Content
- Purpose of the test
- Indications for donating blood
- Types of analyzes
- General (UAC)
- Biochemical
- Quantiferon (QFT-GIT)
- ELISA (enzyme immunoassay)
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
- IGRA
- T-SPOT.TV diagnostics
- Features of blood diagnostics
- Indicators for tuberculosis: interpretation of analyzes
- ESR
- Leukocytes
- Antibodies
- Erythrocytes
- Hemoglobin
- Error probability
- The nuances of the test for children
- Mantoux
- Diaskintest and its features
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease and can be asymptomatic for a long time. Various methods are used to identify pathology. One of the informative studies is a blood test for tuberculosis, which allows you to determine changes in its composition.
Purpose of the test
The disease is provoked by Koch's bacillus, a type of mycobacteria that are transmitted by airborne droplets. The pathogen is characterized by resistance to cold, heat, moisture.
The viability of bacteria in the ground is tens of years; in dried sputum on various surfaces, their activity persists for several months.
Koch's bacillus can be found in the meat, milk of infected animals, and flies and cockroaches can also become carriers.
The danger is that with changes in the lungs, pathology in some cases is asymptomatic. For this reason, preventive studies are carried out all over the world, which include a tuberculin test (Mantoux reaction) and fluorography, X-rays.
If there is a suspicion of tuberculosis, a blood test is prescribed to help identify abnormalities in its biochemical composition.
Indications for donating blood
Indications for donating blood are:
- Contact with an infected person.
- The presence of darkening in the fluorographic image.
- Fever, weakness.
- Chronic cough.
- Loss of appetite.
- Weight loss.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Great sweating at night.
- Contraindications to the tuberculin test.
Patients after organ transplant operations, HIV-infected patients, patients with diabetes mellitus undergo regular examination. Also, a blood test must be taken when applying for a job in a number of institutions.

Types of analyzes
There are different types of research. The doctor prescribes the type of analysis, taking into account the patient's history, the purpose of the examination.
Important information: The clinical picture of the development of tuberculous pleurisy in humans
General (UAC)
There are no markers that can accurately determine tuberculosis or the localization of a pathological focus in a clinical study. This type of analysis detects inflammatory processes in the body.
The level of leukocytes and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increase. With an extensive form of distribution, an increase in the level of neutrophils is observed. The method can be used for primary diagnostics.
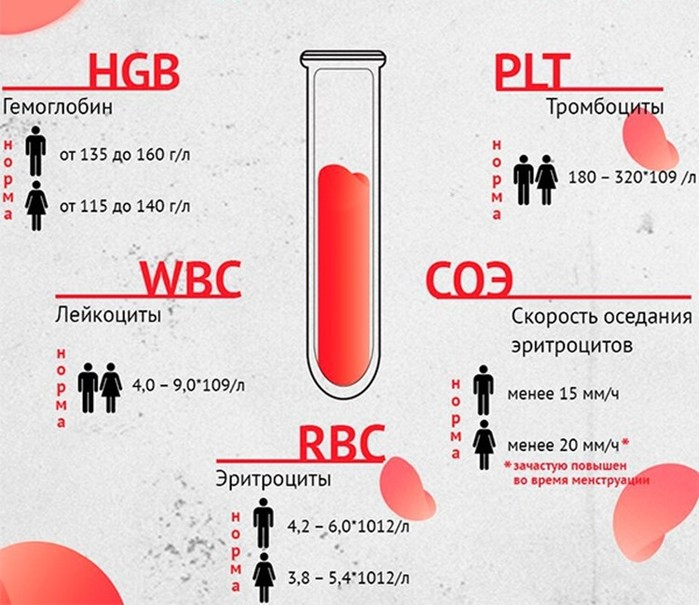
Biochemical
Biochemical research is considered informative in severe pathology. In this case, the level of protein, urea, cholesterol, lysozyme rises. The analysis allows you to identify an inflammatory focus in the liver. In the blood, the amount of bilirubin, ALT and AST enzymes increases.
Quantiferon (QFT-GIT)
The quantiferon test is based on the detection of antibodies produced by cells in response to infection with tuberculosis bacteria. The method allows you to accurately determine the presence of infection. The test does not require the introduction of bacteria and antigens into the body. It is prescribed for contraindications to the tuberculin test.
ELISA (enzyme immunoassay)
With the enzyme immunoassay, a large number of blood parameters are examined, antibodies to pathogenic microorganisms are detected. Their high level indicates infection.
With the help of ELISA, it is impossible to identify the stage of the disease. The study is not used instead of a tuberculin test, after BCG and with immunodeficiency, since the result may be incorrect.

PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
PCR diagnostics is one of the most informative methods in determining tuberculosis. The study shows the presence of mycobacteria in the body, the localization of foci, reveals extrapulmonary forms of pathology, the stage of the disease.
Regular polymerase chain reaction (PCR) during treatment allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy.

IGRA
IGRA, like the quantiferon test, detects antibodies to pathogenic pathogens. It is used to diagnose latent and active tuberculosis. However, these forms of pathology cannot be distinguished using IGRA.
T-SPOT.TV diagnostics
The T-SPOT study is characterized by the accuracy of the results, the absence of contraindications, the possibility of conducting it in patients with immunodeficiency, diabetes mellitus, and a tendency to allergies.
The analysis shows the immune response to the presence of bacteria in the body.
The method detects any form of the disease, but does not allow distinguishing latent tuberculosis from active tuberculosis.
Important information: Information about Koch's pathogenic bacillus
Features of blood diagnostics
A feature of blood tests for tuberculosis is the absence of contraindications. For this reason, it is often prescribed instead of a tuberculin test.
Diagnosis of blood is reliable, it allows you to identify a latent infection. It is unlikely that you will get incorrect results. Tests are mainly carried out for a fee.
To obtain reliable results on the eve of the study, it is necessary to exclude smoking, alcohol intake, it is advisable to avoid stressful situations, physical and mental stress. Diagnosis is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach.
Indicators for tuberculosis: interpretation of analyzes
It is up to the doctor to decipher what the results show. Inflammation is evidenced by changes in ESR, the level of leukocytes, antibodies, hemoglobin.
ESR
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases with any inflammatory process.
Normally, the numbers differ between adults and children:
- up to 10 years - 10 mm / hour;
- for women under 50 years old - 20 mm / hour;
- after 50 - 30 mm / hour;
- for men under 50 years old - 15 mm / hour;
- after 50 - 20 mm / hour.
With tuberculosis infection, indicators can increase up to 80 mm / hour, regardless of age and gender.
Leukocytes
With tuberculosis, a shift in the leukocyte formula is observed.
The indicators change as follows:
- The level of neutrophils increases in absolute and relative terms by 15-20%. Their morphology changes to granular, which indicates infectious and inflammatory processes.
- The number of stab neutrophils increases.
- The level of lymphocytes decreases.
- The number of monocytes increases by 10-18%.

Antibodies
Antibodies are produced in the body to fight off foreign bacteria. A specific immune response to tuberculosis is shown by ELISA, IGRA, QFT-GIT tests. Normally, immunoglobulins are absent.
Erythrocytes
A change in the level of red blood cells is noted with active tuberculosis. For small lesions, the number of red blood cells may not change. A decrease in their concentration and a change in morphology are observed in the case of extensive lesions. This increases the number of immature cells.
Important information: Features of the manifestation of genital tuberculosis in men and women
Hemoglobin
At the initial stages of pathology or with small lesions, changes in hemoglobin are not observed or the deviation from the norm is insignificant. A drop in protein levels is observed in severe disease.
Error probability
A number of studies are used to make an accurate diagnosis. Blood tests are important. Some types of tests accurately detect not only inflammation, but also the presence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
The diagnosis is suitable for patients with allergies, other infectious diseases, which is a contraindication for a tuberculin test. The risk of false results is present, but considered low.
The nuances of the test for children
For the prevention of the disease in children, the Mantoux test and the diaskintest are mainly carried out.
Mantoux
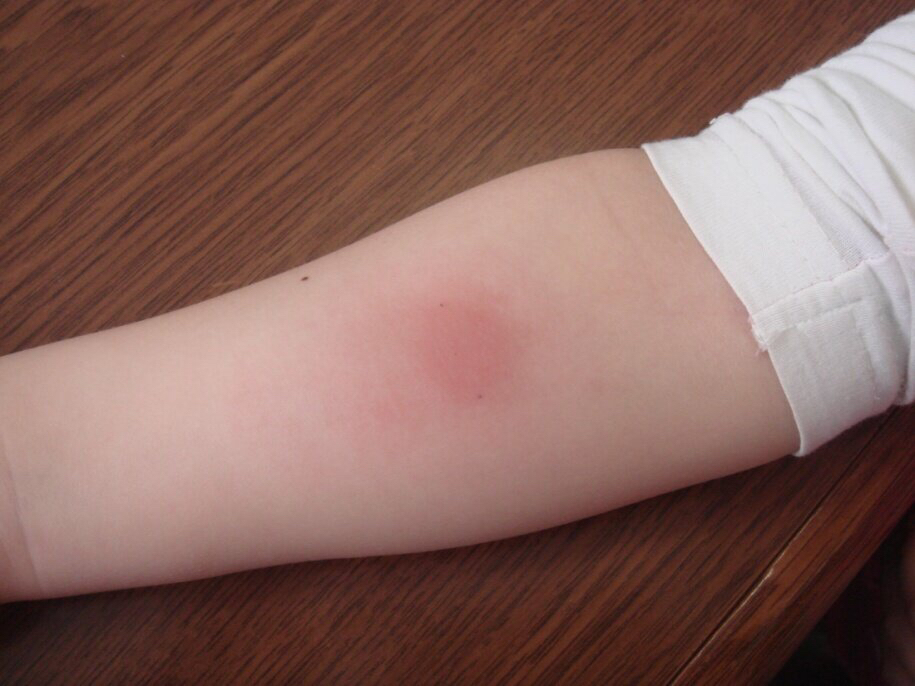
Tuberculin test is the introduction of the drug Tuberculin under the skin, which causes the body's immune response. At the injection site, there is a slight inflammation in the form of a papule. After 72 hours, it is measured.
Thus, the immune response to the tubercle bacillus is assessed. If the papule remains small, then there is no infection. Severe inflammation indicates the presence of mycobacteria.
A positive result can be observed in allergies, asthma, epilepsy, and other infectious diseases. In such cases, a blood test is prescribed.
Diaskintest and its features
Diaskintest is based on an immune response to a recombinant tuberculosis protein. The study reveals the presence of the pathogen and the activity of bacteria.
Diagnostics is not carried out for patients with acute allergies, skin and infectious diseases, epilepsy. The results are analyzed after 72 hours according to the size of the papules and the severity of hyperemia. Before checking, the infiltrate should not be scratched or wetted with water.