Content
- Anatomy of hearing
- Description of the outer ear
- Middle ear description
- Inner ear description
- Hearing organ functions
- Which leads to pain
- Allergic reactions
- Neuralgic pathologies
- Trauma
- Infections and inflammations
- Therapies
- Auricle video
Reasons indicating painful manifestations in the auricle, there are many, from injuries and allergic reactions to immune diseases. Timely diagnosis and treatment started can remove almost any symptoms without further manifestation, regardless of whether the organ hurts outside or inside. This makes it possible to avoid dangerous complications.
Anatomy of hearing
The human ear, from an anatomical point of view, is a complex organ that allows you to maintain a certain connection with the outside world. It is he who gives the individual accurate information about the location and movement, without which the personality is not complete.
In the organ, the auditory centers are distinguished, the peripheral part and the border at which the pontine-cerebellar angle is connected - the area where the nerve endings of the vestibular cochlear region are concentrated. The unique structure of the ear provides sound transmission and also converts various vibrations or vibrations into nerve impulses.
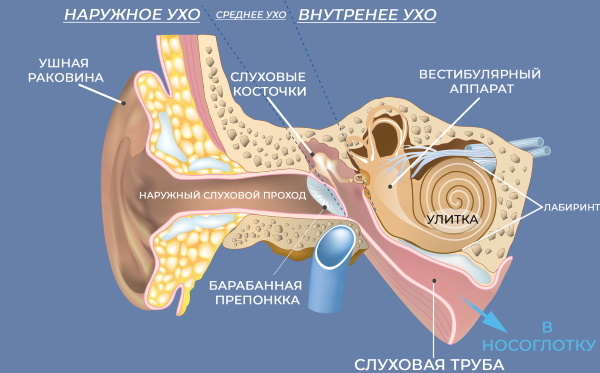
In medical practice, there are 3 sections of the hearing organ located in the peripheral lobe:
- middle ear;
- outer ear;
- inner ear.
The central region of the ear is represented by the auditory tract, cortical and subcortical regions. The organ contains the tympanic membrane, cavity and auditory tube. The bony section of the external passage has a fixing function in all areas.
Description of the outer ear
The outer ear (from the Latin name - auris externa) is the auricle, eardrum and external auditory canal. The main function of the area is to capture vibrations and vibrations. In turn, the main component of the outer ear is the auricle, which is characterized by a modeled cartilage with an elastic structure.
Next to it are various bulges and depressions, which are covered with a layer of skin. An exception is a lobe formed from a skin fold.
The upper layers of the skin in the shell are tightly connected to the cartilage in the anterior and posterior anatomical projections. The shell is located between the mastoid region of the temporal bone tissue and the mandibular joint. Supplied with muscle fibers made up of a number of small muscles. It is their contraction that allows the shell to move.
The ear canal of the type has a length of 3-4 cm. In practice, the external and internal regions are distinguished, which differ from each other in connective tissue - the rotation of the ear canal.
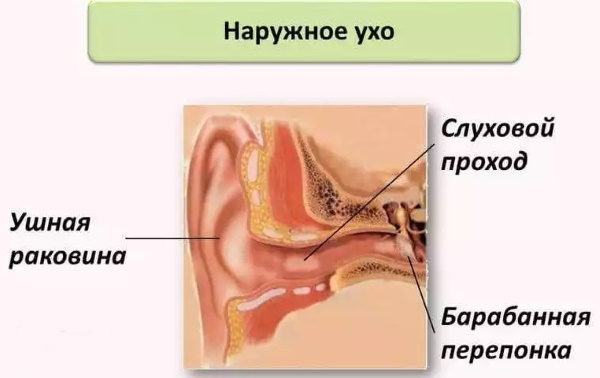
The external ear canal is characterized by a sinuous shape, which allows it to connect with the bones of the entire organ. The cartilaginous region is characterized by many hair follicles that form sweat and sebaceous glands. In this area is sulfur, which consists of a substance containing numerous cells of the old epithelium.
Anadromous cartilage forms the so-called groove, which is supplemented from above with additional connective tissue. Because of this, the outer layer of the ear can expand and contract in the area of the cartilaginous part. The bony area is made of thin skin on which no hairs or glands form. It fits snugly against the inner walls of the ear canal.
Since the tympanic membrane begins at the auditory lumen, foreign bodies often cannot linger at the initial border of bone and cartilage tissue. This is also helped by such protective elements as hairs or sulfur, which protect the membrane from injury, loss of firmness or elasticity.
The main functional features of the outer ear:
- capturing high-frequency sounds;
- definition and ability to install a sound source;
- protection against infections, viruses and other microorganisms, in particular - dust and dirt.
The innervation of the outer region of the ear is especially sensitive and runs in the region of the trigeminal, greater and vagus nerves. The connection with the central nervous system is explained by the presence of a cough reflex manifestation when touching the back walls of the passage.
Middle ear description
The middle ear (from the Latin name auris media) is characterized by the presence of a cavity that slightly exceeds 1 cubic meter in volume. cm. There are 3 separate bone elements that are connected to each other by a chain of cartilage.
The middle ear has the following elements:
- the tympanic cavity, in which the auditory ossicles are located - the tympanic region;
- auditory tube - tubotympanic region
- the process of the mastoid type is the mastoid region;
- eardrum.
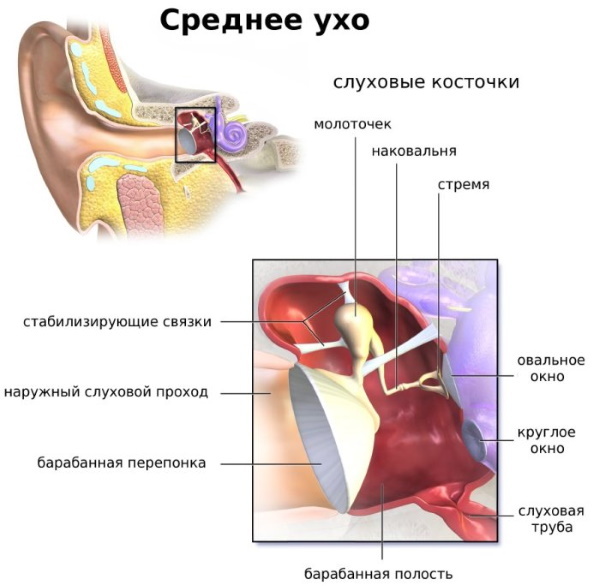
The membrane has an oval shape and a small size of 9 × 11 mm. Usually its thickness is 0.1 mm. Surrounded by 2 separate layers: mucous and fibrous. The outer auditory region continues in the skin layer, while the fibrous one is characterized by collagen bundles, which are located in a radial and circular form. In the center of them is the so-called navel, in the direction from which the mucous fibers diverge.
Radial fibrous bundles are connected to each other, forming a hammer, which passes into the periostice. Its handle is characterized by a protrusion in the area of the membrane, ending in a funnel-shaped depression. Folds of the tympanic membrane are located in the area of the malleus, which separate its relaxed sections, devoid of any hairiness and attached to the anatomical notch inside the ear. Most of the membrane is characterized by a dense surface.
Also, the tympanic membrane is the side wall of the inner ear cavity, which is formed due to the lateral regions of the bony curl. The medial walls are located together with the connective tissues - the inner membrane organ.
The tympanic cavity is a section that is filled with air. Located between the inner and outer ear, within which the upper, middle and lower regions are distinguished. The cavity is characterized by the presence of a malleus, stirrup and incus, from which the auditory ossicles are formed - the elements that connect the membrane to the inner ear.
Also in the middle ear there is a special muscular section that protects the organ from excessively high and intense sounds, which is possible due to its reflex contractions. The contraction of the muscular structure of the membrane is limited by vibrations of the bones, which leads to a weakening of sounds in the region of 15-20 dB.
The mastoid process or the system of the temporal bone region is characterized by the presence of numerous cavities that are connected to each other. The largest of these is the cave (antrum). This area in the ear is characterized by a pneumatic process that is adjusted based on the individual characteristics of each person. An underdeveloped system is characterized by the presence of dense bone tissue, which affects the quality of hearing.
Inner ear description
The inner ear or auris interna is located in the temporal bone. Based on anatomical concepts, it is characterized by a labyrinth, which is conditionally divided into receptor regions: the peripheral part (cochlea) and the vestibular organ. There are also semicircular canals here.
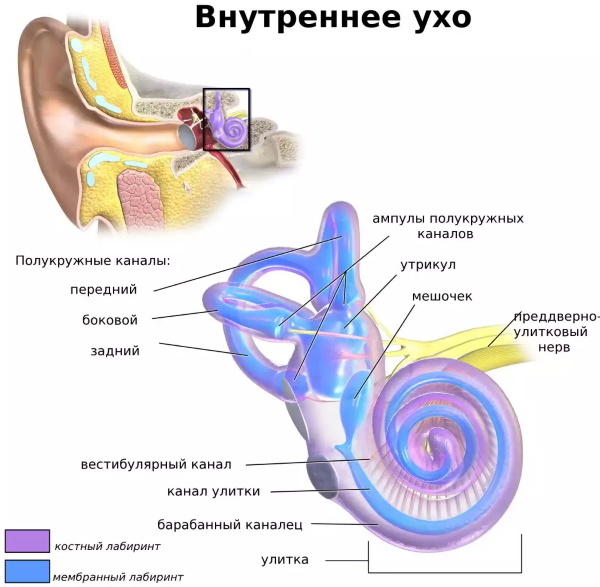
The morphological features of the inner ear are characterized by the presence of a membranous and bony labyrinth, which have a mechanism that makes it possible to constantly rebuild bone tissue.
The membranous area of the cochlea contributes to the formation of a spiral passage, which visually resembles a triangle. It is formed on the basis of the inner membranes of the organ or membranes. Inside the snail there is a liquid of a lymphatic nature, and here the fibrous threads are stretched.
Each of these fibers allows the sound to resonate at a specific frequency. There are approximately 25-28 thousand such threads. On the inner walls of the canals is the so-called receptor field, which consists of nerve hairs. The death of these cells often leads to a pathological process called sensorineural hearing loss.
Hearing organ functions
The physiological function of the organ of hearing is described based on the anatomical features of the organ.
Each department has its own tasks, of which the most important are:
- outward - capturing sounds and tonality
- middle and outer - transmission of sound waves using neural connections;
- eardrum and external - protection against bacterial infections, excessively loud sounds and various damages;
- inner ear - transformation of the kinetic energy of sound and membrane vibrations.
Also, the human ear is responsible for the natural regulation of the body in space, which is possible thanks to the presence of a built-in vestibular apparatus, which consists of 2 separate sacs - oval and rounded. All of them are filled with a special liquid and are connected to each other. Sensitive hairs are located on the inner side, which are part of the neural fibers.
Any angular acceleration in space is perceived by the ear due to the presence of receptors located in the semicircular canals. Their function is to excite during the process of pressure on the internal fluid. Such energy is fixed with the help of hairs and sacs, the complex of which is called the otolith apparatus.
Such an evolutionary apparatus consists of numerous highly sensitive hairs, which are immersed in a jelly-like substance. They all form a special membrane that contains calcium bicarbonate elements or otoliths. The influence of the environment accelerates them, so that the ear recognizes the movement that is transmitted to the central nervous system.
The functional features of the vestibular apparatus are as follows. Under strong pressure, the liquid inside the membrane fibers moves, which is characterized by irritation of sensitive receptors. Those, in turn, are able to send a signal to the brain about the movement of the body in space. Thanks to this, the person's movements are evened, the neck, trunk and other muscles prevent falling.
Which leads to pain
Regardless of whether painful sensations appear outside or inside the auricle, the most common cause of discomfort is the rapid development of otitis media. The severe course of the pathology is characterized by the spread of the inflammatory process up to the ear cartilage.
Often, otitis media occurs as a result of the introduction of infectious bacteria, however, in some cases, its development can manifest itself as a result of severe hypothermia or injury. Rapid diagnosis and timely treatment at the initial stage is characterized by a rather mild course of the disease.
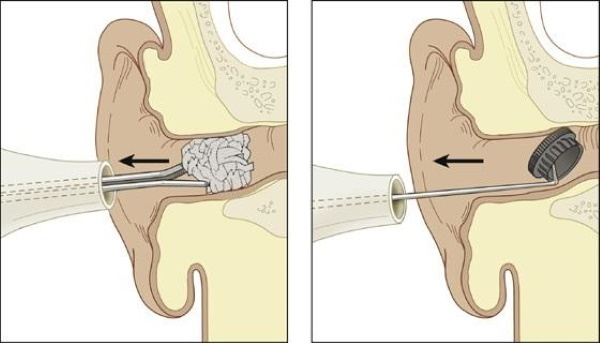
Also, often a factor provoking painful sensations in the ear is the presence of foreign objects in the internal canal. Often this phenomenon manifests itself in young children who are not aware of their actions. Sometimes it is almost impossible to pull out an element stuck inside without surgical intervention.
The auricle can also hurt from the inside or outside due to reasons:
- Insect bites, which provokes not only painful sensations, but also swelling. In this case, you should quickly contact your doctor to avoid the risk of hearing loss.
- Using ear sticks. Numerous studies have proven the harm of these devices in cleaning the inner ear area. Deep cleaning of the auricle can injure or damage the eardrum.
- Getting burns that can be localized under the ear or in the shell itself. In this case, it is best to apply a cold compress, after which, if possible, contact the emergency room.
- Fluid in the inner ear. Especially often it occurs due to improper bathing of a child or immersion in water. Since the liquid is able to linger in the organ, this can provoke the development of the inflammatory process.
- The presence of acne, blisters and other types of rashes in the auricle.
- Complications during various dental operations, which often provoke the development of diseases that can harm the nasopharynx.
The auricle hurts outside or inside rather rarely due to a fracture of the cartilage, which is typical for athletes involved in martial arts, boxing. In this case, painful sensations are given to the temples, there is a high risk of hearing loss.
Allergic reactions
Allergic reactions can often cause pain. So, anaphylactic conditions are characteristic of patients who have increased dryness of the ear tube and decreased secretion of the internal substance that protects the shell.
The auricle hurts from the outside, often due to exposure to chemical, plant or animal allergens. Painful sensations can also be localized inside the ear. In this case, we are talking about the defeat of soft tissues and cartilage, which is accompanied by redness, rash and itching.

The most common foods that can cause allergic and fungal reactions in the body are:
- cosmetic preparations;
- hygiene products;
- Food;
- detergents, washing powders;
- medications;
- some types of ornaments.
In order to exclude an allergic factor, the patient for some time refuses to use the drug, agent or element for which there is even a slight suspicion.
Neuralgic pathologies
Often, pain in the outer region of the auditory shell can be characterized by neurological manifestations that are associated with the occipital region. Also, painful sensations are often indicated by inflammatory processes in the nervous or muscle tissues of the face. In this case, the patient feels pulsating discomfort. Severe pain can provoke pinching of various nerves, including the most severe case - damage or inflammation of the trigeminal nerve endings.
This pathology belongs to those diseases that are practically not amenable to treatment. Acute pain can occur when chewing or opening the mouth, which is due to the creation of compression and squeezing of nerve endings. Such manifestations are characterized by inflammatory processes in the cartilage of the ear, which often appear in the form of jaw clicks.
The defeat of the anatomical structure of the ear in the presence of developing osteoarthritis is characterized by a slow clinical course with often irreversible consequences for humans.
Trauma
Strong mechanical stress that can damage some elements of the internal or external structure of the ear is a fairly common cause of many painful sensations.
The most common causes of ear injuries are:
- small hematomas;
- high physical pressure on the ear;
- cartilage piercing;
- external or internal bruising;
- blue discoloration or redness of the skin inside the shell;
- purulent abscesses;
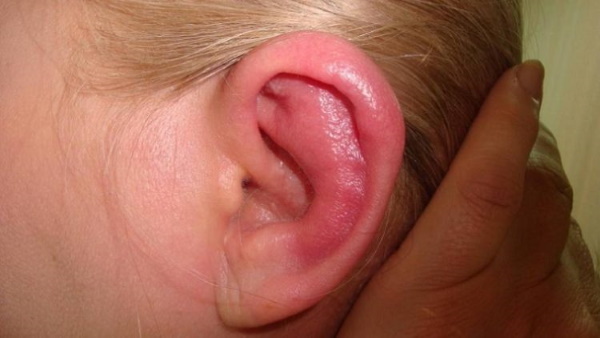
- scratches, cracks and tears of internal tissues.
The auricle hurts outside and inside, often after a severe bruise. Such damage is characterized by the appearance of inflammatory processes, and in some cases, the introduction of infection into the internal tissues.
Infections and inflammations
Based on statistical indicators, the auricle often hurts due to the presence of an inflammatory process that occurs as a result of damage to toxins from microorganisms and bacteria. This can cause the appearance of purulent abscesses, which causes additional discomfort.
Such cases often lead to a dangerous disease of furunculosis, which is characterized by inflammation of the fatty glands. The pathological process is characterized by changes of the necrotic type in the tissues that were affected. A neglected disease provokes a complete loss of hearing and further spread of the infection.
The etiological significance of factors that are characterized by painful sensations due to the development of furunculosis are as follows:
- Lowered immune system. A strongly weakened immune mechanism can greatly aggravate the ongoing disease, which makes the progression of furunculosis more rapid.
- Vitamin deficiency and other useful microelements. This condition contributes to the inhibition of the secretion of various substances that are capable of arresting the symptoms of pain syndrome.
- Diabetes. Such a pathological process significantly slows down and complicates the regenerative properties of cells, due to which wounds cannot heal quickly.
- Staphylococcal infection. Such infection with the help of microorganisms can greatly complicate the course of treatment of pain in the auricle, including further activation of the inflammatory process.
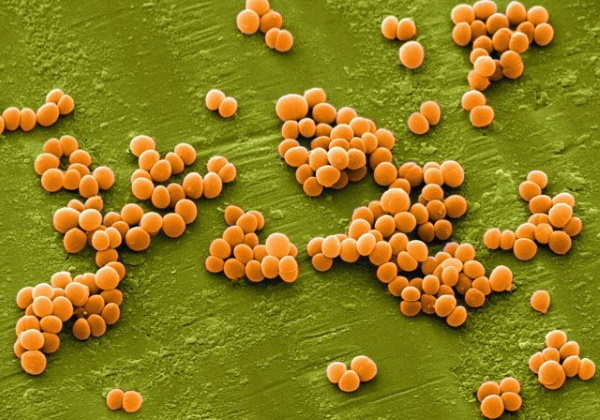
As with many other inflammations, furunculosis is often accompanied by severe pain during the chewing process, which radiates to the temples. The pathological process often extends to the eardrum, due to which a lesion of the ear cartilage is diagnosed.
Severe radiating pain may be accompanied by another inflammatory disease, mastoiditis, which affects the temporal bone, located slightly further than the auricle. The pathological process is most often characterized by a rapid deterioration in hearing, the presence of abscesses and high fever.
Also, in practice, the following diseases affecting the human ear are distinguished:
| Disease | Characteristic |
| Rhinitis | Inflammatory type syndrome affecting the epithelial lining of the nose. Often it moves to the area of the auricle, which provokes pains of varying degrees outside and inside. |
| Angina | Tonsillitis of an aggravated nature, which manifests itself on the basis of a local inflammatory process in the nasopharynx. It can develop as a result of staphylococcal and streptococcal infection. Painful sensations go to the outer ear region. |
| Parotitis | Inflammatory lesion affecting the salivary glands and some nerve endings. The infectious type of the disease is popularly referred to as "mumps". |
| Sinusitis | Inflammation of a chronic or acute nature inside the maxillary sinuses. Painful manifestations are usually localized in the jaw or external area of the auricle. |

Also a common cause of ear infection is enlargement of nearby lymph nodes, which is common in water sports. This exposes the hearing organs to the harmful effects of moisture, including additional pressure on the ear from the fluid.
Therapies
The auricle hurts outside or inside - this is a clear reason for quickly contacting a specialist. In this way, most of the negative health and hearing consequences of the patient can be avoided. The main treatment for ear diseases consists in taking medications, the purpose of which is determined by the nature and type of pathological disorder. Etiotropic drugs are often prescribed that act on the underlying cause of the disease.
To relieve pain, symptomatic drugs can be used that affect certain manifestations. The destruction of harmful microflora in the presence of infectious diseases is provided by antibiotic pills, ointments or injections into the inner ear. Various antibiotics are also effective in the presence of purulent growths. For the prevention of the organ of hearing and disinfection of the external surface, antiseptic-type agents can be prescribed.
If painful sensations are caused by hematomas, the doctor prescribes ointments that promote resorption. The healing of soft tissues is often accompanied by itching, which is a normal reaction of the body. Antihistamines are especially effective when there is a cause indicating an allergic reaction.
First aid may consist in cleansing the ear with a cotton swab soaked in Vishnevsky's ointment or Flucinar. In the presence of bacterial infection or ear injuries, antibiotics of complex action are used - Augmentin or Amoxicillin.

In the event of hyperthermia, antipyretic drugs are especially effective, which are prescribed for the complex therapy of inflammatory processes and various febrile conditions. They also help with severe pain.
The effect of drugs can be enhanced by mechanical pressure on the auricle, which is carried out with the help of special relaxing massages. They improve the trophic capacity of tissues, as well as increase the general innervation and relieve painful syndrome.
Surgical intervention of the auricle is reached only when in the internal tissues organ, there are a large number of purulent formations, plugs or any other types of treatment not help. If the ear hurts outside or inside, while the pathological process is not accompanied by complications, drug therapy is enough.
Auricle video
Middle ear anatomy: