Content
- What is analysis?
- Where can I check in, how much does it cost
- Varieties of PCR
- Advantages and disadvantages of PCR
- To identify which infections PCR is suitable (scope of application of the method in medicine)
- Samples for research
- Rules for the delivery of biological fluids for PCR
- How to prepare for PCR analysis
- Swabbing procedure (for women and men)
- How are PCR tests deciphered
- Video about PCR analysis
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a modern laboratory method for generating a large number of copies of individual sections of nucleic acids (DNA or RNA). PCR is used in many areas of biology and medicine. In medical diagnostics, this method is used to determine infectious diseases.
In molecular biology, the purpose of copying can be a piece of DNA to study the function of a particular gene or other experiments (cloning genes, introducing other genes, identifying mutations). In a forensic examination, DNA is examined to match the genetic material of suspects at the crime scene.
What is analysis?
In the diagnosis of diseases using the PCR method, a specific section of the DNA of the infectious agent is isolated in the patient's biological material. If this site is found, this is direct evidence of the presence of the pathogen in the patient's body.
PCR can also detect changes in the patient's genetic material., which help to determine congenital diseases, changes in the immune system, predisposition to various diseases.
When carrying out PCR analysis, a certain part of the DNA or RNA molecule of the causative agent of the disease contained in the biological material is isolated from the sample by special methods. Then this area is duplicated many times with the help of enzymes.
An amount of DNA is synthesized that can be visually recorded. Only a certain part of the DNA molecule is copied.
PCR requires the following components:
- DNA template (a piece of DNA that is repeatedly copied and identified),
- primers (specially synthesized single-stranded short DNA molecules needed to seed DNA synthesis),
- DNA polymerase (an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of DNA polymerization), deoxynucleoside triphosphates (nitrogenous bases are the molecules that make up DNA).
- Other components (magnesium ions, buffer solution).
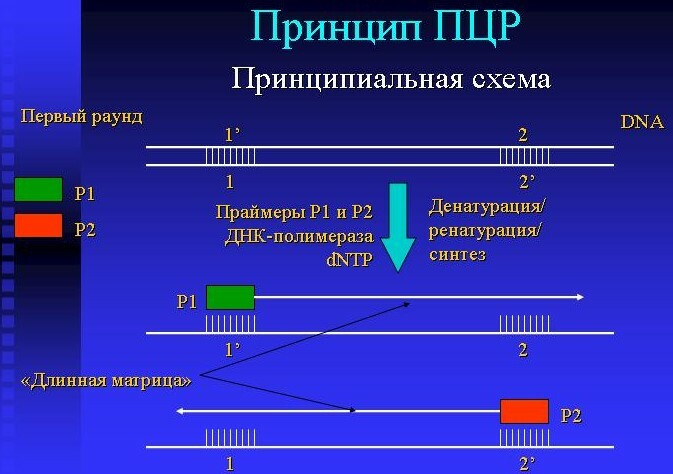
Polymerase chain reaction is a method that requires special equipment (amplifier), it consists of the following steps:
- Denaturation of the template DNA, in which double-stranded DNA is cleaved into two strands. This stage lasts for 30-40 seconds.
- Attachment of primers to specific regions of DNA occurs within 20-60 seconds.
- Polymerization is the synthesis of new DNA strands using an enzyme.

After repeated repetition of these stages, the required number of copies is synthesized (after 20 cycles, the number of copies reaches more than a million).
Registration of virus DNA is carried out after amplification in a special device (if PCR is used with detection in end point) or directly in the amplifier during the reaction (if real-time PCR is used) fluorescent method.
Where can I check in, how much does it cost
PCR analysis can be done in any medical laboratory accredited for this analysis.
The cost of the test depends on the type of infection:
| Laboratory | Infection / cost |
| KDL | Cytomegalovirus DNA - 230 rubles DNA of the herpesvirus type 6 - 250 rubles. RNA coronavirus SARS-CoV-2/1600 rubles. |
| Hemotest | Cytomegalovirus DNA - 250 rubles Herpes simplex virus type 6 DNA - 240 rubles. RNA coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 - 1700 rubles. |
| Invitro | Cytomegalovirus DNA in the blood - 400 rubles. DNA of human herpesvirus types 1 and 2 in scraping of skin epithelial cells - 570 rubles. RNA coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 - 1990 rubles. |
| Citylab | Cytomegalovirus DNA - 240 rubles Human herpesvirus type 6 DNA - 290 rubles RNA coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 - 1800 rubles. |
Varieties of PCR
Polymerase chain reaction is a method for which different methods of setting up the analysis have been developed.
These methods were designed to reduce the risk of false positive and false negative results, or to perform quantitative or qualitative analysis, as well as for the determination of different nucleic acids: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (ribonucleic acid).
According to the method for determining the reaction products, two types of PCR are distinguished:
- Real-time PCR - amplification and detection are carried out simultaneously in one device. With this modification of PCR, it is possible to determine the amount of the desired DNA sequence at each cycle of DNA synthesis.
- End-point PCR - a kind of PCR analysis, in which the results are recorded by the method of fluorescence in a special device, after the end of the polymerase chain reaction.
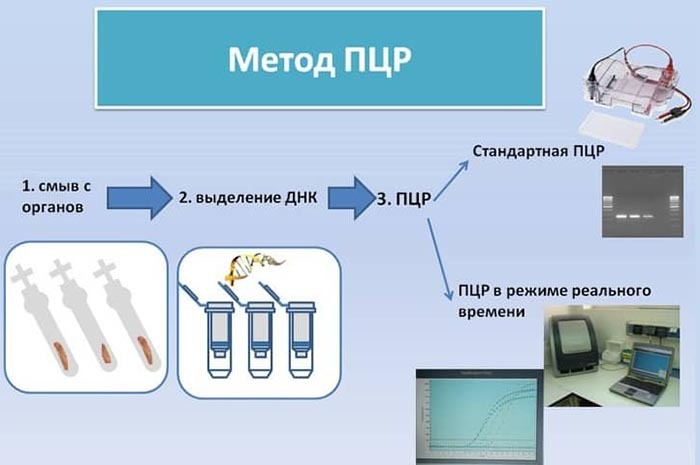
In laboratory practice, there are different ways of setting up the analysis, such as:
- Hot-start PCR. The peculiarity of this method is that the reaction starts only when a certain temperature is reached. The reaction components (especially enzymes) are blocked and start working only at a certain temperature. This method improves the accuracy of the analysis. If the reaction mixture is heated gradually, there is a risk of the formation of reaction by-products and, therefore, inaccurate analysis results.
- For the detection of viruses with an RNA genomefor example, hepatitis C type or human immunodeficiency virus, a method called reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) is used. The RNA of the virus is first converted into a complementary DNA molecule. The resulting DNA is then used as a template for PCR.
- Multi-primer PCR - a method of carrying out the reaction, in which several DNA sequences are simultaneously copied in one sample. This method allows you to reduce consumables and reduce the cost of analysis.
- PCR method using NASBA technology (Nucleic acid sequence based amplification) is that the RNA of the virus is used as a template for copying the genetic material. With the help of special enzymes (transcriptase, RNA polymerase, RNase), complementary DNA (cDNA) is formed in the reaction medium, as well as a complex of RNA and cDNA molecules. The difference between this modification and standard PCR is that not DNA, but RNA is accumulated as genetic material. The difference between this method and the RT-PCR method is that RNA is not only a template for cDNA synthesis, but also an amplification product (that is, the final product of the reaction).
DNA molecules are destroyed in the body for a very long time and can be detected in a patient even if antiviral or antibiotic therapy has already worked. Therefore, the standard PCR method does not allow evaluating the effectiveness of therapy.
Unlike DNA, RNA molecules can be isolated exclusively from living cells or viruses, and after the destruction of living cells, the RNA molecule is also rapidly destroyed. This modification allows you to control the effect of therapy already at the time of its implementation.
Advantages and disadvantages of PCR
Compared to other laboratory methods for detecting infections, the PCR method has several advantages:
- PCR method is a direct method determination of the genetic material of a virus or bacteria in a sample. Unlike other methods that determine indirect signs of infection, the PCR test directly indicates the presence of a virus in the body.
- High specificity of the method, that is, the ability to identify a specific pathogen is associated with the fact that genetic material is determined that is unique to a given organism (virus, bacteria, microscopic fungus). Therefore, the specificity of this method is close to 100%.
- High sensitivity of the method (also close to 100%) is the amount of sample that can be determined by this method. Even a small amount of virus or bacterial molecules in biological material is determined. This makes it possible to identify the carrier of the virus even before the onset of symptoms.
- The method is universal for detecting DNA / RNA of any viruses or bacteria. With the help of PCR, it is possible to determine any infections, as well as chronic diseases.
- Fast analysis method, duration is about 4-6 hours.

Flaws:
- The polymerase chain reaction is a method of direct detection of the pathogen's genetic material (DNA), and it does not allow evaluate the effectiveness of therapy, since the DNA molecule is not destroyed for a long time, even if the therapy is already worked.
- The high sensitivity of the method may be its disadvantage. For example, after completion of therapy, PCR still detects the DNA of dead cells in a healthy patient, thus obtaining a false positive result.
- Different manufacturers of PCR tests can detect the same infections using different systems. Therefore, the results of determining the same infection in laboratories may differ. Dynamic quantitative tests are recommended to be performed in the same laboratory.
- Some tests, especially genetic tests, can be quite expensive.
- To carry out PCR tests, expensive equipment, reagents, and well-trained qualified personnel are required. The accuracy of the analysis results depends on the quality of the reagents and the method of taking biological samples.
To identify which infections PCR is suitable (scope of application of the method in medicine)
PCR method is used for the identification, that is, the qualitative determination, as well as for the quantitative determination of DNA and RNA of pathogens of various infections:
- human immunodeficiency virus (HIV);
- hepatitis viruses A, B, C, D, G;
- pathogens that cause diseases of the urogenital tract, for example, Chlamydia trachomatis, Trichomonas vaginalis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Ureaplasma;
- pathogens that cause dysbiosis of the urogenital tract and candidiasis, for example, microorganisms such as Saccharimonas aalborgensis, microscopic fungi of the genus Candida;
- causative agents of human papillomavirus infections;
- TORCH and Herpesvirus infections;
- pathogens of natural focal infections that can be spread by birds, animals, blood-sucking insects, for example, borreliosis, encephalitis, West Nile fever;
- gastrointestinal infections;
- causative agents of tuberculosis;
- respiratory infections (Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae);
- nosocomial infections (Enterococcus, Acinetobacter baumannii, Klebsiella pneumoniae).

Also, the viral load is determined by the PCR method, the dynamics of the disease and the effect of the therapy are investigated.
The polymerase chain reaction in medicine has another important application - it is the determination of polymorphisms of human genes (local changes) and mutations. Minor local changes in the DNA sequence of different genes are the cause of the development of various diseases.
These diseases can be inherited. The PCR method allows you to identify these mutations and prevent the development or alleviate the course of diseases.
PCR is used to detect mutations that cause the development of diseases such as:
- violation of blood clotting;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- metabolic disorders (for example, lactose intolerance);
- impaired reproductive function (mutations that cause male infertility);
- breast and ovarian cancer;
- autoimmune diseases.
Samples for research
Depending on the type of infection detected, samples for analysis can be samples of biological fluids, tissues, epithelial cells:
- blood serum / plasma, peripheral, umbilical cord blood;
- samples of mucosal epithelium (cervical canal, vagina, urethra);
- scrapings of the conjunctiva, nasal cavity, oropharynx;
- semen, prostate secretion;
- scraping from erosive and ulcerative lesions;
- urine;
- sputum;
- feces;
- other biological fluids (amniotic, cerebrospinal fluid, amniotic fluid, articular fluid);
- biopsy material of the lungs, liver, gastrointestinal tract;
- bronchoalveolar lavage.
Rules for the delivery of biological fluids for PCR
Polymerase chain reaction is a method that requires strict adherence to recommendations even at the stage of collection of biological material.

Inadequate sampling can lead to false positive or false negative results.
- If a special transport medium is required for the transportation and storage of biological material prior to analysis, it is recommended to use a transport solution manufactured by the same company that supplies the PCR kits test.
- Sampling for PCR test is carried out separately from samples intended for other studies. Disposable sterile instruments, containers and gloves are used for selection.
- It is recommended to take samples for analysis before the start of therapy and 2 weeks after its end.
- It is recommended to donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach. Whole blood is stored in anticoagulant tubes (EDTA, citric acid sodium). Other anticoagulants, such as heparin, are not allowed because they inhibit the PCR reaction. Serum is stored without anticoagulant.
- When collecting urine, it is necessary to collect the morning urine (first portion), about 30-40 ml. It is allowed to store the sample until it is sent to the laboratory for no more than 2 hours.
- Before collecting saliva, rinse the mouth with saline. It is recommended not to eat for 4 hours before collecting the sample. The amount of sample is from 3 to 5 ml. Saliva is collected immediately before analysis; the material can be stored frozen at minus 20 ° C.
- Disposable tubes are used to collect sputum samples. The required sample volume is from 5 to 10 ml. Before analysis, the sample can be stored at 4 ° C for 24 hours.
- The synovial fluid is collected with a syringe. It is recommended to use disposable sterile equipment for collection and storage of material. The required sample volume is 1 ml.
- To take a sample of the epithelium of the mucous membranes, probes (for example, from viscose) or cytobrushes are used.
How to prepare for PCR analysis
Correct collection of material is necessary to obtain correct test results, therefore it is recommended to observe the following rules:
- It is recommended to collect biological material during an acute course of infection, but antibacterial agents should not be taken at this time.
- Before taking samples from the vagina, it is recommended to stop taking any vaginal medications, and also not to carry out procedures such as douching for 24 hours.
- Before taking a sample from the urethra, you should refrain from urinating for 1.5-2 hours, treat the external entrance of the urethra with saline.
- It is recommended that urine samples be collected on an empty stomach in the morning.
- Before collecting saliva, food, medication, and alcohol are discontinued 12 hours prior to sample collection. Before collecting the sample, the oral cavity and teeth are cleaned with a toothbrush without paste, the oral cavity must be thoroughly rinsed with water, without the use of additional agents. Saliva is collected with a syringe.
- When taking scrapings from the oropharynx, do not eat or drink water for 2 hours. It is not recommended to use throat sprays, chewing gums, lozenges, or brush your teeth.
- When collecting sputum, it is recommended to thoroughly process the oral cavity: brush your teeth, rinse your mouth. Collect morning mucous or purulent discharge. A 3 ml sample is sufficient for testing. To increase the volume of secretions, you can take expectorant inhalations or drugs.
- A smear from the conjunctiva of the eye is taken on the inner side of the lower eyelid, without touching the eyelashes.
Swabbing procedure (for women and men)
When examining the urogenital tract in women, scraping of the vaginal mucosa, urethra and cervical canal is performed. Samples are taken prior to manual inspection. Sampling is performed using sterile probes with a swab or cytobrush.
Before the procedure, the outer area of the urethra is treated with a sterile solution, excess mucus is removed from the vagina and cervix. The probe is inserted into the urethra or into the cervical canal to a depth of 0.5-1.5 cm. The material is collected with gentle rotational movements.
A swab is taken from the back of the vagina. When removing the probe, it is not recommended to touch the walls of the vagina with it.
The probe (its working area) is washed in a test tube with a transport liquid, which is supplied by the manufacturer of a kit for PCR diagnostics, and squeezed against the walls of the test tube. Sometimes the kit manufacturer recommends breaking the probe and leaving the working part directly in the tube. This reduces sample loss.

It is not recommended to take smears for PCR after colposcopy. Before taking the material, it is recommended to stop taking vaginal tablets and drugs in 2-3 days. The smear is taken no earlier than 2-3 days after the end of menstrual flow.
When taking a smear from men, the outer region of the urethra is treated with a sterile solution, and excess secretions are removed. A sterile probe is inserted 3-4 cm to collect a sample. The working part of the probe is washed in a test tube with a transport solution.
How are PCR tests deciphered
In the results of the PCR test, in addition to the name of the analysis and the test results, it is indicated norm or reference values with which the obtained result can be compared:
| Analysis name | Result | Norm |
| Chlamidia trachomatis DNA | Positive | Negative |
| Micoplasma hominis DNA | Negative | Negative |
A positive result means the presence of a pathogen DNA in the biological material, a negative result means its absence.
When assessing viral load, DNA is quantified. In this case, the table of results contains the numerical value of the number of copies of the detected DNA, for example:
| Index | Result | Reference values |
| Quantification of Hepatitis B Virus DNA | 4.3 * 10v 3 st. | <300 clinically insignificant; > 300 positive |
In the case of qualitative and quantitative analysis, the results are assessed by the attending physician.
When analyzing the results obtained, the following errors are often encountered:
- Early control PCR test after the end of the course of antibiotics (after 1-2 weeks). The DNA of the infectious agent remains in the patient's body for several weeks after the cells of the infectious agent are destroyed by therapy. Therefore, the obtained positive result is false positive, and the conclusion that the therapy did not work is erroneous. If we are talking about causative agents of infection on the skin epithelium, then the test is recommended not earlier than a month after the end of treatment.
- When interpreting PCR analysis of some infections, for example, cytomegalovirus infection, a positive result does not always mean the course of the infectious process and the need for therapy. In only 60% of cases with a positive PCR result, patients develop clinical signs of the disease.
- When interpreting PCR tests for human papillomavirus a positive test can be mistakenly interpreted as the cause of the development of oncological processes, although in 90% of patients, HPV infection resolves in 6-24 months. If the result is positive, it is necessary to conduct a study of the epithelium of the cervix, and only then assess the risk of cancer.
- In studies of infections of the urogenital tract in women, it is recommended not only to determine opportunistic infections, but also to compare their number with the number of Lactovacillus, which are considered the main representatives of the normal microflora of the vagina. Such an analysis allows you to determine dysbiosis, correctly interpret the results of the PCR test and prescribe therapy.
Polymerase chain reaction is a method that is used to quantitatively study viral and bacterial load. It should be borne in mind that for some infections there is no clear regulation that allows you to determine the clinical significance of the results obtained.
This means that the interpretation of the results is subjective and can be erroneous. So, for example, opportunistic Ureaplasma, Micoplasma, Gardnerella in the absence of complaints and clinical signs of inflammation, they do not require therapy. Unreasonable prescription of therapy leads to an increase in cases of dysbiosis and vaginosis.
Video about PCR analysis
PCR diagnosis of viral infection: explanation of the method: