Content
- Composition and function of saliva
- What should be the normal saliva?
- Causes of thick saliva
- In adults
- In pregnant women
- In children
- The appearance of thick saliva and dryness in sleep
- For what diseases does the character of saliva change?
- How to relieve the condition when saliva is viscous and viscous?
- Which doctor should I go to?
- Pharmacy treatment
- Folk remedies
- Video about thick saliva in your mouth
Normally, the secretion produced by the salivary glands should be watery. Its volume should be sufficient for normal chewing and swallowing of food. If saliva becomes thicker and dry mouth occurs, you should consult a doctor to determine the cause of the change in the nature of the secret. Factors in the development of such a condition may be the presence of a disease in the body. In this case, not only symptomatic therapy will be required, but also the elimination of the root cause.
Composition and function of saliva
Human saliva refers to mucus that is produced by the salivary glands.
It has several functions:
- digestive;
- bactericidal;
- protective;
- mineralizing;
- hormonal.

Saliva is 98% water, the remaining 2% are organic and inorganic compounds. However, the consistency and composition of the secret can change during the day, which depends on the individual characteristics of the organism, as well as on food consumption, state of wakefulness or sleep.
What should be the normal saliva?
The saliva of a healthy person is a transparent, colorless and odorless secret. The daily rate of mucus produced by the salivary glands varies from 1 to 2 liters. The main task of saliva is to "wet" the oral cavity.
In this case, a person should be comfortable when chewing food, swallowing and talking. The composition of the mucus in question includes enzyme compounds, so the process of digesting food begins already in the mouth. Also, the secret has antiseptic properties that contribute to the disinfection of consumed products.
Causes of thick saliva
Thick saliva in the mouth, the causes of which are varied, most often occurs due to the appearance of disorders not only in the oral cavity, but in the body as a whole. Also, the occurrence of this symptom can be affected by dehydration, taking medications, eating too sweet, salty or fatty foods.
In adults
The main factors provoking the appearance of a viscous secretion of the salivary glands include:
- excessive consumption of drinks containing caffeine or alcohol;
- the presence of diabetes mellitus;
- dehydration;
- hypertension;
- xerostomia (pathological dryness in the mouth);
- the use of drugs (antidepressants, hormonal, antihistamines);
- smoking;
- autoimmune diseases;
- acute infectious processes.
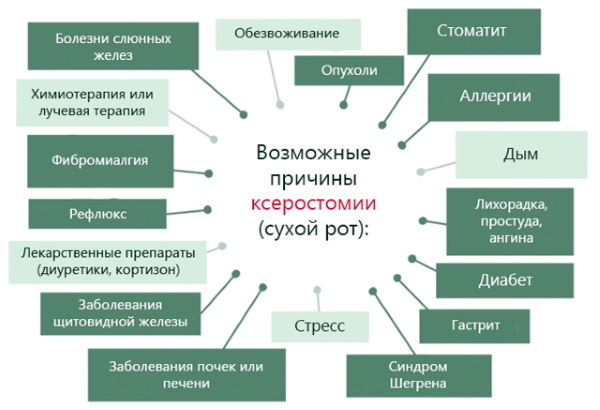
Also, saliva can become thick due to the development of pathologies of the salivary glands, for example, sialostasis, mumps, sialoadenitis, Mikulich's disease.
In pregnant women
In women, during gestation, the secret can become overly viscous as a result of:
- toxicosis;
- frequent bouts of heartburn;
- changes in the acid-base balance in the stomach;
- abuse of highly salty food (because of this, there is an increase in the need for fluid).
Most often, the symptomatology under consideration manifests itself as a result of a restructuring of the hormonal background. The increased production of estrogen affects the secretion of salivary fluid and the epithelium of the oral cavity.
In children
Thick saliva in the mouth (the causes of which may differ in children and adults), most often accompanied by a desiccation of the mucous membrane.
In a child, a similar phenomenon can occur as a result of:
- the development of diseases of the oral cavity, for example, stomatitis, candidiasis, cheilitis;

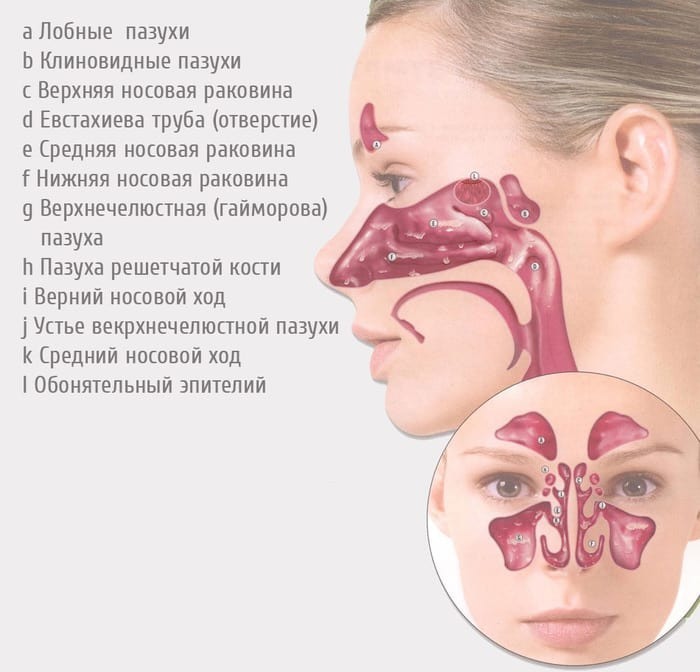
- difficulty in nasal breathing due to a runny nose, sinusitis, sinusitis;
- increased body temperature with an infectious disease or acute respiratory viral infection, which contributes to the appearance of dehydration.
Also, a change in the consistency of the secret can occur due to the development of pathologies of the oral cavity or upper respiratory tract.
The appearance of thick saliva and dryness in sleep
Thick saliva in the mouth, the pathological causes of which are presented below, can be accompanied by desiccation of the mucous membrane at night, which is due to:
- difficulty breathing through the nose (due to the development of respiratory pathologies);
- dehydration, which can occur due to the consumption of excessive amounts of salty or spicy foods;
- breathing through the mouth (while snoring).
It can also happen due to too dry air in the house.
For what diseases does the character of saliva change?
Thick saliva in the mouth, the causes of which may be associated with the development of certain diseases, may have additional symptoms:
| Pathology name | Characteristic |
| Diabetes | Hyperglycemic conditions often provoke a change in the consistency of saliva and a dry mouth. |
| Fungal candidiasis | An infectious process that occurs due to a weakened immune system, most often occurs as a result of prolonged use of antibiotic and corticosteroid drugs. Candidiasis can be a signal of the development of diabetes mellitus, AIDS, tuberculosis. This phenomenon provokes a decrease in saliva production and a change in its consistency. In this case, the appearance of not only dryness and whitish plaques in the oral cavity is possible, but also burning / itching of the tongue, a taste of metal. |
| Sinusitis | In chronic disease, the paranasal sinuses are affected. Sinusitis is characterized by the appearance of thick mucus with an unpleasant odor in the nasal cavity, swelling and thickening of saliva. Headache is possible, in some cases it is complicated by fever. |
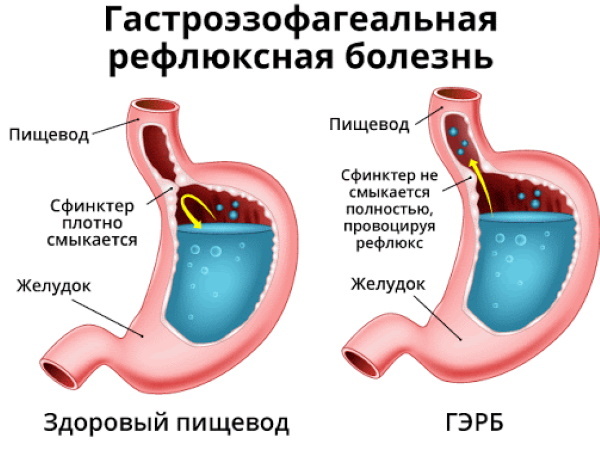
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) | With GERD, the lining of the lower esophagus becomes inflamed. Pathology is accompanied by frequent throwing of stomach contents into the area under consideration, which provokes the development of heartburn. To neutralize the negative effects of digestive juice on the esophagus, an additional amount of salivary gland secretion is produced, which becomes viscous. |
| Periodontitis and periodontal disease | Inflammation of the gums leads to the destruction of epithelial tissues, particles of which enter the salivary fluid and change its consistency and color. As a result, the amount of saliva produced decreases, it becomes viscous and becomes whitish. |
| Gastroenteritis | The inflammatory process of a bacterial or infectious nature of an acute form, occurring in the stomach and small intestine, is manifested by loose stools, frequent bouts of vomiting. As a result, dehydration occurs, which, in turn, causes a decrease in the production of salivary secretion and a change in its consistency. |
| Acute infectious diseases (for example, salmonellosis, cholera, hepatitis, dysentery, typhoid fever). | Acute infections, accompanied by increased temperature, vomiting, loose stools, often lead to a state of dehydration. Water imbalance can negatively affect the production of mucus by the salivary glands. |
| Xerostomia | This pathology means damage to the salivary glands, which is complicated by pronounced drying out of the oral cavity. In this case, the secret becomes viscous, a burning sensation appears, the tongue becomes denser, and a violation of the receptors occurs. In some cases, painful sensations and a sore throat may occur. |
| Endocrine Disorders | Hormonal imbalances most often occur during pregnancy, menopause, and puberty. This phenomenon can also be a factor in the development of thick saliva and dry mouth. |
| Pharyngitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis | Infectious conditions cause damage to the tonsils. In this case, small neoplasms with purulent contents appear, the rupture of which creates uncomfortable sensations in the oral cavity. Inflammation is characterized by an increase in body temperature, which provokes a lack of water in the body and negatively affects the activity of the salivary glands. |
| Sialoadenitis, Sjogren's disease, sialolithiasis, Mishulin's disease | These pathologies are characterized by damage to the parenchyma and ducts of the salivary glands. This condition is accompanied by a decrease in the amount of secretion produced and a change in its consistency. As a result, the mouth becomes dry and the saliva becomes viscous. |
| Autoimmune diseases | Such pathologies are characterized by a severe course. In this case, the defeat of the glands of external secretion (including salivary glands) occurs. |
In the event of a change in the consistency of saliva against the background of the development of pathological conditions, not only dry mouth may occur, decreased secretion production, but also impaired taste perception, burning / itching of the mucous membrane, thickening of the tongue, sore throat, cracks on lips.
How to relieve the condition when saliva is viscous and viscous?
Thick saliva in the mouth, the reasons for which are described above, can be accompanied by uncomfortable sensations, while the process of chewing food and swallowing is disrupted. In this case, you need to take measures to get rid of this condition, which are aimed at moisturizing the mucous membrane.
To do this, you should:
- follow the drinking regime;
- rinse the mouth with a water-saline solution;
- using unsweetened hard candies and gum to increase saliva production;
- use artificial saliva in the form of medications;
- irrigate the oral cavity with a special moisturizing spray.
You should also give up tobacco, alcohol / caffeine drinks, and use a humidifier. Dairy products can cause dehydration in the body, so the use of this food should also be limited. During this period, it is best to brush your teeth with a soft-bristled brush to avoid injury to the gums.
Which doctor should I go to?
If the nature of the fluid of the salivary glands changes, in which there is frequent thirst, dryness, burning sensation and redness of the mouth, you should consult your dentist. He should study the patient's medical history and examine the lymph nodes, oral mucosa, and the thyroid gland. After that, the doctor will send you for blood tests (general and biochemical) to identify a possible infectious process in the body.
In some cases, it is possible to conduct pharyngoscopy and laryngoscopy (visual examination of the pharynx and larynx) to exclude damage to the upper respiratory tract. Also, the specialist may refer the patient for x-rays of the sinuses, sialography and / or ultrasound examination of the salivary glands.
If the appearance of thick saliva is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, pain in the throat, runny nose, cough, vomiting, then you need to make an appointment with a therapist, who, in turn, will determine the primary source of the onset of painful symptoms.

In this case, FGDS, ultrasound and X-ray examination of some organs may be required. If necessary, the doctor can refer the patient to narrowly qualified specialists, for example, an otolaryngologist, immunologist, neurologist.
Pharmacy treatment
Most often, when saliva viscosity appears, complex therapy is required, the action of which is aimed at increasing the amount of secretion produced, its liquefaction and elimination of the main cause of the unpleasant states.
To eliminate the main symptom, the doctor may prescribe:
- mucolytic agents;
- reflex drugs;
- resorptive drugs;
- artificial saliva substitutes.
When the nature of the secretion and dry mouth changes, you should regularly massage the gums, rinse the oral cavity with a soda-salt or herbal solution, and clean the tongue from plaque. For cleaning your teeth, it is recommended to use pastes based on astringent medicinal plants.
It is also allowed to use moisturizing sprays, steam inhalation and breathing exercises. If the phenomenon in question arose as a result of the development of any disease, then you must first eliminate the root cause. In some cases, surgery may be required.
Folk remedies
For the treatment of conditions that provoke a change in the nature of saliva, you can resort to alternative medicine. This therapeutic method should only be used after consulting a therapist. Recipes for folk remedies, the action of which is aimed at activating the production of a secret and its dilution.
Coniferous broth:
- To prepare the medicine, you need to grind dry bark and pine needles in a coffee grinder (in equal proportions).

- Then 1 tbsp. l. the resulting mass should be placed in a saucepan, pour ½ liter of hot boiled water and put on the included stove.
- After boiling, it is recommended to cook the mixture for 5 - 7 minutes. over low heat.
- Next, the broth must be left for 1 hour for infusion, and then filtered. The finished product should be taken in 2 tbsp. l. twice a day.
Peach oil mixture with propolis tincture:
- To make a medicine, you need to thoroughly mix the main components in a 2: 1 ratio.
- The resulting mass is recommended to coat the oral mucosa 2 times a day.
Sage tea:
- To prepare a drink, you need 2 tbsp. l. Place dried medicinal leaves in a milled form in a heat-resistant container and pour ½ liter of boiling water.
- After that, the mixture must be left for 1 hour to infuse.
- Over time, the solution should be filtered.
- Prepared tea is recommended to be consumed during the day, 100 - 150 ml.
Aloe Vera Honey Blend:
- To prepare a medicine, it is worth chopping an aloe leaf to a mushy state.

- Then, juice should be squeezed out of the resulting mass using a small calico or gauze.
- Next, the healing liquid must be mixed well with 1 tbsp. l. natural honey.
- The finished medicine is recommended to be taken 2 times a day for 1 tbsp. l.
To avoid the appearance of thick saliva in the mouth, the reasons for which do not relate to the development of pathological conditions in the body, it is recommended control your drinking regime, quit smoking, do not abuse dairy products, coffee, carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks, use humidifiers in the house, visit the dentist in a timely manner and prevent the development of a chronic form of disease (especially ENT organs).
Video about thick saliva in your mouth
What saliva can tell you about you: