Content
- Tuberculosis of the spine and bones: characteristics of the disease
- Causative agents
- Reasons for the appearance
- Symptoms and Signs
- Infected or not: transmission routes
- Classification of the disease
- The clinical picture of the course of the disease in adults: stages and stages
- Diagnostic methods
- Differential
- Basic principles of treatment
- Drug therapy
- Physiotherapy
- Plaster corset
- Plaster bed
- Surgical intervention
- Recovery prognosis
- Rehabilitation and features of the body's recovery
- Possible consequences and complications
- Prevention methods
Spinal tuberculosis is a chronic inflammatory disease that occurs due to damage to the bone and cartilaginous tissues of the vertebrae by the mycobacterium pathogen. The pathology is characterized by a long asymptomatic period and a large number of complications - from abscesses and systemic infection of the body to pinching of the spinal cord. The disease is treated with antimicrobial drugs combined with physical therapy to make the patient's life easier.
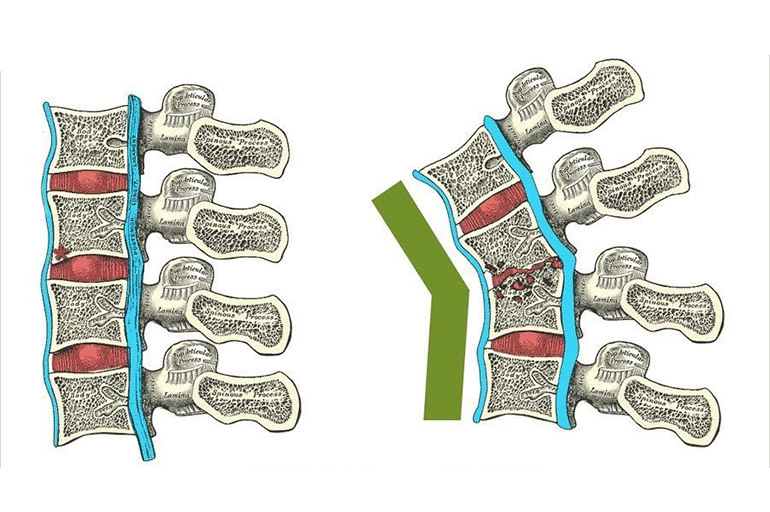
Tuberculosis of the spine and bones: characteristics of the disease
The disease occurs as a result of the vital activity of bacteria in the tissues of the vertebrae.
Its consequences are the destruction of the affected areas of the bones and general disorders in the spinal column. The disease is considered one of the most common forms of tuberculosis - in second place after pulmonary tuberculosis.
Causative agents
The causative agent of the disease is considered mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis), or Koch's bacillus. It can survive in humans, animals, birds and be transmitted between them. Mycobacterium got its name due to the property of forming filamentous branched structures, similar to mold.
Reasons for the appearance
Spinal tuberculosis occurs due to the ingestion of Koch's rods into the bone tissue of the vertebrae. Risk factors that increase the chance of contracting mycobacterium:
- contact with sick people or animals;
- vertebral injuries, especially open fractures;
- improper nutrition, incl. hunger strikes without a doctor's supervision or chronic malnutrition;
- excessive physical activity;
- severe stress;
- violation of sanitary standards in the place of residence of the patient;
- lack of proteins and vitamins in the body;
- prolonged local or general hypothermia;
- diseases affecting the immune system;
- bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol, taking drugs.
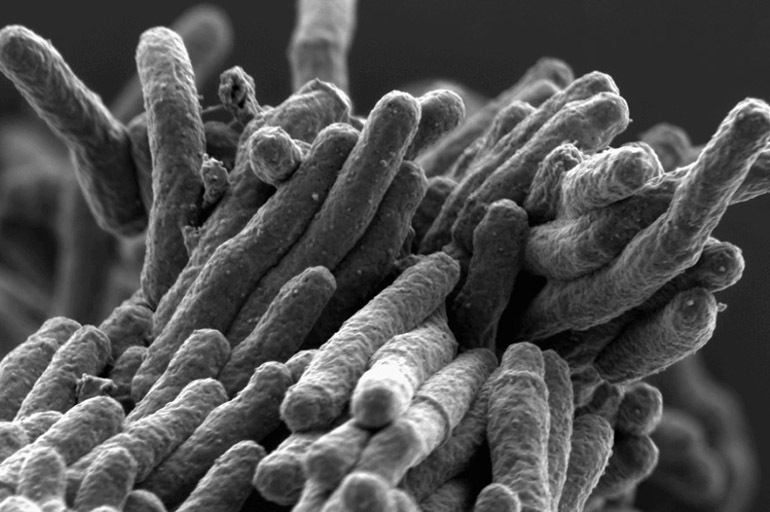
The risk of infection with Koch's bacillus is higher if the human body is weakened by another disease or other external factors.
This creates favorable conditions for the reproduction and further life of the microorganism.
Symptoms and Signs
The disease is asymptomatic for the first few months. This is due to the low activity of the bacillus and its suppression by the human immune system. As the pathology develops, more and more pronounced symptoms begin to appear, including:
- increased body temperature;
- pain in the affected area, aggravated by physical exertion and weakening during rest;
- decreased performance, increased fatigue, weakness;
- limitation of the mobility of the spine;
- hardness, constant tension and hypertonicity of the back muscles;
- deformation of the vertebrae, the appearance of a tumor or hump in the affected area.
Important information: The clinical picture of the development of focal pulmonary tuberculosis
In the advanced stages of the disease, in the absence of proper treatment, there is a complete curvature of the back patient, constant tilt of the trunk, as well as numerous symptoms of abscesses and other accompanying complications.
Infected or not: transmission routes
Tuberculosis is a disease, the causative agent of which is transmitted from one carrier to another. You can get infected not only from humans, but also from animals and birds. Ways of transmission of the disease:
- airborne - by inhaling bacteria that have entered the external environment from an infected organism when sneezing, coughing, talking;
- contact-household - when interacting with the patient's personal belongings;
- alimentary - through food and water;
- transplacental - in utero to a child from an infected mother.
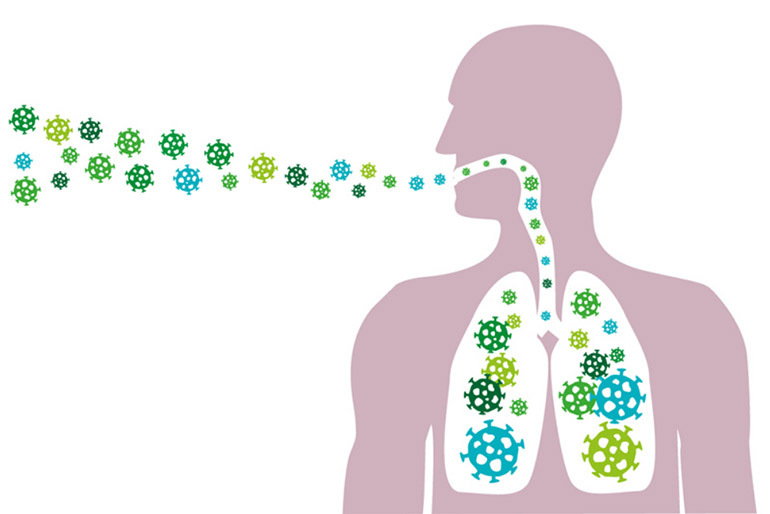
Spinal tuberculosis is not contagious, since bacteria cannot enter the external environment.
Only the combined form of the disease can be transmitted, in which bones and other organs, such as the lungs, are simultaneously affected.
Classification of the disease
Spinal tuberculosis is classified according to the localization of foci of the disease:
- anterior spondylitis - on the vertebral bodies and the roots of the arches;
- posterior - on processes and vertebral arches.
By the type of tissue affected:
- bone - affects the tubular substance inside the bone;
- synovial - affects the joints, eventually spreads to cartilage and synovial tissue.
By the site of the lesion:
- local - 1 vertebra is affected;
- common - 2;
- plural - more than 2.
There is also a combined form of the disease, in which foci of infection arise in several organs at once. The most common is combined pulmonary and spinal tuberculosis.
The clinical picture of the course of the disease in adults: stages and stages
Pathology develops gradually, with a slow increase in lesions and an increase in symptoms.
The disease is divided into 5 stages:
- Primary osteitis is the initial infection of 1 vertebra.
- Progressive spondyloarthritis without disturbances - the localization of foci of infection expands to adjacent bone structures.
- Progressive spondylitis with dysfunction of the spine. At this stage, pronounced symptoms begin to appear: pain, curvature, difficulty walking, etc.
- Chronic destructive spondylitis. The affected sections of the spine stop functioning completely.
- Post-tuberculous spondylarthrosis. Further destruction of tissues in bones and joints.
It is necessary to start treatment of pathology from the moment of detection. Then the healing process will be easier, and the likelihood of complications will decrease.
Diagnostic methods
The following methods are used to diagnose the disease:
- examination of the patient with an assessment of the clinical manifestations of the disease;
- chest x-ray;
- MRI of the affected area.
After confirming the primary diagnosis, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound scan, CT scan, biopsy of infected tissues, and histological examination of the affected area. This helps to establish an accurate clinical picture for the appointment of an effective treatment.
Important information: The clinical picture of the course of fibrocavernous pulmonary tuberculosis
Differential
Differential diagnosis is most often required when tuberculosis is detected in children. The doctor needs to exclude pathologies similar in symptoms: Scheuermann's disease - Mau, Calvet, congenital developmental anomalies. Diagnosis is made by analyzing detailed X-ray images.
In rare cases, the disease must be distinguished from metastases and malignant tumors. In this case, the patient is prescribed an additional histological examination of tissues and the body is checked for the presence of tumor markers.
Basic principles of treatment
In the treatment of tuberculosis of the spine, complex therapy is recommended. Medicines and physiological procedures should be aimed at both destroying foci of infection and eliminating secondary symptoms and consequences of the disease.
Drug therapy
With tuberculosis, the patient must be prescribed antibacterial drugs. Their type depends on the strain. Before prescribing a medicine, bacteria are tested for resistance to various antibiotics and tablets, after which the most effective drugs are selected. In addition to the main treatment, the patient is prescribed vitamins, pain relievers, sedatives, antipyretics, chondroprotectors, pre- and probiotics. The exact set of drugs and their dosage is prescribed by the doctor and depends on the severity and form of the disease.

Physiotherapy
In addition to medication, the patient is advised to attend physiotherapy procedures. Among them:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetotherapy;
- laser therapy;
- phonophoresis.
Physiotherapy is effective as an adjunct to medical treatment. It slows down the growth of bacteria, relieves inflammation, reduces pain and the intensity of other symptoms of tuberculosis.
Plaster corset
This method of artificial fixation of the vertebrae is used for patients with severe forms of tuberculosis. The patient is suspended on a special apparatus that straightens the bones and puts them in the desired position. After that, the patient's body in the affected area is tied with bandages and covered with cotton wool for fixation. A plaster cast is placed on top. She continues to keep her back straight. In the abdomen, a hole is left on the cast for free breathing.
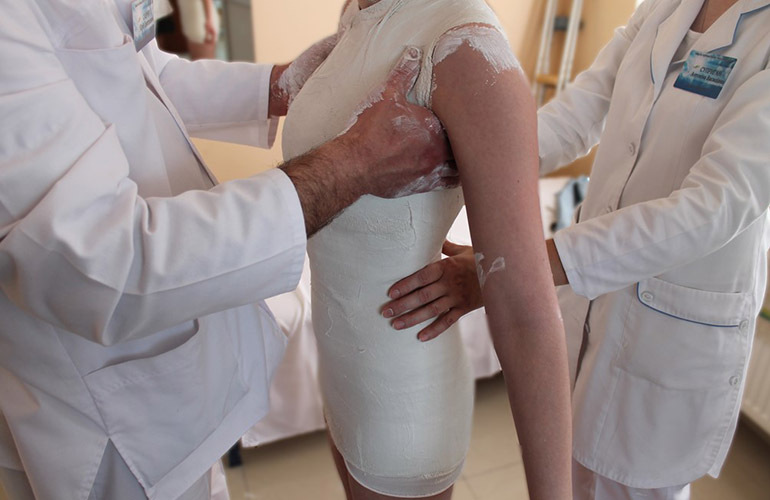
The area of application of the corset depends on the localization of tuberculosis:
- in case of a disease of the lumbar and lower thoracic vertebrae, a bandage is applied to the armpit area;
- in case of damage to the cervical spine, a corset with a collar is made;
- for vertebral disease, a shoulder bandage is used in the upper chest.
When the condition improves, the plaster corset is replaced with a removable leather one. It performs the same function, but is more comfortable and easier to wear.
Plaster bed
According to the principle of application, a plaster bed is similar to a corset. It is applied to the back and side surfaces of the body. The crib fixes the damaged spine in a relaxed state. This provides maximum relief and allows the patient to rest comfortably in the supine position.
Important information: Features of the development and course of miliary pulmonary tuberculosis
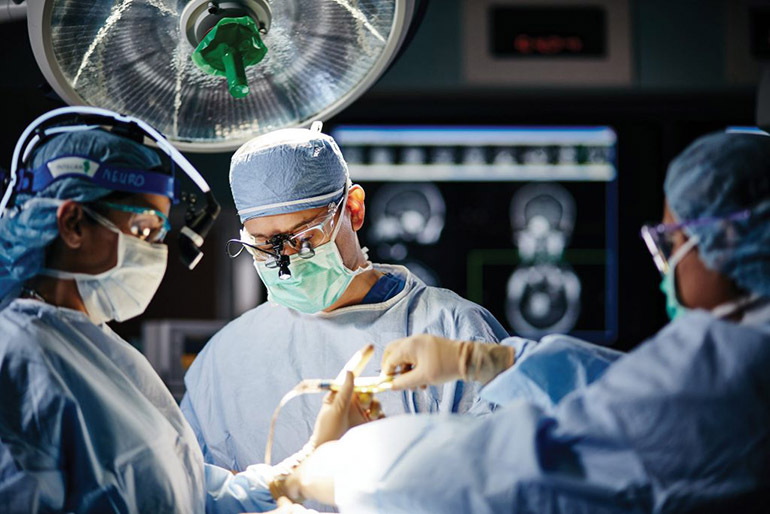
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention is recommended when drug and physiotherapy methods of treatment are ineffective. During the operation, the doctor removes all areas of the damaged vertebrae along with the foci of infection. In their place, implants are installed that restore normal mobility. The surgeon selects the technique of the operation individually, depending on the location of the lesion and its intensity.
Recovery prognosis
With timely detection and proper treatment of the disease, the prognosis for the patient is favorable. In most cases, it is possible to completely restore damaged tissues and return to a full life. But in the absence of proper therapy and bringing the disease to late stages, complications may develop up to permanent deformation of bones and tissues, paralysis or death.
Rehabilitation and features of the body's recovery
With advanced forms of tuberculosis of the spine with complications and impaired musculoskeletal functions, the patient needs rehabilitation. Depending on the severity of the disease, the characteristics of the organism and other factors, the recovery period takes from 1-2 months to 1 year or more.
During rehabilitation, the patient needs:
- perform physical exercises under the supervision of a doctor to restore lost functions;
- attend physiotherapy procedures: massage, magnetic therapy, therapeutic baths as prescribed by the doctor;
- work with a psychologist;
- undergo preventive diagnostics;
- walk regularly in the fresh air;
- visit a neurologist, orthopedist, traumatologist and other doctors, depending on the characteristics of the course of the disease.

The rehabilitation period can take place both in a hospital or a special sanatorium, and at home. It depends on the patient's condition and the nature of the medical procedures he needs.
Possible consequences and complications
Complications of spinal tuberculosis:
- abscesses;
- paraplegia (paralysis) due to pinching of the spinal cord;
- fistulas;
- radicular syndrome;
- secondary immunodeficiency;
- paresis;
- rachiocampsis;
- instability of the vertebrae;
- amyloidosis;
- neurological disorders.
In the absence of proper treatment, pathology leads to irreversible consequences, including disability.
Prevention methods
To reduce the risk of developing pathology, you must adhere to the following measures:
- avoid contact with infected people and their personal belongings;
- timely get vaccinated against tuberculosis;
- regularly clean the home;
- comply with sanitary standards when using food and water;
- undergo routine medical examinations and annual fluorography;
- strengthen immunity.
Keeping a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and giving up bad habits reduces the risk of developing tuberculosis. A strong, healthy organism with developed immunity is less susceptible to this disease.