Content
- The concept of arbitrary memory in psychology
- History of the study of arbitrary memory
- Stages of mastering arbitrary forms of memory
- Arbitrary modal-specific memory in children and adolescents with different types of dysontogenesis
- results
- Development of arbitrary memory
- Exercise "Imagination"
- Exercise "Drawing from memory"
- Exercise "Revitalization"
- Exercise "Colorful stairs"
- Random memory video
In the life of every person, a special memory plays a role: both at work and in training. In psychology, it is customary to distinguish an arbitrary and an involuntary type of memorization, the first of which is fundamental in the development of personality. This makes it possible to more effectively assimilate information and interact with society.
The concept of arbitrary memory in psychology
Memory is a type of human mental activity, which is characterized by skills such as:
- accumulation;
- preservation;
- application of information received from external sources.
Based on various psycho-emotional aspects, it is customary in psychology to classify memory into various types, including voluntary and involuntary.
Voluntary memory in psychology is a process of conscious characterization that allows achieve the desired goal based on a conscious statement of the problem itself and further actions for it implementation. Such memory sets itself the task of special training, memorizing certain information. The very process of memorization and further reproduction is a special, previously thought out action.
Voluntary memorization is determined by the obligatory setting of a clear goal for memorizing this or that information. Such a phenomenon allows a person to advance in mental development, professional activity, that is, to learn the most necessary things.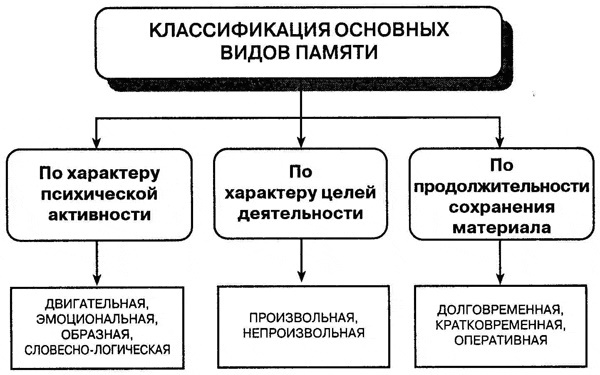
Arbitrary memory differs from involuntary classification in that any memorization and further reproduction in human psychology, characterized by the absence of special goals or techniques to help learn the alleged item. In this case, everything happens unconsciously and is not controlled by the person himself.
History of the study of arbitrary memory
One of the most striking examples of the study of arbitrary memory is the activity of the Russian psychologist P.I. Zinchenko, who in 1961 conducted a number of studies aimed at studying the phenomenon.
In this experiment, unexpectedly for all subjects, the professor of psychology asked to remember everything that they could remember on the way to work.
Research has shown that subjects were most likely to remember:
- what they did (but not what they thought or dreamed of);
- what hindered or contributed to the achievement of the desired goal;
- something unusual or strange;
- something that had nothing to do with the existing circle of knowledge.
The author began to compare the productivity and effectiveness of the involuntary type of memorization based on the same information for everyone. At the same time, it was taken into account how important the material is to the subject based on the goals, motives or methods of completing the task.
Through research, the psychologist obtained an objective result that information that is associated with psychological chain in the mind, is remembered much better than the material that has nothing to do with the conditions for achieving goals.
In the 60s, the relationship between mnemonic means and the effectiveness of various organizational issues, including the quality of memorization, was studied in detail. Soviet psychologist A.A. Smirnov, considering the development of the mnemonic function in humans, emphasized that when teaching, it is especially important to have external systematized methods that are inherent in arbitrary memorization.
The very concept of "internal and external memory" began to be actively popularized by A.N. Leontiev, in 1972 Using the term, the professor was able to describe the process of connecting external means, which indirectly affects the effectiveness of memorization.
IN. I. Laudis in 1976 pointed out that in the process of developing memorization in children, external manifestations are initially used to indicate the external regulation of the internal psychological plan and existing ideas. Only after this, the child's personality can show the regulatory ability to memorize and recall.
Stages of mastering arbitrary forms of memory
Voluntary memory in psychology is a process that is formed on the basis of a child's intellectual development. It develops even in preschool age, while the initial manifestations are noticeable during plot or role-playing games.
The main prerequisites for the formation of voluntary memorization in a preschooler:
- high activity and frequent participation in games;
- the development of communication skills, which, in addition to communication, allow you to interact with imaginary objects;
- performing different actions that are associated with moments from the past or future. For example, when it is necessary to talk about something that has already passed or to complete a certain task not at the present time, but a little later.
Initially, the child learns such premises by observing adults, gradually adopting experience and knowledge. The most important component of voluntary memorization is participation in games.
In the process of the game itself, the child's mind develops quickly, the necessary skills and abilities are acquired. Verbal games, in addition to improving the speech apparatus, are able to develop memory and thinking. At the same time, didactic games teach you to follow rules or instructions step by step.
The mastery of involuntary thinking includes 3 stages:
- Suggestions from an adult who can repeat, tell, or retell. This also includes various leading questions such as "What happened next?"
- Identification of tasks that teach the recollection and memorization of information.
- Children's awareness of the need to develop special methods of memorization.
Voluntary memorization is formed even in the process of growing up - when the child gradually learns actions that contribute to a better perception of information, as well as its retention in memory. These skills allow you to reproduce the data obtained with greater accuracy. This formation process ends at about 13-15 years.
Teaching a child at school significantly increases the speed of assimilation of the work of arbitrary memory, which is gaining more and more meaning. So, when studying, the amount of data received that needs to be memorized is growing. At the same time, the child draws attention to the fact that the information is not always shown as brightly and clearly as he would like.
For the most versatile development, it is not enough to remember only what you like. Learning a subject that the child does not like contributes not only to improving memorization skills, but also sufficiently improves willpower and concentration.
Improving voluntary memorization and its active use in practice is especially important for intellectual development of the child, including the ability to quickly acquire skills logically think.
Arbitrary modal-specific memory in children and adolescents with different types of dysontogenesis
Voluntary memory in psychology is one of the most studied and important functions in the development of a child. Research activities reflected the importance of logical thinking along with the mnestic process.
Through the efforts of V.V. Lebedinsky, 6 types of psychiatric dysontogenesis were identified that affect the quality of cognitive processes in a child.
So, the development of mental abilities can be characterized by the following characteristics:
- detained;
- deficit;
- distorted;
- damaged;
- disharmonious;
- underdevelopment.
Psychologists have conducted tests examining the quality of voluntary memory in children in comparison with various developmental disabilities. At the moment, a neuropsychological theory is becoming popular, which explains the presence of disorders in a child, based on poorly developed modal memory. This also affects overall school performance.
The goal of almost all studies is to study the properties of voluntary memorization in children, which differ from each other based on the types of psychological development.
As part of testing, psychologists pursued the following goals:
- comparison of indicators of voluntary memory of auditory and visual types, including character retention and memorization in those children who suffered from schizophrenia or various organic disorders;
- determining the relationship between the organization of training using incentives and the effectiveness of memorizing verbal information in different groups;
- comparative tests of voluntary, involuntary, tactile and visual memory in children;
- implementation of a comparative analysis of properties and parameters that would take into account the gender or age of the subjects.
Hypotheses that scientists have tried to prove or disprove:
- the level of development of voluntary memory in a child is closely related to the presence of cognitive or mental abnormalities;
- distant or weakly expressed semantic images can affect the symptoms of a mentally unhealthy child;
- modal memory is capable of influencing in different ways the success of memorization itself in a child with some kind of deviation.
 Thus, scientists could track a fairly large sample of subjects, each of which differed based on the diagnosed disease. The most common mental illnesses are schizotypal disorder and schizophrenia. The treatment of a patient in a psychiatric hospital was also taken into account.
Thus, scientists could track a fairly large sample of subjects, each of which differed based on the diagnosed disease. The most common mental illnesses are schizotypal disorder and schizophrenia. The treatment of a patient in a psychiatric hospital was also taken into account.
results
The conducted research practice allowed us to draw a number of conclusions that relate to the level of modal-specific memorization in children.
Scientists have discovered the following features:
- The quality of voluntary memorization is higher in children without mental disabilities, while those with schizophrenia were characterized by residual organic thinking disorders.
- All study groups began to better perceive and study the material after the introduction of various stimuli, enhanced associations and simplifications.
- The introduction of various connections between associations, based on their semantic load, has different effects on the level of memorization of information. The complication of the task made it possible to differentiate a child with abnormal developmental disorders.
- Children diagnosed with schizotypal disorder performed the task close to the normative indicators, while a child with schizophrenia operated on the data much worse.
- Specific or tactile memorization turned out to be the most difficult in the studied groups. In order to memorize information most effectively, visual or auditory memory was suitable.
- Various discrepancies were found in individual components of involuntary memory in sick and healthy children based on the characteristics of different sexes.
Also, scientists were able to identify the presence of organization using stimuli that affect the process of voluntary memorization, based on the presence or absence of cognitive dysontogenesis. Such testing makes it possible to identify a child with developmental disabilities, since his memory and information reproduction are not very effective.
Development of arbitrary memory
The development of voluntary memory in preschoolers should begin as early as possible, constantly improving and practicing various techniques. In addition to pedagogical training, parents need to approach this process as well.
The most popular and effective games for improving memory in children:
| Name | Description |
| "Pictures" | The child is shown a certain image for a short period of time. After that, the picture is taken away, the adult asks to describe what he managed to remember - in the most detailed details. |
| "10 differences" | In addition to the classical technique, which is characterized by the search for differences between simultaneously located pictures, the task can be complicated. So, first you should show one image, after which - the second. Then you need to ask the child to point out the differences. |
| "Portrait" | Can be conducted by both a parent and a teacher or member of an educational group. It is necessary to show the child a certain person, and then go behind the screen, door, or simply walk away, while changing any element of the image. After that, go back to the child and ask about what was changed in the guise. |
| "Description" | After a successful walk, the parent can remember various details with the child on the way home. So, a preschooler can point to an unusual person passing by, or an interesting object. After that, it is necessary to name the various details of the observed object. The more such details, the better for memory. |
| "Try to repeat" | For this game, counting sticks, matches, beads or any other objects are taken. An adult needs to lay out any composition from them, and then give the child a few seconds to memorize. Then the preschooler must repeat the composition in as much detail as possible. |
| "Zoo" | An adult lays out a certain number of soft toys, from 3 to 7. For 30 sec. the child is given the opportunity to remember their location, after which the preschooler turns his back. At this time, the adult changes toys. The task is to tell what has changed. |
In addition to developing voluntary memory, the games described above improve the skills of attention, concentration and, in some cases, perseverance. The main thing is to practice various techniques as often as possible, improving them if necessary.
Exercise "Imagination"
The main goal of the exercise is to memorize the words spoken by an adult using their figurative sketch on paper. Then you need to repeat them, looking at the picture. The main thing is to pronounce as many objects as possible so that the child focuses on the visual component.
The exercise includes several stages:
- The simplest words are given: table, person, chair, sun.
- An adjective is added to the spoken words: an old table, a tall man, a bright sun.
- Words are complicated by various abstractions: sadness, joy, a fairy tale.
 The number of words spoken should increase gradually. The exercise can be made more difficult by creating images using the counting sticks. Difficulties like these make it possible to develop memory most effectively.
The number of words spoken should increase gradually. The exercise can be made more difficult by creating images using the counting sticks. Difficulties like these make it possible to develop memory most effectively.
Exercise "Drawing from memory"
Exercise allows you to develop not only the quality of memorization, but also concentration. To complete it, you must give the child a pencil and a sheet of paper. An adult should show any drawing within 30 seconds, after which - ask the preschooler to remember and redraw it.
It is desirable that the images are drawn with a simple pencil. For a start, ordinary geometric shapes are suitable, after which it is recommended to complicate the task - to increase the number and complexity of drawings, show color pictures and abstractions.
Exercise "Revitalization"
The purpose of the exercise is to improve auditory and visual memory. You should show the child any animal, and then offer to revive it in your head. After that, the preschooler should talk about what was in his view.
The child needs to describe the animal itself, including what it does. In case this exercise is too difficult, you can resort to visual cards. In addition to animals, the child can be shown a variety of objects.
Exercise "Colorful stairs"
This exercise requires 5 different colored cards. Within 10 sec. the child must carefully consider them, and then remember the sequence of the color palette. Then the cards are covered with paper or any other object.
After that, the adult invites the preschooler to close his eyes, mentally imagining the location of the cards. The child needs to list them as accurately as possible, in accordance with where the colors are located. The final step is to validate the answer with the original image.
Since human psychology is not limited to simple exercises and games, in addition to them, the development of arbitrary memory will help: the correct daily regimen, physical activity and a healthy diet. Consumption of food in portions rich in essential amino acids and trace elements, as well as a good 8-hour sleep, are the best companions for effective memorization of information.
Random memory video
Arbitrary memory: