Many of us know the word "sacral", which can be translated into Russian as "sacred".By the way, in translation from the Latin language the sacrum bone of our skeleton is called "os sacrum".What can be sacred in the sacrum?
According to ancient beliefs, it was believed that this one bone can resurrect a person. In some modern religious movements of pseudo-Hinduism it is believed that it is within this bone( naturally, on the astral or subtle plane) that the energy of the Kundalini is located.
Our task is simpler. We will not look for sacred images in the skeleton, but we will tell you what is sacroiliitis, what causes to it, how it manifests itself and is treated.
Contents
- 1 Sacroiliitis - what is it?
- 2 Reasons for the development of sakroileitis
- 3 Bilateral sakroileitis
- 3.1 Classification
- 3.2 Sacroiliitis degrees
- 4 Symptoms of sakroileitis
- 5 Diagnosis
- 6 Sacroiliitis treatment - drugs and procedures
- 6.1 Forecast
Sacroiliitis - what is it?
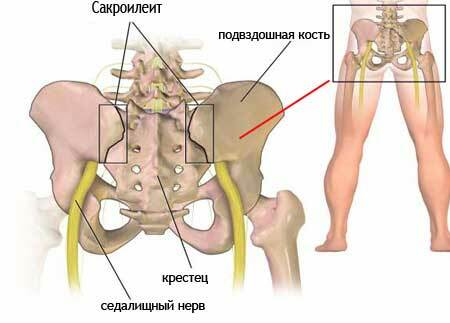
Sacroiliitis is an inflammation of the sacroiliac joints. Theoretically, the connection between the sacrum and the iliac bones is referred to the joints, but the connection between them is very tight, called amphiarthrosis.
This is the position of the sacrum, "on the stretch marks" between the iliac bones, to close the pelvic bones in a single ring. The role of these "stretch marks" is played by the sacroiliac joints.
The sacroiliac ligaments are one of the strongest in the body. Only the joints of the skull bones with the help of twisty sutures are stronger than them. But the skull bones coalesce into a single conglomerate, and between the pelvic bones and the sacrum there are normally articulate cracks.
The closest analogue of such a connection in the pelvic ring is the lonnoe articulation, the rupture of which sometimes occurs with rapid delivery. This is a serious complication requiring urgent surgery.
- The value of the sacroiliac joint is very large: it centers and stabilizes the sacrum, which makes it a reference point for the entire vertebral column, head, trunk, internal organs and upper extremity belt.
If you consider that a person wears lower, upper and winter clothes, and at the same time carries the goods - you can understand what the load is on the sacrum and the sacroiliac joints.
- Why is the value of this inflammatory process so great for doctors?
Yes, because these joints( both left and right) belong to the axial skeleton. And with the involvement of other joints( rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis), the involvement of the sacroiliac joint( as well as the temporomandibular joints) in the process indicates an increase in the severity of the process, and also allows for more serious treatment.
Reasons for the development of sakroileitis
There are two large groups of causes that lead to inflammation. The first is autoimmune diseases, in which symmetrical inflammation occurs. This group stands apart, because there are no special problems in these joints, just inflammation is a "marker" of the system process.
The second group consists of diseases that cause common arthritis and other localizations, but on the one hand. More often right-handed people develop right-sided sakroileitis( since their supporting leg is also right, and is loaded more), and left-handers have left-sided sacroiliitis.
In this case, this group of reasons includes:
- violation of joint biomechanics( eg, increased overload associated with limb shortening in inflammatory processes);
- pregnancy;
- osteoporosis in the postmenopausal period in women;
- congenital malformations( subluxations);
- prolonged sedentary work, which leads to weakening of the pelvic ring;
- tumors of pelvic bones, retroperitoneal space and pelvic cavity;
- infectious lesions( syphilis, Lyme disease).
Two-sided sakroileitis

When two-sided sakroileitis is detected, on the one hand, the diagnostic search is significantly narrowed, but on the other hand, it "turns" the other way.
So, most likely, traumatic, congenital and tumor disorders are excluded, and most of the arthritis is infectious. After determining bilateral sakroileitis, the patient is likely to identify either an autoimmune disease( psoriasis complicated by arthritis), or Bechterew's disease.
In rare cases, bilateral lesions of the sacroiliac joint can talk about the infectious process of brucellosis or tuberculosis etiology, for which symmetrical lesions are also characteristic.
Classification
Like many other joint disorders, sacroileitis is divided into the following variants:
- Specific. This means that the inflammation has some characteristic features, by which you can determine the cause with great certainty. Such sakroileitis include tuberculosis, syphilitic and brucellosis arthritis;
- Nonspecific. A common inflammatory process with the development of classical inflammation and the attachment of suppuration. Usually, it requires surgery, or a massive antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy, to dispense with operative treatment in the early stages of the disease;
- Aseptic process. It is he who underlies autoimmune inflammation, in which there is no microbial infection and suppuration.
Degrees of sacroileitis
Since the basic and the fastest preliminary method for diagnosing sacroileitis is radiological, any pathological process in this joint can be "decomposed" into stages. There are four degrees of sacroiliitis:
- First degree: there is a moderate fuzziness of the joint space, but still it is determined;
- The occurrence of sclerosis, a symptom of "strands of pearls", or signs of usurization( uneven expansion of the slit);
- Exacerbation of signs and appearance of joint closure of the joint - ankylosis;
- On the fourth degree, the joint joint is completely closed, and the sacroiliac joint acquires a single bone character. Full ankylosis develops.
Symptoms of sakroileitis

Symptoms of sakroileitis photos
As it is an inflammatory disease, the main symptoms of sacroiliitis are pain and impaired function. Most patients are concerned about the following complaints( the process can be either one-sided or symmetric):
- There is pain in the buttock, with irradiation in the thigh. With the retraction of the straight leg back from the tension of the gluteus muscle, the pain intensifies;
- Often there is a phenomenon of pain enhancement during exercise with pronounced signs of arthritis;
- Stiffness appears in various parts of the spine, most often in the morning and in the lumbar region;
- There may be pain in the sacrum, especially after a load;
- Facilitates lying on the back with knees bent at the knees and legs apart. This posture weakens the pressure on the sacroiliac ligaments.
Other signs of inflammation, such as redness, soft tissue swelling, local feeling of heat with sacroiliitis may be invisible, as this joint is "hidden" away from the surface of the body. Therefore, pain and impaired function are the backbone of clinical diagnosis.
Diagnostics
In order for the doctor to send a patient to the examination, in addition to the above signs, inflammation should be confirmed with routine laboratory tests. For example, there may be:
- leukocytosis in peripheral blood;
- shift of the leukocyte formula to the left, to young, or even myelocytes;
- increased ESR;
- positive immunodiagnostic data for a specific microorganism( in the case of a specific pathogen);
- affection of distant joints, presence of skin eruptions, dactylitis, lesion of nail plates( this occurs with psoriatic arthritis);
- expressed a general reaction of the body: fever, intoxication, soft tissue swelling, talking about diffuse inflammation - phlegmon in the intermuscular spaces of the pelvis.
The most rapid and informative method of diagnosis, as already mentioned, is the radiography of pelvic bones with a targeted, large survey of sacroiliac joints in a direct projection with the mandatory capture of two joint cracks all along their length.
Magnetic resonance imaging is indicated for suspected soft-tissue formations( paracancreatic nature, tumor metastases), as well as when determining tactics before the operation for draining large purulent foci in infectious complications.
Treatment of sakroileitis - drugs and techniques
 The treatment of sakroileitis is not always directed to the sakroileitis itself, and this is an important point. In the event that it is a marker of autoimmune inflammation, then they treat "all at once", according to international schemes.
The treatment of sakroileitis is not always directed to the sakroileitis itself, and this is an important point. In the event that it is a marker of autoimmune inflammation, then they treat "all at once", according to international schemes.
In this case, sacroileitis is only a definite proof for the onset of more serious( basic) therapy.
For example, with psoriatic arthritis, the presence of sakroileitis indicates the involvement of axial joints in the autoimmune process, which serves as an indication for the administration of cytostatics( eg, Methotrexate) and monoclonal antibodies( eg, MabThera).
In case of Bechterew's disease( ankylosing spondylitis), in which sakroileitis is one of the leading symptoms of defeat, specific therapy is also prescribed.
Treatment of other variants of lesion most often involves from itself the rational use of antibiotic therapy( with determining the sensitivity of the pathogen), anti-inflammatory therapy, then - the course of restorative treatment( massage, physiotherapy).Follow-up treatment is carried out by an orthopedist, a doctor-arthrologist.
In the case of an autoimmune process, the current is conducted by a rheumatologist, and with these diseases( Bechterew's disease, psoriasis), treatment is only conservative, no operations with sacroileitis are indicated.
In the event that the patient has signs of sakroileitis on the radiograph, he needs urgent consultation of a rheumatologist. Begin the treatment in the form of massages and physiotherapy with the therapist in this disease, or, even more so, declare the narrowing of joint cracks on the roentgenogram "a sign of osteochondrosis" illiterate, since precious time can be missed. Sacroiliitis, whose treatment is started, can lead to disability and the development of ankylosis quite elsewhere.
Forecast
As a rule, for infectious causes and timely treatment of sakroileitis, against the background of immunity, the prognosis is favorable. If the biomechanics of the joint and muscle fatigue are disturbed, with the development of the aseptic process, the treatment is longer, including both massage, exercise therapy, and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Finally, "rheumatic" sakroileitis - symptoms, treatment, the prognosis of which indicates a lesion of connective tissue - can last for many years. Everything will depend on the activity of the autoimmune process.