Herpes stomatitis is infectious disease of the oral mucosa cavities and surfaces of the gums, the causative agent of which is the herpes simplex virus. This ailment most often occurs in children from 1 to 3 years old, as well as in adults aged 20 to 35 years.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis involves strengthening general and local immunity, saturating the body with additional vitamins and minerals, and improving the quality of nutrition. Drug therapy for this disease is based on the intake of antiviral drugs, the constituent components of which suppress the cell division of pathogenic microorganisms.
Herpes stomatitis is considered a chronic recurrent disease, the symptoms of which appear immediately after the weakening of the protective functions of the human immune system. The herpes simplex virus, which has penetrated the tissues of the infected mouth, is difficult to respond to all methods of treatment.
Pathogenic microorganisms of this type are capable of being in a latent state for a long time without showing any signs of their presence.
After the patient's body is exposed to prolonged hypothermia, infection with other infections, the person is ill eats or rests little, the hidden herpes virions are activated with the appearance of pronounced signs stomatitis. In adults, this type of disease is considered quite common.
Record content:
-
1 Views
- 1.1 Chronic
- 1.2 Spicy
-
2 Stages
- 2.1 Prodromal
- 2.2 Catarrhal
- 2.3 Rashes
- 2.4 Fading away
- 3 Symptoms and Signs
- 4 Causes
-
5 Diagnostics
- 5.1 Initial inspection
- 5.2 Microbiological examination
- 5.3 General analysis of blood and urine
-
6 Treatment methods
- 6.1 Acyclovir
- 6.2 Zovirax
- 6.3 Metrogyl Denta
- 6.4 Alphabet Classic
- 7 Possible consequences and complications
- 8 Herpes stomatitis video
Views
Herpes stomatitis is divided into 2 main types that can be detected during the diagnostic examination of the patient.
Chronic
Chronic herpetic stomatitis is characterized by a latent form of the course. In this case, a person is a carrier of the herpes simplex virus, but at the same time, symptoms of the disease are very rarely found in him. The manifestation of signs of this type of disease occurs in the off-season, as well as during a period of weakened immunity.
During an exacerbation of the disease, an infected person is highly contagious, and his saliva contains millions of herpes virions. After the onset of the extinction stage, the patient's symptoms of a viral lesion of the oral mucosa completely disappear. Moreover, such a person remains a source of infectious microorganisms.
Spicy
Acute herpes stomatitis is a very contagious disease characterized by a rich clinical picture of multiple lesions of the oral mucosa and gum tissue. This type of disease is characterized by dynamic development and extensive inflammatory process.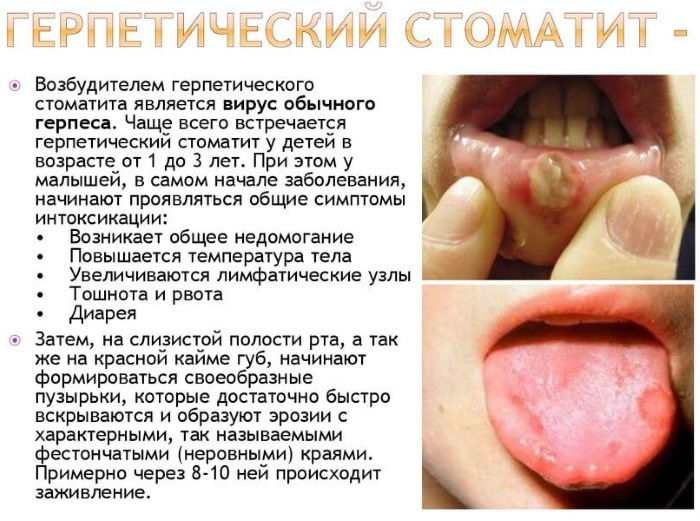
To determine the presence of this disease, it is enough for a dentist to examine the patient's mouth. A microbiological study of the composition of the patient's saliva only confirms the presence of an excess amount of herpes simplex virions.
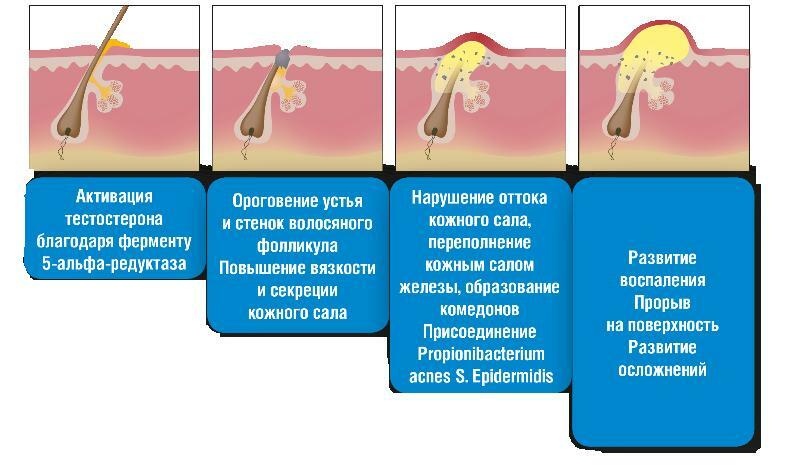
Stages
Herpes stomatitis (treatment in adults includes taking antiviral drugs) is a viral disease, in the pathogenesis of which there are 4 main stages of its development.
Prodromal
The prodromal stage of herpes stomatitis includes the period when the infectious agent of this disease enters the surface of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, and also penetrates the cellular structure of the infected fabrics.
A sick person becomes a carrier of the herpes simplex virus, but at the same time is not yet a distributor of this disease. At this stage of the development of the disease, pathological symptoms are completely absent, and the infected person himself is unaware of infection.
Catarrhal
The catarrhal stage of herpes stomatitis occurs immediately after the end of the incubation the period of development of virions, and favorable conditions will be created for disease-causing activity virus. In this case, the patient shows the first signs of local inflammation of certain areas of the oral mucosa or gum tissue.
Most often, the disease begins to manifest itself in the area of primary penetration of a viral infection, which occurred at the time of infection. The appearance of the catarrhal stage of herpetic stomatitis indicates a weakening of the protective functions of the patient's immune system.
Rashes
This period of development of herpetic stomatitis is characterized by an acute and intense clinical picture. On the surface of the mucous membrane of the patient's oral cavity, a multiple rash of a viral origin is found, which resembles small blisters. Inside these vesicles, ichor accumulates, mixed with lymphatic fluid.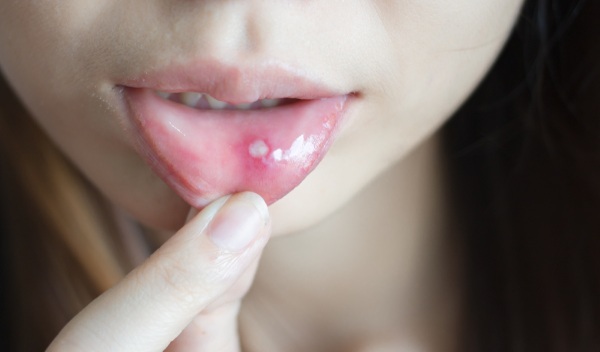
As they mature, these blisters burst, and millions of pathogenic microorganisms enter the human saliva. The stage of the rash of herpes stomatitis is characterized by acute inflammation that can spread to the tissues of the tongue, larynx, and even lymph nodes.
Fading away
After the end of the period of ripening of the herpes rash, reaching the peak of the severity of the inflammatory process, the mechanisms of regeneration of damaged tissues are triggered. Clinical manifestations of the pathogenic activity of the herpes simplex virus gradually fade away, a stage of stable remission begins.
A patient who has survived the acute phase of herpetic stomatitis has a false impression that he has managed to completely recover from this disease. In fact, the infection becomes chronic or latent until the next weakening of the host's immune system.
The table below describes the main degrees of severity of herpetic stomatitis, which are detected by the results of a diagnostic examination of the patient.
| The severity of herpes stomatitis | Characteristics of the pathological process |
| Easy | The mild severity of herpetic stomatitis is characterized by a complete absence of signs of intoxication of the body. Examination of the patient's oral cavity reveals from 2 to 3 small bubbles filled with blood and lymphatic fluid. Areas of the mucous membrane with signs of ulcerative formations are quickly restored. |
| Medium | The moderate degree of herpetic stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of the first signs of general intoxication of the body caused by the pathogenic activity of the herpes virus. The mucous membrane of the patient's oral cavity has symptoms of acute inflammation with multiple rashes. |
| Heavy | Severe herpes stomatitis is accompanied by a large number of inflamed blisters that are common throughout the oral mucosa. The pathological process involves neighboring organs, in the tissues of which a certain number of herpes simplex virions also enter. According to the results of a diagnostic examination, the patient shows pronounced signs of severe intoxication of the body. |
Mild to moderate severity of herpetic stomatitis causes fewer complications and negative consequences. The lack of timely therapy leads to the transition of this disease to a severe form that requires long-term treatment.
Symptoms and Signs
Herpes stomatitis (treatment in adults includes the intake of vitamin-mineral complexes) is a disease, the signs of which can be detected only during the period of its next exacerbation.
This disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- general malaise and fatigue after performing minor physical exertion;
- an increase in body temperature, which is kept within the range of 37-37.5 degrees Celsius (most often this symptom the disease manifests itself in the evening, when there is a physiological decline in the protective functions of the immune systems);
- an increase in the tissues of the lymph nodes, which indicates the progression of the pathogenic activity of the herpes simplex virus;
- the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and gum tissue have signs of edema, are distinguished by a rich red color and are hyperemic;
- local foci of acute inflammation that form at the site of the future appearance of blisters;
- red rash, represented by single formations or multiple small acne;
- blisters filled with a mixture of blood and lymphatic fluid that form at the base of the rash (biotransformation of these formations occurs as the herpes virions, contained inside rash);
- ulceration of the oral mucosa and gum tissue, which appear after a violation of the integrity of the herpetic vesicles;
- headache and fever;
- bad breath due to the presence of a focus of chronic infection;
- painful sensations while eating or drinking.
The average duration of the manifestation of the above symptoms is 10-12 days from the moment the first signs of the acute phase of herpetic stomatitis appear. During this period of time, the passage of all stages of the development of this disease is observed.
In the absence of adequate therapy measures aimed at suppressing the pathogenic activity of the herpes simplex virus, the patient's body temperature may rise to 39-40 degrees. Moreover, this symptom is accompanied by extensive intoxication of the whole body, severe fever and severe edema of the tissues of the oral cavity and larynx.
Causes
Herpes stomatitis (treatment in adults provides for a general strengthening of the protective functions of the immune system) can develop only if the oral cavity of a healthy person is infected with viable virions of this virus.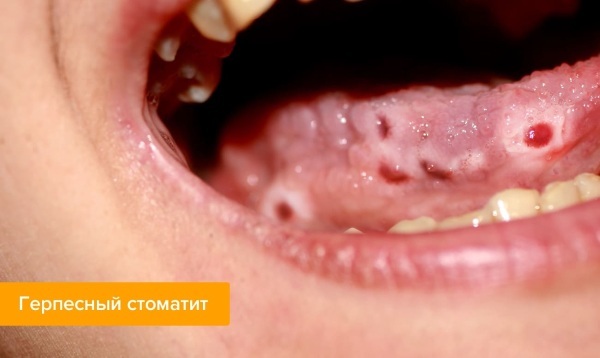
The following causal factors are distinguished, the influence of which leads to the onset of this disease:
- prolonged hypothermia of the body;
- congenital or acquired immunodeficiency;
- hematological diseases of the blood and hematopoietic system;
- the presence of malignant neoplasms in the patient's body, the pathogenic effect of which weakens the protective functions of the immune system;
- infection with concomitant bacterial, viral or fungal microorganisms;
- neglect of the rules of hygienic care of the oral mucosa and gum tissues;
- infection with the herpes simplex virus at the time of kissing with a carrier of this microorganism;
- using other people's toothbrushes that are the source of this disease;
- too poor or unbalanced diet, which leads to a weakening of the immune system;
- infection with the causative agent of herpes stomatitis in medical institutions, when a doctor or nursing staff work in violation of the rules of sterility.
Determination of the source of herpetic stomatitis is an important stage in the diagnostic examination of the patient. Establishing the reasons that influenced the onset of this disease allows you to localize the further spread of the viral infection.
Diagnostics
Patients with signs of damage to the oral mucosa and gum tissue undergo several stages of diagnostic examination.
Initial inspection
After the first symptoms of herpetic stomatitis develop, a person should seek medical help from a dentist. A specialist of this profile performs an initial examination of the condition of the oral mucosa and gum tissue.
The doctor palpates the lymph nodes, and also writes out a referral for testing. The average cost of an initial examination by a dentist is from 700 to 1500 rubles.
Microbiological examination
Microbiological examination of saliva and mucus present in the patient's oral cavity is considered the most informative diagnostic method. Isolation of herpes simplex virus virions is carried out using the PCR method.
Carrying out this type of diagnostics involves the implementation of the following algorithm of actions:
- The patient passes into the sterile conditions of the manipulation room, designed for sampling of biological material.
- The employee of the diagnostic institution performs the collection of mucus and saliva from the patient. Biological material is collected using smears.

- The patient's saliva and mucus samples are placed in sterile plastic containers that are sealed with airtight lids.
- The collected biological material is transferred to the laboratory department for microbiological examination using the PCR method.
This type of diagnosis involves the use of sophisticated medical equipment that detects the presence of DNA molecules of the simplest herpes virus. If fragments of this microorganism are present in the patient's saliva and mucus, then the test results will be positive. The average cost of this diagnostic method is from 3000 to 4500 thousand. rub.
General analysis of blood and urine
Conducting a clinical study of capillary blood, as well as morning urine, is a prerequisite for a comprehensive examination of a patient with signs of herpetic stomatitis.
These analyzes reflect the general state of health of the patient, the consequences of acute inflammation of the oral cavity and the degree of intoxication of the body. Capillary blood is donated from the ring finger bundle. On average, 1 ml of biological material is enough to conduct a qualitative study. Urine collection is carried out on an empty stomach in the morning from 07-00 to 10-00 h.
Treatment methods
Herpes stomatitis (treatment in adults includes the complex use of drugs of therapy) is a disease that requires regular use medicines.
In this case, agents of the local and general spectrum of action are used, which suppress the pathogenic activity of the virus.
Acyclovir
Acyclovir is an antiviral drug that is a synthetic analogue of the purine nucleoside, which has a detrimental effect on various genotypes of the herpes virus.
This medication is available in the form of white tablets. Acyclovir is prescribed for a course admission at a dosage of 200 mg up to 5 times a day, observing the time interval between taking each tablet of 4 hours. Duration of treatment is 5 days.
In the presence of severe symptoms of herpetic stomatitis, it is possible to extend the therapeutic course up to 10 days. The average cost of this medication is 31 rubles. for 20 tablets.
Zovirax
Zovirax is a tablet drug, the active ingredient of which is acyclovir at a dosage of 200 mg. This drug has a pronounced antiviral activity, suppressing the pathogenic manifestations of herpes, as well as reducing the severity of pathological symptoms. Adults should take Zovirax 1 tablet up to 5 times a day.
The duration of the therapeutic course is from 5 to 10 days, depending on the stage and severity of herpetic stomatitis. The average cost of this drug is 150 rubles. for 25 tablets.
Metrogyl Denta
Metrogyl Denta is a local drug with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. This drug is applied directly to the surface of a rash or ulcer that is caused by the herpes simplex virus.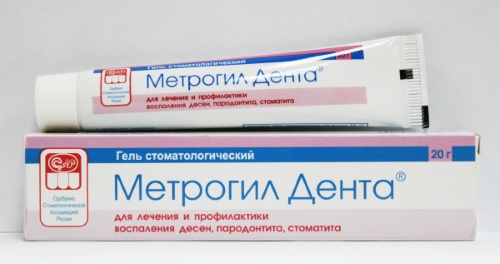
Metrogyl Denta accelerates tissue regeneration, eliminates signs of edema, and promotes faster healing of the gums. The medication is applied 2-3 times a day after oral hygiene. The duration of treatment with this drug is 10-12 days. The average cost of the drug Metrogyl Denta is within 235 rubles. per tube 20 g.
Alphabet Classic
Alphabet Classic is a drug that contains 13 vitamins and 10 vital minerals. In the complex therapy of herpetic stomatitis, this medication is used to strengthen the patient's immune system and increase the body's resistance to a viral infection.
Therapy with a vitamin and mineral complex involves taking 3 tablets of the Alphabet 1 time per day. In this case, in the morning, at lunchtime and in the evening, you need to drink 1 tablet of a different color, each of which contains a set of different vitamins and minerals. The average cost of this medication is 355 rubles. for 60 tablets.
Possible consequences and complications
Complications of herpes stomatitis occur in adults who have severe illnesses immune system, or do not properly treat inflammatory processes inside the oral cavity.
In this case, the following consequences may occur:
- acute inflammation of the gums;
- the appearance of a large number of non-healing ulcers;
- perforation of the cheek wall, caused by the progression of the inflammatory process, accompanied by a violation of tissue regeneration;
- gum recession with further exposure of the neck of the tooth and its root;
- spread of the infectious process to the tissues of the tongue, tonsils, larynx;
- infectious destruction of the tooth enamel surface with their further loss;
- the addition of a secondary bacterial infection that enters the ulcerative formations on the surface of the mucous membrane of the mouth and gums;
- a significant decrease in the quality of life associated with the constant presence of a feeling of pain, which intensifies at the time of eating and drinking.
Herpes stomatitis is an infectious disease of viral origin that affects the oral mucosa and gum tissue. This pathology is most often found in adult men and young women who lead an active lifestyle, are in contact with a large number of people.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis includes taking antiviral drugs, vitamin-mineral complexes and drugs that increase the resistance of the immune system. To prevent seasonal exacerbations of the disease, preventive therapy methods are used.
Herpes stomatitis video
About herpes stomatitis in children: