Content
- Definition
- Views
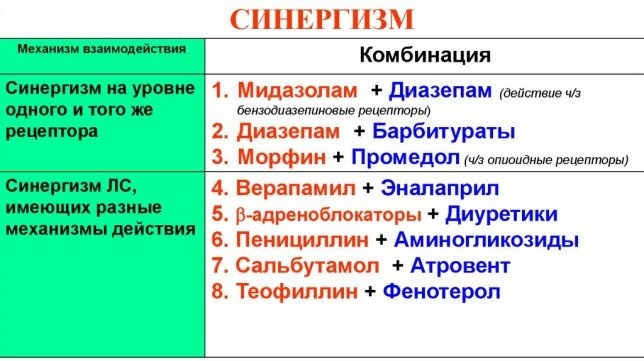
- Effect summation
- Sensitization or sensitizing effect of drugs
- Effect potentiation
- Additive action of drugs
- Features at different stages
- Suction phase
- Distribution stage
- Biotransformation (metabolism) stage
- Stage of withdrawal
- Causes
- Influence on the body
- A heart
- Organs of the gastrointestinal tract
- Thyroid
- Consequences
- Synergy video
To achieve the most positive result from the drug treatment passed in modern pharmacology, the synergistic effect is increasingly used. This phenomenon can manifest itself in two forms: potentiation and summation of effects. With the right combination of medications, you can slow down the body's addiction to antibiotics, reduce the likelihood of adverse reactions and improve the condition of internal organs, tissues.
Self-medication is fraught with the development of severe complications. For example, antidepressants can several times to enhance the final therapeutic effect, and also increase the likelihood of negative effects on the body of anticholinergics and antihistamines. To undergo combined drug therapy, the patient should be assigned a complex examination of the body so that the attending physician correctly diagnoses and draws up an individual scheme treatment.
Definition
Synergism in pharmacology is the simultaneous action of several substances at once on a certain pathological process. Thanks to the interaction of drugs in traditional medicine, it is possible to achieve positive results in cases where, when used separately, medications were found to be ineffective.
In total, it is customary to distinguish 4 types of drug interactions:
- Chemical.
- Pharmacodynamic.
- Physicochemical.
- Pharmacokinetic.
As a result of a chemical reaction between drugs, new substances are formed that are characterized by completely different biological activity.

For example, if a patient takes calcium and tetracyclines at the same time, then insoluble complexes will be formed, which will practically not be absorbed in the intestine.
Those drugs that have an alkaline reaction are neutralized in an acidic environment, while losing 100% of their therapeutic activity. For this reason, it is forbidden to enter the patient with a solution of sodium caffeine-benzoate simultaneously with novocaine hydrochloride.
| Interaction of drugs | ||
| Drug 1 | Drug 2 | Result |
| Oral hypoglycemic drugs | NSAIDs | Displacement of the second drug by plasma proteins, enhancement of the hypoglycemic effect |
| Phenylbutazone | Slowing down the metabolism in the oven, increasing the hypoglycemic effect | |
| Aminoglycosides | NSAIDs | Violation of renal excretion of aminoglycosides, an increase in their concentration in the blood |
| Digoxin | NSAIDs | Decreased excretion of digoxin by the kidneys (significant decrease in GFR), increased concentration of cardiac glycosides |
| Indirect anticoagulants | NSAIDs | Displacement of the components of NSAIDs from the connection by plasma proteins, enhancement of the anticoagulant effect. There is a risk of internal bleeding |
| Phenylbutazone | Slowing down metabolism in the liver, increasing the anticoagulant effect | |
| Lithium preparations | NSAIDs | Impaired renal excretion of lithium, increasing its toxicity and final concentration in blood plasma |
| Methotrexate | NSAIDs | Decrease in renal extraction of methotrexate, increase in its content in the blood. Additionally, the toxicity of the drug increases by 60% |
| Phenytoin | Phenylbutazone | Slowdown of metabolism, increased toxicity and total concentration of phenytoin in blood plasma, increased therapeutic effect |
 The pharmacodynamic principle of drug interaction is due to their effect on certain receptors. Many drugs change their properties when combined. If the medications prescribed to the patient affect the same receptor, then we are talking about direct interaction, in all other situations - indirect.
The pharmacodynamic principle of drug interaction is due to their effect on certain receptors. Many drugs change their properties when combined. If the medications prescribed to the patient affect the same receptor, then we are talking about direct interaction, in all other situations - indirect.
When using drugs that have a calming effect on the central nervous system (for example, tranquilizers, antipsychotics), you can reduce the dosage of general anesthetics by 30-40% during anesthesia. This effect is due to potentiation (one drug enhances the therapeutic effect of another).
As an example of the physicochemical interaction of drugs, one can consider the ability activated carbon to adsorb toxins on its surface, thereby reducing the likelihood of their penetration into organism. This property of the enterosorbent is actively used in traditional medicine to normalize the patient's condition when harmful substances enter the gastrointestinal tract.
Pharmacokinetic interaction of drugs is permissible only in the process of distribution and biotransformation. The intensity of absorption of the components of the drug can be changed by those drugs that affect the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, the pH level. The use of antacids reduces the therapeutic effect of sulfonamides and acetylsalicylic acid. But Diphenin, which blocks the intestinal transport systems, slows down the absorption of folic acid.
Views
Synergism is a widespread concept in pharmacology, since this phenomenon describes the principle of interaction between medications that have a different principle of action. A significant increase in the hypotensive effect can occur with the use of ACE inhibitors and calcium antagonists as a result of their influence on various mechanisms of regulation of vascular tone.
For the safe use of several drugs at once, you need to make sure that there is no antagonistic effect between them. Only with a rational combination of drugs will it be possible to reduce their daily dosage, due to which the likelihood of adverse reactions will also be minimized.
In traditional medicine, it is customary to divide synergy into several key categories:
- Rational combinations. The composition of drug therapy includes pharmacological agents to increase the safety and effectiveness of treatment. In the first case, the B-2-adrenergic agonist Salbutamol in combination with Euphyllin enhances the bronchodilator effect. The simultaneous use of acetylsalicylic acid with omeprazole reduces the likelihood of a patient developing a stomach ulcer.
- Irrational combinations. This category includes drugs that reduce the overall effectiveness of pharmacotherapy. With the combination of ACE inhibitors with Aspirin, the frequency of hospitalization of patients increases significantly due to the development of decompensated heart failure. Additionally, there is a decrease in the hypotensive effect in arterial hypertension.
- Potentially dangerous combinations. Medicines reduce the safety of pharmacotherapy by 30-50%. When a potentially dangerous combination drug therapy is prescribed by the attending physician, 8-10% of patients develop unwanted drug reactions.
Medical statistics confirm that about 80,000 patients die each year due to improperly formulated combination treatment.
Effect summation
Thanks to the correct combination of medications, the final result of the completed therapeutic course will correspond to the sum of the pharmacological effects of each of the medicinal drugs prescribed by the attending physician funds. For example, if a patient with heart failure takes Furosemide and Ethacrynic acid at the same time, then this is fraught with the summation of their diuretic action.
Sensitization or sensitizing effect of drugs
With sensitization, in 95% of cases, patients are prescribed drugs of different principles of action, which makes it possible to enhance the pharmacological effect of only one of the drugs used. It is on this principle that the positive therapeutic effect of the polarizing mixture is based, which is in great demand in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction.
To improve the patient's condition, the following drugs are simultaneously used:
- Glucose solution 5% (500 ml).
- Potassium chloride 1.5 g.
- Insulin 6 U
- Magnesium sulfate 2.5 g.
If it is not possible to use magnesium sulfate and potassium chloride, then they can be replaced with Panangin solution (20 ml). The principle of operation of the polarizing mixture is based on the fact that insulin and glucose increase the transmembrane current of K + ions inside the heart cell by 40%. Thanks to this, cardiologists manage not only to prevent, but also to stop serious deviations of the heart rhythm.
The sensitizing principle of action of medications allows to increase the final concentration of iron ions in the patient's blood plasma. This effect is achieved due to the simultaneous use of vitamin C (ascorbic acid) with those pharmacological agents that contain iron.
Effect potentiation
In the presence of appropriate indications, the combination drug therapy includes drugs, the combination of which can enhance the pharmacological effect of each of the jointly prescribed drugs. The patient should be treated under the supervision of the attending physician, since in this case there is a high likelihood of adverse reactions.
The maximum hypertensive effect in anaphylactic shock can be achieved through the simultaneous use of the alpha-adrenergic agonist Norepinephrine and the glucocorticosteroid Prednisolone. To achieve a positive bronchodilator effect in status asthmaticus, the patient is prescribed a phosphodiesterase inhibitor Euphyllin and Prednisolone.
Additive action of drugs
Synergism in pharmacology is a type of interaction of the same or completely different according to the principle of action of pharmacological agents, in which the final therapeutic effect of the combination therapy is enhanced, but the likelihood of the development of side effects also increases action. For each patient, an individual treatment regimen is drawn up, since not only the patient's age and the form of the disease diagnosed in him are taken into account, but also the presence of concomitant pathologies.
The additive action of medications is a type of synergy in which the final effect the action of all simultaneously applied drugs corresponds to the activity of each substance in separately. For the safe treatment of patients with bronchial asthma, pulmonologists include the phosphodiesterase inhibitor Theophylline and B-2-adrenostimulant Salbutamol in the combined drug therapy. Thanks to the completed treatment, the lumen of the bronchi expands by 30-40%.
Features at different stages
In order for combined drug therapy to be not only effective, but also safe, it is necessary to take into account the principle of drug interaction at the stage of absorption, distribution, biotransformation, as well as during excretion from organism.  With the right combination of drugs, it is possible to significantly improve the general well-being and quality of life of the patient, even with severe chronic pathologies.
With the right combination of drugs, it is possible to significantly improve the general well-being and quality of life of the patient, even with severe chronic pathologies.
Suction phase
The intensity of absorption of drugs within the gastrointestinal tract can change under the influence of other medications. This is possible in cases where the drugs used interact with each other at a chemical level, and also change the acidity of the contents of the stomach and intestines. In pharmacology, there are drugs that stimulate and inhibit the absorption of drugs. The main properties of drugs must be indicated by the manufacturer in the instructions.
The maximum impairment of drug absorption occurs when active and auxiliary components of one medication become insoluble under the action another medicine.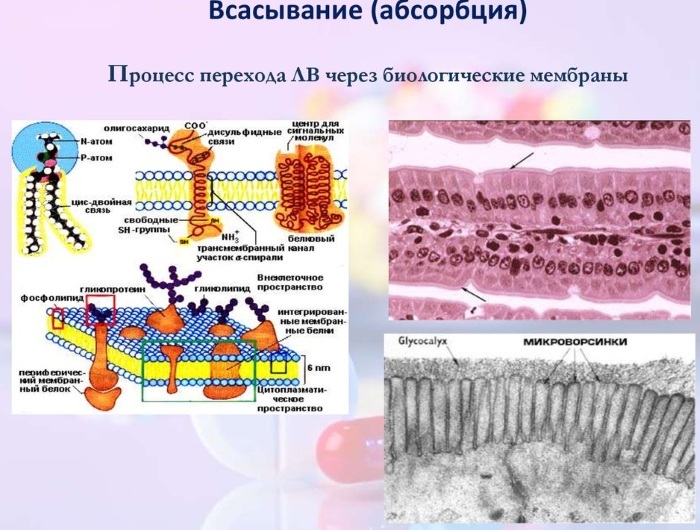
For example, macrolides and fluoroquinolones, due to their interaction with ferrum, aluminum, magnesium and calcium, form specific complexes that are practically not absorbed in the intestine. Cholestyramine reduces the absorption of Cephalexin, Clindamycin, Thyroxine and Tetracycline by 90%.
Distribution stage
The components of the drugs used are carried throughout the body through the bloodstream. The efficiency of drug distribution directly depends on the state of hemodynamics in tissues and organs. 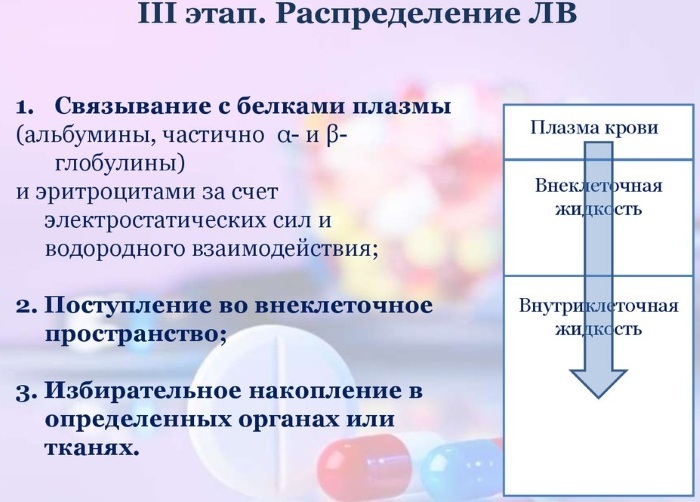 Thus, in patients with chronic heart failure, with a decrease in cardiac output, renal perfusion decreases, due to which the effectiveness of loop diuretics deteriorates.
Thus, in patients with chronic heart failure, with a decrease in cardiac output, renal perfusion decreases, due to which the effectiveness of loop diuretics deteriorates.
If the interaction of drugs occurs at the stage of biotransformation, then the drugs used can reduce the activity of liver enzymes. Moreover, one drug can increase or decrease the effectiveness of another. By observing the recommended dosage, maximum synergy can be achieved.
Some drugs are excreted from the body unchanged, but there are also drugs that undergo biotransformation. This metabolic conversion of chemicals into more hydrophilic compounds falls into 2 categories - conjugation and metabolic transformation.
Conjugation is a biochemical process due to which actively acting various chemical groups of molecules of endogenous connections.
Metabolic transformation is characterized by reduction, oxidation or hydrolysis of the drug by microsomal liver oxides. As a result of biotransformation, drugs undergo dramatic changes or completely lose their pharmacological activity.
Stage of withdrawal
Synergism in pharmacology is a type of drug interaction in which it is possible to achieve the maximum therapeutic effect, which is extremely important in the treatment of heart failure, bronchial asthma, stomach ulcers and duodenal ulcers intestines. When excreted, drugs interact with each other, thereby affecting tubular secretion, glomerular filtration and reabsorption.
Many medications reduce the glomerular filtration rate by reducing the volume of circulating blood or by reducing the tone of the renal arteries. This significantly increases the concentration of drugs that are removed from the body by passive filtration. 4
This is fraught with the development of numerous adverse reactions. For example, a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate when Furosemide is prescribed to a patient leads to inhibition of the filtration of aminoglycoside antibiotics, which increases nephrotoxicity.
Causes
In all areas of traditional medicine, the combined use of drugs is in great demand to achieve synergy (enhance the therapeutic effect of drugs). Only the attending physician should select medicines, taking into account the age and general condition of the patient, the form of the disease diagnosed in him and the presence (absence) of concomitant complications. For this reason, self-medication is strictly prohibited.
A combination of drugs is used to achieve the following results:
- Correction of the main drug composition.
- Achieving the maximum therapeutic effect.
- Reducing the intensity of the development of the body's resistance to antibiotics.
- Simultaneous positive effect of drugs on different tissues and organs.
- Reducing the likelihood of adverse reactions.
The main task of combined drug therapy is the choice of drugs in a relatively low dosage to neutralize the anti-regulatory mechanisms that one of the medicinal funds. Synergism helps to improve the efficacy and tolerance of concomitant medications.
For combination therapy, in 95% of cases, patients are prescribed drugs with a different mechanism of action. For example, in cardiology, correctly selected drugs allow to achieve the normalization of blood pressure, as well as to eliminate the counter-regulatory mechanisms of increasing blood pressure as much as possible. The disadvantage of combination therapy is that in some cases patients have to take drugs that are not needed.
Influence on the body
Combination treatment involves the simultaneous administration of 2 or even more drugs from different groups. An individual treatment regimen drawn up by a doctor allows a faster, exiled therapeutic effect to be achieved. If the patient adheres to the recommended dosage and frequency of administration of drugs, the likelihood of disease progression and the development of complications is minimized.
A heart
The combined use of drugs in 99% of cases is prescribed to patients with a high risk of developing cardiovascular complications (stroke, heart attack), as well as when it is impossible to achieve the desired effect when using only one drug.
In cardiology, the following combinations of drugs are in greatest demand:
- Thiazide diuretics and ACE inhibitors.
- Sartans (angiotensin 2 receptor blockers) and calcium antagonists.
- Thiazide diuretics and calcium antagonists.
- ACE inhibitors and calcium antagonists.
- Thiazide diuretics and angiotensin receptor inhibitors 2.
Numerous clinical studies have shown that the simultaneous use of diuretics and antihypertensive drugs that block the activity renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, allows not only to improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system, but also to reduce the likelihood of occurrence by 90% adverse reactions.
Organs of the gastrointestinal tract
Proton pump inhibitors are recommended for effective treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. This category includes: Omeprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantoprazole. These medicines help to normalize the secretion of acid in the stomach.
Lipophilic non-ionized drugs are much better absorbed by the gastrointestinal mucosa than hydrophilic ionized drugs. Ketoconazole and other antifungal drugs (azole derivatives) are ineffective when used with histamine H2 receptor blockers. Barbiturates are prescribed together with antacids, which can reduce the likelihood of a patient's sleep disorder by 99%.
Vincristine, Cyclophosphamide and Procarbazine inhibit the absorption of Digoxin, thereby reducing its effectiveness. That is why gastroenterologists recommend buying Digoxin in capsule form. The use of antacids helps to reduce gastric acidity. But such preparations contain salts of alkali and alkaline earth metals. Antacids are contraindicated during pregnancy, lactation, as well as Alzheimer's disease and chronic constipation.
Antisecretory drugs reduce the body's production of hydrochloric acid. Prokinetics stimulate the motility of the stomach and intestines, due to which drugs from this category often included in combination drug therapy for the treatment of flatulence and intestinal obstruction.
Thyroid
The combined drug therapy, which necessarily includes medicines containing iodine. Taking magnesium and iron preparations at the same time as hormonal agents can reduce the activity of the latter. Thyroxine forms stable complexes with iron, which reduces the final absorption of Levothyroxine, which is prescribed to patients with primary hypothyroidism.
Correctly selected drug therapy can prevent the formation of goiter associated with iodine deficiency in the body. After the end of treatment, in 90% of cases, it is possible to restore the natural size of the thyroid gland.
Consequences
Synergism in pharmacology is the phenomenon of mutual enhancement of the effectiveness of the drugs used. But drug therapy will be safe and effective only if all the pharmacological properties of specific drugs were taken into account when drawing up an individual treatment regimen.
The use of incompatible drugs is fraught with the development of the following complications:
- Deterioration of the cardiovascular system. Most often, patients are diagnosed with acute cerebral edema, myocardial infarction, an increase in blood pressure to critical levels.
- Disturbances in the work of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract (profuse diarrhea, internal bleeding, exacerbation of a previously diagnosed gastritis or ulcer).
- Allergic reactions: bronchospasm, urticaria, Quincke's edema, itching and burning of the skin.
- Disturbances in the work of the central nervous system. The patient's condition may worsen due to lack of motor coordination, hallucinations, psychosis, tremor.
- Liver disorders (eg, hepatitis).
- Development of diseases of the hematopoietic system.
- Decreased visual acuity, hearing impairment.
- Disorders of the kidneys (acute renal failure).
- Uterine bleeding.
- Oral tissue necrosis.
Every year, more and more drugs appear in pharmacology, with improper combination which the patient has adverse reactions of varying severity, and also develops complications. In some cases, the irrational use of medications leads to the death of the patient.
Safe synergism of medicinal substances is possible only if for the preparation of an individual scheme treatment, the doctor was guided by the collected anamnesis of the patient, and also studied as much as possible all the properties of the prescribed drugs. It is strictly forbidden to compose combination therapy on your own, as it is life-threatening.
Synergy video
Pharmacodynamics in simple terms:
