Content
- Norm
- Reasons for the decline to 114 g / l
- Diagnostics
- How to raise
- Treatment for iron deficiency anemia
- After blood loss
- With vitamin B12 deficiency
- An alternative approach
- Video about hemoglobin
Hemoglobin, a protein that contains iron, is present in red blood cells and is responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. On the way back with venous blood, it carries carbon dioxide to the lungs, which is then removed with exhaled air.
The iron-containing protein structure is produced in the bone marrow simultaneously with the formation of immature red blood cells. About 350 million hemoglobin molecules are present in the erythrocyte and each is capable of carrying 4 oxygen molecules. If the proportion of red blood cells in the body is too low, for example, 114 g / l, mild anemia develops, which is more common in women than in men.
Norm
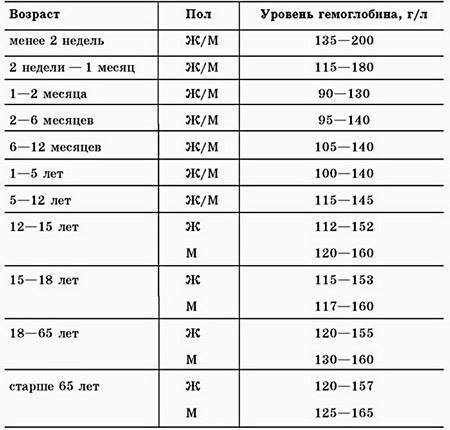
The hemoglobin measurement result is displayed in grams per deciliter (g / dl) or per liter, g / l. The norm of hemoglobin is different in children, men and women.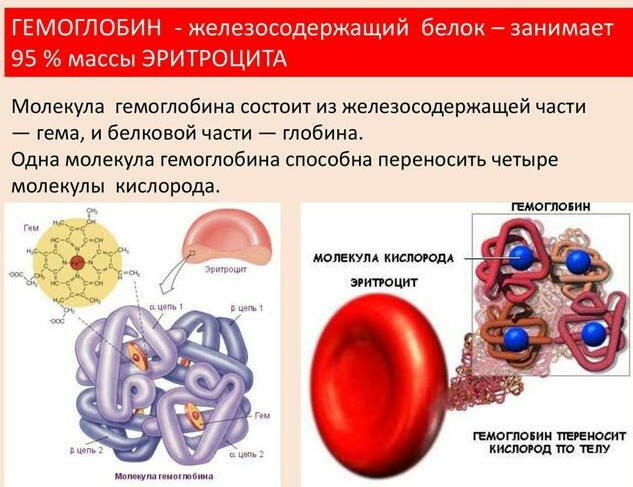
Approximate normal values for women are from 12 to 16 g / or 120-160 g / l.
While this is considered the standard level, there are certain variables. During pregnancy, the volume of plasma and the mass of red blood cells increases, which leads to a dilution of hemoglobin and a decrease in its level. It was found that even in women with normal iron intake, the concentration of the protein compound falls from the beginning of the first trimester, reaching the lowest level towards the end of the second trimester, 113-108 g / l. However, in the second trimester, hemoglobin begins to rise.
Reasons for the decline to 114 g / l
Hemoglobin 114 in women is quite common. In most cases, this is considered a mild failure, without pathological conditions and symptoms. Menstrual blood loss and the growing habit of following a low-calorie, low-meat diet all lead to a decrease in hemoglobin in women. The range of values is often reduced in athletes, vegetarians, the elderly, and blood donors.
A sharp drop in the level can lead to various diseases. At the same time, many critical illnesses, such as cancer, kidney and liver complications, can cause a decrease in hemoglobin levels. Anemia predominates in many seriously ill patients. If there is not enough hemoglobin in the blood, organs and tissues do not receive enough oxygen. This is manifested by pallor, fatigue, weakness, trouble concentrating, dizziness, and headaches.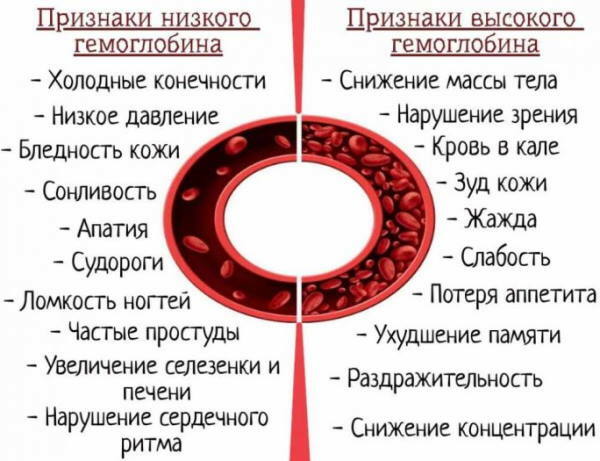
Below average values can be caused by:
- some medications (chemotherapy, antiretrovirals);
- bone marrow aplasia;
- collagenopathies;
- iron deficiency;
- deficiency of vitamins (B6, B12, B9);
- bleeding;
- liver diseases;
- serious infections;
- chronic renal failure;
- hypothyroidism;
- malignant neoplasms;
- peptic ulcer;
- splenomegaly (enlarged spleen);
- thalassemia;
- vasculitis;
- sickle cell anemia.
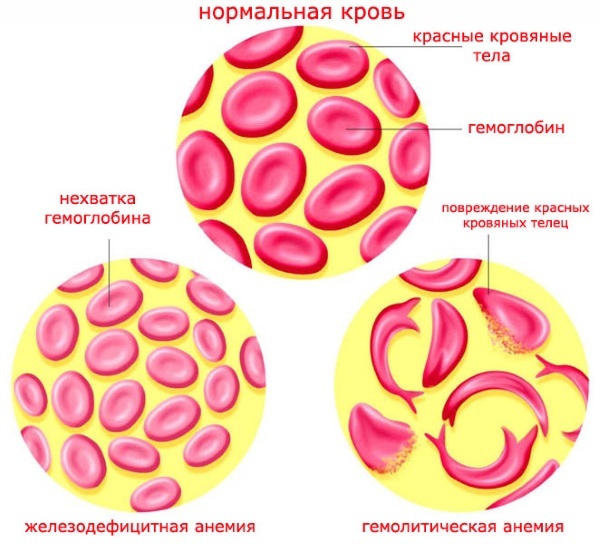
In women, low hemoglobin values (from 114 to 108 g / l) are observed in acute or chronic hemorrhagic processes:
- bleeding from a wound;
- too frequent donation of blood;
- hypermenorrhea (the presence of especially heavy menstrual flow);
- frequent nosebleeds;
- gastrointestinal bleeding (stomach ulcer, colon ulcer),
- frequent urination.
Diagnostics
Iron protein is measured as part of a routine blood test. The hemoglobin test measures the amount in the blood. Concentration can be determined alone or in conjunction with hematocrit, a test that measures the proportion red blood cells (erythrocytes) in the blood to quickly assess the red blood cell count person. It is also part of a complete blood count.
To measure hemoglobin, blood is usually mixed with a liquid containing cyanide, which binds tightly to hemoglobin molecules. By shining light through the resulting solution (cyanmethemoglobin) and recording the amount of light absorbed, hemoglobin levels in the blood can be determined.
If necessary, blood tests are prescribed for the following indicators:
- erythrocytes;
- the average content of hemoglobin in the erythrocyte (MCH);
- the average concentration of the protein compound in the erythrocyte (MCHC);
- erythrocyte volume (MCV).
How to raise
Various minerals and vitamins can increase the level of the protein compound. People with low levels are prescribed mineral or vitamin supplements to help the body produce more protein. In addition, these vitamins and minerals are found in various foods.
| Minerals and vitamins | Products containing them |
| Iron | Eggs, cereals, green leafy vegetables, beans, meat and seafood. |
| Vitamin B 6 | Meat, fish, vegetables, nuts and seeds. |
| Vitamin B9 (folic acid) |
Green leafy vegetables, beans and fruits. |
| Vitamin B12 | Fish, meat and dairy products. |
| Vitamin C | Citrus fruits, broccoli, potatoes and tomatoes. |

If your hemoglobin level is too low, your doctor will first do blood tests to find out the cause. If it is, for example, an iron deficiency, taking glandular drugs is sufficient for treatment. If the patient is suffering from severe blood loss, a blood transfusion may be required. If there is another disease behind the low Hb value, appropriate treatment is started.
Anemia does not require special treatment unless it is associated with a deficiency of iron, folate (B9), or cobalamin (B12). To do this, it is enough to adjust the diet.
Treatment for iron deficiency anemia
Hemoglobin 114 in women caused by iron deficiency can be corrected by diet therapy, taking iron supplements, which should not be taken without first consulting a doctor.
The main means of pharmacotherapy:
| Form of preparation | Compound | Daily dose |
| Sorbifer Durules, tablets | Ferrous sulfate, ascorbic acid. | 2 tablets |
| Actiferin kompozitum, capsules | Ferrous sulfate, serine, folic acid, vitamin B12 | 2-3 capsules |
| Gyno-tardiferon tablets | Ferrous sulfate, ascorbic, folic acid. | 1-2 tablets |
| Ferro-gradimet, tablets | Iron sulfate | 1-2 tablets |
| Maltofer, ferrum lek, drops | Iron hydroxide polymaltose 3-valent. | 35 to 100 drops |
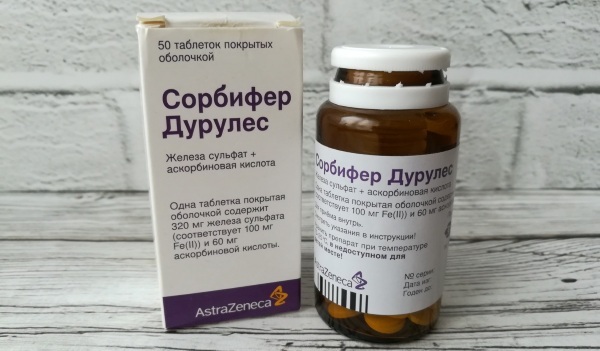
Glandular medications can cause indigestion, constipation, and diarrhea. Tablets or capsules are taken 2 hours before or after a meal. Doctors recommend a joint intake with vitamin E, succinic acid or honey. These substances contribute to the rapid absorption of iron. It is not recommended to take more than 100-300 mg of iron per day.
After blood loss
Anemia associated with blood loss is a direct result of a decrease in circulating red blood cells. In an adult, the total blood volume is approximately 5 to 6 thousand. ml and loss of 500 ml of blood does not represent serious or long-term consequences. But if 1000 ml or more is lost, serious acute ailments may occur.
Several health problems contribute to iron loss, including chronic bleeding of the gums, hemorrhoids, or stomach cancer. In addition, long-term medication can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. Parasites can also cause anemia as they drain blood and nutrients for the human host.
Treatment involves restoring blood volume through intravenous saline, dextran, albumin, or plasma. For large blood loss, transfusion of fresh whole blood is the preferred treatment.
With vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 and folic acid are nutrients that cannot be produced by the body and must be taken with food. Vitamin B12 reserves in the body are stored for 3 to 5 years, and folic acid reserves are insignificant.
Vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies are not common in healthy adults because the body is able to build up adequate reserves that are continually replenished through dietary intake or supplementation.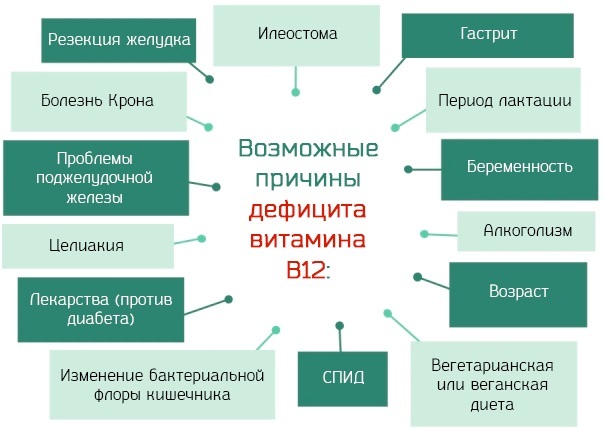
However, some groups of people are at risk of developing these deficiencies:
- Senior citizens.
- Patients with intestinal problems.
- Alcohol abusers.
- Subjects on a vegetarian or vegan diet.
- Women during pregnancy who need more vitamins.
- Subjects exposed to long-term use of certain medications.
Patients with intrinsic factor deficiency or with clinical conditions causing general malabsorption require vitamin B12 by injection. Folic acid is a supplement that should be taken by mouth.
All women of childbearing age who are expecting or not excluding pregnancy are advised to take folic acid before and during pregnancy to ensure adequate supply and normal development fetus.
If the patient lacks vitamin B12 and folic acid, then he will need both. In such cases, if a patient with vitamin B12 deficiency takes only folic acid, macrocytic anemia (an increase in the size of red blood cells, leading to a decrease in hemoglobin) can be reversed, but neuropathies (nerve damage) caused by B12 deficiency will still occur.
Sometimes taking a good multivitamin rich in vitamin B12 may be enough. Taking 200-300 mcg of vitamin B12 per day is enough to fill a mild deficiency. These can be drops, tablets, or capsules.
In some cases, stronger therapy is required with intramuscular injections at doses of about 500 mcg 2-3 times a week.
An alternative approach
A number of herbs are traditionally used by herbalists to treat anemia and increase red blood cell count. But before starting treatment with drugs, you should normalize the digestive tract, increase immunity.
The following collection can help with this:
- Blackberry and raspberry leaves - 30 g.
- Chamomile flowers - 20 g
- Melissa - 10 g.
- Celandine - 20 g.
- Mallow flowers - 30 g.
- Figs - 100 g.
- Calendula flowers - 40 g.
- Rosehip berries - 100 g.
Chop herbs and berries, mix, 2 tbsp. l. pour 500 ml of boiling water into the mixture, leave for 1 hour. Strain and take 1/2 cup three times a day 20 minutes before meals, warm.
Hemoglobin 114 in women can be increased with the help of vitamin collection:
- Peppermint - 30 g.
- Dandelion root - 20 g.
- Ivan grass - 25 g.
- St. John's wort leaves - 20 g.
- Red clover - 20 g.
- White nettle - 20 g.
- Rosehip berries - 50 g.
- Blueberries - 30 g.
- Badan rhizomes - 15 g.
Pour 200 ml of boiling water 1 tbsp. l. chopped ingredients and leave under the lid for half an hour. You need to drink the infusion three times a day, 1/3 cup (before meals). The standard course of treatment for anemia is 25-30 days.
Small fluctuations in hemoglobin values (116-114 g / l) are normal. and may be related to factors such as age, physical activity, or a period of certain stress. However, one should be concerned about the subsequent decrease and the appearance of alarming symptoms. A low concentration can be talked about when the hemoglobin level drops by about 20% from the normal range in women.
Video about hemoglobin
Hemoglobin norm: