Content
- General concept of tuberculous granuloma
- Reasons for the appearance
- Signs of inflammation
- Structure and cellular composition
- Necrotic zone
- Epithelioid cells
- Pirogov-Langhans cells
- Morphogenesis: dynamics and stages of development
- Varieties of granulomas: classification
- Depending on the composition of the cells
- From the size of education
- From the rate of cellular metabolism
- Reverse development
- Paraspecific tissue reactions
- Nuances of diagnosis
- Treatment principles
- Outcomes and prognosis for recovery
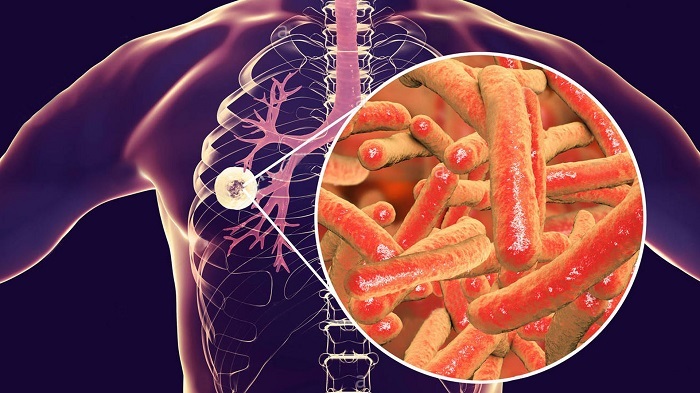
A tuberculous granuloma is a small nodule or accumulation of several formations formed as a result of an inflammatory process in the lung tissue. The existence of a specific form of the pathological process is due to the introduction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis into the patient's body. At the initial stage of the inflammatory process, the tubercles are small.
General concept of tuberculous granuloma
Nodules formed in the lungs are divided into 2 types:
- miliary, 3 mm in size;
- submiliary (less than 1 mm);
- the size of solitary formations exceeds 1 cm.
A tuberculous nodule consists of a large number of cells capable of phagocytosis. The etiological causes of tubercles are divided into internal and external. Endogenous factors - when insoluble formations arise as a result of metabolic disorders.
Exogenous factors are biological, organic and inorganic products, medicines.
Reasons for the appearance
Tuberculosis of the lungs is caused by Koch's bacillus. In the lung tissue, the pathogen multiplies, but the patient's immune system does not respond to its presence in the body.
Bacterial waste causes inflammation in the lung tissue. During this period, the patient's immune defense is activated. Bacteria interact with macrophages and lymphocytes, forming the basis of the tuberculous tubercle.
Signs of inflammation
Lung disease is accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process. With granulomatosis, activated macrophages are formed in the lungs. These cells are epithelioid in shape. The inflamed tissues are surrounded by plasma formations and lymphocytes.
There is a zone of hyperemia in the focus of inflammation. The patient complains of manifestations of intoxication: weakness, joint pain, weight loss. The nature of the inflammatory process and the rate of its development depend on the percentage of giant cells and lymphocytes in the focus of inflammation.
In the lung tissue, incomplete phagocytosis occurs, stimulating T-macrophages and B-lymphocytes.
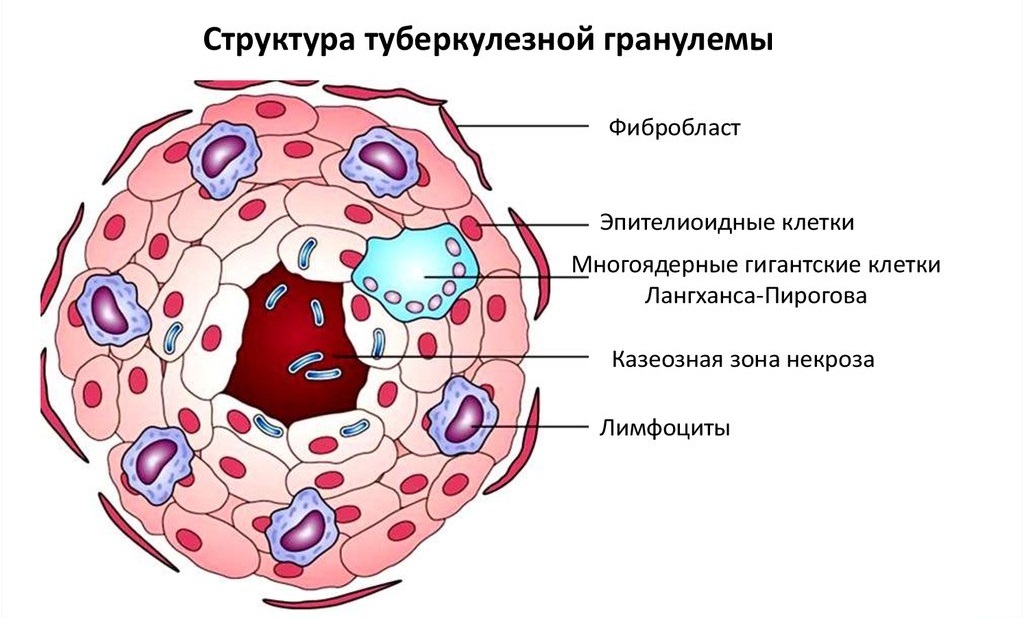
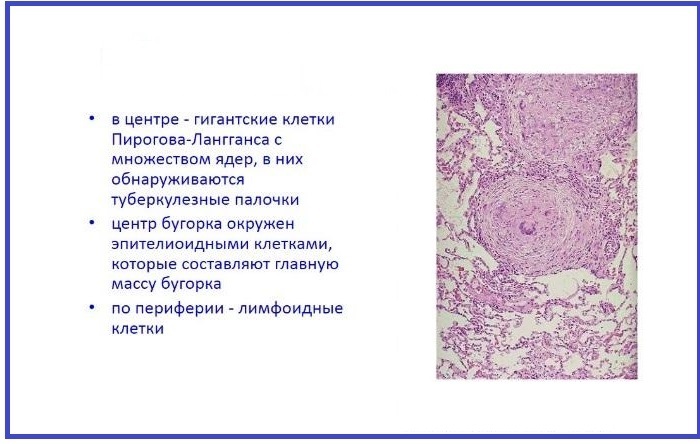
Structure and cellular composition
The main components of the bumps are cells that cause inflammation in the lung tissue. In the first phase of the infectious process, the nodules consist of an epithelioid group of cells, the necrotic substance is completely absent. With an exacerbation of the pathological process, areas of dead tissue appear in the central part of the nodules. The composition of the caseous focus is heterogeneous, such formations predominate as:
- epithelioid lymphocytes;
- plasma macrophages;
- Pirogov-Langhans cells;
- agrophilic group of fibers.
Important information: The clinical picture of the development of tuberculous pleurisy in humans
Necrotic zone
Inside the tuberculous nodule there is a curdled content. The following factors influence the formation of a caseous area:
- exposure to toxic products;
- rapid death of the cell population;
- vasospasm, causing tissue necrosis.
The curdled content in the central part of the tubercle is saturated with serous secretions. Further development of the disease leads to a change in the consistency of the substrate. The patient coughs up a cheesy mass, cavities are formed in the lungs, which are the main source of contamination of the lungs with mycobacterium tuberculosis. The micropreparation for necrosis contains rounded areas covered with a green-yellow mass.
Epithelioid cells
Macrophages, unable to destroy the causative agent of tuberculosis, form a similar type of cells. They are located around the dead tissue in several layers, are large and flat in shape. Areas located near the foci of necrosis are subject to destruction, metabolism is disrupted in cells. Epithelioid formations go through 2 phases of development:
- immature;
- mature.
Pirogov-Langhans cells
Multinucleated giant structures are formed from epithelial formations by division of the nucleus. Epithelioid cells are the main component of tuberculous inflammation.
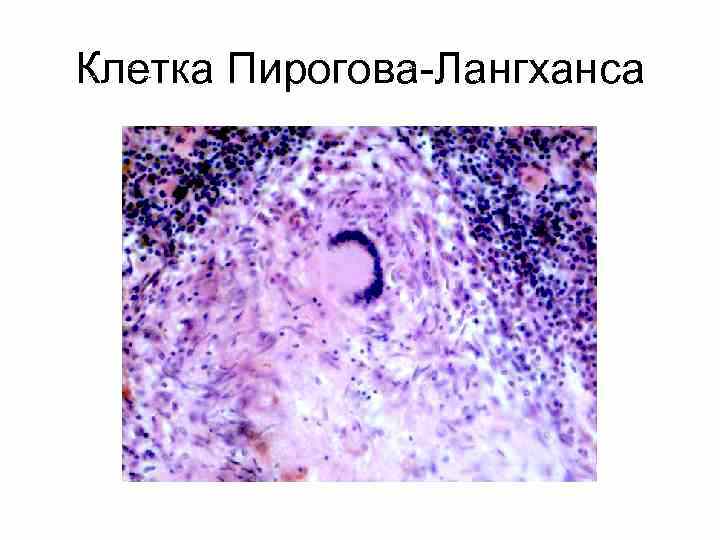
The cytoplasm contains the causative agent of the disease or its individual fragments.
The cells contain the following structural units:
- lysosomes;
- mitochondria;
- enzymes.
If the patient has weak immunity, the epithelioids, interacting with bacteria, cause an exacerbation of the tuberculous process.
Morphogenesis: dynamics and stages of development
The development of tubercles in tuberculosis goes through 4 stages:
- First phase. Monocytes are formed in the area of lung tissue where mycobacteria have accumulated.
- Second phase. Evolution of cells is observed, followed by the formation of macrophages.
- During the third period, monocytes and macrophages are formed in epithelioid structures. They cannot destroy harmful microorganisms, but they deliver lymphocytes to the inflamed area, which form an epithelioid tubercle.
- The fourth stage is characterized by the appearance of Pirogov-Langhansa multinucleated cells, indicating a formed nodule in the lung.
Varieties of granulomas: classification
The division of tuberculous nodules into separate groups is associated with their cellular structure. There are 4 types of tubercles:
- lymphocytic;
- giant cell;
- epithelioid;
- mixed.
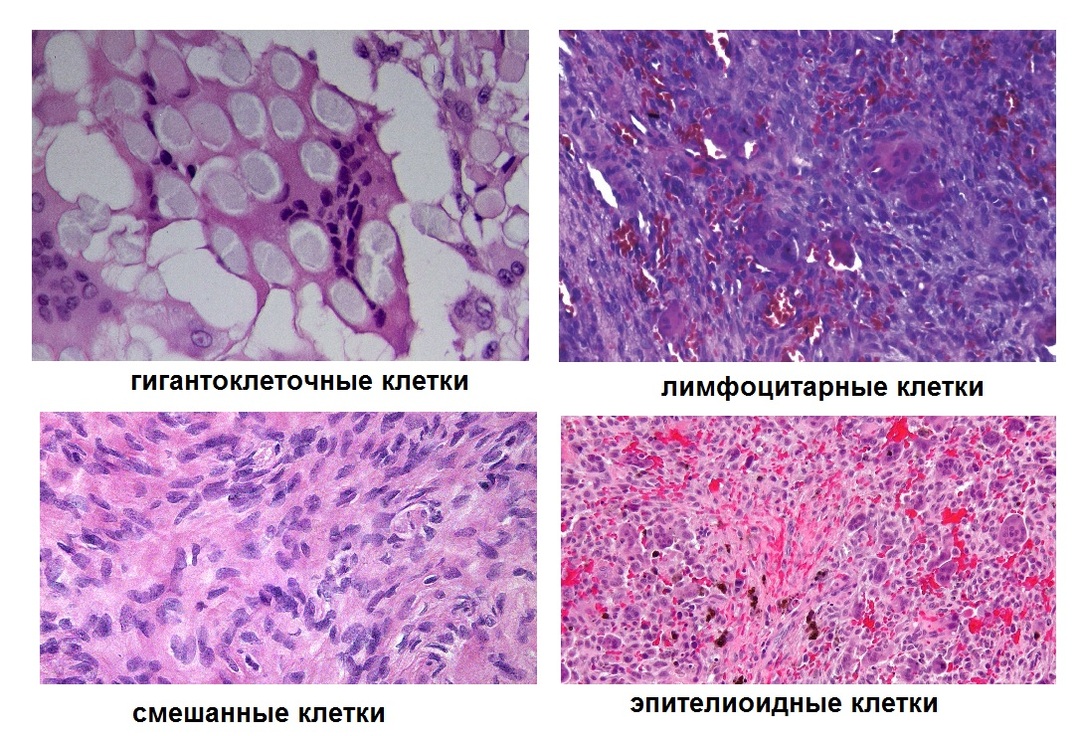
The nodules located in the lungs have a heterogeneous composition, which changes as a result of exposure to factors such as:
- strengthening of the immune defense;
- the effectiveness of anti-tuberculosis treatment.
Important information: The clinical picture of the development of cavernous pulmonary tuberculosis in adults
Depending on the composition of the cells
A special role is assigned to the formations of Pirogov-Langhansa. In the cytoplasm of the giant cell, the nucleus is located on the periphery, there are no lysosomes. Cells do not combine into peptide information molecules. The composition of the structural unit is determined using modern diagnostic methods. The patient is prescribed a tomography of the diseased organ. The presence of exudate in the lung tissue indicates the development of a tuberculous process. The tubercles merge with the formation of a large focus with a diameter of 1 cm.
From the size of education
A tuberculous nodule may occupy a lobe or segment of the lung. A large mass is located in the region of the transition of the terminal vessel into the alveoli of the acinus, located in the back of the lung. Conglomerates are formed as a result of the fusion of several tubercles and are large in size.
Granulomas are divided into several groups depending on the metabolic rate. Some nodules have a minimum process speed. They are formed from giant cells. The tubercles, which have an intensive metabolism, acquire large sizes due to the effect of toxic substances. The appearance of such granulomas is a distinctive feature of the tuberculous process, since Koch's bacillus is a toxic structure that destroys healthy tissues.
Reverse development
A decrease in the inflammatory process is characterized by resorption of foci of inflammation, a change in density curdled contents and the formation of a capsule around the tuberculous tubercles, consisting of a connective fabrics. Large lesions are covered with scars due to the penetration of fibroblasts. In the process of regression of the pathological process, the fibers go through the stage of hyalinosis.
The reverse development indicates the activation of the body's defenses.
Paraspecific tissue reactions
The response of the immune system, reflecting its reactivity, occurs in the heart or vascular bed, as well as in the parenchymal organs. Its signs are manifested by thrombovasculitis, nodular infiltrates containing macrophages and lymphocytes. Paraspecific reactions occur in the endocrine organs, articular tissues, and the gastrointestinal tract.
Nuances of diagnosis
Examination of a patient suffering from pulmonary granulomatosis has its own characteristics. The doctor prescribes the following examinations for the patient:
- Fluorography. In the picture, the phthisiatrician sees multiple points that resemble grains of sand. Large nodules appear as large, dark areas.
- Radiography. Provides similar information, but the patient is exposed to more radiation.
- CT or MRI. The methods establish not only the presence of tubercles, but also determine other diseases of the lungs.
- Blood tests. The doctor pays attention to such indicators as: the number of formed elements, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- Mantoux test, Diaskintest, sputum and saliva test. Research confirms the development of tuberculous granuloma.
Important information: How is PCR taken for tuberculosis
Treatment principles
The mechanism of therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating pathological formations in the lungs in the form of nodules includes the use of the following drugs:
- Cyclophosphamide;
- corticosteroids;
- Azathioprine;
- Methotrexate;
- Mycophenol mofetil;
- 15-deoxypergesamine.
The patient is injected with intravenous immunoglobulin. To achieve this goal, the doctor prescribes Retuximab and Infliximab.
If the disease is in an advanced stage, pulmonary hemorrhage often occurs. In this case, plasmapheresis is included in the course therapy.
To restore airway patency, a tracheotomy is performed. The tactics of treating the disease include the use of antibiotics. If there is no positive dynamics in the treatment of the disease, surgical treatment is prescribed.
AB therapy is carried out using drugs such as:
- Ceftriaxone;
- Cefepim;
- Cefazolin;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Levofloxacin.
If pulmonary hemorrhage develops, venous access is provided for infusion. The patient is given oxygen, measures are taken to prevent asphyxia.
In a hospital setting, the patient is connected to a ventilator.
Additional diagnostic measures are carried out:
- CT;
- FBS;
- spirography;
- MRI;
- ECG;
- HIV test.
Outcomes and prognosis for recovery
The development of tuberculous granuloma ends with the formation of a chronic process, accompanied by granulomatous pneumonitis. It is not uncommon for patients treated with corticosteroids to develop an allergic reaction.
In the case of a lethal outcome, an interstitial granulomatous reaction with predominant changes in the lungs is determined at an autopsy.
The unfavorable end of the disease is manifested by the generalization of the tuberculous process, the appearance of complications - spontaneous bleeding, pulmonary and heart failure.
During the recovery period, the nodules are resorbed and scarred in the patient's lungs. The patient's general condition improves, immunity increases. The doctor notes a positive trend after X-ray examination. Recovery occurs when the patient adheres to the complex treatment and its effectiveness.