Content
- Definition of pathology
- Classification
- Factors affecting the development of GERD
- Signs and symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
- Drug treatment
- Therapeutic diet and lifestyle
- Traditional medicine methods
- Surgical operations
- Video about GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease called the inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract. It occurs due to the reflux of the contents of the stomach into the esophagus. Complex treatment, necessarily includes diet and drug therapy. Surgery is performed only in extreme cases.
Definition of pathology
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD for short) is considered a common gastrointestinal pathology. During the meal, food passes through the tubular channel and enters the stomach. The walls of the esophagus are composed of several layers that continually contract and expand. In this way, food is promoted. This is called intestinal peristalsis.
At the bottom of the esophagus, at the junction with the stomach, there is a muscle ring (sphincter). It relaxes to allow food to pass into the stomach. Once food is ingested, gastric juice, the main ingredient for digestion, is secreted. At this point, the sphincter contracts to prevent aggressive acid from entering the esophagus. If this happens frequently, it is called gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Numerous complications develop against the background of GRED. The disease is considered relevant and problematic due to a difficult and atypical clinic, is characterized by a tendency to life-threatening consequences. Reflux in chronic form leads to esophagitis, changes in the structure of the mucous membranes. With an advanced disease, it goes into the 4th degree, which is characterized by severe complications.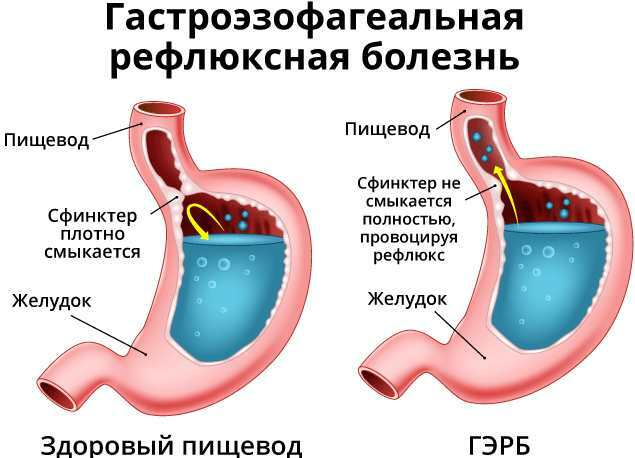
What are the consequences of GREB:
- Esophageal stricture. In this case, scar tissue forms at the site of the ulcerative lesion. As a result, the channel narrows.
- Diseases of the ENT organs, exacerbation of pathologies of the respiratory system. When gastric juice enters the throat, the ligaments become inflamed, pharyngitis and laryngitis develop. When acid enters the respiratory tract, symptoms of pulmonary pathologies appear, asthma worsens.
- When gastric juice enters the oral cavity, tooth enamel is destroyed. This causes tooth decay and other diseases of the gums and teeth.
- Perforation of the walls of the esophagus. Usually the breakthrough occurs in the mediastinal region. As a result, sepsis develops, respiratory arrest, severe bleeding appears - up to death.
- Ulcers in the esophagus begin to bleed. They can be hidden or explicit. The former are the most dangerous - they are difficult to detect immediately, which complicates treatment. Latent bleeding can lead to death of a person.
- Esophageal stenosis (narrowing of its lumen). In such areas, the passage of food is difficult, severe pains appear. Because of this, a person refuses to eat, which leads to anorexia and disruption of all internal organs.
- Barrett's esophagus. The last stage of the disease, when the mucous membranes of the organ are completely affected. This often leads to the development of adenocarcinoma (malignant tumor).
The easiest complications include temporary failures in the work of internal organs and systems, which quickly recover after treatment.
Classification
Gastroesophageal reflux disease has a separate classification.
It is divided into 3 types:
- Non-erosive. The pathological process affects the esophageal mucosa. It turns red, becomes inflamed, but negative manifestations affect only small areas.
- Erosive. Erosion appears on the mucous membranes of the esophagus. Often they merge, forming a large lesion area, often complicated by bleeding.
-
Barrett's esophagus. This is the most severe and dangerous form of the disease. The pathological process covers all layers of the esophagus completely.
According to the degree of manifestation of symptoms, it happens:
- mild, when discomfort and signs of GERD appear no more than 1 time in 7 days;
- medium - from 3 times a week;
- severe - symptoms appear daily, maybe several times.
According to the degree of the disease, GERD is divided into 4 degrees:
- Negative. Despite the patient's complaints and the presence of clinical symptoms, the mucous membranes of the esophagus are not affected.
- Esophagitis. When carrying out endoscopy, shallow single lesions of the mucous membrane are recorded. The patient complains of symptoms typical of GRED.
- Erosive esophagitis. During endoscopy, multiple mucosal lesions are observed. They are all of different depths and diameters.
- Peptic ulcer. This is the most severe and dangerous degree of damage to the esophagus. In this case, bleeding often occurs. The walls of the organ may become embittered and perforated.
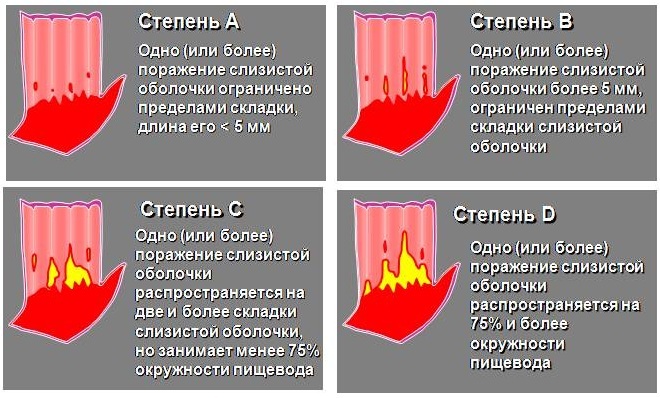
According to the Los Angeles and Savary-Miller classifications, degrees are designated A, B, C, and D. Moreover, edema of the mucous membrane and erythema are not considered signs of reflux. According to the clinical manifestations of GERD, the Montreal classification (esophageal and extraesophageal) can be applied.
Factors affecting the development of GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease often affects people who have hormonal disruptions, weakened muscle framework. The human body is designed in such a way that the pressure in the stomach is greater when compared with the chest cavity. Therefore, the return of the contents back to the esophagus would be a constant occurrence if the protective sphincters were not inhibited.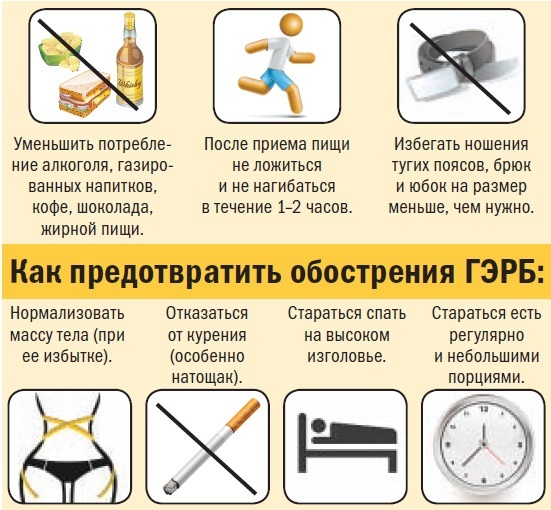
Their weakening provokes a reverse reflux of gastric juice. Disorders of the sphincters most often occur due to the weakness of the muscular frame, which may be associated with hormonal imbalances. Also, often the valves squeeze the hernia of the esophagus. Occasional muscle relaxation is observed with a sharp decrease in pressure. But this phenomenon lasts about 10 seconds.
Other reasons:
- Distension of the stomach due to eating a large amount of food - due to large portions, overeating. The enlargement of the organ can cause the simultaneous ingestion of food together with liquids, poorly processed coarse food.
- Excessive stretching of the stomach by aerophagia.
- Mechanical obstruction. It can be triggered by tumors, cicatricial stenosis, narrowing. Or obstruction is caused by congenital defects and abnormal structure of the gastrointestinal tract, diaphragmatic hernia.
- Disturbances in the work of the peripheral and central nervous system. For example, in diabetes mellitus, after dissection of the vagus nerve, due to diabetic neuropathy. Bacterial and viral infections can disrupt the functioning of the nervous system.
- Obesity. With excess weight, the pressure in the abdominal cavity increases, which provokes the reflux of gastric juice into the esophagus.
- Pregnancy. Among the causes are hormonal changes in the body and an increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity.
- Hernia of the opening of the diaphragm. It has a separate canal for the esophagus that connects to the stomach. With a hernia, part of it ends up in the chest cavity. Compression occurs, which provokes a weakening of the sphincters.
Risk factors include bad habits - excessive or frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking. This reduces muscle tone and weakens the sphincters. Also, risk factors include a sedentary lifestyle, some foods (chocolate, mint, fatty foods and caffeine), heavy physical activity.
Signs and symptoms
Since gastroesophageal reflux disease develops due to the reflux of gastric juice back into the esophagus, the main symptoms are associated with disruption of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Signs of GERD:
- Heartburn. This is the first early symptom that occurs with GERD. Patients experience a burning sensation in the esophagus or behind the breastbone. Heartburn most often appears after eating, strenuous physical activity, drinking alcohol. Some people experience a burning sensation in the esophagus when smoking. The reasons include fried, fatty and spicy foods, carbonated drinks. Heartburn worsens with exercise, bending, and lying down.
- Belching. With GRED, it always tastes bitter or sour. Sometimes it is accompanied by nausea, vomiting. Belching is provoked by carbonated drinks and foods that cause flatulence (for example, cabbage, bread, sweets), overeating.
- Regurgitation of food. The symptom is rare. More often it occurs due to the return return of fluid, when the body is tilted forward.
- Odinophagy. While eating, a person feels soreness in the esophagus, stomach.
- Dysphagia. This is the name of the difficult passage of food through the esophagus, as if a large stone is moving inside. This is often accompanied by painful sensations. As a result, the patient begins to refuse food and quickly loses weight.
- Severity in the esophagus, stomach. It often appears when lying down or after eating.
- Pain in the upper abdomen behind the sternum, in the esophagus.
GERD can be further aggravated by extraintestinal indirect manifestations:
- Strong headache;
- nasal congestion and discharge, but not associated with a cold;
- often there is a dry cough that cannot be treated;
- short-term hoarseness of the voice;
- bad breath;
- frequent bronchospasm;
- increased salivation.
With dysphagia or after poorly chewed food, mucous membranes can be injured. Especially if a person swallows large pieces. This provokes additional inflammation and increased pain in the esophagus. But GREB is of great concern if the pathology is asymptomatic.
Diagnostics
Gastroesophageal reflux disease may not be immediately identified by the main symptoms, as they are similar to many other diseases. Normal acidity of the stomach should be 1-2 pH, and at the bottom of the esophagus - 5.5-7 pH. This is verified using impedance pH measurements. The method helps to register refluxes by resistance to electric current, which is sent to the esophagus. Acidity is determined using sensors.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy became the main diagnostic method. During the study, the doctor takes a sample for histology to assess the condition of the mucous membrane and to clarify the presence or absence of development of Barrett's esophagus.
Other diagnostic methods:
- Radiography. Helps to detect diaphragmatic hernia, strictures, ulcers. In 50 percent of cases, the presence of reflux is noted.
- Manometry. This method measures the pressure of the lower muscle valve of the esophagus.
- Bernstein's test. A 0.1 percent hydrochloric acid solution is injected into the esophagus. If the test is positive and the person feels a slight burning sensation, then this indicates the presence of GERD.
- Alkaline test. After taking antacids, clinical symptoms disappear, which is characteristic of the disease.
- Electromyography. It helps assess the motor function of the esophagus.
- In the presence of extraintestinal, indirect signs, the patient is sent for examination to an otolaryngologist. This helps to determine the presence or absence of an inflammatory process in the pharynx and larynx.
For chronic heartburn and for early diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus, endoscopy (gastroscopy) is performed. At the same time, tissue is taken for biopsy. This will show if the malignant process has begun.
Treatment methods
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is treated in a comprehensive manner. The main goals of therapy are to eliminate symptoms, restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and prevent complications. First, conservative treatment is carried out. Additionally, doctors strongly recommend leading an active lifestyle, giving up bad habits, observing a daily routine, providing the body with good rest.
Drug treatment
The drugs are prescribed depending on the form and stage of the disease. Several types of drugs are used for therapy.
| Group of drugs | Description, treatment |
| Antacids | They are prescribed to treat mild GERD. Alginate preparations (eg Refluxaid) are preferred. They work longer and more effectively than traditional antacids. The drugs eliminate negative symptoms. They should be taken immediately after meals and at bedtime. They also relieve side effects. Magnesium hydroxide improves digestion, suppresses the manifestations of acidosis. The antacids Amphojel and AlternaGEL normalize stool in case of constipation, and Phillips Milk liquefies stool. Aluminum hydroxide increases stomach acidity and inhibits pepsin activity. But antacids cannot reduce the frequency of reflux, but they do reduce heartburn. Among the common ones are Maalox, Gevikson. |
| Histamine receptor blockers | They are prescribed for mild to moderate disease. There are mainly 4 blockers used:
They are very effective in suppressing excess gastric acid. Therefore, the drugs are taken at night or on an empty stomach. When they treat a mild form of the disease, up to 80 percent of patients recover. Also, drugs are good for preventing relapse. But with prolonged use, their effectiveness decreases. |
| Prokinetics | They are prescribed only for mild disease. In a serious condition of the patient, prokinetics are prescribed together with drugs that inhibit the production of gastric juice. Among the most common are Cerucal, Metosolv, Raglan. For treatment, metoclopramide 10 mg per day is often used. This is the most common therapeutic regimen. The drug is prescribed in a short course, it is dangerous to take them for a long time. They can provoke serious complications, even death. |
| Proton pump inhibitors | These are very powerful drugs that suppress gastric acid production. Shown to be highly effective in the treatment of GRED. They are well tolerated by patients and rarely cause side effects. Among the most common are Dexilant, Prevacid, Nexium. But at the same time, they violate calcium hemostasis, increase the risk of fractures during menopause. Can cause other serious complications with prolonged use. They are prescribed in courses of 2 weeks. But drugs are prohibited for pregnant women, children under one year old. The maximum number of courses per year is no more than three. |
| Analgesics, anti-inflammatory | They are prescribed if severe pain appears. But more often they use complex drugs that simultaneously relieve inflammation (for example, Ibuprofen, Nise). |
| Antispasmodics | Often, negative symptoms are caused by muscle spasms. Eliminate them with antispasmodics (No-Shpoy, Spazmogon). |
Other medications may be prescribed depending on the cause and symptomatology.
Therapeutic diet and lifestyle
Diet is the second important part of the therapeutic regimen for GRED. Overeating is strictly prohibited. You need to eat in small portions (no more than a clenched fist) three times a day, and arrange light snacks in between. The latter should be 4 hours before bedtime, no later than 23:00.
Any heavy food that irritates the stomach and causes gas formation is excluded from the diet:
- fatty;
- whole milk;
- spicy;
- apples;
- smoked;
- grape;
- pickles and pickles;
- legumes;
- citrus;
- coffee;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- fresh baked goods;
- cabbage;
- sweet.
Preference is given to lean food, fresh vegetables and fruits. Cooking methods - boiling, stewing, baking. Salt intake should be kept to a minimum. Food that is too hot or cold is excluded.
You should also adhere to a few more rules. After eating, you need to be in an upright position for an hour, you can sit, but not lie down. Physical activity and body bending are allowed only 2 hours after eating. Do not wear clothes that tighten the body in the abdomen and chest area. During sleep, the head should be on a raised pillow. In a severe form of the disease, it is advisable to take a semi-sitting position.
Traditional medicine methods
Traditional methods of treatment do not belong to the main therapy, but they help to speed up recovery, restore the work of the gastrointestinal tract, and prevent the development of complications. Aloe juice has a healing and anti-inflammatory effect. It is mixed with honey (1 tsp. l), insist 2-3 hours and eat after meals.
Fresh nettle leaves have a hemostatic effect. They also accelerate the healing of ulcers and erosions. You can use ready-made pharmacy infusions or prepare them yourself. Collect, wash and dry the nettle leaves. Grind and pour boiling water (2 tbsp. l / 250 ml of water). Insist 2 hours, filter and drink in small portions during the day. For taste, you can add 1 tsp to the drink. l. granulated sugar. The course of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
Celery juice has a general healing effect and has a beneficial effect on the esophageal mucosa, contributing to its recovery. To do this, you need to use 1 tbsp. l. before eating.
Chamomile officinalis has a healing, anti-inflammatory, calming effect. Reduces pain at the same time. A ready-made collection is sold at the pharmacy. In a glass of boiling water, 1 tbsp is brewed. l. raw materials. Insist 2 hours and drink in small portions during the day.
Surgical operations
Surgical intervention is indicated only when conservative medicine has not given positive results or in the presence of severe complications. To strengthen the sphincter, Nissen fundoplication is prescribed. During the operation, part of the stomach is sutured to the esophagus.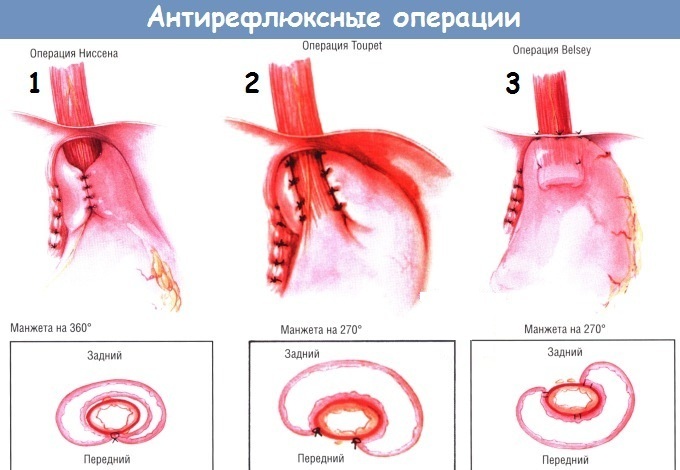
They also carry out endoscopic plication (stitches on cardio), radiofrequency ablation of the esophagus (damage the muscle layer to scar and reduce reflux). Gastrocardiopexy is performed in the presence of a hernia of the esophageal opening. During the operation, it and the stomach are sutured to the abdominal wall and diaphragm. Restore the work of the sphincter of the cardiac department.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is called the chronic course of the pathology. Accidental reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus occurs in almost every person and is normal if this is a rare and short-term occurrence. Chronic GERD requires treatment. The sooner it is started, the better the chances of a full recovery.
Video about GERD
About gastroesophageal reflux disease: