Content
- Characteristic
- Functions and properties
- Anatomy and structure
- Dislocation
- Classification
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Reduction of joints
- Applying a tight bandage
- Taking pain medications
- Taking anti-inflammatory drugs
- Limiting physical activity
- Wearing orthopedic shoes
- Osteoarthritis
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Wearing orthopedic insoles
- Massage
- Weight loss
- Decreased physical activity
- Removal of inflammation
- Taking medication to repair cartilage
- Surgery
- Folk remedies
- Foot Anatomy Videos
Chopard's joint and adjacent Lisfranca lie at the base of the human foot. These joints connect the metatarsus, tarsus and heel bone, providing support for the entire arch of the foot. The Lisfranc and Chopard joints maintain the integrity of the foot. Any disruption in the work of the Chopard and Lisfranc joint completely blocks the movement of the lower extremities, creating discomfort and pain, and can lead to the development of chronic diseases.
Characteristic
The human foot has 3 main sections: metatarsus, tarsus, and toes. In turn, each section includes many small bones, which are united by joint blocks. The Chopard joint unites the transverse joint of the tarsus, and also connects the calcaneal-cuboid and talo-navicular joints. The Lisfranc joint connects the metatarsus and tarsus.
They attach the metatarsus to the bones of the heel and help to fix the position of the leg in a static state and during movement. These two joints fully ensure the union of the arch of the foot and its position. The ligament of the Chopard and Lisfranc joints prevents the foot from twisting too much, and maintains the small joints in one state for ease of movement.
Functions and properties
The Chopard and Lisfranc joint has a complex structure that allows you to fix many small joints and bones inside the human foot. Most of the bones and joints in the foot are stiff and flat to provide increased support for the lower extremities. Their active movement can lead to deformation of the bones and feet, dislocation and fracture.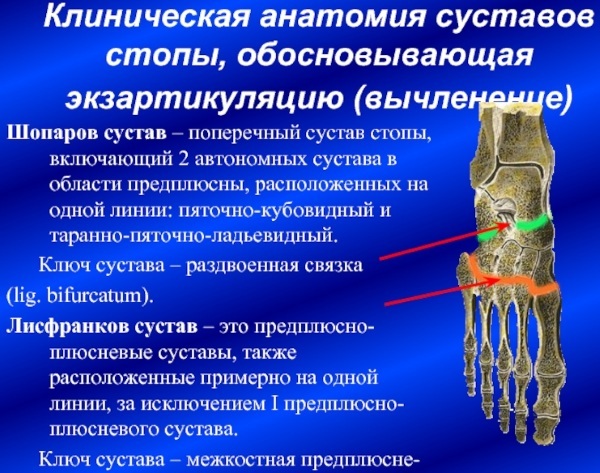
The main functions of the Chopard and Lisfranc joints are:
- stabilization of the position of small joints in the foot;
- fixation of the joints of the metatarsus, heel and tarsus;
- maintaining the position and arch of the foot;
- attachment of the metatarsus and tarsus to the heel;
- ensuring the required angle of rotation of the foot;
- maintaining the integrity of the entire foot.
Anatomy and structure
The Chopard and Lisfranc joint is located in the center of the foot, which consists of the tarsus, metatarsus and toes. Tarsus located at the toes and consists of a group of bones, which includes:
- wedge-shaped;
- cuboid;
- scaphoid;
- calcaneal;
- ramming.
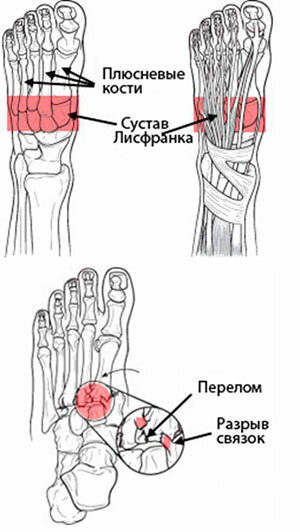
The metatarsus is located closer to the base and includes 5 tubular bones. The Lisfranc joint connects the metatarsus and tarsus together, extending across the entire foot. This joint has wedge-shaped and cuboid-metatarsal joints that connect all the small blocks of the joints and the bones of the foot to each other. The Lisfranc ligament has 3 bundles that connect the metatarsal bone and the medial bone.
The joints inside the foot almost do not move, they are flattened as much as possible and perform the functions of support and support the entire body in an upright position. With such a structure, it is important for the bones and joints of the foot to maintain their maximum stable position to ensure the desired type of mobility of the lower extremities.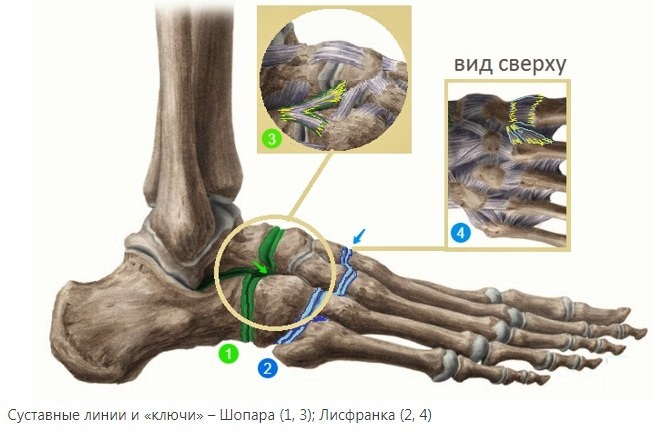
The Chopard joint in the foot also transversely connects the calcaneo-cuboid and talonavicular joints. This joint has a bifurcated ligament that begins at the calcaneus and is attached to the metatarsal bones on both sides. The Chopard joint ensures the integrity of the foot and preserves it during movement. In the event of a violation of the integrity of the Chopard joint, the patient completely stops mobility in the foot.
Dislocation
The joint of Lisfranc and Chopard is subject to frequent trauma. The Lisfranc joint is subject to dislocations and relocation dislocations due to the peculiarities of its location in the foot. Dislocation of this joint can cause intense physical exertion or a sharp change in the position of the foot.
Due to the peculiarities of their location, these joints are prone to dislocation even with slight pressure on the foot in a certain position. After dislocation of the joint, severe pain occurs, the mobility of the rest of the foot may be impaired and its integrity may be impaired.
Classification
The Lisfranc joint, like the Chopard joint, can be dislocated in different ways.
Depending on the type of violation of the position of the bones, dislocation of this joint is distinguished:
- full, when the joint completely changes its position;
- incomplete with a partial change in the position of the joint.
Depending on the place of injury, joint dislocations are divided into:
- internal;
- external;
- dorsal-external;
- plantar;
- combined.
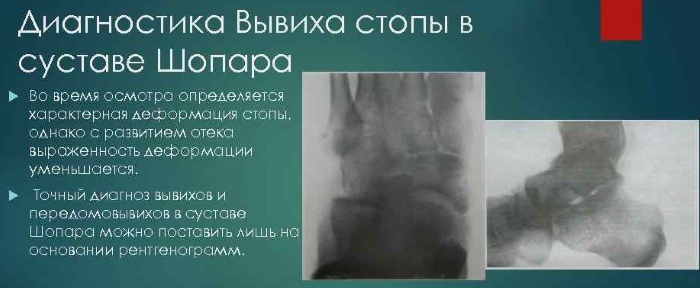 Due to the peculiarities of the location of the joint of Lisfranc and Chopard, it is rather difficult to determine the presence of a dislocation in it. For accurate diagnosis and determination of the type of dislocation, it is necessary to make an X-ray in 3 projections (direct, lateral and at an angle of 30-40 degrees) with viewing all interosseous spaces. In rare cases, an additional X-ray of the healthy foot is used for comparison.
Due to the peculiarities of the location of the joint of Lisfranc and Chopard, it is rather difficult to determine the presence of a dislocation in it. For accurate diagnosis and determination of the type of dislocation, it is necessary to make an X-ray in 3 projections (direct, lateral and at an angle of 30-40 degrees) with viewing all interosseous spaces. In rare cases, an additional X-ray of the healthy foot is used for comparison.
Symptoms and Signs
The joint of Lisfranc and Chopard often undergoes dislocations, after which in patients immediately or after 5-10 hours. manifests itself:
- impaired foot mobility;
- soreness when moving, pressing. Sometimes the patient cannot step on the injured leg;
- inflammation and redness of soft tissues at the site of injury;
- the formation of subcutaneous hematomas;
- deformation of the foot;
- full or partial immobility of the fingers;
- swelling of the foot.
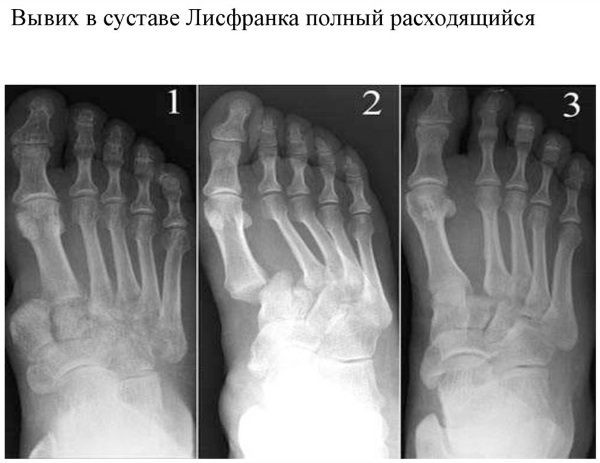
 With the dislocation of individual parts of the Lisfranc and Chopard joints, soreness in the foot may not appear immediately, but after a day after the injury. In this case, inflammatory processes in the tissues, as well as puffiness, develop gradually.
With the dislocation of individual parts of the Lisfranc and Chopard joints, soreness in the foot may not appear immediately, but after a day after the injury. In this case, inflammatory processes in the tissues, as well as puffiness, develop gradually.
Causes
Dislocation of the joint of Lisfranc and Chopard can be of different degrees and occur for many reasons.
The main ones include:
- increased physical activity when the foot is in the plantar flexion position;
- a blow to the foot or a strong kick on an object;
- falling on the foot;
- squeezing the foot with heavy objects (falling of large objects on the leg, moving the foot with wheels);
- pinching of the foot as a result of falling objects or an accident.
A joint dislocation can occur even with strong point pressure on the foot, which is in an arched position.
Treatment methods
Dislocation of the Lisfranc and Chopard joints requires immediate treatment. The main methods include:
Reduction of joints
If possible, the traumatologist performs a procedure to reposition the dislocated joint of Lisfranc and Chopard into place. This procedure is carried out only after anesthesia and X-ray removal under the supervision of a specialist by pressing on the toes. The joint is adjusted until a slight crunch appears, when the bones return to their normal position.
Applying a tight bandage
Rigid fixation of the injured joint ensures the immobility and integrity of the foot. With proper tightening of the foot, the partially dislocated joint can independently return to its previous position. The fixation bandage helps relieve pain.
Taking pain medications
Dislocation of the joint of Lisfranc and Chopard is a very complex injury, which is accompanied by increased painful sensations up to the development of shock. To relieve pain, the patient must be injected with drugs in the provision of emergency medical care, and pain relievers are also prescribed.
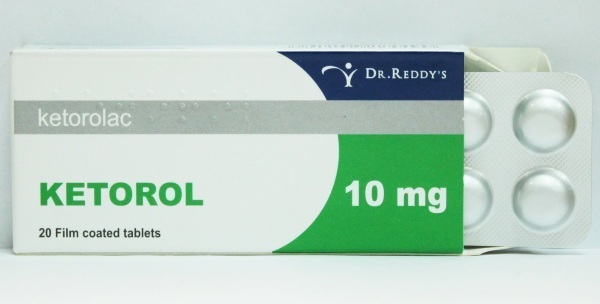
Ketarol allows you to quickly relieve pain in the lower extremities with dislocated joints. The drug is prescribed 1 tab. as the pain syndrome intensifies.
Taking anti-inflammatory drugs
To relieve inflammation from the damaged area of the joints, medications are prescribed. Ibuprocene has strong anti-inflammatory properties that promote tissue healing. The medicine is taken in 1 tab. 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days.
Limiting physical activity
During the recovery period, it is important to reduce the load on the foot damaged by the dislocation. For this, the patient is provided with a sick leave.
Wearing orthopedic shoes
With a complex dislocation, which can be associated with a fracture, even after the joints in the foot have been repositioned, soreness and impaired mobility can persist for a long time. To quickly recover and reduce the load, the patient may be advised to wear orthopedic shoes.
The special shoe relieves stress on the foot, providing support for the arch, and also removes the increased impact on the heel thanks to the soft insert in the shoe. In the correct orthopedic block, the foot quickly assumes a natural position and recovers.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoartosis of the foot is a degenerative disease that damages and changes the position of the metatarsal bones and phalanx of the big toe. With this disease, the cartilage on the joint of Lisfranc and Chopard is gradually destroyed completely. The disease develops slowly, causing more and more discomfort, pain and damage to the joints. This condition can be greatly aggravated by the occurrence of injury and serious injury.
Symptoms and Signs
Osteoartosis develops rather slowly and at the initial stages is manifested by slight discomfort when walking and, in rare cases, by the appearance of mild pain syndrome.
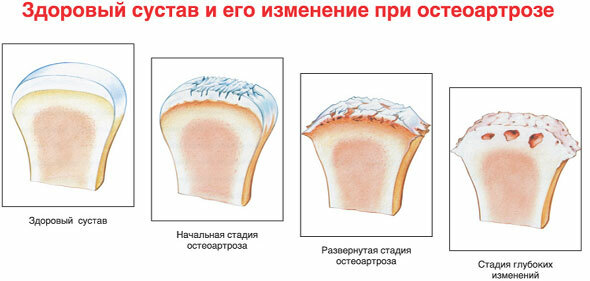
In the acute stage of the disease, patients with osteoarthritis appear:
- persistent pain in the foot, which intensifies when walking or performing certain movements;
- swelling of the joints;
- increased fatigue of the feet;
- when making movements with the foot, a slight crunch.
Causes
Osteoartosis of the Lisfranc and Chopard joints can occur as a result of many reasons, which include:
- defects and deformation of the foot;
- dislocations, fractures of the foot;
- foot bruises;
- professional features (increased physical activity on the legs of ballet dancers, standing on their feet for a long time while performing work);
- increased body weight;
- hereditary predisposition.
Often, a patient may have several causes at the same time. In this case, damage to the foot is a catalyst for accelerating the development of osteoarthritis.
Treatment methods
Treatment of osteoarthritis requires an integrated approach, so the patient is assigned several treatment options at the same time. As such, they are used:
Wearing orthopedic insoles
When wearing orthopedic insoles, the foot provides not only the necessary support for the foot, but also increased blood flow and increased metabolism in the feet.
Massage
In the absence of an acute manifestation of the disease, massage is prescribed to patients. Massage helps restore blood supply to the joints of the foot and improve lymph drainage.
A systematic course of massage allows you to improve the condition of the foot for a long time, restore nutrition to the cartilage and foot joint.
Weight loss
Patients with osteoarthritis of the joints of Lisfranc and Chopard are required to establish dietary nutrition to reduce body weight. Salty and spicy should be completely excluded from the diet. The reduction in weight helps to reduce the load on the feet during movement.
Decreased physical activity
Reducing the load on the foot helps to restore the state of the cartilage tissue. At the same time, it is impossible to completely remove the effect on the feet. The patient is recommended therapeutic exercises, which helps to restore nutrition and blood flow inside the foot.
Removal of inflammation
To relieve inflammation, medications are prescribed, which quickly relieve inflammation from the affected areas.
Diclofenac actively relieves inflammation in osteoarthritis of the foot and promotes tissue regeneration. Take the medicine in 1 tab. 3 times a day for 30-40 days. The drug ketoprofen has increased anti-inflammatory properties. The medicine helps to reduce swelling. The medicine is prescribed in 1 tab. 2-3 times a day for 20-30 days.
Taking medication to repair cartilage
Preparations including glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate are the basis of cartilage tissue nutrition. These substances help to restore the normal structure of the cartilage of the foot joint.
Glucosamine-chondroitin complex is prescribed to relieve pain and restore the condition of the joints of the feet. It is taken in 1 tab. 2-3 times a day for 1-2 months.
Artra contains substances in an increased concentration necessary for the restoration of cartilage tissue. The medicine is prescribed in 1 caps. 1-2 times a day in courses up to 2 months.
Surgery
In the event of serious damage to cartilage and bone, the patient is prescribed a surgical operation. The damaged parts of the bone are removed from the foot under anesthesia and metal screws are inserted in their place. In some cases, the joint is immobilized by fixing it with metal screws that are attached to the bone. In these cases, the foot loses a small part of its mobility, but the functionality of the lower extremities is fully restored.
Folk remedies
As additional means in the treatment of osteoarthritis, traditional medicine methods can be used:
- Aspic. Long-term cooking of beef or pork bones and cartilage saturates the broth with useful substances that help restore the tissues of the feet. To restore cartilage tissue, it is recommended to eat jellied meat during the treatment period 1-2 times a day in small portions.
-
Kalanchoe. To relieve swelling and inflammation from the cartilage, Kalanchoe tincture helps. This composition of the tincture helps to improve the blood supply to the joint. To prepare it, the stems and leaves of the Kalanchoe must be washed and cut into large pieces. Kalanchoe (100 gr) must be chopped with a blender or through a meat grinder until smooth. The mass of Kalanchoe is poured with 300 ml of vodka and placed in a cool place for 3-5 days. Then the tincture is filtered and the foot is rubbed for 10-15 minutes with light massaging movements 2-3 times a day for 14-20 days.

The joints in the Chopard and Lisfranc feet are key to maintaining the condition and functionality of the foot. Their damage causes serious violations up to complete immobilization of the limb. Competent diagnosis of the disease of this joint requires high qualifications, as well as the methods of treatment. However, the strict implementation of the prescribed complex treatment allows you to quickly restore the condition of the foot and remove the pain syndrome.
Foot Anatomy Videos
Foot joints: