Content
- Why does paraproctitis occur?
- Classification, symptoms and signs of different forms of paraproctitis
- By etiological basis
- Banal
- Specific
- Post-traumatic
- By localization
- Subcutaneous
- Submucosal
- Ischiorectal
- Pelviorectal
- Retrorectal
- By the activity of the inflammatory process
- Spicy
- Infiltrative
- Chronic
- By the location of the inner opening of the fistula
- Front
- Rear
- Side
- In relation to the fistulous tract to the fibers of the sphincter
- Intrasphincter (subcutaneous-submucosal)
- Transsphincteric
- Extrasphincter
- By the location of the pathological process
- Surface
- Deep
- Diagnostics of the paraproctitis
- Complaints and anamnesis
- Rectal examination
- Anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy
- Fistula probing
- Fistulography
- Endorectal ultrasound
- Bacteriological examination
- Paraproctitis treatment
- Operation
- Drugs
- Folk remedies for maintaining the condition
- Antiseptic baths
- Douching with chamomile decoction
- Diet
- Dispensary observation
- Complications of paraproctitis and prognosis of the disease
- Video about paraproctitis
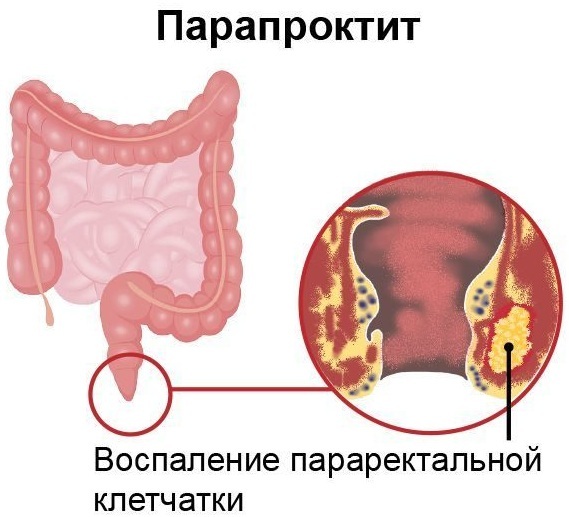
Paraproctitis is inflammatory lesion of peri-rectal tissue
, which is a complication of the painful condition of the anal crypts and glands. This disease occurs in a chronic or acute form, and its main causative agent is streptococcal infection, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.Paraproctitis is classified according to the localization of the pathological process inside the rectum. The main danger of this disease is the rapid development of a large number of complications.
Why does paraproctitis occur?
The mechanism of development of paraproctitis is associated with the penetration of infectious microorganisms into the pararectal tissue.
The development of the inflammatory process in this part of the rectum occurs under the influence of the following reasons:
- anal fissure;
- chronic proctitis;
- hemorrhoidal disease;
- frequent constipation;
- too loose stools;
- cryptitis;
- complications after surgery on the rectum;
- sphincteritis;
- trauma to the rectal mucosa.

The harbinger of the onset of paraproctitis is the introduction of pathogenic bacteria into the tissue of the anal gland, from which microbes migrate to the pararectal tissue. Timely relief of the focus of chronic infection allows you to normalize the functions of the rectum.
Classification, symptoms and signs of different forms of paraproctitis
The classification of paraproctitis according to the localization of the pathological process is carried out by a proctologist after a comprehensive examination of the patient. Certain types of this disease are also divided according to the nature of its origin.
By etiological basis
The etiology of paraproctitis should be established at the initial stages of diagnosis. The availability of information about the nature of the origin of this ailment contributes to the construction of a more effective system for further treatment.
Banal
Banal paraproctitis is a disease of adrectal tissue, which occurs due to its infection with mixed microflora. This is Staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus, Proteus or E. coli. This type of paraproctitis is also called simple.
The patient has the following symptoms:
- swelling of the rectal mucosa;
- increase in overall body temperature;
- fever;
- pain inside the anus;
- the formation of abscesses and fistulous canals;
- discomfort during bowel movements.
Quite often, banal paraproctitis is the first stage in the development of a more complicated form of this ailment with the spread of extensive inflammation.
Specific
Specific paraproctitis is manifested by similar symptoms, but its infectious agents are tuberculosis bacillus, pale spirochete (causes syphilis), actinomycosis.
This type of inflammatory lesion of pararectal tissue is difficult to treat with medication, and is also accompanied by frequent relapses.
Post-traumatic
Posttraumatic paraproctitis has standard clinical manifestations, but its nature of origin is associated with the consequences of trauma. In this case, damage to the perrectal tissue occurs during bowel movements, anal sex, falls from a height on sharp objects, and gunshot wounds.
By localization
Paraproctitis (classification according to the localization of pathology is carried out by isolating the focus of the infectious and inflammatory process), which has impaired the functions of the rectal tissue of the rectum, can develop in the subcutaneous or submucosal layer of the posterior passage.
Subcutaneous
The development of subcutaneous paraproctitis begins with bouts of acute pain in the anus. At the time of defecation, the discomfort increases. As the inflammation progresses, the patient's general body temperature rises to 38-39 degrees. In conditions of localization of a purulent process in the anterior part of the anus, problems with urination may appear.
Submucosal
This type of paraproctitis is characterized by acute or chronic inflammation of the perrectal tissue, localized under the layer of the mucous membrane. During the examination of the anus, an edematous state of the tissues is found, palpation of the pathological focus is painful. As the disease progresses, abscesses may form, spreading over large areas of peri-rectal tissue.
Ischiorectal
Ischiorectal paraproctitis also occurs under the name "ischial rectal".
This disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- fever;
- increased body temperature;
- an attack of dull pain in the depths of the pelvis;
- pain during bowel movements;
- disorders of urination.
Ishiorectal paraproctitis is always accompanied by the formation of a large amount of pus, which quickly spreads over the surface of the pelvic tissue. The risk of developing severe complications increases.
Pelviorectal
Palviorectal paraproctitis is characterized by the presence of an inflammatory process, during which the infection is localized deep in the pelvic tissue directly above the muscles that raise the posterior passage.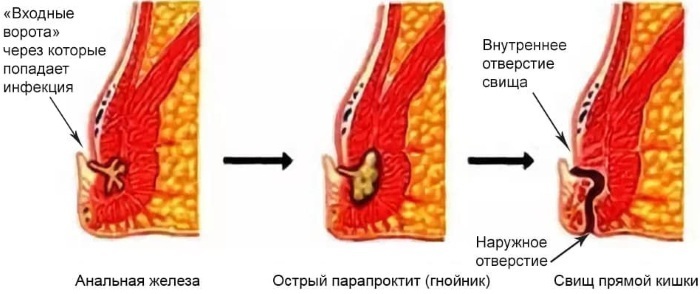
This type of pathology has similar symptoms, and its difference is a deeper location of pain. On external examination, pelviorectal paraproctitis is not detected. Only palpation of the anus makes it possible to determine the presence of a painful seal with its bulging into the lumen of the rectal walls.
Retrorectal
Retrorectal paraproctitis is diagnosed in 2.5% of all patients with proctological diseases. The pathology of this type is characterized by the presence of intense pain sensations inside the rectum, which spread to the sacrum area.
During bowel movements and pressure on the surface of the coccyx, the feeling of discomfort only increases. Palpation of the anus reveals a strong protrusion of the posterior rectal wall, which can be the cause of moderate bleeding of the mucous membrane.
By the activity of the inflammatory process
Paraproctitis (classification according to the localization of this disease is carried out with the simultaneous determination of the severity inflammatory process) is a pathology of the anus that develops in acute, chronic or infiltrative form.
Spicy
Acute paraproctitis always develops dynamically with the simultaneous manifestation of the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the anus;
- increased body temperature;
- chills;
- pain during bowel movements;
- swelling of the rectal mucosa;
- the formation of an abscess.

In the presence of pathology in the region of the anterior rectal wall, signs of compression of the urethral canal with impaired urination may appear.
Infiltrative
Infiltrative paraproctitis is characterized by a progressive inflammatory process with the formation of abscesses, as well as the release of sacral contents from the rectum. In most cases, this type of pathology develops at the stage of the transition of the disease from an acute to a chronic form.
Chronic
Chronic paraproctitis is diagnosed in 30-40% of all patients seeking medical help from a proctologist. This disease occurs after the acute phase of inflammatory lesions of pararectal tissue.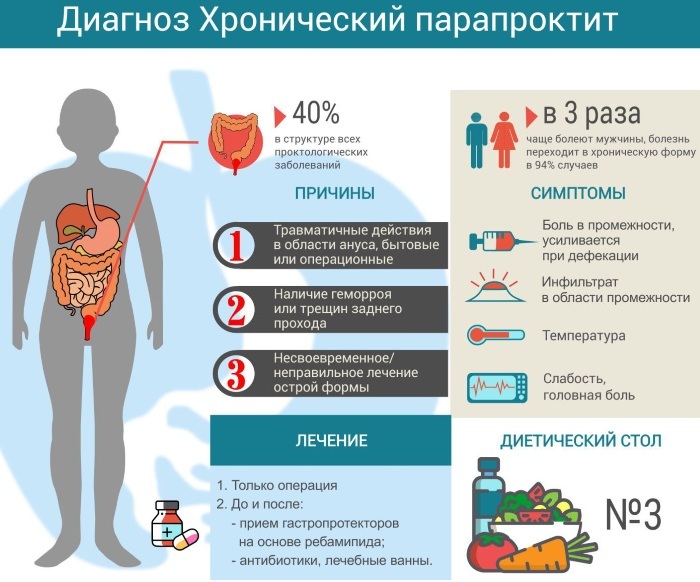 Chronic paraproctitis is characterized by the presence of not only pain inside the rectum, but and the formation of fistulous passages, from which purulent contents follow, resulting from abscess.
Chronic paraproctitis is characterized by the presence of not only pain inside the rectum, but and the formation of fistulous passages, from which purulent contents follow, resulting from abscess.
By the location of the inner opening of the fistula
Paraproctitis (classification according to the localization of pathology includes determining the location of the fistulous course) is a disease, a common symptom of which is the release of pus and ichor.
Front
This type of paraproctitis is characterized by the localization of the fistulous canal in the region of the anterior rectal wall. In men, the standard symptoms of this disease are accompanied by squeezing of the urethra and problems with emptying the bladder.
Rear
In the presence of posterior paraproctitis, the fistulous canal extends from the rectal wall, connecting to the outlet between the anus and the coccyx.
Side
In conditions of lateral localization of the fistulous tract, purulent contents and sacral fluid are secreted through the opening on the right or left side of the anus.
In relation to the fistulous tract to the fibers of the sphincter
Paraproctitis (classification according to the localization of the focus of pathology is impossible without diagnosing the location of the fistulous canal along relation to the fibers of the sphincter) is a proctological disease, accompanied by attacks of severe pain in the back aisle.
Intrasphincter (subcutaneous-submucosal)
Intrasphincteric fistula is located at the beginning of the crypt of the rectum, and its opening occurs over the muscle tissues of the sphincter. 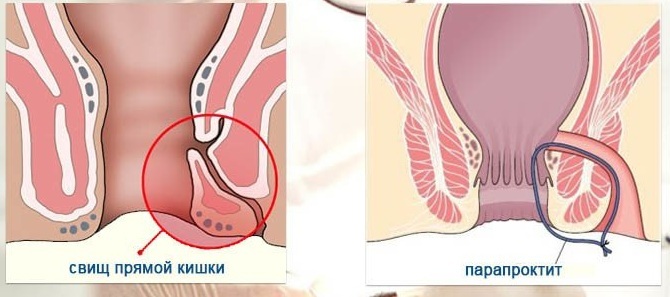 This means that the entire fistulous canal is located at a great depth away from the anus.
This means that the entire fistulous canal is located at a great depth away from the anus.
Transsphincteric
A transsphincteric fistula leads to damage to only one or several groups of muscle fibers of the anus.
Extrasphincter
The extrasphincteric fistulous tract is located bypassing the anus, opening in the tissues of the perineum. Pathology of this type can have deep accumulations of purulent contents.
By the location of the pathological process
Paraproctitis is classified according to the depth of the location of the pathological process.
Surface
Superficial paraproctitis affects exclusively the upper layers of pararectal tissue, provoking inflammation of the rectal mucosa with minimal risk of complications. This disease is readily amenable to anti-inflammatory treatment.
Deep
Deep paraproctitis is characterized by damage to muscle tissue in the depths of the pelvis. Pathology affects large areas of the rectum, constantly progresses, and accumulations of pus lead to the constant formation of fistulous canals.
Diagnostics of the paraproctitis
Determination of all forms and types of paraproctitis is carried out by a proctologist in a sterile diagnostic room.
Complaints and anamnesis
At the initial stage of the examination, the proctologist conducts a conversation with the patient. The doctor is interested in the current symptomatology that the patient feels, establishes the severity and duration of the pathological process.
Rectal examination
Rectal examination includes examination of the anus and rectal cavity, as well as palpation of its mucous membrane.  This type of diagnosis can be performed immediately after the completion of the anamnesis procedure.
This type of diagnosis can be performed immediately after the completion of the anamnesis procedure.
Anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy
Anoscopy is an effective method for diagnosing rectal pathologies, which is performed using an anoscope. This method of examination allows you to detect signs of paraproctitis at a distance of 12 cm from the anus.
The diagnostic procedure is an examination of the rectal cavity with the use of instrumental expansion of its lumen. Sigmoidoscopy is also aimed at determining the physiological state of the rectal mucosa. This method of examination is carried out by introducing a special tube into the anus, which simultaneously illuminates the anus and blows it out to create better viewing conditions.
Fistula probing
Fistula probing is an informative procedure that allows you to determine the direction of the drainage canal, as well as its depth. This type of diagnosis is performed using local anesthesia. In the zoning process, proctological tools are used.
Fistulography
Fistulography is a type of X-ray examination. A contrast agent is injected into the cavity of the patient's fistulous canal with further fluoroscopy of the tissues that are located in the area of the fistulous canal. This procedure is absolutely painless, and its implementation allows you to obtain comprehensive information about the internal structure of the fistula.
Endorectal ultrasound
Endorectal ultrasound diagnostics can be classified as one of the most informative methods for determining paraproctitis. The principle of its implementation is that a special endoscope device is introduced into the rectal cavity of the patient.  The doctor performing the diagnostics examines the mucous membrane and pararectal tissue of the patient's anus in real time. The procedure itself is painless.
The doctor performing the diagnostics examines the mucous membrane and pararectal tissue of the patient's anus in real time. The procedure itself is painless.
Bacteriological examination
For bacteriological examination, mucosal smears are taken in the area of acute or chronic inflammation of rectal tissues. In the presence of infiltrate discharge, pus samples are taken. Biological material is examined by isolating a specific strain of bacterial infection.
Paraproctitis treatment
Paraproctitis therapy involves the use of conservative and surgical methods of treatment. To minimize the risk of developing a relapse of the disease, it is recommended to use a set of therapeutic measures.
Operation
Surgery is a radical, but also the most effective method of treating paraproctitis.
Surgical operation to stop the focus of infectious inflammation of the pararectal tissue is performed as follows:
- The patient receives general anesthesia.
- With the help of proctological instrumentation, the lumen of the rectal walls is expanded.
- The doctor gains access to the source of the inflammatory process.
- Excision of the altered tissues is carried out with simultaneous scraping of the bottom of the wound with a Volkman spoon.
- Wound surfaces are sutured.
- Tissues with purulent cavities are opened to cleanse them.
- The fistulous canals are being sanitized.
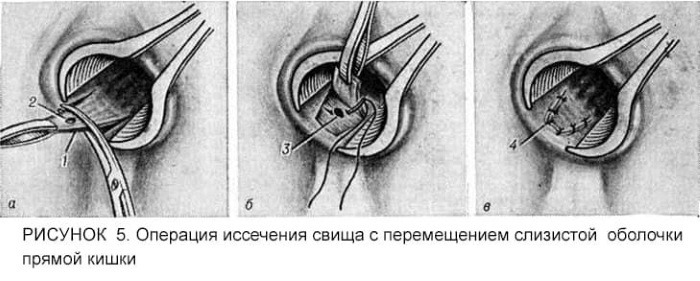
Upon completion of surgical procedures, the patient is transferred to the general therapy ward, where he undergoes further rehabilitation, is under the supervision of medical personnel. The duration of the operation depends on the severity of the clinical case, the presence or absence of complications.
Drugs
In the process of treating paraproctitis, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents are used. Sterile cotton swabs are used to destroy microbes localized inside the fistulous passages. The surface of each turunda is treated with an abundant layer of Levosin or Levomekol ointment, and then they are injected into the open fistulous canal. Antibiotics are selected based on the results of bacteriological analysis.
In most cases, drugs of the following types are used:
- Gentamicin - intramuscularly, 3 mg per 1 kg of body weight.
- Oxacillin - is active against gram-positive microflora, and its dosage is 0.25 g intravenously.
- Boncefin is a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent with a dosage of 1 g of active substance administered intravenously every 8 hours.
- Erythromycin is a tablet preparation that destroys gram-positive microorganisms. It is taken at 0.25 g 3-4 times a day.
- Azithromycin is effective against coccal microbes, and its dosage regimen is 0.5 g 1 time per day 1 hour before meals.
It is strictly forbidden to carry out self-treatment of paraproctitis with antibiotics. The selection of drugs in this group should be performed only by a proctologist based on the data on the resistance of bacteria to a particular type of medication.
Folk remedies for maintaining the condition
There are folk recipes for the treatment of paraproctitis and the healing of fistulous formations inside the rectum, as well as the tissues surrounding it.
Antiseptic baths
To apply this folk method, the following rules of the instruction must be observed:
- Dissolve 3 manganese crystals in 1 liter of warm water.
- Collect half a basin of water with a temperature of +40 degrees.
- Pour 1 liter of potassium permanganate solution into a basin.
- Immerse your buttocks in an antiseptic.
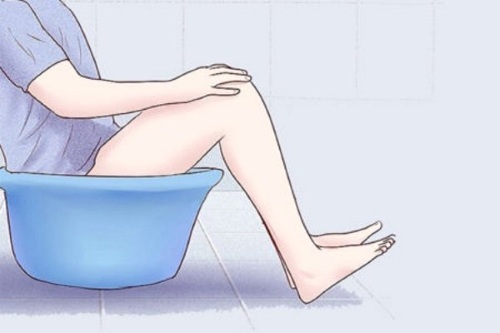
In a basin with a solution of potassium permanganate, you need to sit 2-3 times a day for 15 minutes. To maintain a comfortable temperature, it is recommended to periodically add warmer water.
Douching with chamomile decoction
Chamomile has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect, accelerates the regeneration of damaged tissues.
To use this method of alternative treatment, you must adhere to the following algorithm of actions:
- Pour 2 tbsp. l. dried chamomile in a metal container.
- Pour 1 liter of water over the medicinal plant.
- Boil.
- Boil for 3 minutes.
- Turn off the broth for infusion and cooling.
- After 4 hours, warm the antiseptic to room temperature.
- Collect the broth in an enema.
- Douching of the rectum and fistulous passages.
This therapeutic procedure is performed in the morning and in the evening. The duration of treatment depends on the dynamics of healing of damaged tissues, reduction of the inflammatory process.
Diet
In order to speed up the healing process of fistulous canals and wound surfaces caused by paraproctitis, it is recommended to follow the dietary rules. The table below lists the products that are allowed and prohibited for admission to patients with inflammation of the pararectal fiber.
| Allowed food | Prohibited foods and drinks |
|
|
A person suffering from paraproctitis should eat 5-6 times a day in fractional portions. Overeating, eating too fatty, spicy, rough foods will lead to pain during bowel movements and exacerbation of the inflammatory process.
Dispensary observation
Patients who have undergone acute or chronic paraproctitis should 1-2 times every 12 months. undergo a routine examination by a proctologist for the timely prevention of recurrence of the disease and the appearance of postoperative complications.
Complications of paraproctitis and prognosis of the disease
Lack of adequate treatment of paraproctitis or too late seeking proctological help entails the development of the following complications:
- the formation of a tumor neoplasm that occurs against the background of chronic inflammation;
- incontinence of feces and gases;
- opening of anal bleeding;
- replacement of the rectal mucosa with scar tissue;
- narrowing of the walls of the anal canal;
- the formation of insufficient muscle tone of the sphincter;
- necrosis of infected rectal tissue;
- bacterial blood poisoning.
Treatment of paraproctitis in the early stages of its development provides a positive prognosis for the complete restoration of rectal functions with relief of the inflammatory process.
Paraproctitis is a dangerous disease characterized by inflammation of the peri-rectal tissue. The development of this pathology is provoked by bacterial microorganisms in the form of streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Paraproctitis is classified by the nature of origin, localization of the inflammatory process and the form of its course.
This disease is accompanied by severe pain inside the anus, fever, chills, discharge of purulent contents from the anus and fistulous canals. Treatment of this pathology includes taking antibacterial drugs, suturing wound surfaces using a surgical operation. Complication of paraproctitis is dangerous for the patient's life, as it can lead to necrosis of rectal tissue and bacterial blood poisoning.
Video about paraproctitis
Acute paraproctitis. Diagnostics and treatment:
