Content
- The effect of massage on muscles
- Human Muscle Atlas
- Human muscle anatomy and techniques for working out them using massage
- Muscles of the head and neck
- Back muscles
- Abdominal muscles
- Muscles of the buttocks
- Arm muscles
- Leg muscles
- Video about human muscles for massage
Massage induces relaxation, relieves stress, and new research has shown that deep touching relieves pain and promotes healing of muscle lesions in humans. There are various techniques for this, the drawings of which with captions can be seen later in the article.
The effect of massage on muscles
Massage is a manual procedure in which muscles are pressed, stroked and rubbed. Massage therapy has many benefits and few risks when administered by a trained professional.
Effect on the body:
- Relieves tension. Deep kneading relieves tension that builds up in muscles and lining called fasciae. Transverse massage helps to separate muscle fibers and break up adhesions that may form in the muscles.
- Increases blood flow. Massage therapy restores the flow of fluid, oxygen and other nutrients to the damaged area. In many cases of injury, massage can shorten the time it takes for the muscle to heal properly.
- Increases the range of motion. For any injury or chronic poor posture, range of motion may be reduced due to muscles that are short and tense or have internal adhesions. Massage therapy breaks down adhesions and lengthens muscles, helping to restore the correct range of motion.
- Reduces pain. Massage therapy blocks pain signals, removes metabolic products such as lactic acid and carbon dioxide from the muscles.
Human muscles (a drawing with the signatures of various massage techniques can be found in the reference literature) after medical manipulations become functional.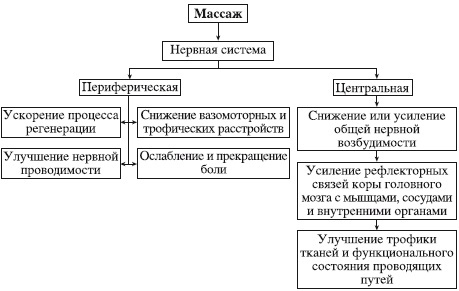
There are many different types of massage, including the common ones:
- Swedish massage. It is a gentle form of massage that uses long strokes, kneading, deep circular motions, vibration and tapping.
- Deep massage. In this case, slow and powerful blows are used to affect the deep layers of muscles and connective tissue. The technique is used more often to repair damaged muscles.
- Sports massage. The technique resembles Swedish massage and is intended for athletes to prevent or treat injuries.
-
Trigger point massage. At the same time, attention is focused on areas of dense muscle fibers that are formed in muscles after injury or excessive stress.

Massage is considered part of complementary and integrative medicine. It is increasingly being offered alongside standard treatments for a wide range of conditions and conditions.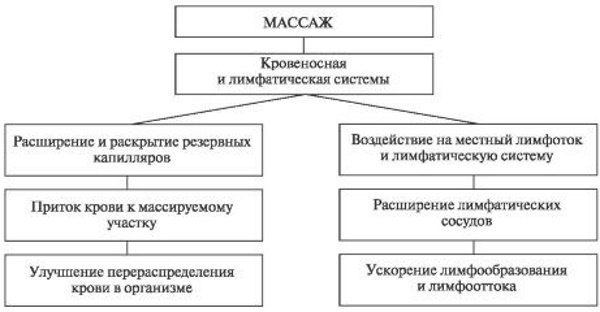
Despite its benefits, it is not intended to replace conventional medical treatments. There are certain risks of massage.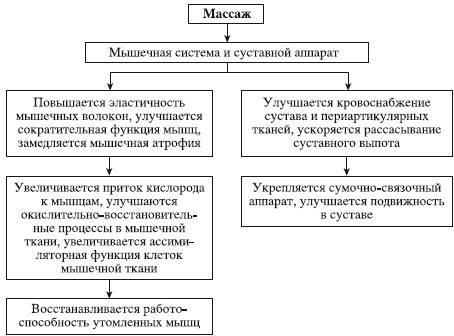
Manipulations cannot be carried out in the event of:
- bleeding disorders or taking blood-thinning drugs;
- burns or healing wounds;
- deep vein thrombosis;
- fractures;
- severe osteoporosis;
- complex cases of thrombocytopenia.
Human Muscle Atlas
Human muscles (the figure with the captions is presented later in the article) is about ½ of the body weight. There are 3 types of muscle tissue:
- visceral;
- heart;
- skeletal.
Smooth or visceral muscles are under involuntary control. It is present in the walls of the internal hollow organs. Cardiac is the main element of the heart myocardium and is responsible for rhythmic contractions.
Skeletal muscles attach to and move bones, contracting and relaxing in response to voluntary messages from the nervous system. Skeletal muscle tissue is made up of long cells called muscle fibers that have a striped appearance. Muscle fibers are organized into bundles supplied by blood vessels and innervated by motor neurons. About 700 muscles are attached to the bones of the skeletal system.
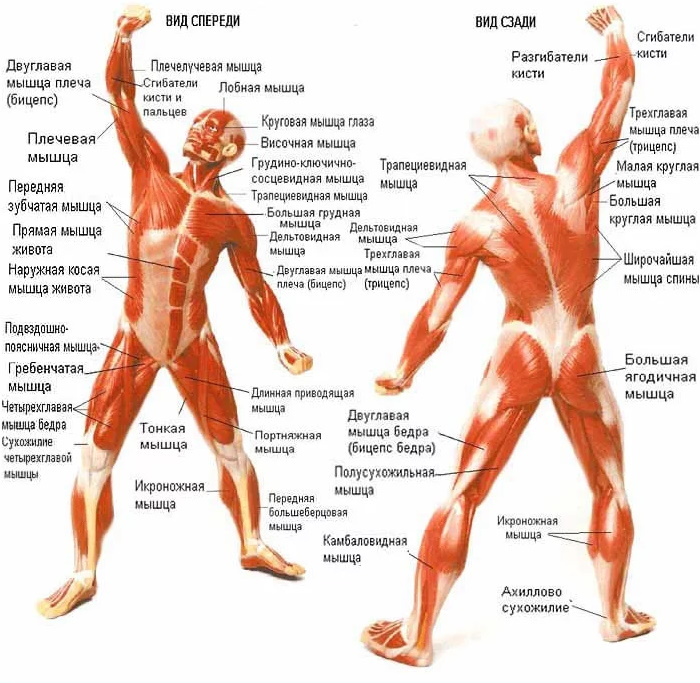
The main skeletal muscle groups of the human body are:
- Superficial and deep anterior muscles of the upper body.
- Superficial and deep back muscles of the upper body.
- Front and back muscles of the shoulder.
- The anterior and posterior muscles of the forearm.
- The anterior and posterior muscles of the upper leg.
- The back muscles of the lower leg.
- Anterior calf muscles.
- Respiratory muscles
Human muscle anatomy and techniques for working out them using massage
The therapist must know and understand the anatomical structures and their location, as well as their functions, interactions. The appropriate medical terminology should be able to correlate with the practice of therapeutic massage, indications, contraindications.
In addition to knowing the types of muscle tissue, the massage therapist should understand the following properties:
| Muscle Anatomy | Fiber bundles |
| Nerves and blood supply | |
| Attachments of muscles (tendons) | |
| Physiology | Muscle contractility |
| Extensibility | |
| Irritability | |
| Excitability | |
| Elasticity | |
| Functions | Muscle movement, insertion |
| The movement of the main muscle and helpers: synergists and antagonists | |
| Diseases | Stretching |
| Atrophy | |
| Myalgia | |
| Muscular dystrophy | |
| Muscle fatigue | |
| Fibromyalgia |
 Having knowledge of anatomy and physiology, determining on the basis of this the appropriate type of massage, you can achieve the desired physiological result.
Having knowledge of anatomy and physiology, determining on the basis of this the appropriate type of massage, you can achieve the desired physiological result.
Muscles of the head and neck
A person's neck and head muscles perform many tasks, including movement, chewing, swallowing, speech, facial expressions, and eye movement. The figure with the signatures of these structures is presented later in the article.
| Mimic | Draws in the skin for an infinite number of facial expressions, lip movements. |
| Chewable | Move the lower jaw in relation to the rest of the skull. |
| Temporal | Raise the jaw strongly during chewing and gently during speech. |
| Eye muscles | Provide movement from above, below, laterally and medially, as well as rotation of the eyeball. These muscles produce extremely subtle movements almost constantly throughout the day with tremendous speed and precision. The inner muscles of the eye work tirelessly to dilate the pupils and focus the lens of the eye for clear vision. |
| Muscles of the neck | They are responsible for basic movements in the muscular system of the head and neck. They move their heads in all directions, pulling the skull and jaw towards the shoulders, spine, and scapula. Working in pairs on the left and right side of the body, control flexion and extension of the head and neck. Working individually, turn the head or bend the neck to the left or right. |
| Muscles of the tongue | Allows the tongue to perform a series of complex movements when chewing and swallowing, as well as to reproduce speech. Of these, 4 sets of external muscles (connecting the tongue to the surrounding bones) move the tongue in almost any direction. |
While most muscles connect to bones and only move them, facial muscles mainly connect bones to skin.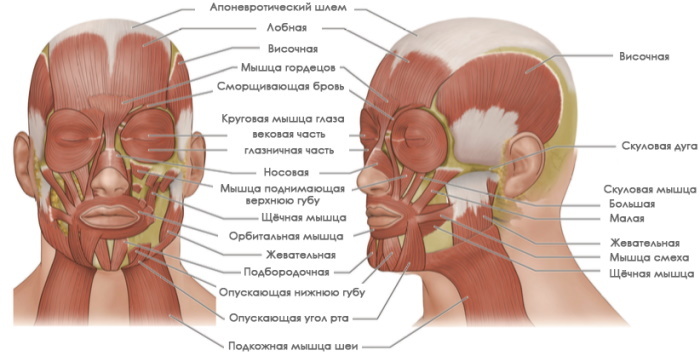
A head massage is a massage of the head, neck and shoulders using a range of techniques that release tension in the upper body.
- Stroking.
- Kneading.
- Circular friction.
- Point massage, acupressure.
All actions on the scalp stimulate the nerves and blood vessels around this area, relieve muscle tension. The procedure can be carried out with your fingertips using essential oils.
Neck massage is directed to a group of muscles such as sternocleidomastoid, scalene and upper trapezius. This relieves stress, relieves headaches.
The most common techniques are:
- Acupressure.
- Mobilization. Includes pressure on the spinous and transverse processes located in the cervical spine.
- Rolling skin. Twisting the skin with the fingers is effectively used to reduce the restrictions imposed by the fascia as well as to increase blood flow.
Back muscles
The muscles of the person (drawing with captions will help you understand the massage technique) in the chest, upper back, control many movements of the arms and head.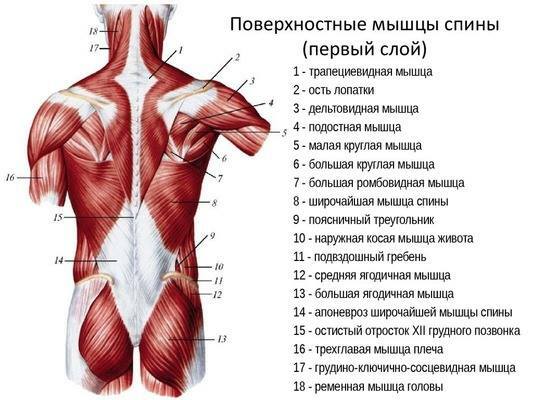
| Major muscles | Actions |
| Latissimus muscle | Superficial muscle leading the shoulder to the trunk |
| Pectoralis major, coracohumeral, biceps brachii, anterior deltoid | Shoulder flexion |
| The infraspinatus, large and small round, the broadest muscle of the back, triceps muscle of the shoulder, the back of the deltoid | Shoulder extension |
| The pectoralis major muscle and the coracohumeral | Connect the humerus in front with the shoulder blade and ribs, bending and bringing the arm to the front of the body. |
| The large circular muscle on the back of the arm and the latissimus dorsi | They expand and bring the hand to the scapula and vertebra. |
| Muscles of the diaphragm | A strong, thin, domed muscle that spans the entire lower border of the rib cage, separating the chest from the abdominal cavity. The contraction of the diaphragm causes it to descend towards the abdominal cavity, expanding the space in the chest cavity and expanding the lungs, filling them with air. |
| Intercostal muscles | Raise the ribs during deep breathing to further expand the chest and lungs and allow more air to flow to the body. |
| Lower back, erector spine and square loin muscle | They flex the spine laterally, provide posture and body stability, keeping the spine upright. |
The lower back massage focuses on a variety of muscles, including the latissimus dorsi, square the lower back muscle and the erector muscles that are located around the lower half of the skeleton.
- Acupressure is a technique used to massage the lower back.
- Kneading is applied to areas containing soft tissue and involves slowly stretching and contracting the muscles. Increases cellular metabolism and stretches connective tissues.
- Myofascial release. Relieves tension in myofascial structures.
- Push-up. A technique in which muscle tissue is grasped from both sides of the back and pulled towards the center helps to stretch, relax the muscles, and reduce pain.
The upper back massage is performed on the muscles of the middle and upper spine.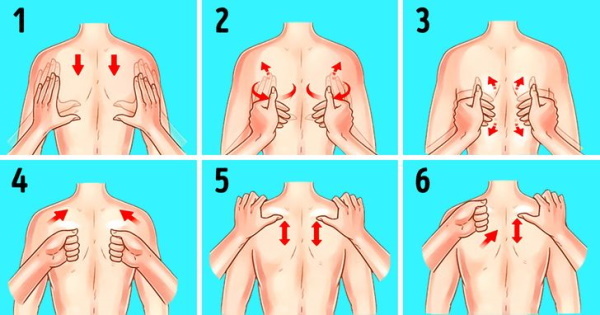
For this, the following techniques are used:
- Acupressure. It is performed on trigger points and muscle nodes using the fingertips. Muscle nodes break down and soften when pressure is applied.
- Friction is performed with your fingertips to increase blood flow throughout the body.
- Myofascial release helps to relax tense muscles, increase the temperature of soft tissues. This increases the elasticity and flexibility of tissues, increases blood circulation and lymphatic circulation.
- Twisting the skin involves grasping and rolling the skin between the toes, which looses tight muscles and fascia.
- Eflorage (Swedish massage) increases muscle temperature, muscle elasticity.
Abdominal muscles
The transverse and rectus muscles of the abdomen, lower back and pelvis are separated from the muscles of the chest by the muscular wall of the diaphragm. They protect the abdominal organs, participate in the movement of the trunk, the formation of posture, and body stability.
Attached to the pelvis are the muscles of the buttocks, lower back, and thighs. The psoas and iliac major muscles serve as flexors of the torso and hip at the hip joint, and also rotate the hip laterally. The muscles of the abdomen and back form a kind of muscle corset that supports the spine and relieves stress on the intervertebral discs.
Abdominal massage is performed in the area of:
- transverse;
- straight;
- external and internal oblique muscles.
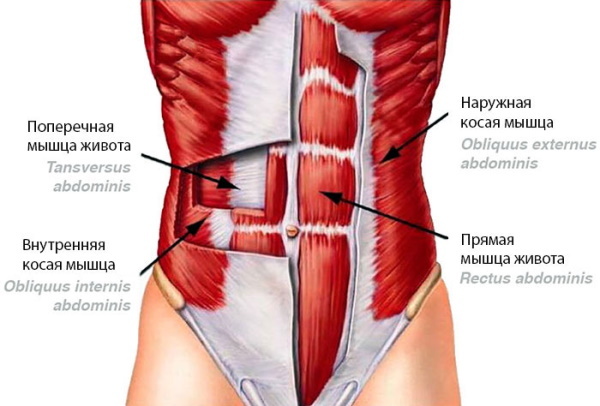
A number of techniques are used to relieve stress:
- Kneading improves blood flow, lymph flow, relaxes tissues.
- Deep stroking is performed with the palm of the hand in the direction of the muscle fibers. Used to lengthen and mobilize soft tissues.
- Twisting the skin helps to relax. By rolling your skin and muscles slightly, you can relax your body. The pressure on the skin stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system in the body.
- Compression relaxes and stretches the muscles and relieves stress.
Muscles of the buttocks
Attached to the pelvis are the muscles of the buttocks, lower back, and thighs. All of them, including the gluteus maximus and hamstrings, expand the hip to support body weight. Other muscles in the pelvis, such as the psoas major and iliac muscles, serve as flexors of the torso and hip at the hip joint and also laterally rotate the hip.
Massage techniques:
- Squeezing muscles increases blood circulation, increases muscle temperature. At the same time, cellular metabolism is enhanced.
- Kneading is used to improve blood flow and ease muscle tension.
- Deep strokes are performed with flattened hands and fingers. Strong pressure is used to penetrate deep into the muscle tissue.
- Kneading trigger points, which are located in the center of the muscle fiber. While massaging the buttocks, the pressure on the pain points helps to break down and soften the muscle nodes.
Arm muscles
The human muscles (the figure with the captions clearly illustrates them) in the chest and upper back are used to move the humerus:
- The deltoid and supraspinatus muscles pass between the scapula and humerus to abduct and flex and extend the arm. These muscles allow you to raise your arm or swing it, as if you were throwing a ball from below.
- Rotation of the humerus is achieved by the action of the subscapularis, infraspinatus, and circular minor muscles that run from the scapula to the humerus. These 3 rotator cuff muscles, together with the supraspinatus muscle, end in broad tendons that completely surround the head of the humerus and form a structure known as the rotator cuff. Its function is to hold the humerus in place.
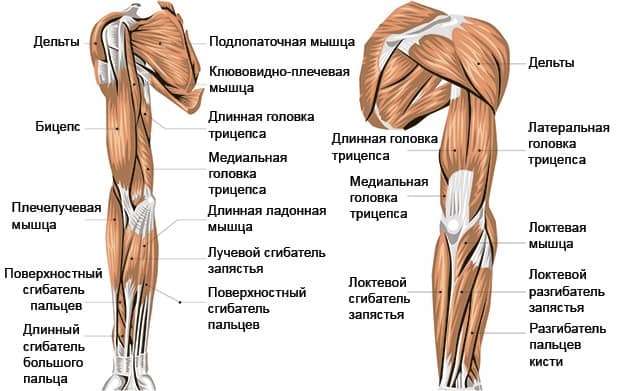
The shoulder muscles are responsible for flexion and extension of the forearm at the elbow joint.
- Flexion occurs due to a group of 3 muscles - flexors. They are located on the front of the shoulder and extend from the humerus and scapula to the ulna and radius of the forearm.
- The biceps brachii acts as an instep support for the forearm, turning the radius and moving the palm forward.
- On the back of the shoulder is the triceps brachii muscle, which acts as the extensor of the forearm at the elbow and the humerus at the shoulder.
Most of the muscles that move the wrist, hand, and fingers are located in the forearm. These thin, belt-like muscles extend from the humerus, ulna, and radius and penetrate the carpal, metacarpal, and phalangeal bones through long tendons.
Muscles on the front of the forearm, such as the radial flexor of the wrist and the superficial flexor of the fingers, form the flexor group that flexes the arm at the wrist and each of the phalanges. Muscle tendons run through a small corridor in the wrist known as the carpal tunnel.
On the back of the arm, the extensor muscles run from the humerus to the metacarpals and phalanges in the form of long thin ribbons. The extensors are usually somewhat weaker than the flexor muscles.
The muscles of the forearm produce two specific movements:
- supination (forward rotation), which is carried out by the biceps of the shoulder and the instep support muscle of the forearm;
- pronation (backward rotation) of the forearm and hand, which is produced by the round pronator of the forearm.
The muscles of the instep and pronator round originate in the humerus and ulna and attach to opposite sides of the radius to rotate the wrist in opposite directions.
The arm massage focuses on the muscles that make up the upper and lower arm.
- Deep blows are aimed at penetrating further into the muscle tissue, relieving tension. Deep stroking helps raise muscle temperature by creating friction between hands and skin.
- Friction is a method of increasing the temperature of the muscles, helping to break down the collagen fibers that accumulate in the muscles.
- Kneading is performed on areas containing soft tissue. At the same time, pulling and compressing actions are used to relieve constraint and increase cell metabolism.
- Lymphatic drainage is upward pressure on the muscles. Helps remove metabolic waste through the glands and flush excess fluid.
Leg muscles
Supporting, balancing and moving the body is the work of the muscular system of the legs and feet. From the big, strong muscles of the buttocks and legs to the tiny thin muscles of the feet and toes, all muscles exhibit tremendous strength by continually making small adjustments to balance, whether the body is at rest or movement.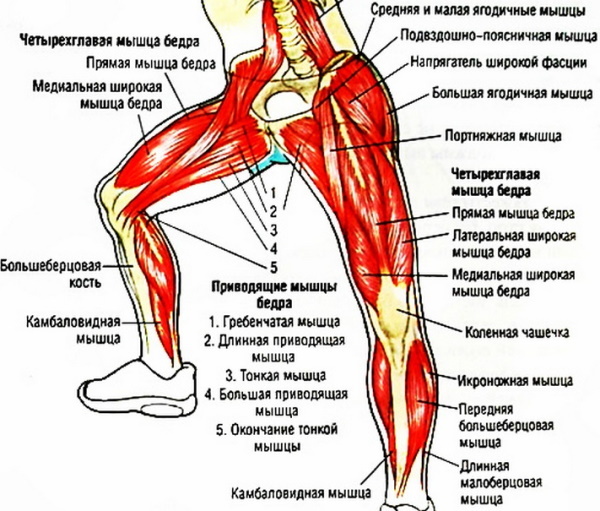
The powerful muscles of the hip, glute and pelvis drive the flexible, articulated hip joint.
The foot massage focuses mainly on the muscles around the front and back of the foot. Many muscles are located here, including: the anterior tibial muscle, abductor thumb, long and short extensor of the thumb, posterior interosseous and psoas muscles.
Massage techniques:
- Acupressure or acupressure is performed with the fingers and involves applying pressure to specific areas of the foot. Helps break down nodes and increase blood flow.
- Friction is performed with your fingertips, puts pressure on muscle fibers, breaks down the collagen fibers that accumulate in the muscles.
- Rolling the skin, twisting is aimed at reducing the restrictions created by the fascia.
- Pressure on trigger points to soften and destroy muscle nodes. Painful points are more often located in the middle of the muscle fiber.
Anatomy is a valuable part of massage therapy. A deep understanding of the internal systems, the interaction of human muscles, will help you learn about the many reactions of the body to massage methods and get the benefits from them. And also drawings with signatures, advice from experienced masseurs will help to master some massage techniques.
Video about human muscles for massage
Anatomy for masseurs:



