of a complete blood count and other tests are necessary for a specialist to draw up an effective treatment regimen.
Video about mononucleosis
Komarovsky about infectious mononucleosis:



