Content
- History and schools of thought
- Definition
- Characteristics and properties
- Functions and role
- Forms of manifestations
- Psychological theories and schools
- Perception management techniques
- The illusion of Niño disappearing
- Illusion by William Eli Hill
- Necker cube
- Accommodation video
Psychological research accommodation mechanism taken over from physiology, optics and biology, and are rooted in astronomy. This was studied even before the corresponding term was introduced. The mechanism that underlies the focusing of the human eye on near and far objects was of scientific interest.
History and schools of thought
The first scientist who tried to explain this process was Johannes Kepler, born in 1571. and studied not only ophthalmology, but also astronomy, mathematics and mechanics. Among his achievements is the discovery of the role of the lens in the physiology of vision. His theory of accommodation was described in one of his works on optics in 1611. Kepler came up with the idea that the "place of sight" is on the retina.
The next scientist to study accommodation was Christopher Scheiner, a German physicist, astronomer, mechanic and mathematician. As you know, the study of astronomy presupposes an understanding of some optical mechanisms. So, in 1619 Scheiner wrote the essay "Oculus, hoc est fundamentum opticum", in which he outlined his understanding of the eye as an organ.
He studied the refractive power of eye fluids. Christopher established that the refractive power of the lens and aqueous humor in the organ of the eye are practically equal to the forces of physical objects - respectively, glass and water. Vitreous moisture occupies an intermediate position in terms of its ability to refract. Scheiner confirmed by observation the assumption set forth by Kepler about the "place of sight" first in the bull's eye, and in 1623. and on the human.
The first prominent scientist in the fields of physiology, philosophy, and psychology to study accommodation was René Descartes. In psychology, Descartes is studied as one of the "pillars" of modern theory, to which the first views on processes of contradiction, dynamism of personality, consciousness and soul (then all these terms are practically identified). In one of his treatises, written in 1677, Rene Descartes described the mechanism for changing the shape of the lens depending on the location of the object.
For the first time the term "accommodation" was used in ophthalmology, introduced by the German surgeon and ophthalmologist from Elbing - Karl Heinrich Burov in 1841. The very mechanism of adaptation of the lens to the examination of close, then distant objects was already known to science and was called "adaptation".
The theory of accommodation has already been examined and presented in detail by another German psychologist - Hermann van Gemholtz. His contribution to the theory is no less significant - it was Gemholtz, 11 years later, in 1855. found that the thickness of the lens and thus the degree of refraction of light changes during accommodation.
| Basic theories of accommodation of perception | ||
| Scientist | Year | Hypotheses, assumptions, achievements |
| Johannes Kepler | 1611 | Study of the lens and its role in focusing vision |
| Christopher Scheiner | 1619 | The refractive power of the lens and the aqueous humor in the organ of the eye are practically equal to those of glass and water. |
| Rene Descartes | 1677 | The first detailed description of the accommodation process. |
| Carl Jung | 1801 | He proved that the mechanism of accommodation is due to deformation of the lens. |
| Ronald Shahar | 1992 | He put forward and confirmed the theory according to which the deformation of the lens increases with age. |
Definition
Accommodation is a specific mechanism of visual perception, which consists in changing the shape of the lens and allowing the incoming image to focus on the retina. Schiffman defines the function of accommodation in fine-tuning the lens, due to which he focuses rays of light reflected from objects that are at different distances from the organ.
Accommodation is, in developmental psychology, one of the components of the general process of adaptation of the child and is inseparable from another psychological, or rather, the mechanism of socialization - assimilation. It was studied by Jean Piaget.
In the work "eye diseases" Helmholtz in 1855 described the process of accommodation as a single, but divisible into two aspects, the process of considering only near or only distant objects. This "or" contains the duality of the accommodation mechanism.
As Schiffman points out, accommodation is a reflex process that is not realized by the individual, but can be felt by him. Lens deformation is felt as a specific tension of the eye muscles.
Characteristics and properties
Accommodation is provided by contraction and relaxation of a specific ocular muscle. Thanks to these contractions, the shape of the lens becomes either horizontally elongated, or, on the contrary, becomes more like a "spherical" one.
Scientists determine the volume and length by the properties of accommodation:
- Volume - a value measured in diopters and denoting a change in the optical power of the lens through its deformation. Optical power is the ability to refract incoming light rays, which, in turn, are repelled by objects. Light in this case provides an opportunity to determine the position of an object in space.
- Length - a value measured in meters, centimeters or even millimeters and denoting that part of the space that is accessible to the accommodation mechanism. These are the so-called "limit values", beyond which it is no longer possible to clearly see objects.
In addition, thanks to many foreign studies, certain patterns of formation and development of the accommodation mechanism have become known. For example, Haynes, Haight and Held in 1965. found that the accommodative system is laid in infancy. A newborn who is less than a month old sees only objects located closer or at a distance of 19 cm from him. The further the subject is from the infant, the more blurred it is.
Banks in 1980 supplemented the theory with the fact that the development of the accommodation system during 2-3 months of life is the most active, and reaches a climax comparable to the level of development of the adult system, at about the age of 9-10 weeks. Thus, during the second month of life, the system actively begins to respond to changes in the position of objects in space.
It is known that accommodation can perform its functions only within certain distances. Two characteristics follow from this property: the closest point of clear vision and the "marginal value".
Closest point of clear vision - the term denoting the closest distance at which it is still provided the opportunity to consider the subject with the most relaxed ciliary muscle - that is, with the maximum accommodation. Maximum accommodation is achieved either by maximum compression of the muscle that regulates the position of the lens, or by its maximum relaxation.
Objects that are closer than the point of closest clear vision will be blurry to human perception. It is important to take into account that long-term viewing of objects at close distance also strains the eye muscle and the organ itself, and this leads to deformation of the lens and impaired visual acuity.
Functions and role
The main function of the accommodation mechanism is to regulate the shape of the lens and thus change the incoming image from more fuzzy to sharper.
Accommodation is one of the most important mechanisms of visual perception in the psychology of perception. It allows not only to consider individual distant or close objects, but also to distinguish between "figure" and "background" - that is, to isolate parts of the whole object.
Thus, accommodation allows a person to navigate in the space around him. Thanks to this mechanism, a person has an idea of the approaching objects, the position of the object in space and the position in space of the perceiver himself.
Isolation of objects from the environment, concentration of attention is also performed with the participation of accommodation.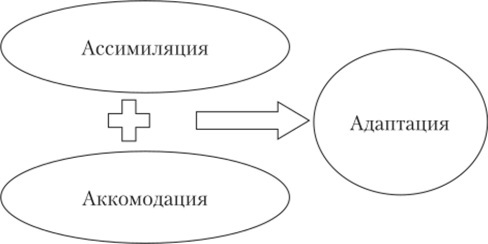
Thus, accommodation performs the following functions:
- Ensuring the selection of objects from the environment.
- Concentration of attention on certain objects and subjects.
- Determination of the texture of surrounding objects.
- Determination of the constituent parts of the structure of objects.
- Determination of the position of objects in relation to space.
- Isolation of moving objects, fixation of a potential threat: fast movements, rapidly approaching objects.
The role of the accommodation mechanism in providing a holistic process of perception and orientation in space. In turn, disturbed accommodation entails not only physiological inconveniences, physical stiffness, but also psychological consequences.
Thus, a person who is unable to isolate objects of interest from the environment feels constrained and uncomfortable. This is the emotional background of an insecure person. If focusing pathologies are detected at a very early age, infancy or congenital, this may be the cause of mental retardation.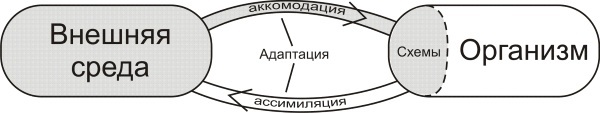
As you know, vision provides the overwhelming majority of information from the outside world. A person who is unable to focus on the constituent elements of the environment does not adapt well to changing conditions.
Forms of manifestations
Accommodation is characteristic of all mammals and consists in a change, deformation of the lens in the eyeball.
For example, in order to focus on a distant object, the lens must extend, become almost flat. But already in order to focus on a relatively close subject, the organ must, on the contrary, shrink and become "convex".
The deformation of the lens is regulated by contractions and relaxation of the ciliary muscle, which connects with the ligaments of the lens and holds it in the desired position.
Thus, the work of the ciliary muscle consists of two synergistic processes:
- Shrinks as the object approaches the eye;
- Relaxes as the object moves away from the eye.
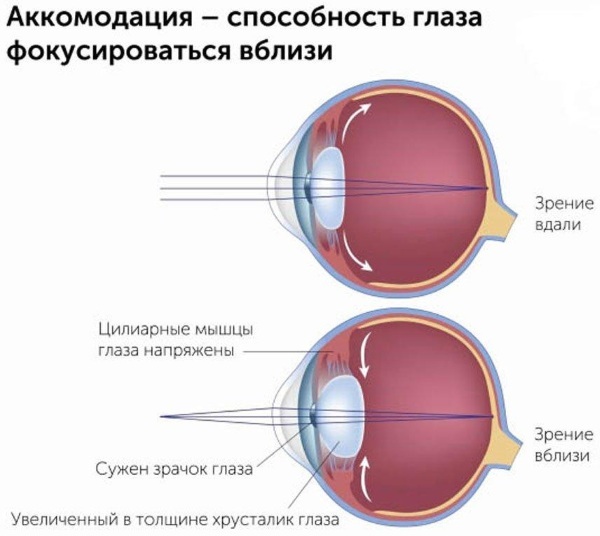
The synergy of the ciliary muscle is manifested in the antagonistic processes: relaxation is opposite to contraction, and vice versa. The unity of these interrelated processes allows you to adjust the shape of the lens.
For example, accommodation is manifested when a person alternately examines something remote from him, then close to him. To achieve the "minimum" and "maximum" tension of the ciliary muscle, you must wait until vision is fully focused on the subject.
Accommodation is carried out by the ciliary muscles, which, in turn, are affected by the oculomotor or oculomotor muscles. The ciliary muscle holds the lens with ligaments and, when it contracts, stretches it, giving it a more elongated shape.
Psychological theories and schools
Experimental psychology was founded in 1879. Wilhelm Wundt. At the same time, such an approach to understanding human sensations, perception and psychology in general, as structuralism, prevailed.
Accommodation is a complex composite process in the psychology of structuralism, which is also a part of visual perception. Structuralism was built on the study of the basic "particles" that make up holistic processes. Adherents of this approach argue that any integral consists of particles, atoms. Thus, the structuralists represented by the students of Wilhelm Wundt and Bradford Titchener identified the structure of perception, and, as a consequence, its mechanisms.
Gestalt psychology arose as a reaction to the approach of Wundt and his followers and positioned perception as mutual influence both on each other and on the person, perceived objects and irritants.
The principles of perception that Gestalt psychology has established include the following:
- Select the shape and background.
- Differentiation.
- Closures.
- Good shape.
- Isomorphism.
The constructivist approach is based on the fact that the individual is more responsible for shaping the surrounding reality than the actual physical characteristics of objects. The main role in the process of perception is given to the perceiver - that is, the observer, the subject.
From this, adherents of the constructivist approach have established that perception goes beyond the formula "stimulus-response" or "stimulus-perception by means of sensory organs." The experimental confirmation of the theory was carried out by the studies of Irwin Rock, Julian Hochberg, Richard Gregory in 1988-1990.
An ecological approach to understanding perception was proposed by James Gibson in the middle of the 20th century. This theory, in contrast to the constructivist approach, makes the perceiving person an object of perception. It turns out that, exploring the surrounding reality, the perceiver only assimilates information without processing it.
However, Gibson set aside a special place for the accommodation mechanism. From an ecological point of view, as the distance between the observer and any texture increases, it seems that its individual elements are reduced and form a solid, flat, smooth figure or surface.
Accommodation is, in the psychology of the information approach, the processing of information given by the environment in a specific form, similar to a program. It was founded, among other things, by David Marra, who laid out the basic definitions in his monograph Vision. The environment here acts as a source of information, certain values of characteristics: shapes, outlines, lines, and so on. The processing of the received information becomes the function of consciousness, but taking into account only the illumination, like a computer program or a photo editor.
The neurophysiological approach determines perception, first of all, by the work of neural connections and impulses, the interaction of peripheral nerve centers with the brain. Francis Crick in 1994 described perception from a neurophysiological perspective in The Striking Hypothesis.
Cognitive neuroscience is an approach that studies thinking and perception as processes provided by the brain at the neural - that is, at the cellular - level. Each of the processes, for example, thinking, perception, attention or memory (higher mental functions) are due to the work of different parts of the brain.
| Approach name | Representatives | Year | Main positions |
| Structuralism | Wilhelm Wundt, Edward Titchener | 1879 | Perception consists of separate processes and mechanisms. Accommodation is a mechanism consisting of separate interconnected processes. |
| Gestalt psychology | Max Wertheimer, Wolfgang Köhler, Kurt Koffka | 1912 | The main thing in the accommodation mechanism is the mutual influence of muscle contraction, light refraction and picture perception. If we change the course of one component of the accommodation mechanism, then the final result of perception will also change. Accommodation acts as a sub-process of perception and implements the principle of "figure and background". |
| Constructivist | Irwin Rock, Julian Hochberg, Richard Gregory | 1988 | The subject constructs the surrounding reality more than reality affects the subject. Accommodation is arbitrary. |
| Ecological | James Gibson | 1947 | The individual perceives the surrounding reality as it is. In the process of perception, a person is a passive link. The accommodation mechanism is not arbitrary, it is regulated by lighting. |
| Informational | David Marra | 1982 | Reality is represented by a set of certain information. The brain processes it using certain computational operations. Accommodation is a genetically inherent involuntary mechanism. |
| Neurophysiological | Francis Creek | 1994 | Perception is conditioned by the work of neurons and physiology. Accommodation is an involuntary mechanism carried out with the help of the ciliary muscle and reflexes. |
| Cognitive neuroscience | Bernard Baars, Gage Nicole | 1970-1990 | Perception is one of the cognitive functions of the brain, which is determined by the work of specific neuronal centers in the cerebral cortex. Accommodation is arbitrary and acts as a sub-process of separating an object from the environment, orientation in space. |
Perception management techniques
Perception can be distorted by influencing the factors that form the general image of perceived reality, or by working on the attitudes of the individual. Perception is conditioned not only by the physical characteristics of the perceived objects, but also by the psyche of the subject of perception. So, for example, one and the same object can be perceived by two individuals in different ways.
The perceptual attitude is the "expected result of perception." That is, if a person received the knowledge that the picture shows the silhouette of a certain woman, then with a large probability, the individual will complete the missing details in consciousness and endow the picture presented by the experimenter with female features.
The illusion of Niño disappearing
Optical illusion based on the retinal lateral inhibition mechanism. The figure shows 12 points that cannot be seen at the same time. Only by moving his gaze over the picture, along the grid of Ludimar Hermann, the perceiver can see either 2 or 3 points that move with the gaze of the individual.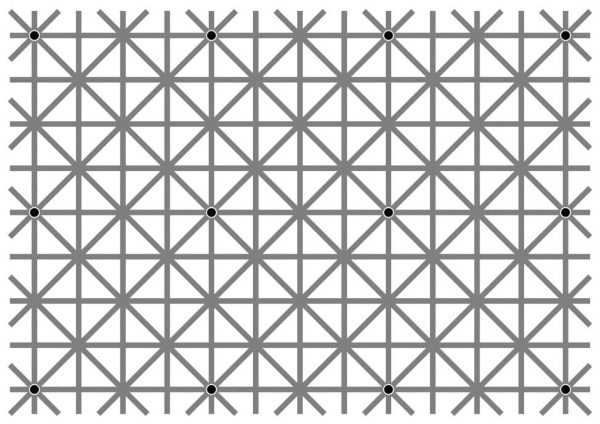
The mechanism of lateral inhibition is to provide contrast, highlight the figure from the background by giving the figure clarity and sharpness.
Illusion by William Eli Hill
The picture, the perception of which according to the research results depends on the age of the respondent. Psychologists have established that people under the age of 30 saw a girl in the image. The elderly woman in the picture presented was perceived by the rest.
Most likely, this is due to perceptual attitudes and the work of the unconscious - older people pay more attention to the signs of old age.
Necker cube
The Necker Cube is an illusion that is a three-dimensional cube. Despite the simplicity of optical illusion, it is almost impossible to determine which side of the cube is near and which is far. Only with the help of a conscious concentration of attention on one of the sides of the figure, it becomes possible to determine its position in three-dimensional space.
The psychology of perception distinguishes accommodation as one of the mechanisms of visual perception. Thanks to this mechanism of accommodation, it becomes possible to consider close and distant objects, focusing attention at certain points.
Author: Svitkevich Julia
Accommodation video
Definition of accommodation: