Content
- Indications for research
- Preparation for analysis
- Analysis
- Indicators are normal
- Decoding the results
- Rheumatoid factor
- Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- C-reactive protein (CRP, CRP)
- Antinuclear antibodies (ANA)
- Where can you do
- Video about rheumatic factor
Blood test for rheumatic factor determines the amount of proteins called rheumatoid factors. Rheumatoid factors are immunoglobulins that are produced by the immune system. In a healthy body, the immune system attacks viruses and bacteria.
Rheumatoid factors are antibodies that react with antigens of their own body, that is, autoantibodies. The cause of the formation of autoantibodies can be transferred diseases, but sometimes they are formed spontaneously. Autoantibodies are produced in autoimmune diseases. Rheumatoid factors can attack healthy cells in joints, glands, and other organs.
These proteins get their name because they were first identified in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, but they are found in patients with other diseases, as well as in healthy people.
High levels of rheumatoid factor can be one of the signs of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and Sjogren's syndrome (dry mucous membranes). Also, rheumatoid factor can be determined in healthy people, especially in the elderly, and patients with autologous diseases may have a normal level of rheumatoid factor.
Rheumatoid factors can be represented by different immunoglobulins: class A (IgA), class G (IgG), class M (IgM). Most of the existing tests detect IgM antibodies. Rheumatoid factor IgA is more associated with joint destruction. A positive value of rheumatoid factors can be evidence of a more aggressive and destructive course of rheumatoid arthritis.
A change in the concentration of IgA antibodies indicates the activity of the disease, the concentration of IgG antibodies indicates a change in the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation. High concentrations of IgM antibodies are often associated with syndromes not associated with joint disease, such as vascular inflammation.
Indications for research
A rheumatic factor (a blood test is one of the studies that a rheumatologist prescribes if an autoimmune disease) indicates rheumatoid arthritis and helps distinguish it from other diseases with similar symptoms. Another diagnosis that can be made with this test is Sjogren's syndrome.
As a rule, an analysis is prescribed if symptoms such as appear:
- joint pain;
- joint swelling and thickening under the skin;
- burning sensation in the joints, difficulty in movement.
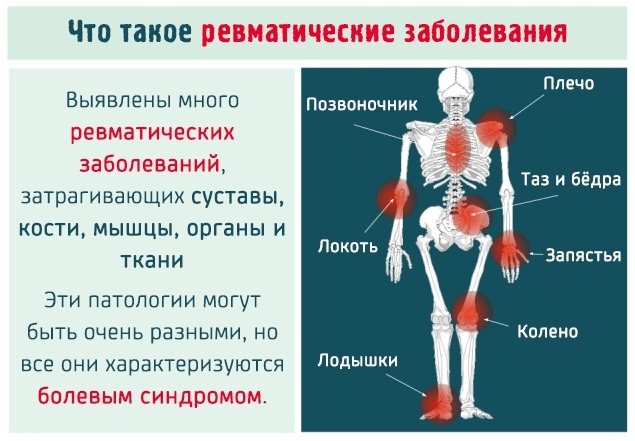
An increased level of rheumatoid factor can be a sign of diseases such as:
- oncological diseases;
- chronic infections;
- connective tissue diseases;
- Sjogren's syndrome;
- systemic erythematous lupus.
However, the presence of these immunoglobulins alone is insufficient for a diagnosis. If the level of rheumatic factors in the blood is low and is interpreted as negative, this is not an indication for canceling the diagnosis. In 20% of cases, rheumatoid arthritis occurs without an increase in the level of rheumatoid factors (seronegative form). The seronegative form of the disease is milder.
Preparation for analysis
- Serum samples are recommended for analysis. Blood plasma can be used. Lithium heparin or sodium heparin can be used as anticoagulants, but not EDTA.
- Blood for rheumatic factor is taken on an empty stomach in the morning or in the afternoon 5-6 hours after the last meal. When studying the dynamics of indicators, it is recommended to take tests in the morning, since blood counts can change during the day.
- During the day before donating blood, it is necessary to exclude the intake of alcoholic beverages, reduce physical activity, not take medications that may affect the results of the study (consultation of the attending doctor).

- It is not recommended to donate blood after medical procedures: X-ray, fluorography, physiotherapy.
- It is not recommended to smoke for an hour before donating blood.
- When studying the dynamics of changes in blood parameters, as well as evaluating the effect of therapy, it is recommended to take tests in the same laboratory.
Analysis
A medical professional in a laboratory takes a blood sample from a vein in his arm.
This procedure only takes a few minutes:
- before taking blood, the skin over the vein is treated with an alcohol solution;
- a tourniquet is tied around the arm to ensure rapid filling with blood;
- a needle is inserted into the vein;
- a tube attached to a needle quickly fills with blood;
- the puncture site is sealed with a plaster;
- the sample is sent to the laboratory, where the laboratory assistant determines the level of rheumatoid factor by enzyme immunoassay.
When analyzing for rheumatic factor, antibodies (most often class M immunoglobulins) are determined, which interact as antigens with class G immunoglobulins in the body. These antibodies are synthesized in the tissues of the joints, then enter the bloodstream. By reacting with the body's own immune proteins, these altered antibodies damage blood vessels and joints.
Most often, class M immunoglobulins are defined as a rheumatic factor, but about 15% of patients with arthritis have rheumatoid factor - class G immunoglobulins.
Indicators are normal
Normal values of rheumatic factors differ for patients of different ages, but do not depend on gender:
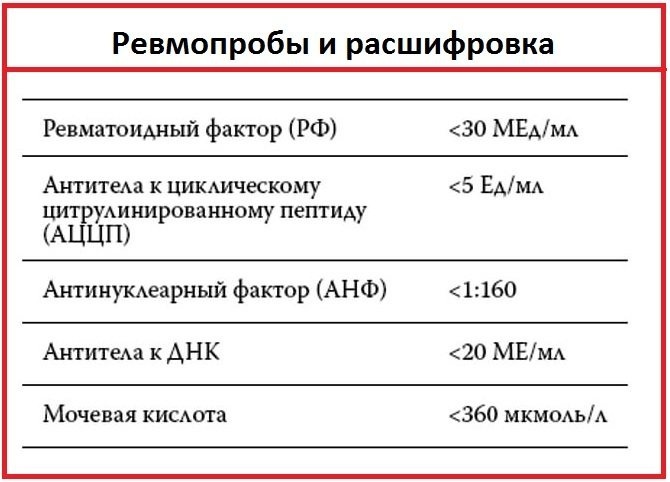
| Age group | The norm of indicators of rheumatoid factors, IU / ml |
| Children and adolescents | Up to 12.5 |
| Adults, under 50 | Up to 14 (according to some sources up to 20) |
| Seniors, over 50 years old | To 10 |
Decoding the results
A rheumatic factor (blood test is only one of a whole list of tests that are prescribed for the accurate diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis) can also be detected in hepatitis. To increase the accuracy of the diagnosis and classification of rheumatoid arthritis, additional tests are prescribed - antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide (ACCP).
This indicator is manifested in 30% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have a negative result in the analysis of rheumatoid factors, therefore it is recommended for early diagnosis of the disease.
Other indicators that are recommended to be investigated in the detection of rheumatoid arthritis are anti-keratin antibodies, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein.
Rheumatoid factor
The norm is considered to be a result of 0-20 IU / ml (international units per milliliter of blood).
Rheumatoid factor concentrations of 20 IU / ml or more are elevated.
If antibodies of classes G, A and M are analyzed in the sample, then the results are compared with the following control values:
- Rheumatoid factor IgG level:
- less than 20 IU / ml - negative result;
- 20-25 IU / ml - questionable result;
- more than 25 IU / ml - a positive result.
- Rheumatoid factor IgA level:
- less than 20 IU / ml - negative result;
- 20-25 IU / ml - questionable result;
- more than 25 IU / ml - a positive result.
- Rheumatoid factor IgM level:
- less than 10 IU / ml - negative result;
- 10-12.5 IU / ml - a dubious result;
- more than 12.5 IU / ml - a positive result.
 Elevated levels of all three types of antibodies - class G, A and M with a probability of 99% are a sign of rheumatoid arthritis. Only elevated antibodies of class A can be the result of the development of Schönlein-Henoch disease. Any other combination of antibodies can appear with hepatitis C or other chronic diseases. If questionable results are obtained, retesting is required.
Elevated levels of all three types of antibodies - class G, A and M with a probability of 99% are a sign of rheumatoid arthritis. Only elevated antibodies of class A can be the result of the development of Schönlein-Henoch disease. Any other combination of antibodies can appear with hepatitis C or other chronic diseases. If questionable results are obtained, retesting is required.
70% to 90% of people with high levels of rheumatoid factors in their blood have rheumatoid arthritis. However, patients who do not have rheumatoid arthritis may have elevated levels of rheumatoid factor.
It is also believed that the absence of high concentrations of rheumatoid factor in the presence of rheumatoid arthritis is an indicator of a milder course of the disease. In remission, levels of rheumatoid factors can be high.
Also, high concentrations of rheumatoid factors can be a consequence of other diseases, such as:
- prolonged infection;
- bacterial endocarditis;
- crayfish;
- diabetes;
- lupus;
- dermatomyositis;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- leukemia;
- scleroderma;
- Sjogren's syndrome;
- inflammatory lung diseases such as sarcoidosis;
- mixed connective tissue disease.
A rheumatic factor (a blood test is a study that is necessary in identifying most diseases) can sometimes be positive in healthy people, especially in old age. Thus, studies were carried out, where it was shown that in healthy blood donors at the age of 30-59 years, 4% of donors had a positive rheumatoid blood factor, and at the age of 60-89 years - 30%.
Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies
This test is often performed in addition to a blood test for rheumatic factor. The test shows the concentration of proteins that are produced during inflammation. A result of up to 20 IU / ml is considered the norm.
An increased protein content - more than 20 IU / ml is found in people with rheumatoid arthritis, as well as in the early stages of this disease. The high content of ACCP indicates that with a 97% probability the patient has a disease - rheumatoid arthritis.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
The analysis shows at what speed the erythrocytes stick together and settle to the bottom of the test tube within an hour.
Normally, in men under 50 years of age, ESR is less than 15 mm / h (millimeters per hour), in men over 50 - less than 20 mm / h. In women under 50 years old - less than 20 mm / h, in women over 50 years old, this value is in the range from 0 to 30 mm / h.
Normally, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is low. With any inflammatory reaction, the cells become heavier and the rate of their sedimentation decreases. The ESR value does not indicate a specific disease, it is a sign of inflammation and can show how actively present diseases, especially in the case of syndromes such as:
- polymyalgia rheumatica;
- systemic vasculitis;
- temporal arteritis.
C-reactive protein (CRP, CRP)
A complete examination for rheumatoid arthritis is not limited to the analysis of rheumatoid factors. The CRP test reflects the degree of inflammation. The analysis determines the concentration of a protein that the liver produces during inflammation. The level is considered to be the norm - less than 10 mg / l.
CRP levels often rise before symptoms appear, so this test helps doctors detect disease early. An increased content of this protein is a sign of inflammation, necrosis, and tissue damage. Protein concentration quickly returns to normal (within 6-10 days) in response to appropriate therapy. Therefore, this analysis is used to determine the effectiveness of treatment.
The increased protein content can be a consequence of autoimmune diseases, acute heart diseases, infections.
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA)
This is a group of tests that measure the concentration of autoimmune antibodies to nucleic acids and to certain proteins associated with these nucleic acids.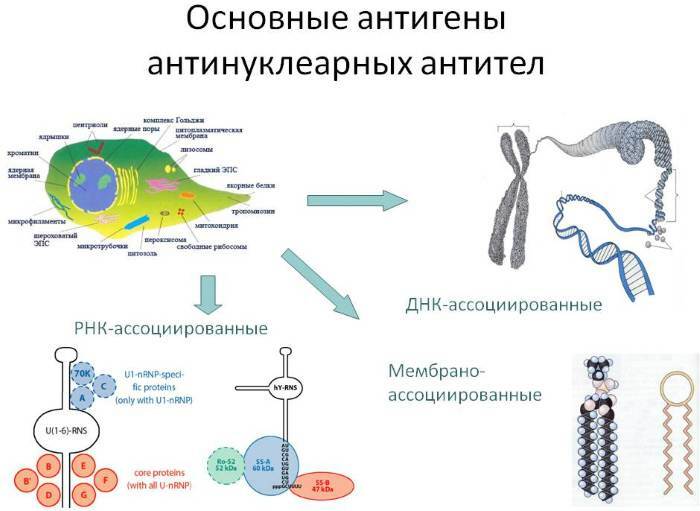
If the result is positive, then in 90% of cases, the patient may have some kind of connective tissue disease. A positive test is also manifested in infectious, oncological diseases or inflammations.
Where can you do
You can take the analysis for a fee in medical laboratories or in paid clinics:
| Laboratory | Analysis | Analysis cost, rub. |
| KDL | Rheumatoid factor | 300 |
| Hemotest | Rheumatoid factor | 540 |
| Ab rheumatoid factor IgA | 1190 | |
| Invitro | Rheumatoid factor | 560 |
| Rheumatoid factor, IgA | 1070 | |
| Citylab | Rheumatoid factor | 520 |
You can make a blood test for rheumatic factor for free in a polyclinic, having a compulsory medical insurance policy. To do this, you need to register at any clinic: fill out an application addressed to the head physician, indicating passport data, OMS policy, SNILS. Then you need to come to an appointment with a rheumatologist and get a referral for research.
You can preliminarily clarify with the insurance company that issued the compulsory medical insurance policy, whether this analysis is paid for under a medical policy. An appointment with a rheumatologist, as well as a study of rheumatoid factors in the blood, are included in the list of medical services that are provided for primary care for suspected diseases such as polyarthritis and other lesions connective tissue.
Video about rheumatic factor
About rheumatoid factor:
