Mesenteric lymphadenopathy can be an independent disease in children or as a result of certain disorders. Pathology is an inflammatory reaction of the lymph nodes to infection, which are located in the abdomen.
It is important to visit a pediatrician in a timely manner, undergo a comprehensive examination and specially prescribed treatment. Otherwise, there is a high probability of serious complications, up to and including death.
Record content:
- 1 Location and function of the abdominal lymph nodes
- 2 Normal sizes in children
- 3 Causes of pediatric mesenteric lymphadenopathy in the intestine
- 4 Types of pathology
- 5 How is abdominal mesenteric disease manifested?
- 6 Differences from other gastrointestinal diseases
- 7 Risks and complications
- 8 Which doctor should I go to?
- 9 Diagnostics
-
10 Treatment methods
- 10.1 Drug therapy
- 10.2 Diet therapy
- 11 Folk remedies
- 12 Video about lymphadenopathy
Location and function of the abdominal lymph nodes
The main feature of mesenteric lymph nodes is their location. This is the abdominal cavity, so they cannot be felt. Abdominal lymph nodes provide lymph drainage from organs located in the abdomen.
With their inflammation, symptoms appear that are similar to the manifestations of intestinal disorders, infections. Therefore, it is important to go to the hospital in a timely manner.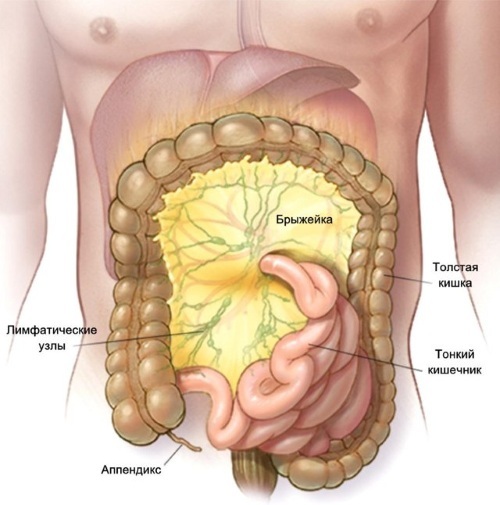
Abdominal lymph nodes are necessary for the human body to perform the following functions:
| Name | Description |
| Drainage | Lymph nodes drain excess fluid from tissues where dissolved crystalloids are present. |
| Transport | The function is to transport and absorb colloidal substances, proteins, fats. |
| Protective | Lymph nodes have immune cells, prevent the penetration of foreign substances into the human body. |
| Hematopoietic, immunocytopoietic | Functions that are responsible for the maturation of B-lymphocytes and the synthesis of plasma cells. |
| Immune | Ensuring the constancy of the cells of the genetic fund. |
Abdominal lymph nodes are located in the abdominal region, this is the lower abdomen, next to other internal organs. Their main function is to filter the intercellular fluid, remove toxins and infectious agents. They also support the normal functioning of the immune system.
Normal sizes in children
The inflammatory process that affects the abdominal lymph nodes is more often diagnosed in children aged 10 to 13 years. This is due to a poorly developed immune system. The exact number of lymph nodes in adults and children in the abdominal cavity cannot be determined, it all depends on the individual physiology of the human body.
According to medical research, this number ranges from 10 to 15. As for the established dimensions of the abdominal lymph nodes, they do not exceed 10 mm. It all depends on their location. The splenic nodes are small and in most cases do not exceed 5 mm.
Para-aortic lymph nodes reach 10 mm. In the abdominal cavity, the lymph nodes are small in size, within 3-7 mm. In children, the lymph nodes are constantly enlarged compared to the adult body. This phenomenon is due to the characteristic functioning of the immune system.
Causes of pediatric mesenteric lymphadenopathy in the intestine
Of all the provoking factors that cause mesenteric lymphadenopathy in children, the most common are the following diseases:
| Name | Description |
| Adenovirus, enterovirus | Pathogens contribute to the development of acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis and other diseases that affect the upper respiratory tract and nasopharynx. |
| E. coli, salmonella | Pathogenic microorganisms provoke acute intestinal infections. |
| Streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus | Pathogens provoke otitis media, tonsillitis, pharyngitis. |
| Yersinia | Pathogenic bacteria contribute to the development of intestinal pseudotuberculosis. |
| Epstein-Barr virus | The causative agent provokes the development of infectious mononucleosis. |
It is also necessary to mention the provoking factors against which lymph nodes in the abdominal region become inflamed:
- appendicitis;
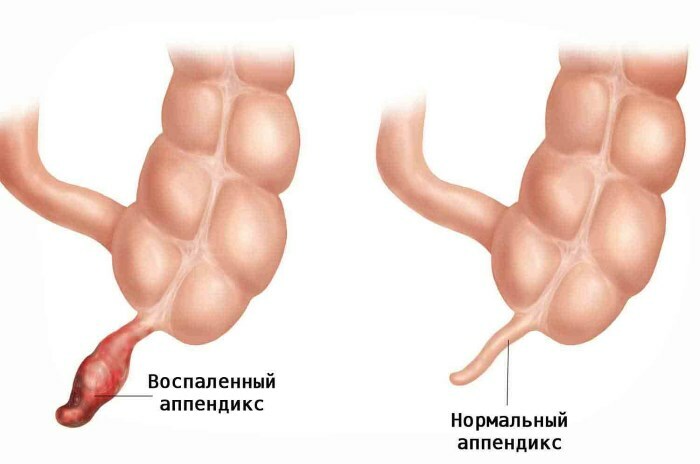
- food poisoning;
- tuberculosis of the lungs, joints, bones;
- hereditary predisposition;
- weak immune system;
- viral hepatitis;
- peptic ulcer;
- purulent processes and erosion in the intestinal region.
Mycobacterium pulmonary tuberculosis also causes mesenteric lymphadenopathy in children. The same goes for parasites, fungi and protozoa.
Types of pathology
In medicine, there is the following classification of mesenteric lymphadenopathy in children:
| Name | Description |
| Acute mesenteric adenitis | The disease is characterized by acute cramping painful sensations. |
| Chronic | The pathology proceeds sluggishly, exacerbations periodically appear, which are replaced by remission. |
Given the course of pathological processes, there is the following classification of the disease:
| Name | Description |
| Nonspecific chronic mesenteric adenitis | The causative agents of the disease are viruses, bacteria, E. coli. |
| Specific chronic | Yersinia, tuberculous, pseudotuberculous. Pathogens are also causative agents. |
A pediatrician will help to establish an accurate diagnosis in a child, taking into account the condition of the little patient and the results of the prescribed diagnosis.
How is abdominal mesenteric disease manifested?
Mesenteric lymphadenopathy in children is accompanied by characteristic symptoms that will allow the doctor to determine the form of mesenteric adenitis and the degree of its development.
Clinical signs of the disease appear depending on the course of pathological processes:
| Name | Symptoms |
| Acute mesenteric adenitis |
|
| Chronic |
|
Tuberculous mesenteric lymphadenitis in children is accompanied by low-grade fever and mild painful sensations. The child's body weight sharply decreases, he is capricious and does not eat well. In rare cases, a cough appears.
Differences from other gastrointestinal diseases
There are specific symptoms of mesenteric lymphadenopathy in children that may help to suspect problems with lymph nodes in the abdominal area:
| Name | Description |
| McFadden's symptom | The patient complains of severe pain syndrome on the left side of the abdominal cavity along the edge of the rectus muscle. The area below the navel is 2-4 cm. |
| Sternberg symptom | Strong painful sensations appear during the probing of the line from the lower right abdomen to the left hypochondrium. |
| Klein's symptom | The pain syndrome moves when the patient turns from the back to the left side. |
Laboratory diagnostics will help to confirm the previously established diagnosis. Taking into account the finished results, the pediatrician selects the most effective therapy regimen.
Risks and complications
Mesenteric lymphadenopathy in children is always accompanied by the risk of serious complications, especially if the child has not been provided with timely medical care.
Children's mesenteric adenitis provokes the following consequences: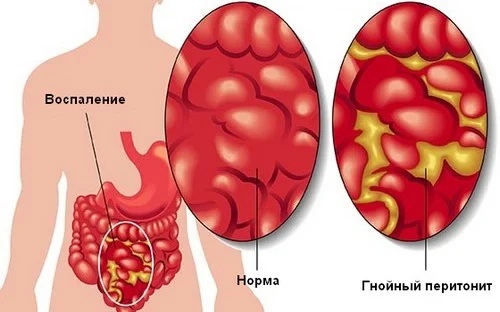
| Name | Description |
| Peritonitis | The pathological condition is characterized by an acute inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity. It is provoked by infection or foreign substances (bile, enzymes). The child is worried about severe abdominal pain, intestinal obstruction, nausea, vomiting appear. |
| Abscess | A purulent inflammatory process that melts the walls of the organ and cells, forming a cavity. The cause is chronic pathological processes. |
| Intestinal obstruction | The condition is characterized by a partial or complete violation of the movement of intestinal contents. The first clinical sign is severe pain in the abdominal region of a cramping character. |
A complication of mesenteric adenitis is also suppuration of the lymph nodes, sepsis, adhesive disease. There is a high probability of death against the background of progressive pathological processes.
Mesenteric infection can cause inflammation of other lymph nodes in the baby's body. Accompanying symptoms are skin rashes, a sharp decrease in body weight, high fever and increased sweating.
Which doctor should I go to?
The diagnosis and treatment of mesenteric lymphadenopathy is carried out by a pediatrician. Considering the results of a complete examination, you may need to consult other specialized specialists. It is important to immediately go to the hospital when the first clinical signs appear. Timely therapy will stop the progression of mesenteric adenitis and prevent possible complications in the child.
Diagnostics
A complete examination of the patient is necessary to establish the site of inflammation and to confirm the defeat of the lymph nodes in the abdominal cavity. It is also necessary to differentiate children's mesenteritis, since many pathologies occur with similar symptoms (appendicitis, enteritis, reactive pancreatitis, sclerosing mesenteritis).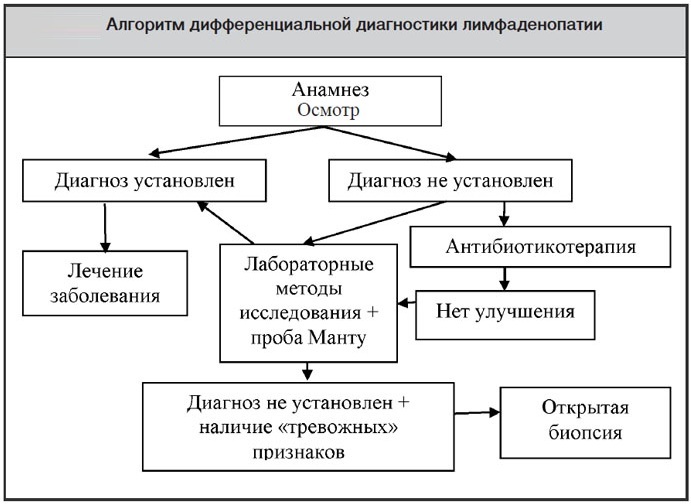
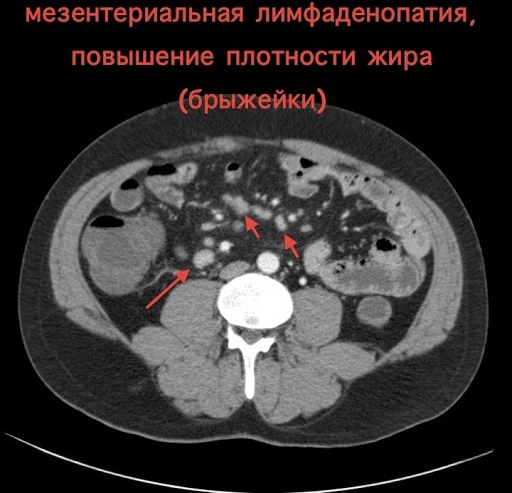
Mesenteric lymphadenopathy in children is diagnosed using the following methods:
| Name | Description |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) | The specialist examines the organs of the digestive system for the detection of pathological processes. Also assesses the condition of the abdominal lymph nodes. |
| General blood analysis | The results will show changes in blood composition. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | A method of examining the lymph nodes in the abdominal region, which allows you to establish the localization of the inflammatory focus and the area of its distribution. |
| Biochemical research | Diagnostics helps to determine the composition of the biological fluid. |
| Stool analysis | The study is prescribed to exclude or confirm parasitic infection of the child's body. |
| Laparoscopy | A minimally invasive method, with the help of which the doctor assesses the state of the internal organs visually. |
| Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, colonoscopy and abdominal x-ray | Examination methods by which the doctor assesses the condition of the internal organs. |
In addition, after a comprehensive diagnosis, the child may need to consult other specialized doctors (surgeon, phthisiatrician).
Treatment methods
Therapy of mesenteric lymphadenopathy in children is carried out using complex methods. It is important to undergo a complete examination in a timely manner and start therapy in order to prevent possible complications.
Patients are prescribed medications, a nutritionist makes a special menu. In the absence of serious contraindications, mesenteric lymphadenopathy can be treated with non-traditional means.
Drug therapy
Medicines are selected by a doctor, referring to the results of diagnostics. The specialist takes into account the condition of the child, the development of pathological processes and the individual characteristics of his body. It is important to strictly adhere to the dosages so as not to aggravate the health of the little patient.
For the treatment of mesenteric lymphadenopathy in a child, the following drugs are used:
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Antibacterial drugs | Ceftriaxone, Ofloxacin | Medicines act directly on the pathogenic flora. The antibiotic is administered intramuscularly or intravenously through a drip. The recommended dosage for children and adults is 1-2 g once a day. |
| Anti-inflammatory drugs | Diclofenac, Indomethacin | Medicines are used rectally. Adults are prescribed 1 suppository (50 mg) 1-3 times a day. Children are advised to use the indicated dosage (50 mg), but once a day. |
| Antispasmodics | Papaverine, Drotaverine | The drugs reduce spasms and pain. Medicines are taken orally 3-4 times a day. The pediatrician chooses the children's dosage, taking into account the age of the patient. Standard prescriptions include 5-20 mg. |
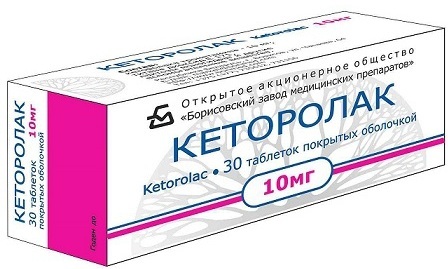
| Analgesics | Ketorolac, Analgin | For children, the medicine is injected. A single dosage depends on the patient's condition and is 10-30 mg every 4-6 hours. The duration of treatment is 5 days. |
| Sorbents | Enterosgel, Sorbeks | Medicines remove decay products from the child's body. The remedy should be taken orally before meals. Children's dosage is 2.5-15 mg 3-6 times a day. For newborns, the medicine can be diluted in breast milk. The course of treatment lasts from 3 days to 3 weeks, taking into account the patient's condition. |
| Enzymes | Pancreatin, Mezim | The medicine is selected for children by age. The standard dosage is 50,000-100,000 units per day. |
Additionally, vitamin therapy is carried out to strengthen the immune system and increase the resistance of the child's body. Detoxification treatment is also prescribed, infusion solutions (Interleukin-2, Roncoleukin) are injected intravenously.
Purulent mesenteric adenitis provides for surgical intervention in order to eliminate pathological processes and prevent possible complications, the affected lymph nodes are removed. After surgical treatment, the child is additionally prescribed drug therapy.
Diet therapy
Mesenteric lymphadenopathy in children is a disease that not only provokes the development of the inflammatory process, but also disrupts the digestive process. Therefore, a special menu is made for young patients in order to reduce the load on the organs of the digestive system.
| Featured Products | Prohibited foods |
|
|
It is also important to adhere to simple rules in order to achieve the most positive result from dietary nutrition:
- Take food in small portions 5-6 times a day.
- Food should be eaten at intervals of at least 3 hours.
- It is not recommended to give your child hot or cold food, all meals should be warm.
It is also important to grind the products or grind them well. It is better to bake or cook the dishes.
Folk remedies
Alternative methods of treatment can be used for mesenteric lymphadenopathy in children, but in combination with other medications. A consultation with your doctor will help prevent the occurrence of an allergic reaction or individual sensitivity.
Effective alternative methods for mesenteric lymphadenopathy:
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Gray blackberry | Grind the dry roots of the plant and pour 10 g with boiling water (500 ml). Put the resulting mixture in a water bath and heat for another 10-15 minutes. Insist the finished broth for 2 hours and strain. | The resulting medicine is recommended to be taken orally. Children in a warm form are prescribed 1 tbsp. every 2-3 hours. |
| Chamomile and calendula | Mix 1 tbsp. pharmacy chamomile and 1 tsp. calendula. Pour the components with boiling water (500 ml) and leave for 1 hour. Cool, strain and take orally. | The recommended dosage for a patient with mesenteric adenitis is 0.5 tbsp. 3 times a day. Chamomile with calendula reduces pain and inflammation. |
| Caraway | Plant seeds (1 tablespoon) pour hot water (0.5 l). Leave for 40-60 minutes and drain. The finished product should be taken orally. | A cumin-based decoction helps restore bowel function. |
| Marjoram | Pour 1 tbsp. dry herbs with boiling water (1 tbsp.). Put the resulting mass on medium heat and cook for 10 minutes. Soak for 3 hours, strain and take orally. | A decoction based on marjoram has an analgesic effect. The medicine is recommended to be consumed in 1 tbsp. every 2 hours. |
| Hazel | Grind the leaves and bark of the plant. Pour ¼ st. the resulting mass with hot water (0.5 l). Insist, strain and take orally. | A ready-made broth from hazel must be taken at ¼ st. 4 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 3 weeks. Then you need to take a break for 7 days and continue therapy. |
You can maintain your drinking regime with chamomile tea with the addition of natural honey or sugar in a small amount. The drink relieves pain well and eliminates many clinical symptoms of mesenteric lymphadenopathy in children. We must not forget about possible complications. Therefore, all the means used should be discussed with the attending physician.
When the first clinical signs of mesenteric lymphadenopathy appear in a child, it is important to immediately show it to the pediatrician. Early comprehensive diagnostics and correctly selected therapy will help prevent complications and eliminate the inflammatory process. Without treatment, the child's condition will worsen when the consequences cannot be avoided.
Video about lymphadenopathy
Lecture on lymphadenopathy:



