In the treatment of dangerous infectious diseases injections of special immune sera are required. To avoid the development of undesirable reactions of the body to the introduction of these drugs, the method of their introduction is used according to Bezredko.
Record content:
- 1 What the PSNI and PSS vaccines contain
- 2 Mechanism of action
- 3 Indications for vaccination
- 4 The timing of vaccine administration
- 5 How vaccination is tolerated
- 6 Possible reactions and complications
- 7 Instructions for use
-
8 Serum injection technique according to the Frequently
- 8.1 Anti-tetanus serum
- 8.2 With butulism
-
8.3 Antidiphtheria serum
- 8.3.1 With a toxic form of diphtheria
- 9 How long does the vaccine last?
- 10 Vaccine videos
What the PSNI and PSS vaccines contain
PSCHI is a vaccine containing specific tetanus antibodies (1 ml contains 100 IU of active ingredient). Additional components of the drug are represented by glycine, which acts as a stabilizer, water for injection and sodium chloride.
PSS (tetanus toxoid) is a protein fraction of horse blood serum, which was immunized with toxoid (tetanus) or toxin. It contains immunoglobulins. It also contains chloroform. Serum is produced in the form of a transparent or yellow liquid.
Mechanism of action
Tetanus is one of the most dangerous infectious diseases - the death rate of children is about 90% for adults, this figure ranges from 20 to 80%. Therefore, the easiest way to protect a person from disease is to vaccinate. The vaccine contains weakened tetanus (if the vaccine is complex, then diphtheria) toxins.
These toxins retain their immunogenic properties, therefore, after being introduced into the body, they cause an immune response to their presence in the form of the production of specific antibodies. The body remembers the structure of this antigen and, in the event of a disease, the antibodies produced recognize the pathogen and help actively fight it. Thus, acquired immunity is developed in the body.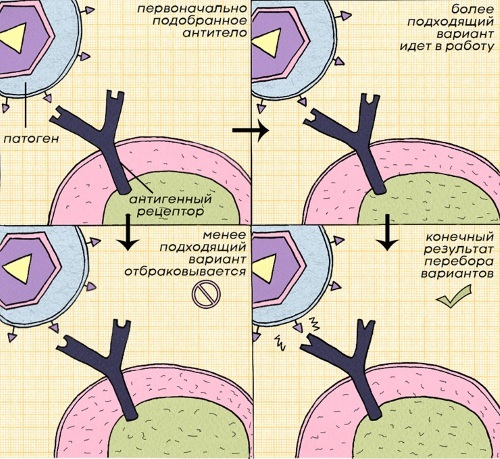
He, in turn, is divided into natural and artificial acquired species. With natural immunity, antibodies are synthesized by the body on its own after suffering diseases. The body acquires passive immunity by artificially introducing antigens against various diseases - that is, vaccination.
After the administration of the vaccine, the maximum concentration of antibodies in the blood is reached in 1-2 days. The period of elimination from the body is 6 to 8 weeks.
Indications for vaccination
The drug is used in 2 main cases:
- For the prevention of disease (including emergency).
- For the treatment of tetanus / diphtheria.
Emergency prophylaxis is carried out in the event of various injuries (industrial, household injuries, frostbite, insect bites, penetrating injuries, splinters, bedsores, etc.), when the causative agent of infection (tetanus bacillus) can enter the body through open wound.
The main habitat of this microorganism is the soil, where it can remain active for several years. Routine vaccination is carried out according to the established vaccination schedule.
The timing of vaccine administration
The introduction of serum for people who have been injured, it is necessary to carry out as soon as possible - within 20 days (if patients were vaccinated against tetanus more than 5 years ago). It is during this period, if the pathogen enters the body, the disease can proceed in a latent form - without the manifestation of the corresponding symptoms.
If a person has not been previously vaccinated against tetanus / diphtheria or does not have a full course of routine vaccinations, in addition to the vaccine, he is injected with a special serum. It helps in a short period of time to create and develop the body's specific immunity to the causative agent of the disease.
How vaccination is tolerated
Vaccination against tetanus and diphtheria is usually easily tolerated - without significant deterioration in well-being. Often, grafting is done with a complex drug that contains several antibodies at once. For example, vaccination against whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus (DTP) or tetanus and diphtheria (DTP).
Such a vaccine is more likely to cause adverse reactions, since it is a multicomponent vaccine. In order to avoid deterioration of health after vaccination, it is recommended within 30 minutes. stay in the hospital - if unpleasant symptoms develop, doctors will provide assistance.
Possible reactions and complications
The body's response to the vaccine can be of 2 types:
- Post-vaccination reaction (develops immediately or within a few hours after the administration of the vaccine and disappears on its own about 3 days after vaccination).
- Post-vaccination complication (causes changes in the body and deterioration of health, which are long lasting, therapy may be required).
The types of reactions and possible complications to vaccination are presented in the table below:
| Body reaction | Symptoms | Frequency of manifestation |
| Local reaction | Swelling, pain, redness, and swelling at the injection site. | From 25 to 80%. |
| Systemic reactions | Increased body temperature. | About 10% of cases. |
| Weakness of the body, irritation. | Up to 25% of the total cases of vaccinated people. | |
| Complications | Brain damage. | 1 case per 300 thousand (for complex vaccination with whooping cough). |
| Severe allergic reactions. | 1 case per 100 vaccinated. |

When vaccinated in childhood, children may complain of pain while walking, itching at the injection site. In adulthood, the rate of vaccination reactions decreases.
It should be noted that the risk of possible complications after vaccination is hundreds, and in some cases, thousands of times less than the risk of complications after an infectious disease.
Instructions for use
Serum with immunoglobulin is injected by intramuscular injection into the anterior lateral part of the thigh in children under the age of 3 years. For older children and adults, the vaccine is administered under the scapula or brachial muscle. Before the injection, the vial with the drug must be kept for 2 hours at a temperature of 18 to 22 0WITH.
The opening of the bottle and the direct vaccination procedure are carried out in compliance with the relevant sanitary standards and rules. To avoid the formation of foam in the preparation, a needle with a wide lumen should be taken to set the vaccine, and a different needle should be used to inject the preparation.
When treating tetanus, the drug is administered intravenously or into the spinal canal. The dosage of the medicine is determined by the doctor depending on the severity of the disease.
Serum injection technique according to the Frequently
Often - a French microbiologist, who proposed a method of administering medicinal sera based on reducing or the prevention of a negative reaction of the body and the development of complications to them (in particular, in the form of anaphylactic shock). This method provides for fractional administration of drugs.
This allows you to neutralize antibodies and reduce the concentration of active substances in the blood, as a result of which the subsequent administration of antigens does not cause the development of complications.
Serum injection often has a specific algorithm:
- The ampoule with the drug must be carefully examined. If there is sediment, turbidity, impurities in the liquid, the ampoule is damaged or there is no label with the necessary information, it is prohibited to use such a medication.
- Before opening, the end of the ampoule must be treated with sterile cotton wool. After opening the ampoule should be covered with a sterile napkin.
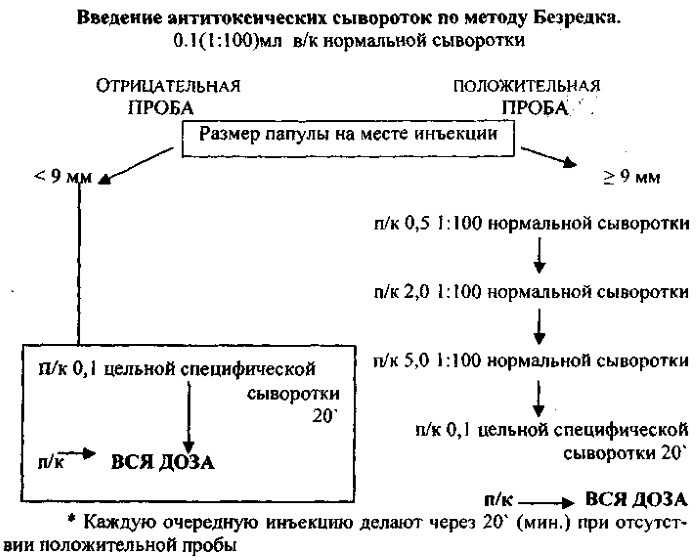
Algorithm for the introduction of serum by Frequently - Before you enter a therapeutic dose, you need to test the body's sensitivity to the drug by means of a sample. For this, a special diluted serum is used (it comes with the drug and is marked in red). The sample is injected subcutaneously into the arm above the wrist, having previously disinfected the site of the future injection. The drug is injected with a special tuberculin syringe with a thin needle. As soon as the cut of the needle enters the skin, 0.1 ml of the diluted serum is injected. If after 20-30 minutes. the diameter of the papule that formed as a result of the injection is less than 0.9 cm, and there is slight redness around it, the test is considered negative.
- After that, 0.1 ml of undiluted serum should be injected subcutaneously into the outer surface of the shoulder.
- After half an hour from the moment of injection (if there is no reaction to repeated administration of the drug), the remaining prescribed dose is injected intramuscularly.
The method often underlies the introduction of most sera used to treat and prevent the development of various diseases.
Anti-tetanus serum
Serum is introduced according to the above algorithm. The dosage of the drug during treatment is 1500-2000 IU for each kg of human weight. Such a high dose allows you to quickly bind tetanotoxin, which, after infection of the body, spreads in the lymph, blood and cerebrospinal fluid of a person, provoking muscle spasms.
If a severe course of the disease is observed, the following serum injection scheme is allowed:
- Intramuscularly - 100 thous. ME (injected into the gluteus muscle or under the scapula).
- Intravenously - up to 50,000 IU. In this case, the indicated dosage is diluted with an isotonic sodium chloride solution (the ratio is from 1: 5 to 1:10) and heated to a temperature of 37 0WITH.
With the introduction of these doses, antitoxic antibodies are produced in the body for 3 weeks, therefore, repeated administration of serum is not required. Additionally, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics. If necessary, anti-shock measures can be taken - warming, the use of stimulants of the cardiovascular and nervous systems, blood transfusions, etc.
If a test for sensitivity to tetanus toxoid has shown a positive result, then its administration can only be carried out with obvious indications (for example, extensive wound contamination).
With butulism
The introduction of serum for botulism is often carried out according to the general scheme with a mandatory test for sensitivity to the drug. The input is prescribed immediately after the establishment of the clinical diagnosis, since it has the maximum therapeutic effect in the first 72 hours from the onset of the disease.
The dosage of a preparation containing equine antitoxin depends on what type of disease the person has. For example, with serotype B, it is necessary to inject 15-20 thousand. IU.
If the type is unknown, then a complex of one-component preparations or polyvalent serum is introduced according to the following scheme:
- 10,000 IU type A antitoxin;
- 10,000 IU type E antitoxin;
- 15-20 thous. IU of type B antitoxin.
Regardless of the severity of the disease, 1 therapeutic dose of serum must be administered intravenously. It is preliminarily diluted in 200 ml of warmed saline solution. If the botulism toxin has already penetrated into the muscle-nervous joints, the injected antitoxin cannot neutralize it, but it can slow down or completely stop the progression of the disease.
And with wound botulism (ingestion of C. Botulinum, causing botulism, into an open wound with their subsequent reproduction) reduces the risk of complications, including death. To avoid the development of allergic and other undesirable reactions of the body to the administration of serum, the patient should first be injected with 60-90 ml of prednisolone.
Antidiphtheria serum
Diphtheria is a dangerous infectious disease caused by diphtheria bacillus. In 95% of cases, the infection affects the mucous membranes of the oropharynx. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets or through direct contact with an infected person. In some cases, cats, horses and dogs can be carriers of the infection.
Anti-diphtheria serum is used to treat diphtheria. Once injected into the body, it neutralizes the infection toxin that circulates in the blood.
People who are hypersensitive to equine serum protein may develop anaphylactic shock. To avoid this, it is imperative that an intradermal test is performed before starting therapy using the above method.
If there is no specially diluted serum, it is prepared independently by mixing 0.1 ml of medicinal serum with 9.9 ml of sterile sodium chloride solution. In case of a negative reaction to the introduction of the vaccine, 0.1 ml of the drug should be injected subcutaneously in undiluted form, and after 30 minutes. - the remaining dose.
Serum dosage depends on the severity and form of the disease:
- Localized form (pharynx, nose, skin of the eyes, genitals) - 10,000-20,000 IU is administered by intramuscular injection.
- Oropharynx with spread (plaque appears on several organs, for example, on the tonsils and larynx) - 20,000-30,000 IU is also injected intramuscularly.
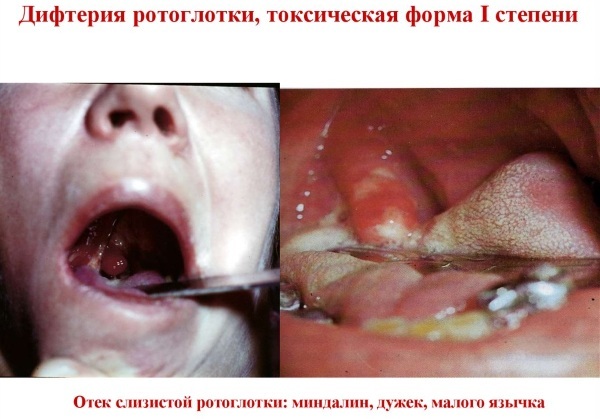
With a toxic form of diphtheria
After a week after the disease, the person either recovers, or the disease (if untreated) turns into a more severe form - toxic. Its occurrence is due to the systemic effect of the diphtheria toxin on the body, which is secreted by the diphtheria bacillus.
This form of the disease is difficult with pronounced symptoms:
- High body temperature - 39.5-41 0WITH.
- Strong headache.
- Pallor of the skin.
- Swelling of the tonsils, shortness of breath.
- Soreness and enlargement of the lymph nodes.
Serum dosage for toxic diphtheria is presented in the table below:
| The degree of toxic diphtheria | Serum dosage (in IU) |
| 1st | 30000-50000 |
| 2nd | 50000-60000 |
| 3rd | 60000-80000 |
The injection is carried out through intramuscular and intravenous administration.
The specified amount of serum is injected once. If necessary, the same dose of the drug is administered after 24 hours. In severe cases of the disease, the total dose can be increased to 90,000-120,000 IU, and sometimes up to 150,000 IU.
With the development of toxic shock, large hemorrhages caused by incoagulability of the blood (DIC syndrome) and other disorders, 2/3 of the dose is immediately administered to the sick person, and within 24 hours. ¾ part of the total dosage is introduced. Simultaneously with the serum, the patient is prescribed antibiotics for 5-7 days.
They do not inhibit the diphtheria toxin, but contribute to the destruction of dangerous microorganisms that complicate the course of diphtheria.
How long does the vaccine last?
The introduction of serum by Frequently allows you to minimize the development of complications after the ingestion of foreign protein into the body. The introduction of a therapeutic dose is usually carried out once - with proper and timely treatment, it allows you to cope with the disease.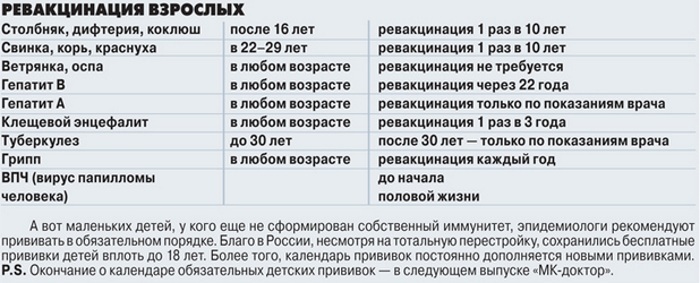
But transferred diphtheria and tetanus do not guarantee that a person will not get sick with them again. Vaccines do not provide such protection against disease. But the developed anti-diphtheria and anti-tetanus antibodies through vaccination protect the human body from the penetration of pathogens.
Therefore, these diseases either do not have time to develop, or they will proceed in a mild form, without causing complications.
The duration of vaccination is directly related to the age at which the person was vaccinated:
- Children of the 1st year of life receive 3 vaccinations against diphtheria and tetanus (at 3 months, 4.5 months and at six months) with a break between them at least 45 days.
- At 1.6 years old, the 1st revaccination is done.
- 6-7 years old - 2nd revaccination.
- 14 years old - 3rd revaccination.
- Children over 18 years of age and adults - revaccination is done every 10 years from the moment of the previous vaccination.
If a person was not vaccinated in childhood, then in order to form specific immunity, he needs to do 3 vaccinations. If the planned schedule for receiving vaccinations is violated or if more than 20 years have passed since the moment of vaccination, a person must be vaccinated twice with an interval between vaccinations of 40 days.
Correct administration of medicinal preparations by the method often minimizes the risk of allergic reactions and prevents the occurrence of anaphylactic shock, provided that all the rules and the algorithm of actions are observed.
Vaccine videos
About the effectiveness of vaccines:


