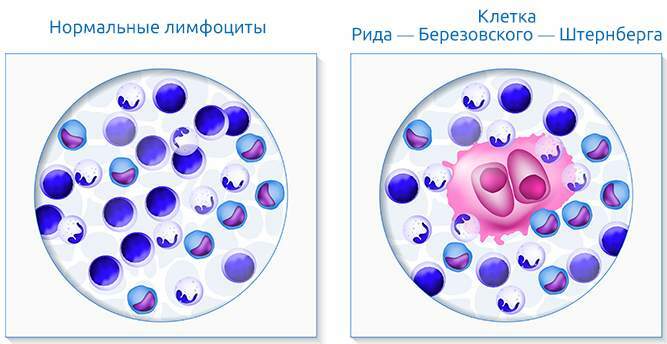
Hodgkin's disease (or nodular sclerosis) is an oncological disease, a malignant lesion lymphoid tissue. It can appear at any age, more often in the period of 20-40 years. A distinctive feature is the appearance of granulomas with Berezovsky's (or Reed-Sternberg's) cells. With timely treatment, the risk of relapse is extremely low, and the survival rate is up to 98%.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about the disease
Views
Hodgkin's disease has other names - malignant granuloma or lymphogranulomatosis. It is impossible to call the pathology only lymphoma. This term can denote several oncological processes at once, often radically different from each other. Therefore, more often Hodgkin's disease is indicated as lymphogranulomatosis.
Its distinctive feature is the formation of certain cells. They are abnormally large in size and have at least 2 cores. Berezovsky-Sternberg cells are absent in other types of lymphomas.
Hodgkin's disease is divided into several types according to the pattern of pathology:
- Lymphocytic. In the affected tissues, lymphocytes predominate, and there are few Berezovsky-Sternberg cells. The prognosis is favorable. The lymphocytic appearance is more often diagnosed in adolescent boys.
- Nodular sclerosis. A distinctive feature is the large volumes of collagen fibers in the affected tissues. The strongest are the cells of Berezovsky-Sternberg. The prognosis is favorable. Nodular sclerosis is more commonly diagnosed in young women.
- Mixed. In the affected tissues, there are many Berezovsky-Sternberg cells, lymphocytes, eosinophils and plasma cells - in equal concentrations. Chemotherapy is required for treatment. The mixed look is more common in people after 50 years.
- With lymphoid depletion. At the same time, there are few lymphocytes in the affected tissues, and mononuclear cells are in the lymph nodes. The prognosis is poor, the disease is not amenable to therapeutic effects. Lymphoid wasting is more commonly diagnosed in older patients.
Hodgkin's disease comes in several forms. Each of them has its own characteristics, some - varieties.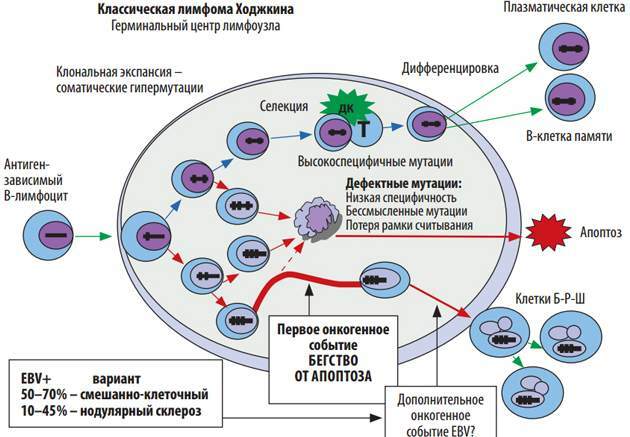
| Disease form | Variety | Features of the disease |
| Lymphatic | Peripheral | It begins to develop with lesions of the cervical, axillary and supraclavicular lymph nodes. They grow mainly on one side, but they can also grow on both. Symptoms are often mild or absent. The general condition of the patient remains good for a long time. This form of the disease responds best to treatment, but it is important to identify it as early as possible. |
| Mediastinal | The defeat of the pulmonary lymph nodes and the mediastinal region occurs after the spread of the pathological process from the axillary or supraclavicular areas or simultaneously with them. The disease can be either a separate form or be observed against the background of the main malignant process, move to other tissues and organs. Often, at first, it is asymptomatic, it is discovered by chance. Symptoms appear when it begins to squeeze the chest. This can lead to the appearance of the Bernard-Horner symptom. The prognosis is worse in comparison with the peripheral form. It becomes unfavorable when going to bones, pleura or lung tissue. | |
| Abdominal | If this is an independent form, then the pathological process begins with mesenteric or retroperitoneal lymph nodes, liver or spleen. Peripheral nodes remain intact until the end of the disease. With the abdominal form, leukopenia and anemia are more often diagnosed. This type of disease is considered the most severe, almost impossible to treat, the prognosis is the most unfavorable. | |
| Pulmonary pleural | Broncho-pneumatic | The first two varieties are most often combined. They are characterized by general symptoms, lesions of peripheral nodes. If the pleura is involved, pleural effusion begins. Sometimes with a hemorrhagic character. The exudate has no specific signs. Sometimes large cells of Berezovsky-Sternberg are also detected. The lung tissue is affected by the invasion method. This leads to the appearance of bronchopneumonic areas, diffuse disorders. Pulmonary lymphogranulomatosis is treatable. But if cancer cells have sprouted from the mediastinum, the prognosis worsens. |
| Pleural | ||
| Pseudotumor | ||
| Gastrointestinal | — | The gastrointestinal tract is involved in the oncological process at later stages, after development in other organs. Much less often the form of the disease is primary. If the mesenteric lymph nodes are affected, functional changes (motor disorders, diarrhea, constipation) occur. The process can go to the intestinal wall. Amyloidosis develops in the last stages of lymphogranulomatosis. With a primary lesion of the gastrointestinal tract, the diagnosis is more difficult, it can be confused with other diseases. |
| Bone | — | The pathological process affects the bones in the late stages of chronic Hodgkin's lymphoma. First of all, it affects the lumbar or cervical vertebrae, then the pelvis, sternum, ribs. In other bones, the process develops less frequently. The clinical picture depends on the site of the lesion, whether the nerve endings and the spinal cord are affected. Sometimes this type of disease is asymptomatic. This form responds well to treatment. |
| Nervous | — | The nervous system is affected secondarily. The process can go to the spinal cord. Sometimes plexitis, neuritis, neuralgia develop. The nervous system is involved in the process in the bone or lymphatic form of lymphogranulomatosis. Sometimes the development of the pathological process affects the brain. |
| Dermal | — | Skin lesions can be in the form of rashes, erythema, pigmentation. Shingles, fungal mycosis are often diagnosed. |
In Hodgkin's disease, one group of lymph nodes is first affected, then others are gradually involved, as well as tissues, organs. But not by the type of metastasis. Each time in a new place, the process begins from the 1st stage, as in the primary lesion focus. With the progression of the disease, fibrous, hyalinized tissues are formed.
Hodgkin's lymphoma can be diagnosed starting from 5 years old, earlier - very rarely and almost never - in newborns under one year old. Most often, pathology appears in men 16-30 years old. The risk increases after 50. With the appearance of lymphogranulomatosis in one twin, the likelihood of the appearance of pathology in the second greatly increases.
Stages and degrees
Hodgkin's disease (nodular sclerosis) is unpredictable. The first symptoms are usually discovered by chance. More often, the disease affects the lymph nodes under the collarbone and in the neck, less often in the armpits. Over time, the malignant process spreads to other tissues and organs, affecting the bones, lungs, and stomach.
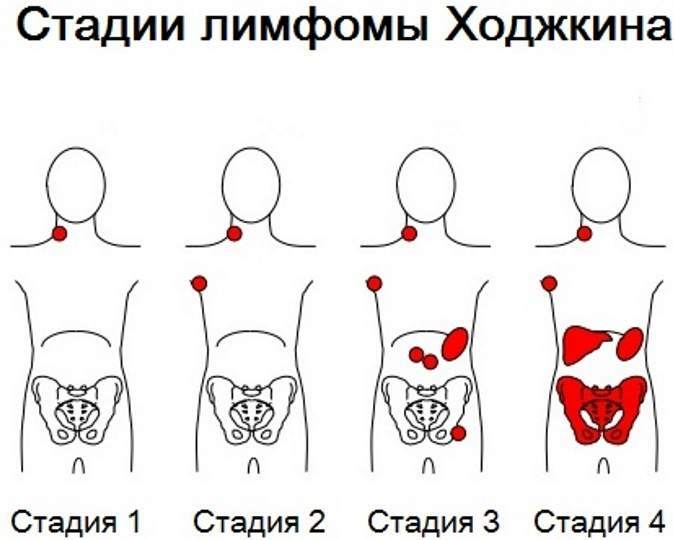
Depending on the development of the disease, it is divided into 4 degrees:
- First. The tumor is located in the area of the lymph node of one organ or adjacent tissues. It is designated IE (I - degree, E - process spread).
- Second. Lymph nodes are enlarged in more than one organ and nearby tissues - below or above the diaphragm. Non-lymphoid granulomas appear. The second degree is designated IIE.
- Third. There is an increase in lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm. If changes begin in the spleen, the pathology is indicated by IIIS, when at the same time the process also affects the non-lymphoid organ - IIIE.
- Fourth. The enlargement of the lymph nodes causes irreversible changes in organs and tissues.
When designating the type of disease, characteristic symptoms are often noted. If they put the letter "A", then this indicates that there is a sign, "B" - absent.
Hodgkin's disease (nodular sclerosis) develops gradually:
- First, reticular cells, similar to lymphocytes, grow. Large, rich in cytoplasm, with a weakly staining nucleus are distinguished. Eosinophilic and neutrophilic leukocytes can be detected. The process leads to partial or complete disappearance of the histological picture of the affected lymph node or organ. In this case, changes are observed, destruction of argentophilic fibers.
- In the second stage more affected cells appear, including large ones with a light nucleus. They resemble epithelial ones. There are even larger ones - with a deformed nucleus or with several at once. These are Berezovsky-Sternberg cells. They are similar to bone marrow megakaryocytes. All of these cells are derivatives of reticular cells. There are few blood vessels in the neoplasms, areas of coagulation necrosis appear. The reticular fibers are destroyed. The number of collagen fibers increases.
- In the third stage in the affected areas, the tissues are replaced with fibrous connective tissue. In enlarged lymph nodes, the disease can proceed in different ways. In some, the process is just beginning, in others it is already the final stage of development. With an exacerbation of pathology, changes may appear only in some parts of the nodes. After a new outbreak, healthy tissues are involved in the process.
With an increase in lymph nodes, starting from the second stage, Hodgkin's disease can already be easily diagnosed with a biopsy. When the pathology progresses, additional characteristic symptoms appear.
Symptoms
Hodgkin's disease (nodular sclerosis) in the initial stage is usually asymptomatic. Clinical manifestations appear much later, and they are quite varied. It can be pale skin, excessive sweating, feverish conditions. A less persistent symptom is itching. With advanced disease, there is a sharp decrease in weight.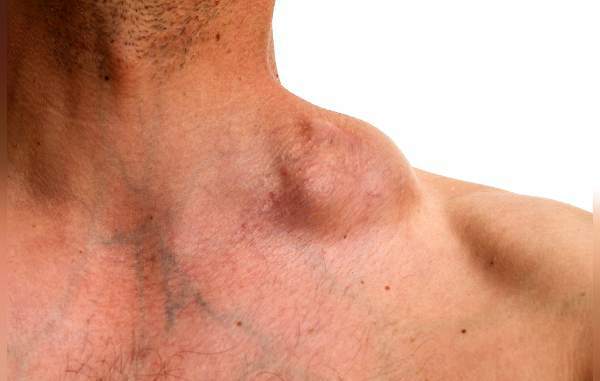
Swollen lymph nodes are the first and main symptom of the disease. At the same time, the general state of health remains normal. First, the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes increase, less often the axillary and inguinal. They are painless, easily move under the skin, as they are not attached to tissues.
The process of affecting the lymph nodes moves from top to bottom. The general state of health of the patient is normal, while the nodes are small. When they increase greatly, they begin to squeeze the surrounding tissues and organs.
This causes symptoms to appear:
- cough (often dry, painful);
- shortness of breath (when squeezing lung tissue, bronchi, after any physical activity);
- difficulty swallowing (first solid food, then liquid);
- swelling of the tissues surrounding the affected area (when the inferior vena cava is squeezed, the legs suffer, the liver and spleen are disrupted);
- digestive disorders - bloating, constipation, diarrhea;
- tissue necrosis, intestinal obstruction may develop;
- violation of the central nervous system (occurs rarely, appears mainly due to compression of the spinal cord), impaired sensitivity throughout the body, more often in the limbs;
- disruption of the kidneys (it is rare, signs may be absent if only part of the organ is affected), in particular, their failure.
Symptoms of Hodgkin's disease can appear due to damage to internal organs. Abnormal cells spread throughout the body, involving new tissues in the process.
The most common symptoms of internal organ damage:
- hepatomegaly;
- splenomegaly;
- violation of hematopoiesis in the brain;
- damage to the bones;
- lung pathology;
- itchy skin.
The list of symptoms can be increased depending on the affected organ. Systemic manifestations of Hodgkin's lymphoma include fever, fatigue, and general weakness. Weight may begin to drop dramatically. Due to a weak immune system, a person is often diagnosed with viral and infectious diseases. The condition worsens even more after radio and chemotherapy.
Reasons for the appearance
The causes of Hodgkin's disease (nodular sclerosis) have not been precisely established.
There are several assumptions that are considered the most likely:
-
Viral diseases. Their DNA fragments penetrate cells and are inserted into the genetic code, producing changes. The affected cell begins to collapse. The formed pathogenic fragments quickly spread, affecting all new cells. It has been proven that the Epstein-Barr herpesvirus does indeed influence the development of Hodgkin's disease. It causes infectious mononucleosis. This is an acute viral disease, due to which the composition of the blood changes. Lymphocytes begin to rapidly divide and break down. Mononucleosis occurs in more than 50% of patients with lymphogranulomatosis. Affects the lymph nodes, spleen and liver (sometimes pharynx).

- Immunodeficiency state, HIV. In such people, Hodgkin's disease appears 5-15 times more often than in others. The reason is the high risk of contracting infections, the Epstein-Barr virus. Immunodeficiency reduces the body's defenses against tumors. Also, the risk of developing Hodgkin's lymphoma increases if a person takes drugs that suppress the immune system.
- Genetic predisposition. Hodgkin's lymphoma is more common in twins, but usually only in one of them. At the moment, it is not possible to establish specific genes that predispose the development of lymphogranulomatosis.
Organ transplantation can also be a cause. At the same time, the protective functions of the immune system decrease, which can cause the development of lymphogranulomatosis.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease can be difficult due to the many symptoms that appear late. At an early stage, pathology is discovered by chance - during a routine examination, a preventive examination. Diagnosis begins with a visit to a therapist.
Appointed:
- CBC (general blood count) allows you to identify changes in the composition, the size, shape and concentration of all types of cells are assessed;
- blood biochemistry (with Hodgkin's lymphoma, the most informative will be liver tests to assess the state of the organ and the appearance of a high concentration of acute phase proteins);
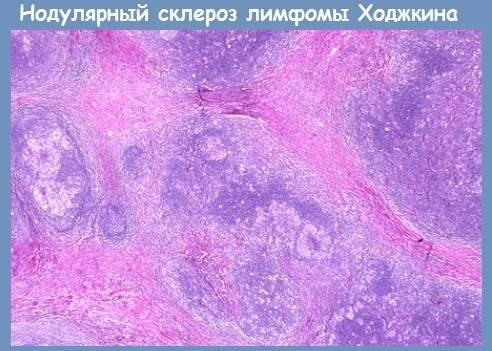
- histology of lymph nodes (to clarify the nature of the pathological process, identify granulomas);
- immunophenotyping of lymphocytes (an accurate method of recognizing different types of lymphocytes, markers of Hodgkin's disease - antigens CD15 and CD 30);
- bone marrow puncture (the goal is to determine whether the material contains Berezovsky-Sternberg cells and the functioning of the hematopoietic system).
Additionally, instrumental examination methods are prescribed.
These include:
- Plain radiography - the simplest method that helps to detect and assess the affected lymph nodes, compression and displacement of internal organs.
- CT (computed tomography). Layered images are obtained, in which even the smallest details are clearly visible. The affected groups of lymph nodes, the size and shape of the internal organs are clearly distinguished. Examination is more informative than radiography.
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination). The study helps the diagnostician to assess the shape and size of the lymph nodes, their density, composition. Internal organs, absence or presence of metastases are also examined.
- Endoscopic examination. It allows you to assess the area of growth of the affected lymph nodes, to determine the organs involved in the pathological process.
 The results obtained help to correctly diagnose, determine the form and type of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. If the diagnosis of Hodgkin's lymphoma is carried out in the clinic under the compulsory medical insurance policy, then it is free. However, the required hardware may not be available.
The results obtained help to correctly diagnose, determine the form and type of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. If the diagnosis of Hodgkin's lymphoma is carried out in the clinic under the compulsory medical insurance policy, then it is free. However, the required hardware may not be available.
Then the examination is carried out in the clinic. The cost will depend on the amount of research. For example, ultrasound - from 600 rubles, MRI and CT - from 4000 rubles.
When to see a doctor
Hodgkin's disease (nodular sclerosis) is treated by a hematologist. A doctor should be consulted for any of the alarming symptoms described above. However, they are absent in the initial stages. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo an annual preventive examination. If treatment is started at stages 1 or 2, then complete remission occurs in about 90% of cases. Later, the prognosis will be less favorable.
Prophylaxis
Hodgkin's disease can be hereditary. Therefore, it is necessary to avoid hypothermia, treat current diseases in time, and strengthen the immune system. Doctors recommend taking multivitamins, avoiding contact with sick people with viral and infectious diseases, and getting vaccinated in a timely manner.
It is important to give up bad habits, to be in the sun as little as possible. Specialized events are not required. Lymphogranulomatosis is not transmitted from a patient to another person.
Treatment methods
The main method of treatment for Hodgkin's disease is medication. It is used for any form of the disease, regardless of the stage. Medications are usually combined with radio or chemotherapy.
Medications
There are now many therapeutic regimens for Hodgkin's lymphoma. They differ in the combination of drugs. The most commonly used schemes are ABVD, BEACOPP, DHAP. The course of treatment is 14-30 days.
ABVD treatment regimen: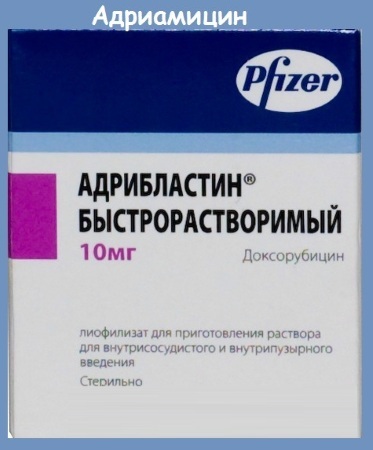
| Drug name | Mechanism of action | Dosage |
| "Adriamycin" (from 400 rubles) | It binds the affected and healthy cells, stops the synthesis of nucleic acids, which prevents the division process. Leads to the formation of free oxygen radicals that destroy cell membranes. This destroys the affected cells. | 25 mg / sq. m |
| "Bleomycin" (from 5800 rub.) |
The drug destroys the DNA of tumor cells, which prevents them from dividing and leads to destruction | 10 mg / sq. m |
| Vinblastine (from 1300 rub.) |
Causes the destruction of the protein tubulin, which is needed for normal performance and cell division | 6 mg / sq. m |
| "Dakarbazin" (from 240 rub.) |
A cytostatic drug that blocks the production of nucleic acids in the cell nucleus. This stops the process of division and growth. | 375 mg / sq. m |
All drugs in the table are used in the same way, administered intravenously. One course - two droppers. After the first one, take a break for 14 days. At stages 1 and 2, when there are no symptoms, two courses of ABVD with radiotherapy are done.
BEACOPP treatment regimen:
| Drug name | Mechanism of action | Application and dosage |
| "Bleomycin" (from 580 rub.) |
The drug destroys the DNA of tumor cells, which prevents them from dividing and leads to destruction | It is administered intravenously, on the 8th day after the start of the course of treatment. Dosage - 10 mg / sq. m. |
| "Etoposide" (from 210 rub.) |
Blocks cell division by destroying DNA in the nucleus | It is administered intravenously, in the first three days of the beginning of the course of treatment (1 time). Dosage - 200 mg / sq. m. |
| "Adriblastin" (from 380 rub.) |
Stops the production of nucleic acids, preventing division. Leads to the destruction of membranes, destruction of cells. | It is administered intravenously, once, on the first day of the beginning of the course of treatment. Dosage - 25 mg / sq. m. |
| "Cyclophosphamide" (130-470 rub.) |
A cytostatic drug that disrupts the production of nucleic acids, fission processes, which blocks the formation of proteins. It mainly affects tumor cells. | It is administered intravenously, on the 1st day of the beginning of the course of treatment. Dosage - 650 mg / sq. m. |
| "Vincristine" (from 200 rubles.) |
Destroys tubulin protein. Violates the formation of proteins and DNA in cells. | It is administered intravenously, on the 8th day after the start of the course of treatment. Dosage - 1.5-2 mg / sq. m. |
| "Procarbazine" (from 20,000 rubles.) |
The drug accumulates in the tissues affected by the tumor and is converted into a toxic substance for cell membranes and organelles | Prescribed in pill form for a week. They are given to the patient from the first day of the course, once every 24 hours. Dosage - 100 mg / sq. m. |
| "Prednisolone" (20-180 rub.) |
Hormonal anti-inflammatory drug, but suppressing the immune system. It is prescribed to reduce the severity of symptoms and inflammation in the affected tissues. | Prescribed in pill form for two weeks. They are given to the patient from the first day of the course, once every 24 hours. Dosage - 40 mg / sq. m. |
At stages 3 and 4, treatment is supplemented by the BEACOPP regimen, 8 courses of chemotherapy. In most patients, this leads to permanent remission.
DHAP treatment regimen:
| Drug name | Mechanism of action | Application and dosage |
| "Cisplatin" (from 90 rub.) |
Substances of the drug penetrate into the structure of tumor cells, change their DNA, causing death | The dropper is put on for 24 hours, on the 1st day of the course, at the rate of 100 mg / sq. m |
| "Cytarabin" (from 900 rub.) |
Prevents the formation of new pathological cells | The dropper is put on for 3 hours. The first on the 1st day of the course, the second after 12 hours. The total dose is 4 g / sq. m, for each dropper - 2 g / sq. m. |
| Dexamethasone (30-340 rub.) |
Suppresses the immune system. It is prescribed to reduce the severity of symptoms and inflammation in the affected tissues. | Assign in the first 4 days of the course, daily, at 40 mg / sq. m |
All drugs are administered intravenously, in the form of droppers. Even after DHAP, the prognosis remains poor. He needs radical chemotherapy with high doses of drugs. Since this destroys all blood-forming cells, a bone marrow transplant is required at the end.
Traditional methods
There are no traditional methods for treating Hodgkin's disease. They can only be used as aids.
Otherwise, it can provoke a deterioration in the forecast. However, you can use some remedies to strengthen the body.
For example, a rosehip infusion is prepared. Take 5 tbsp. l. dry fruits and pour 1 liter of boiling water. They insist on an hour. Then they drink during the day. Or they make a decoction of oats. Take 2 tbsp. l. grains and pour 400 ml of cold water. Cook for 15-20 minutes, cool, filter. Then the broth is drunk during the day.
Other methods
Since 1902 to treat Hodgkin's disease, radiation therapy (radiotherapy) began to be used. Under the influence of gamma rays on the lesion focus, there is a rapid death of Berezovsky-Sternberg and Hodgkin's cells. There are different types of radiotherapy, but for lymphogranulomatosis, radical mantle radiation is mainly used. It is performed at stages 1-2 of the disease.
The bottom line is the simultaneous irradiation of all lymph nodes in which a tumor could form. The course of treatment is 4-5 weeks. In this case, the patient receives a total dose of radiation - 36 Grays. If there are many affected lymph nodes, it increases to 44 Gy. A total of 20 sessions are done.
Each patient receives an average radiation dose of 180 cGy (centi Gray). At stages 3-4, tumor cells spread throughout the body. Treatment with radiotherapy alone becomes ineffective.
Surgical intervention for Hodgkin's disease is prescribed very rarely, only if radio and chemotherapy are ineffective. During the operation, the largest affected lymph nodes and squeezing internal organs are excised. They are also deleted if irreversible changes have occurred in them that pose a threat to life.
Possible complications
The primary group of complications is associated with the localization of the disease. Further - pathologies with the development of various disorders, depending on the affected internal organs.
For example:
- compression and mediastinal jaundice;
- intestinal occlusion;
- lymphatic edema;
- fungal infections;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- neurological disorders;
- degenerative lesions of the central nervous system;
- combination with other oncological pathologies.
Lymphogranulomatosis is characterized by an increase in current non-life-threatening diseases. For example, herpes simplex can become severe and even fatal. Bacterial infections are also often diagnosed. They can take the form of septcemia.
Hodgkin's disease often occurs with a series of remissions and exacerbations. In the initial stage of therapy, it is possible to stop the pathological process. Untreated nodular sclerosis is fatal.
Video about the disease
About Hodgkin's lymphoma:



