A heel spur (plantane fasciitis) is the result of permanent injury to the area of the plantar ligament that connects the area of the calcaneus to the forefoot. As a result of constant exposure in the area of the calcaneus, a calcified outgrowth is formed - an osteophyte, which, in fact, will be the heel spur.
general information
The heel bone in the body has a strictly defined size and shape, which allows it to distribute the body's load. With a constant negative impact, the bone can deform, while in the area of attachment of the tendon, in the area of the foot, the area of the bone grows.
In this case, the heel spur has a non-physiological shape and presses on the surrounding tissues of the foot, causing pain.
On average, heel spurs are from 3-5 to 12 mm, the sharp end of the growth is directed to the area of the toes and is bent upward. For the most part, women over 40-50 years old suffer from heel spurs.
Causes
The main reasons for the formation of a heel spur:
- all kinds flat feet with a sharp increase in the load in the heel area, sharp tension and permanent tendon injuries in the arch of the foot
- physical training of significant strength and intensity, in which heavy loads fall on the foot area
- being overweight when the body needs to redistribute body weight
- age-related changes in ligaments and bones
- consequences of foot injuries, especially in the heel area
- rheumatism
- vascular disorders
- nerve damage in the lower extremities.
Formation mechanism
Under uneven or very heavy loads on the foot and heel, excessive tension occurs on the tendons that are attached to the heel. Overstretched tendons are easily injured and torn, forming an area of inflammation.
In the area of inflammation, tendon fibers are replaced by a scar. Then, at the site of the scar, calcium deposits gradually form, gradually forming a bone protrusion - a heel spur. This protrusion disrupts normal movement, injuring tissue and causing soreness.
Heel spur symptoms
Heel spurs are manifested by fairly typical symptoms: pain in the heels, gait disturbances.
With a heel spur, pain can be in the form of:
- sharp or burning pain when walking with support on the heel,
- severe pain occurs in the morning, when getting up on your feet (starting pain),
- feeling of "hammered nails" in the heel,
- as you walk, the pain subside a little,
- with the accumulation of fatigue, in the evening the soreness increases,
- pain is localized in the heel area or over the entire surface of the foot,
- as it progresses, pain occurs without exertion,
- a painful lump forms in the heel.
Because of pain, there is a violation of gait in the form of transferring the body to the toe, limping, using a cane to support and unloading the sore leg. As a result, transverse flat feet appear.
With a bilateral spur, movement is difficult, patients experience pain and try to walk less, the layer of subcutaneous fat in the heel becomes thinner, which acts as a shock absorber when walking.
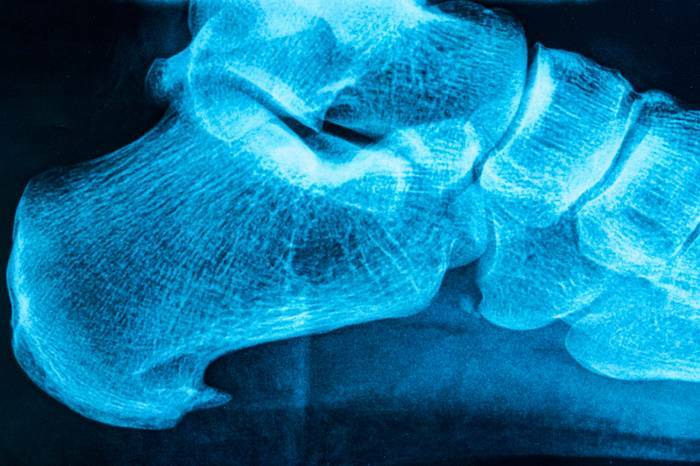
Diagnostics
A heel spur can be suspected on the basis of typical complaints of pain when walking and an examination of the foot with palpation of the calcaneus. But to confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct:
- X-ray of the foot with the identification of a typical growth,
- ultrasound examination,
- conducting blood tests and blood biochemistry to exclude other diseases of the heel region - Reiter's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis.
Heel spur treatment
Heel spurs are diagnosed and treated by surgeons and orthopedists. All methods of therapy can be divided into conservative and operational.
Conservative methods include:
- the use of various orthopedic structures in shoes to relieve the foot and relieve pain (insoles, inserts, special shoes),
- to relieve pain and relieve inflammation, a complex of physiotherapeutic measures is used (mud therapy, paraffin therapy, ozokerite, mineral baths),
- remedial gymnastics, physical education,
- electrophoresis with novocaine, novocaine blockade with severe pain,
- ultrasound therapy on the area of bone outgrowth, shock wave treatment (impact on the outgrowth area with special impulses, with further resorption of deposits),
- directional focal X-ray irradiation of the spur area,
- low-intensity laser therapy for the heel spur area
- the use of vibro-acoustic device Vitaon,
Also, medications are used to relieve pain and inflammation, these include:
- the use of local hormonal drugs (hydrocortisone),
- the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, dimexide),
- gels with decongestant and anti-inflammatory effect (voltaren, diclogel),
- local injection of diprospan into the affected area.
Surgical methods for the treatment of heel spurs are used in advanced and extreme cases, they are resorted to when ineffectiveness of conservative measures and severe pain syndrome, during the operation, the calcaneal spur.
Complications
In advanced cases, heel spurs lead to disruption of human movement and limitation of his ability to work and social activity. With an early and timely start of treatment, the prognosis is favorable, you can completely get rid of the pain and achieve significant improvement.

