Content
- What is it, definition
- Classification
- Chemical addiction
- Non-chemical (behavioral) addiction
- Intermediate addiction
- Characteristics and properties
- Why arises
- How to get rid of
- Fight against gambling addiction
- Fight against love addiction
- Fight against shopaholism
- Methods for professional treatment of addiction
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Relapse prevention
- Video about addiction in psychology
Each person has inherent certain habits and preferencesconcerning all aspects of life, which are determined by his temperament, level of development, natural inclinations. They make a person unique and different from others. However, sometimes habits and preferences, subjugating a person, acquire a pathological character, which in psychology is called addiction.
What is it, definition
Addiction - this is defined in psychology as mania, a morbid addiction to something or someone, an obsessive need to perform any action.
An addict is a person who suffers from a certain form of pathological addiction. In the absence of an object of addiction, the patient experiences severe physiological and emotional discomfort, manifested in deviant behavior and mental disorders. To get this object, a person is able to make any sacrifices, sometimes without stopping even before a crime.
Addictology, which deals with the study of addiction cases, and exists at the intersection of psychiatry and narcology, is a relatively young science.
For the first time, the concept of addiction and addictive disorder (from the English addiction - dependence) was proposed by the Soviet psychiatrist and psychotherapist from Novorossiysk, Professor Ts.P. Korolenko at the beginning 70s last century. For a long time addictology existed as a section of narcology, considering exclusively cases of addiction to alcohol, nicotine, drugs.
At the beginning of the 20th century, Professor Korolenko introduced the concept of non-chemical addictions into everyday life and proposed their classification. Today, the problems of addiction in Russia are dealt with by the Novosibirsk Medical Academy, in which already in the 80s. a research team was formed, which developed its own concept of the disease and methods of its treatment. The works of American scientists from NIDA, the research institute on drug abuse, are also widely known.
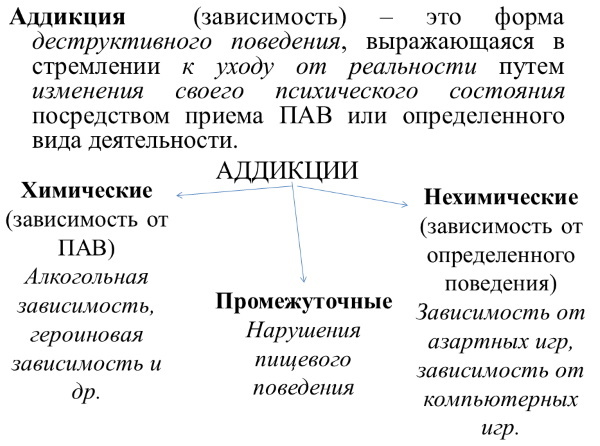
Classification
In any kind of addiction, a person strives for satisfaction. By raising low dopamine levels, he wants to improve his emotional state. Depending on the method chosen to obtain the desired effect, there are varieties of this disorder.
Chemical addiction
In chemical addiction, to achieve the desired state, substances are used that can, by acting on the psyche, cause a powerful release of dopamine, or are themselves its source.

Common forms of chemical addiction include:
| Form of addiction | Description |
| Nicotine addiction | A person needs a cigarette to calm down, make an important decision, and distract from unpleasant thoughts. |
| Alcohol addiction | Obsessive craving for strong drinks, as a way to get away from problems related to work, trouble in the family, financial troubles |
| Substance abuse | Inhalation of volatile substances that cause body poisoning, manifested as a state of euphoria |
| Addiction | The need for pleasant sensations after the injection of hallucinogenic drugs |
| Caffeine addiction | In the absence of a morning cup of coffee, a person feels weak and overwhelmed, in order to "cheer up", he needs a portion of caffeine |
| Drug addiction | It can form with prolonged use of potent drugs that have been prescribed for a disease or are needed to improve your physical data |
Non-chemical (behavioral) addiction
In non-chemical addiction, the factor that causes the body to produce high doses of dopamine is some kind of activity. Over time, the process of producing the "pleasure hormone" becomes impossible without this stimulus. This is how addiction is formed.

Common forms of non-chemical addiction are as follows:
| Form of addiction | Description |
| gambling addiction | Poker games, roulette, uncontrollable addiction to slot machines, computer games. For the sake of the opportunity to play, the addict is able to make any sacrifices, since the possibility of winning has an exciting effect on him, gives him the strongest pleasure. As a rule, a gambling addict is inclined to lie, easily makes a promise "not to play anymore", knowing full well that this is not so |
| Ludomania | A kind of gambling addiction. This is an addiction to the very process of the game, to a feeling of excitement, to the accompanying risk of the game. |
| Gambling | Also a kind of gambling addiction. In this case, the goal of the game is to get a big win, and the game is only a means to achieve the desired |
| Internet addiction | Being in social networks and immersing a person in the virtual world, fencing off from the real world |
| "Brand" addiction | This is an obsessive desire to acquire a certain thing of this brand by all means. Getting what you want gives you a short-term feeling of happiness, but then the interest in buying weakens, and a new "goal" appears. |
| Love addiction | Its object can be a person living in the neighborhood or a famous singer, actor, athlete. Feelings that have nothing to do with true love can manifest themselves in pathological jealousy, importunity, the desire for total control of the object of their adoration |
| Sexual addiction | This is compulsive sexual behavior. An anomaly that is dangerous for others, manifested in the inability of a person to control his own sexual desires. A person suffering from this type of disorder experiences such a strong surge of emotions during intercourse and sensations so vivid that he is ready to do anything for the sake of repeating it, neglecting the opportunity punishment. Most often, this type of behavioral disorder occurs in men and usually takes the form of various sexual perversions. In women, this pathology is less common and manifests itself in promiscuous and dangerous sexual contacts with strangers. |
| Religious addiction | Dependence on any religious organization, a way to escape from mental pain, anxiety, the need to solve any problems, shifting all responsibility to God or a mentor. The most dangerous situation is when a person falls into a sect, whose leaders often use harsh methods of suppressing the will, which cause serious mental disorders |
| Workaholism | Work is perceived not as an opportunity to improve one's own well-being or to realize one's talents, but as a way to escape from unpleasant reality, from annoying family problems. Rest, communication with friends or family, is perceived by a workaholic as a waste of time |
| Sports addiction | Excessive cravings for physical activity. The purpose of the classes in this case is to eliminate feelings of anxiety, improve mood. |
| Shopaholism | It is manifested by a passion for shopping so strong that it deprives a person of the ability to control their own expenses. The euphoria after the purchase is quickly replaced by feelings of guilt and regret over the exorbitant expenses, but then the need for new doses of dopamine pushes the shopaholic on another shopping trip. |
Intermediate addiction
Addiction is (in psychology there are various types of obsessive states) a painful condition, which, in addition to chemical and behavioral forms, can be intermediate. This category includes addictions, which are inherent in the features of various addictions.
Basically, the following various eating disorders:
-
anorexia - fasting in the name of a slim figure, abstaining from meals;

- bulimia - gluttony, which is caused by constant obsessive thoughts about food;
- orthorexia - an attempt to follow the canons of healthy eating, brought to the point of absurdity;
- drancorexia - replacement of normal food with alcohol (usually for the purpose of losing weight).
In psychology, there is also the concept of conditionally addictive behavior, which can include cases that are similar to addiction, but are not. They pose no danger either to humans or to society.
In particular, these include:
- physiological, psychological and emotional dependence of a small child on the mother;
- passion for a certain type of art, science, the presence of a hobby;
- the need of a sick person for any medications: for example, a diabetic cannot do without insulin injections, a person who has recently suffered a serious injury - without an anesthetic.
However, under certain circumstances, conditionally addictive behavior can eventually transform into true addiction. For example, the love of one's work turns into workaholism, and the need for medicine turns into drug addiction that has developed after recovery.
Characteristics and properties
Addiction dictates its own particular model of behavior.
She is characterized by:
- outbursts of extreme irritability for the most insignificant reason;
- absent-mindedness;
- the tendency to brush aside existing everyday problems;
- inability to critically assess their actions;
- sudden mood swings.

If a person has not lost the ability for rational thinking, he can independently determine that his little weakness, an innocent habit, is no longer such and for some time now began to acquire more vivid features pathology.
In this case, the following phenomena will become alarming:
- change of social circle, sometimes - a complete lack of desire to communicate with any of the former friends, dictated by the fear of condemnation. A person feels more comfortable in the company of new acquaintances, comrades in misfortune;
- thoughts and conversations solely about the addiction object. All other life problems have lost their acuteness, seem small and insignificant;
- a new daily routine in which the main place (depending on the type of addiction) is occupied by your favorite game, shopping trips, searching for alcohol;
- psychological discomfort associated with the inability to be close to your object or do what you love;
- uncontrollable rage directed at the one who interferes with the use of the object of addiction and the willingness to go to any lengths to remove the obstacle;
- lack of interest in the opinions of others: domestic scandals and threats from the authorities no longer matter, only the possibility of possessing an object of destructive passion is important;
- deterioration in appearance: as a rule, addiction has a bad effect on well-being: a person is tormented by insomnia, headaches, a feeling of anxiety, which cannot but leave an imprint on his appearance.
Why arises
Addiction is (in psychology, obsessive states have their own classification) a painful addiction, which is always formed in approximately the same pattern:
- A person, performing some action or taking any substance, gets pleasure: his brain is in the response to an external stimulus produces dopamine, which causes an elevated mood, euphoria.
- The action of dopamine ends at some point, but motivation and understanding have already formed the fact that in order to get a new portion of "pleasure" it is necessary to repeat the already committed actions.
- Over time, a stable connection is formed, and dopamine begins to be produced only in response to this stimulus.

However, not every person acts on this principle: after the first experience, most return to their usual activities. The development of events described above is most likely if there is some negative factor that provokes an increased need for dopamine.
This factor can be:
- tense family environment;
- lack of emotional connection between the child and the parents (the most common cause of addiction in a teenager);
- problems with socialization, difficulties associated with getting used to a new team;
- imbalance, as a feature of temperament;
- low self-esteem and self-doubt, which is its direct consequence;
- prolonged stay in a state of stress;
- lack of the ability to soberly analyze their own behavior;
- persistent reluctance to solve problems;
- weakness.
You can become a victim of addiction at any age, but more often this disorder develops in adolescents due to their unstable and extremely vulnerable psyche. The risk increases many times if a similar pathology is present in one or both of his parents or if one of the listed factors exists.
How to get rid of
In some (mild) cases of non-chemical addiction, self-healing is possible. This requires that a person is fully aware of the problem, wants to get rid of addiction and has the ability to objectively assess his behavior.
Fight against gambling addiction
To begin with, it is recommended to draw up a daily routine in which an adequate number of hours will be allocated to the game, and then adhere to the chosen mode, gradually decreasing the "game" periods and devoting the released time to others classes.

When you are tempted to play for money, limit the maximum bet, for example, by setting a limit on the card from which funds will be debited.
This method is good for regulars of virtual casinos and fans of online games, it can be used to combat any other "computer" addictions.
Fight against love addiction
There are several techniques designed specifically for victims of excessive love attachment, for example:
- auto-training and self-hypnosis: techniques aimed at dispelling the aura of romance, which the idol is now surrounded, mentally marking him in the most ridiculous situation, where he will look pathetic and funny;
- look into the future: the essence of the method lies in the idea that the dream has come true and asking the question: what's next;
- search for flaws: instead of endowing the object of your adoration with the most beautiful traits of character, it is better to look for the negative;
- sublimation: an attempt to shift the "focus" of personal interests to something else.
Fight against shopaholism
First you need to find out what is the reason for the irrepressible passion for shopping and what factor makes this passion so strong that it makes it impossible to resist it. Then try to eliminate this factor.

Then you can use the following types of limiters:
- before going to the store, make a shopping list and take exactly as much money as is necessary to implement this list;
- refuse a credit card, which creates the illusion of unlimited financial reserves;
- when going to the store to buy new clothes, first review your wardrobe: it is possible that after such an audit the list of necessary acquisitions will be halved;
- try to change your attitude to shopping: when it ceases to be entertainment, and turns into a heavy necessity, the desire to throw everything in the basket will disappear by itself;
- not to succumb to the "discount" hysteria: it will help to overcome it by the simple thought that a good, in demand product is unlikely to be sold at a discount.
Methods for professional treatment of addiction
Addiction is a morbid condition in psychology that often requires the help of professionals.
For example:
- with chemical addiction;
- with severe behavioral disorders, when a person is not able to adequately assess their behavior;
- in the case when it was not possible to get rid of the pathological addiction on its own.
Diagnostics
The purpose of diagnostics is to determine the severity of the disease - the degree of how strongly the pathological craving has taken possession of a person, and the factor that provoked the formation of addictive behavior. In the process of diagnostics, it turns out whether the addiction managed to cause pathological changes in the psyche, how strong they are and whether the addict is dangerous for others.

To date, there is no single diagnostic method. In chemical addiction, questionnaires are used, each of which is designed for a specific type of addiction. With regard to deviations not associated with the intake of psychotropic substances, here most doctors have to rely on their own intuition.
In recent years, on the basis of the AUDIT test (for detecting alcohol dependence), complex tests have been developed to assess the addictive status, which determine the level of need for an object of addiction.
An assessment is carried out according to several criteria:
- acuity of sensations when using the object (taking a narcotic drug, the ability to play, work);
- tendency to depressive states when it is impossible to do this;
- the risk of developing psychopathy: the likelihood of antisocial behavior that threatens other people;
- the ability to soberly assess their own behavior.
Treatment
The course of treatment is prescribed based on the data obtained during the diagnosis. The main method is psychotherapy - conversations with the patient, during which the specialist, depending on the patient's attitude to his problem, uses various therapeutic strategies.
Namely:
- explains what consequences the lack of treatment will have - if the patient does not want to change anything in his life. At this stage, the specialist's goal is to convince the patient of the need to continue the course of therapy;
- emphasizes how dangerous the consumption of psychoactive substances (PAS), or the constant use of non-chemical stimulants, which pushes the patient to make a decision to abandon them - when the patient develops a desire to cooperation;
- teaches techniques that will allow you to live and enjoy life without an object of addiction: the skills of self-control, relaxation, the ability to resolve conflicts.

With chemical forms of addiction, treatment is also prescribed, which is necessary for intoxication of the body and elimination of physiological dependence on surfactants. It should be borne in mind that the success of treatment largely depends on how well the patient himself is aware of the problem and whether he really wants to get rid of his pathological attraction.
Relapse prevention
The likelihood of repeated addiction remains in any of its forms, since the patient cannot be forced to forget about the pleasant sensations that the object of addiction once gave him. However, it is possible to reduce the risk of relapse, for which classes are conducted aimed at developing skills and abilities that will help overcome pathological addiction and at the right time will play the role of a "brake".
At this stage, the methods of group psychotherapy are widely used, in particular, meetings are practiced former alcoholics (drug addicts) with patients trying to get rid of alcohol (drug) dependencies. To prevent non-chemical forms of addiction, group sessions can also be conducted, moreover, the group includes people susceptible to addiction and those who were able to overcome the addiction.
Video about addiction in psychology
Addiction and Addictive Behavior:



