Natural focal pathologies are diseases that are common to animals and humans.
The causative agents of ailments can persist in nature for a long time in a certain climate, within a limited space, creating a reservoir of infection in the body of an animal or human. Natural focal infectious diseases are especially common among wild, agricultural and domestic animals.
Record content:
- 1 Classification
-
2 Plague
- 2.1 Views
- 2.2 Stages and degrees
- 2.3 Symptoms and Signs
- 2.4 Causes
- 2.5 Treatment methods
-
3 Tick-borne encephalitis
- 3.1 Views
- 3.2 Stages and degrees
- 3.3 Symptoms and Signs
- 3.4 Causes
- 3.5 Treatment methods
-
4 Cholera
- 4.1 Views
- 4.2 Stages and degrees
- 4.3 Symptoms and Signs
- 4.4 Causes
- 4.5 Treatment methods
-
5 Leptospirosis
- 5.1 Stages and degrees
- 5.2 Symptoms and Signs
- 5.3 Causes
- 5.4 Treatment methods
-
6 anthrax
- 6.1 Views
- 6.2 Symptoms and Signs
- 6.3 Causes
- 6.4 Treatment methods
-
7 Tularemia
- 7.1 Views
- 7.2 Symptoms and Signs
- 7.3 Causes
- 7.4 Treatment methods
- 8 Video about natural focal diseases
Classification
In medicine, natural focal infections are classified according to several criteria.
If we consider them by the nature of landscape development, then in nature there are:
- Anthropurgic. In this case, wild and domestic animals are the spread of infection. Such a pattern of distribution is found in foci of typhoid, encephalitis, and leishmaniasis.
- Synanthropic. The infection only circulates in livestock. These include toxoplasmosis, trichinosis.
Classification also occurs by the number of owners:
- Monogostal. The reservoir of infection is only one of the animal species. It has the ability to form only to one genus of hosts or in a certain territory, which, for example, is inhabited by wild animals, for example, armadillos are often carriers of infection.
- Polygostal. Several species of animals act as carriers of the infection. For example, the plague is carried by marmots, ground squirrels, and sandstones.
Natural focal infections are classified according to the number of carriers of the disease:
- Monovector. Pathogens are transmitted by only one species of animal.
- Polyvector. Pathogens are transmitted by several types of vectors at once.
Plague
Natural focal diseases are, among other things, a pathology that manifests itself in an acute form, which are transmitted to humans from an animal and are caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. The disease is one of the most dangerous quarantine infections. The disease is transmitted in different ways, but the most dangerous for humans is airborne. If the correct and quick treatment is not started, then the patient is in danger of death.
Views
In medicine, there are 4 clinical forms of plague:
| Dermal | A spot initially appears on the skin, and then a bubble with a purulent content, then turns into an ulcer. The ulcer gives the person discomfort, surrounded by an area of inflammation. When ruptured, an ulcer with a dark bottom appears. If a person recovers, then a scar remains at the spot. |
| Bubonic |
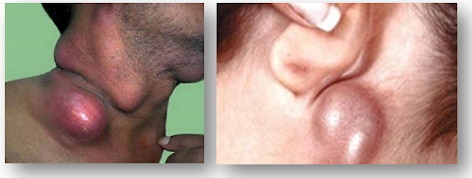 This form is characterized by the appearance of a bubo - an inflamed lymph node that causes pain and discomfort in a person, it can be localized in any part of the body, but more often in the groin area. The skin in this area is dry and hot, with an active course of the disease, it can acquire a purple-cyanotic hue. This form is characterized by the appearance of a bubo - an inflamed lymph node that causes pain and discomfort in a person, it can be localized in any part of the body, but more often in the groin area. The skin in this area is dry and hot, with an active course of the disease, it can acquire a purple-cyanotic hue. |
| Primary septic | It has general signs of the plague process, the symptoms develop quickly, intoxication progresses, vomiting with blood appears, the face becomes cyanotic. Without treatment, the patient dies after 4 days. |
| Pulmonary | The disease develops as soon as possible. Acute intoxication appears, cough with blood flow, shortness of breath and wheezing in the respiratory organs increase. |
Stages and degrees
According to the severity of the course, the plague is divided into several stages of development:
- Lightweight. Not severe intoxication is observed for 5-7 days, the temperature is kept within 37-37.5, there are no neurological disorders.
- Average. Moderate intoxication is observed within 2 weeks, febrile temperature, bradycardia, neurological manifestations.
- Heavy. Severe intoxication, tachycardia, hemorrhages, vomiting interspersed with blood, severe headache.
Symptoms and Signs
The incubation period for infection and contact with infected material lasts about 6 days. In vaccinated people (the vaccine is valid for about a year), the incubation period can last up to 2 weeks. After the disease begins to develop in a mild form, and then complications begin.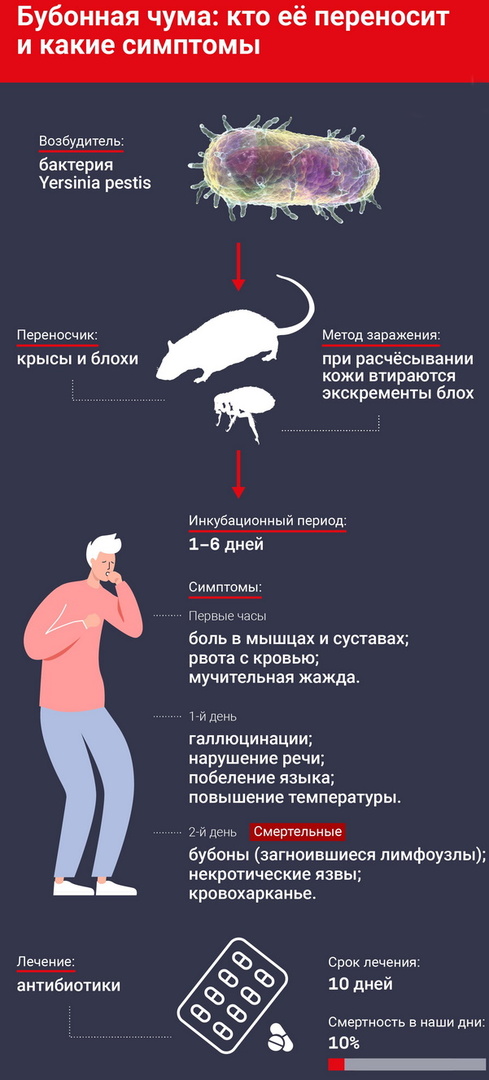
The disease manifests itself in the form of such symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- chills and fever;
- intoxication;
- general weakness;
- joint aches;
- unbearable headache;
- delirium, clouding of consciousness;
- nausea;
- thirst;
- white bloom on the tongue;
- vomiting interspersed with blood;
- pain in the peritoneum, diarrhea interspersed with blood.
Causes
The reservoir and source of the disease are wild rodents: voles, marmots and others. In urban environments, rats can be a source of infection. Dogs that are resistant to human plague can be a source of flea pathogens. In rare cases, a person can also become a source. Often, infection can come from a plague corpse.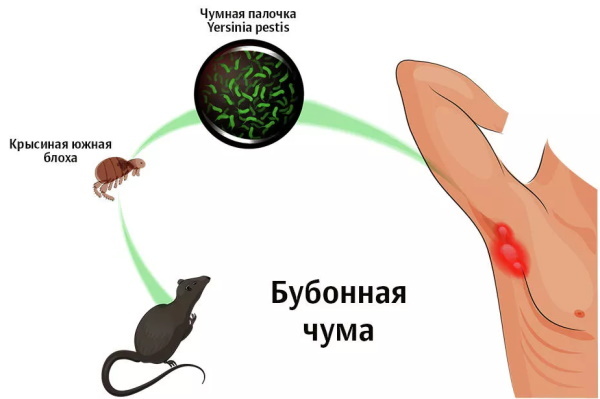
Ticks and fleas are considered carriers of the pathogen. It is fleas that infect animals that carry the pathogen quickly, migrating from place to place. A person becomes infected by rubbing flea excrement into the skin.
Treatment methods
Today, thanks to modern technology, there are a lot of new drugs and treatment methods that help reduce the number of deaths from the plague. But you can only be cured if you identify the disease at the initial stage of its development.
As soon as the first symptoms are identified, the patient is urgently hospitalized. Complex therapy is prescribed, including pathogenetic, etiotropic and symptomatic medications. Epidemics can be avoided if the nursing staff responds quickly.
Antibiotics related to the streptomycin series are considered effective in the treatment of plague: Pasomycin, Streptomycin. The dose is set by the doctor, and the course is up to 10 days.
Also important is detoxification therapy, which includes polyionic solutions, hemodez, rheopolyglucin, and others.
After completing the course of treatment, the patient is under the supervision of an infectious disease specialist for another three months.
Tick-borne encephalitis
Natural focal diseases are, including pathologies, which are infectious and viral in nature. The disease especially affects the central nervous system. The causative agent of the disease is a virus belonging to the family of flaviviruses, which, in addition to this pathology, provoke a number of other serious ailments. These include yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, and hemorrhagic fever.
Views
According to clinical signs and place of distribution, doctors share several subtypes of the disease:
- Far Eastern. This is one of the most severe forms of the disease, which is carried by the taiga tick. This subtype begins to develop immediately from the second phase, manifested in the form of high fever, severe headache, insomnia, vomiting and nausea.
- Siberian. The taiga tick acts as a carrier. This subtype is mild.
- European. The carrier is a dog tick. This form of the disease is characterized by two phases of development, and only 20% of patients develop a second phase.
Stages and degrees
The disease proceeds in several stages:
- First. The virus multiplies in the circulatory system without affecting the nervous system. The fever lasts more than a week. After that, the temperature drops for several days and it is during this period that the virus overcomes the circulatory and nervous system, affects the brain.
- Second. The virus affects the brain, as a result of which there is a severe headache, fear of light, vomiting. There is a strong muscle tension in the occipital region, which does not allow the person to bring the chin closer to the chest.
- Third or as it is often called focal. All brain cells are affected, and the symptomatology depends on which part of the brain the foci of the disease are observed in.
Symptoms and Signs
Natural focal diseases are, among other things, tick-borne encephalitis, which at the initial stage is manifested by symptoms, very similar to flu symptoms:
- chills;
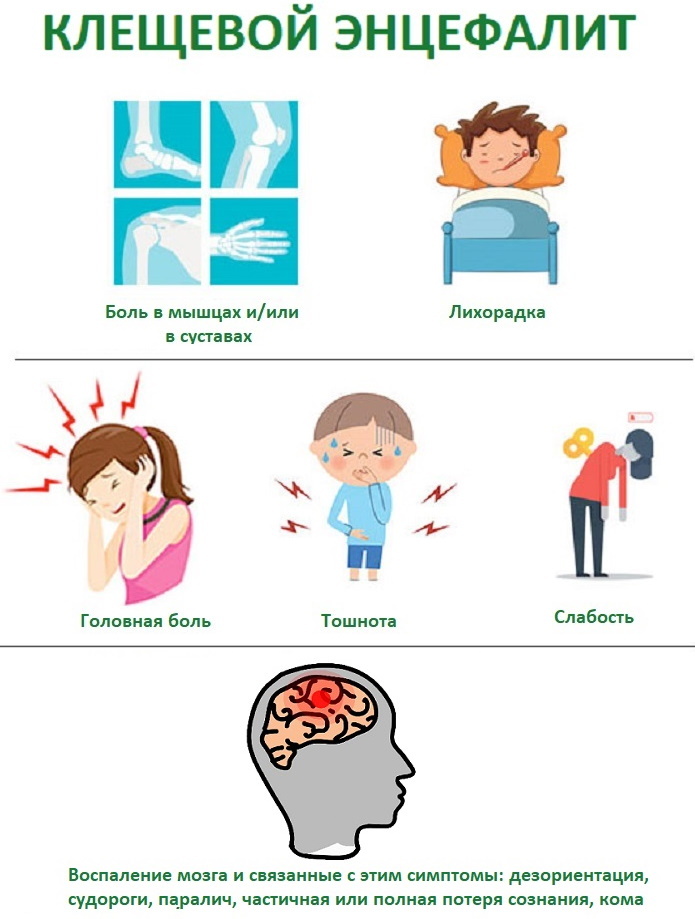
- a sharp increase in body temperature up to 39 degrees;
- headache;
- discomfort throughout the body;
- loss of appetite;
- general weakness;
- vomit.
The main signs of the disease are: headache, convulsions, fear of light, mental disorders, persistent intoxication.
Causes
The main reason for the development of the disease is a viral infection that has entered the body. The causative agent is the encephalitis virus, and the carrier is ticks. The virus can be transmitted through the bite of an infected tick or through food infected with the disease.
Treatment methods
Treatment of the disease is aimed at eliminating the symptoms. The patient is hospitalized and prescribed the strictest bed rest. In some cases, anti-tick immunoglobulin is used to neutralize the virus.
Vitamin therapy is also used in the treatment of tick-borne encephalitis. So, for example, vitamin C helps to improve the functioning of the immune system, improve liver function, so that it better removes toxins from the body. The daily dose of the drug varies between 300-1000 mg. Vitamins of group B are also prescribed.
Cholera
This is an acute intestinal infection, which manifests itself as a result of the ingestion of Vibrio cholerae. The infection mainly affects the small intestine and manifests itself in the form of severe diarrhea, vomiting and intoxication.
During the period of illness, the patient loses up to 40 liters of fluid per day, which can provoke fatal dehydration. Vibrio cholerae is a bacterium that has more than 200 types of serotypes, and only two of them provoke the development of the disease.
Views
According to the clinical and pathogenetic manifestations, several main types of cholera are divided:
- hypovolemic exotoxic;
- normovolemic exotoxic;
- mixed exoendotoxic;
- normovolemic atoxic;
- subclinical.
Stages and degrees
The disease is classified according to several criteria. According to clinical manifestations, they are divided into typical, atypical, erased, subclinical and transient.
According to the severity of the course, there are three forms of the disease: mild, moderate and severe.
Symptoms and Signs
From the moment of infection, it can take up to 5 days, but more often about 2 days.
The disease takes several forms, and each has its own symptoms:
- A sharp loss of body weight and fluid up to 3%.
- The liquid is already gone by 6%.
- Loss of fluid up to 9%.
- Loss up to 10%.
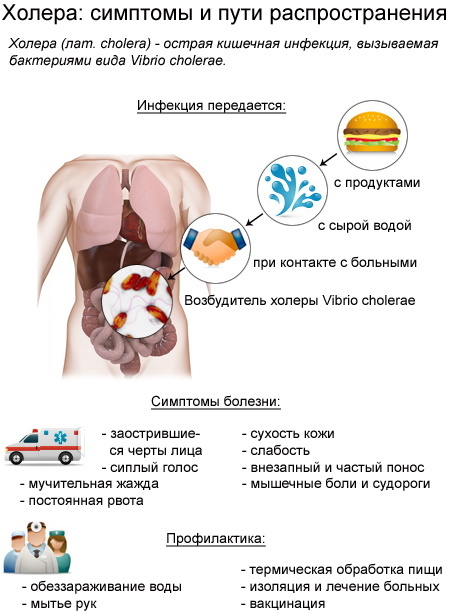
Initially, the development of the disease begins with severe diarrhea. Then vomiting also joins, as well as the strongest thirst. The amount of urine decreases, despite the fact that the person drinks a lot of liquid and its color becomes dark.
Other symptoms are also observed:
- convulsions;
- elasticity of the skin;
- drowsiness;
- general weakness;
- tachycardia.
Causes
The source of infection can be an infected person or a carrier that secretes Vibrio cholerae, but does not have any symptoms of the disease. The disease is transmitted by the fecal-oral route, when the patient secretes bacteria through vomit or diarrhea. The disease penetrates through the oral cavity, but is not transmitted by airborne droplets.
The transmission routes can be:
- water;
- contact and household;
- food.
Treatment methods
At the first symptoms of cholera, the patient is hospitalized and isolated. The patient is prescribed strict bed rest. Every 2 hours, healthcare professionals assess the amount of fluid excreted from the body in order to accurately calculate the amount of saline solution to be administered to the body.
Also, the patient is prescribed diet number 4. There are no special restrictions, but you cannot use strong broths, fresh bread and flour products, fatty meat and fish, milk, raw vegetables and fruits, drinks with gas.
Cholera medications include a saline solution that can be given by mouth or intravenously.
Also, antibiotics are used to neutralize the infection and the most effective are: Tetracycline, Levomycetin and Ciprofloxacin.
In the treatment of cholera, antibacterial agents are used, for example, Furazolidone. The duration of therapy is about 5 days. But after treatment, the patient develops strong immunity.
Leptospirosis
Natural focal infectious disease leptospirosis is a pathology that occurs with serious damage to the liver, kidneys and blood vessels. This ailment is included in the list of the World Health Organization in the category of the most important infectious diseases. Human infection occurs from animals. The causative agent of the disease is the bacterium Leptospira.
Stages and degrees
The disease develops in several stages:
-
First. The bacterium enters the body through mucous membranes and skin, while no traces remain on the body. After the bacterium affects the lymphatic vessels and spreads through them to all organs and the liver, kidneys, lungs and spleen are the first to be affected.
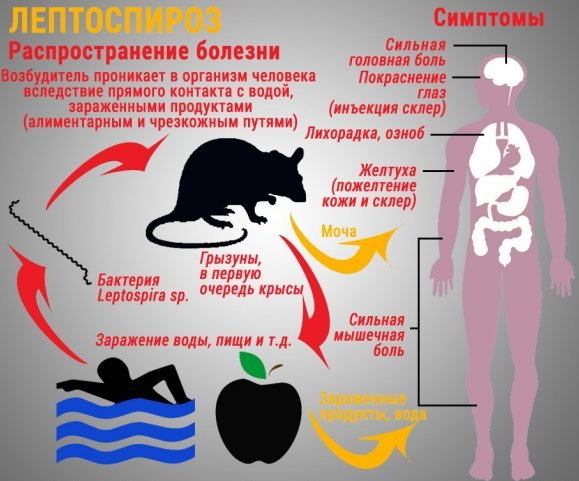
- Second. When the bacteria hit the organs, it begins to actively enter the bloodstream and this stage is considered the onset of the disease and manifests itself with clinical signs.
- Third. The bacterium begins to actively release toxins into the bloodstream, which easily spread throughout the body, poisoning it. As a result, hemorrhage, tissue necrosis, destruction of blood cells begins.
- Fourth. A person begins to develop a pronounced immune response to the aggression of bacteria, the body produces cells that actively fight against the bacteria.
Symptoms and Signs
The clinical picture is varied. Symptoms depend on the form of the disease.
The main symptoms are:
- heat;
- chills;
- skin rash;
- hemorrhage from the nose and into the conjunctiva;
- jaundice;
- damage to internal organs.
Causes
A person can become infected with leptospirosis only from an animal:
- harvest mouse;
- shrew;
- hedgehog;
- marmot;
- gray rat;
- fox.
Also, a person can become infected from domestic animals: cows, goats, sheep, horses.
Treatment methods
Therapy begins with detoxification of the body, which aims to remove leptostyrosis and toxins from the body. Detoxification is carried out with saline solutions or plasma-substituting compounds. Additionally, the circulation of the blood volume is replenished, since the hemorrhagic syndrome provokes a sharp loss of blood and fluid.
Antibiotic therapy is also used in the treatment of leptospirosis. Penicillin drugs are mainly used, and if the patient has an intolerance to such drugs, then macrolides are prescribed.
Also, a special serum or gamma globulin is used in the treatment.
anthrax
Natural focal diseases are, among other things, anthrax, which occurs in an acute form and is very dangerous for human life. Humans and animals become infected with the bacterium Bacillus anthracis.  The disease proceeds with the forcing of carbuncles on the skin or in septic form. The source of infection is wild and domestic animals, infection occurs through contact.
The disease proceeds with the forcing of carbuncles on the skin or in septic form. The source of infection is wild and domestic animals, infection occurs through contact.
Views
There are several types of anthrax:
- cutaneous;
- generalized;
- pulmonary;
- intestinal;
- septic.
Symptoms and Signs
Symptoms of the disease depend on the form:
-
Dermal. Most often, only one carbuncle appears on the skin, but with a severe course of the disease, there may be more of them. If it appears on the neck or face, then it is dangerous because it can block the upper respiratory tract, which ultimately provokes suffocation and death. Symptoms are manifested in the form of high fever, severe intoxication.
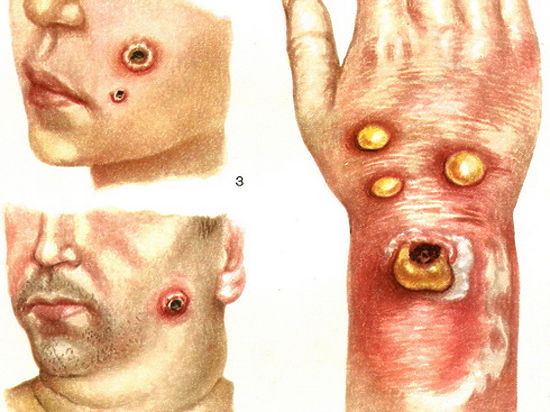
- Pulmonary. Symptoms with this form are erased, the first signs resemble the development of pneumonia or bronchitis. The patient complains of high fever, cough, rhinitis, weakness and pain during breathing.
- Intestinal. The patient has weakness, nausea, vomiting, severe pain in the abdomen, diarrhea with blood, an increase in the size of the abdomen.
- Septic. It manifests itself in the form of severe fever, difficulty breathing, severe pain in the sternum and abdomen, diarrhea interspersed with blood clots.
Causes
Human infection occurs from livestock. A person becomes ill while caring for an infected pet, during the slaughter or processing of infected carcasses. A person can also get infected by eating contaminated meat. Infection can also occur if contaminated air is inhaled.
Treatment methods
Treatment for anthrax will only work if you start therapy as early as possible. It is imperative that the patient is prescribed antibiotics for intravenous and oral administration.
The most commonly used drugs are Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin and Doxycycline. Doctors may prescribe other antibiotics, such as penicillin antibiotics. If a person does not have systemic signs and the edema is not very pronounced, then the treatment takes up to 10 days.
Therapy may also include colloidal and crystalloid solutions, albumin, plasma, and glucocorticosteroids.
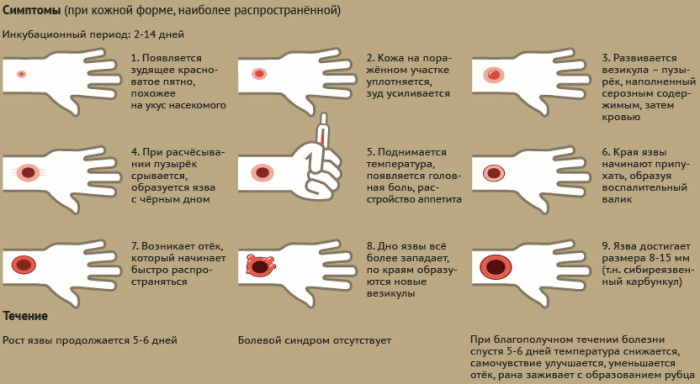
Tularemia
This is a natural focal infection that occurs with a syndrome of fever, specific lymphadenitis and polymorphic manifestations. The disease primarily affects the skin and the lymphatic system. In rare cases, the ailment affects the mucous membranes of the eyes, pharynx and lungs.
Views
Depending on the infection, several types of the disease are distinguished:
- bubonic;
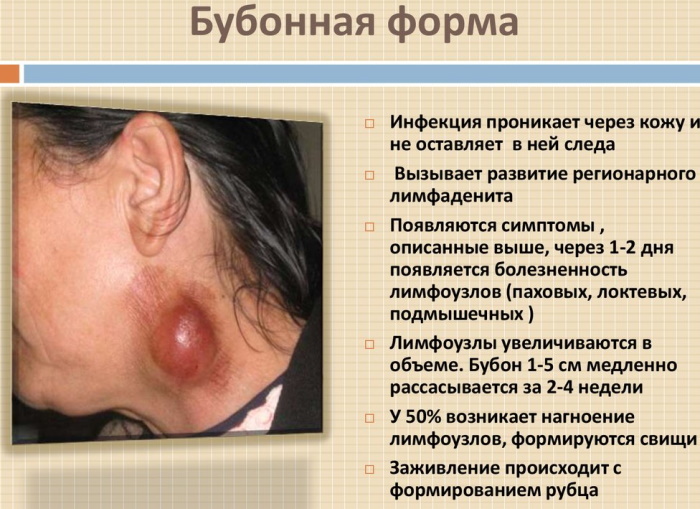
- ulcerative bubonic;
- ocular;
- angina-bubonic;
- pulmonary;
- abdominal;
- generalized.
Symptoms and Signs
The incubation period can last from 7 to 20 days.
The disease at its initial stage manifests itself in the form of:
- fever;
- discomfort in the head area;
- asthenia;
- muscle pain;
- loss of appetite.
Fever is associated with actively developing inflammation, and fever is the body's response to the coccal microflora.
Causes
Tularemia appears in the human body after the introduction of the coccal flora.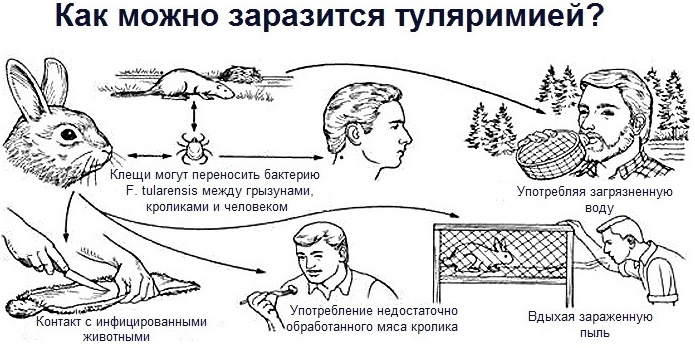
Animals are the source of infection:
- water rats;
- field mice;
- jerboas;
- hares.
The infection enters the body through damage to the skin or mucous membranes.
Treatment methods
Initially, a patient with tularemia is given detoxification therapy. It is used to quickly remove toxins and pathogenic microflora from the body. For these purposes, colloidal solutions are used, to which vitamins from group B are added, as well as sorbents. For the purpose of detoxification, the following solutions are used: Reamberin, Polyvedon, Pyridoxine, Venofundin.
Forced diuresis is also carried out - this is stimulation of urinary excretion, provoked by an artificial means.
To kill the pathogenic flora, antibiotics are used, and more often these are drugs belonging to the aminoglycoside group or from the tetracycline series.
Natural focal ailments are serious diseases, many of which, without timely comprehensive treatment, can threaten a person with death.
If the first unpleasant symptoms appear, then it is better to seek the advice of a specialist, only a timely diagnosis will help to heal and not get complications. For many ailments, there is a special serum that is used as a vaccination. Vaccinated means protected.
Video about natural focal diseases
Expert opinion. Natural focal diseases: