Content
- What parts is the human spine divided into
- How vertebrae are considered
- The main functions of the spine
- Anatomy
- Cervical
- Thoracic department
- Lumbar
- Sacral region
- Coccygeal department
- What does each vertebra in the spinal column affect?
- Spine Anatomy Videos
Supporting structure in the human body is the spine, consisting of 33-34 vertebrae, providing mobility and stability of the frame. Knowledge of their numbering and structural patterns will allow you to easily determine the degree of damage to both the vertebra itself and the vessels or nerves passing through its openings.
What parts is the human spine divided into
Depending on the structure and functions performed, the spine is divided into a number of departments: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal.
In the sagittal relation, the spine has four bends, which determine the rational distribution of the load on the frame and limbs, and also does not allow the development of protrusion or pinching nerve endings.
How vertebrae are considered
The vertebra is an anatomical structure: bone, the inner base of which is represented by the spongy part. Outside, the vertebra is covered with lamellar bone tissue.
The anatomical base of the vertebra consists of 3 elements: bezis, vertebral arch, processes:
- Bezis has the form of a thickened part located anteriorly with the upper and lower surfaces of the vertebrae adjacent to it. There are holes (nutritional) inside the back surface of it. They serve to accommodate blood vessels and nerves that supply and innervate various organs.
- The vertebral arch, together with the body, forms vertebral foramen on all sides, which are located one above the other and form the spinal canal. The spinal cord passes through it.
- The processes of the vertebra are directed from the arch to the side and back. Their role is to balance the range of motion and perform a protective function for the spine. Allocate: unpaired and paired processes.
The articular processes regulate the functional activity of the intervertebral discs. They have articular surfaces that ensure their articulation with each other. In addition to intervertebral discs, ligaments and joints are located between the vertebrae, ensuring their integrity, frame strength and mobility.
The numbering of the vertebrae in the human spine is determined from the occipital compartment to the coccygeal compartment.
- The cervical section has 7 vertebrae, the name of which is denoted by the letter C and numbered: C1-C7. The occipital bone is conventionally named "zero vertebra" (C0). The C1, C2 and C7 vertebrae have a special structure and names. C1- Atlas, C2- Axis (axial), C 7 is protruding.
- The thoracic system consists of 12 vertebrae. They are designated with the letters T or D and are numbered: D1- D
- The lumbar region includes 5 vertebrae, numbered L1-L5.
- The sacral region consists of 5 vertebrae: S1-S5.
- The vertebrae of the coccygeal region are numbered from Co1 to Co5. Bone in adults grows together and forms a single part.
The vertebral segment of the human body is a set of intervertebral disc, ligaments and joints that hold the vertebrae together. They provide mobility and are called motor segments: the numbering is carried out according to the principle of counting the vertebrae: 7 cervical, 12 thoracic and 5 lumbar. The last segment of the lumbar spine is formed by the L5 and S1 vertebrae.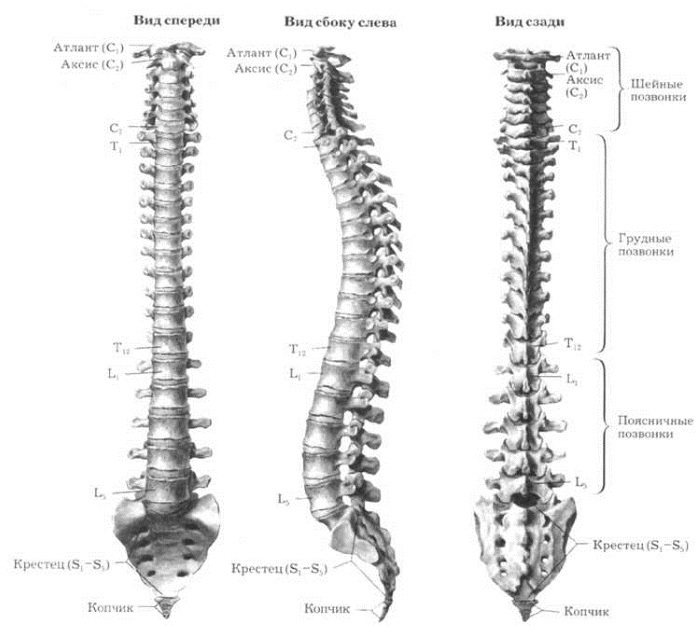
In a developed state, the inner part of the vertebra is the bone marrow, which regulates hematopoietic processes.
The main functions of the spine
The spinal column forms both a flexible and strong frame, the anatomical features of which ensure the correct distribution of the load. It carries a vital purpose:
Spine functions | |
| Support | The spine is the backbone of upright posture and the maintenance of the body in an upright position. He takes on the biggest load. In this case, the weight is also distributed to the pelvis and lower limb areas. |
| Protective | Thanks to the joints of the vertebrae into a strong column, a cavity of the spinal canal is formed inside them to accommodate the spinal cord. The hardness of the bone tissue protects the spinal cord, as well as the nerve plexuses, roots and blood vessels that run through the openings of the vertebral processes. |
| Motor | Due to the fact that along the spinal column there are bends in it, a person is able to stand, walk, bend over, do active physical exercises, turns without damaging the frame or pinching nerves. |
| Depreciation | In the spine there are intervertebral discs that provide less abrasion of the vertebrae, elasticity and flexibility of the spine. They also participate in the distribution of the load on the frame and prevent the displacement of the vertebrae. During physical activity, the discs protect the spine by creating sliding or springy movements. |
Anatomy
Anatomically, the organ is conventionally divided into corresponding sections.
Cervical
The numbering of the vertebrae in the human spine for this compartment is very peculiar. The section is the initial section of the spine, consisting of 7 vertebrae. The functional feature of the section is the implementation of turns, tilts of the head.
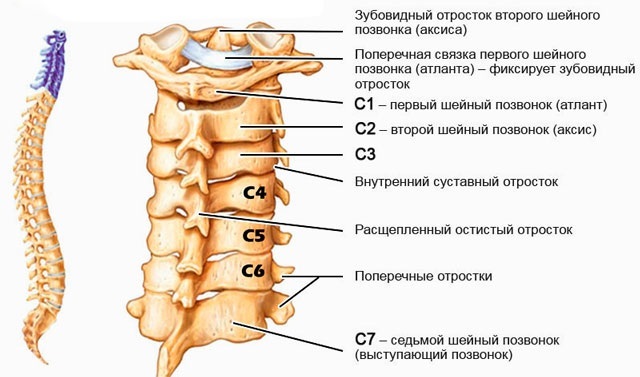
- 1st vertebra, atlas, has a characteristic structure, is distinguished by pronounced hardness. It connects the spinal column to the skull, in particular to the occipital bone. The parts of the atlas are vertebral arches connected by lateral thickenings, which together limit the opening of the spinal canal. The posterior arch is characterized by the presence of holes that conduct vessels and nerves.
- The 2nd vertebra, axis, has a tooth-like shape and plays the role of the basis for the Atlantean. Thanks to the design of the first spirit of the vertebrae, a person can rotate his head. On the sides of the vertebra, articular and transverse processes protrude, providing the formation and stability of the segment.
- The 4th vertebra is characterized by the fact that the intervertebral canal in it has the smallest section.
- 3rd and 5th have the same structure. They are the bed for the vertebral artery that feeds the structure of the brain. The vertebrae serve as the backbone of the cervical spine. They also provide rotation of the head.
- The 6th and 7th expand relative to the initial ones. With the help of the costal fossa, the latter connects to the beginning of the thoracic region and is well palpated when the head is tilted forward through the skin.
Thoracic department
The thoracic region consists of 12 vertebrae, which are convex backward, forming a physiological bend (kyphosis). The thoracic region is the least mobile. 1st vertebra is small, has no spinous process. Segments 3 to 9 are relatively similar in structure, their bodies increase as they approach the joints of the lumbar spine. The vertebrae themselves are large enough, the spinous processes are massive. Their central process is elongated and widened at the end.
From 9 to 12, the vertebrae are large, resembling the shape and structure of the lumbar. Massive processes extend from the arc. The last 2 vertebrae are articulated with ribs 11 and 12.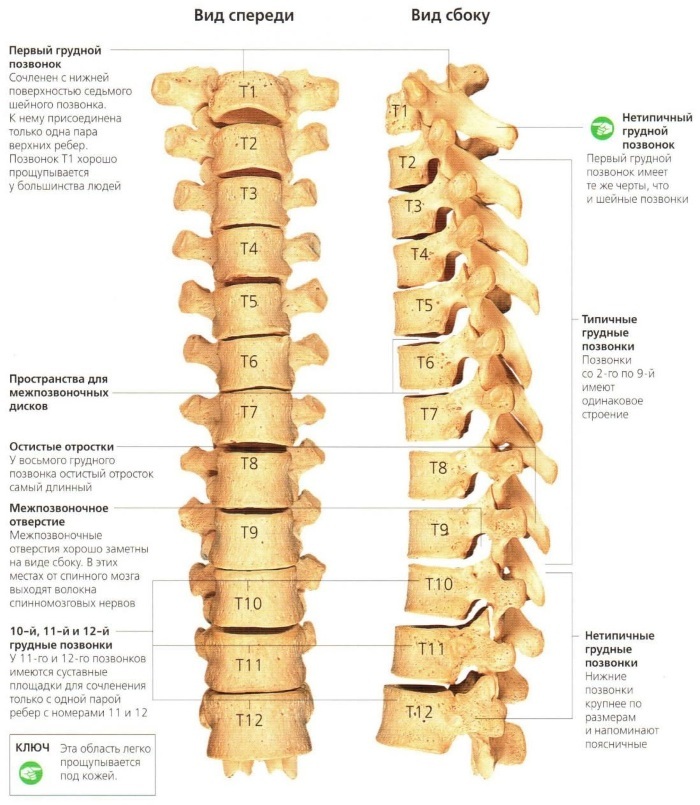
Department functions:
- Is the back wall for the chest;
- provides an upright position of the body;
- maintains posture;
- is a protective frame for the spinal cord and, in conjunction with the ribs, for the internal organs.
Lumbar
The lumbar vertebrae, in the number of five, are the largest, since they experience the greatest stress. Descending towards the coccyx, the openings of the vertebrae narrow, and their bodies become higher. The processes of the vertebrae are massive. Segment bonds exist in the form of discs, joints and ligaments.
The ligaments also regulate the forward-backward and lateral tilt of the torso. The numbering of the vertebrae in this section of the human spine is necessary for the timely diagnosis of pathologies of the genitourinary system.
Department functions:
- due to the special structure, side turns, tilts, rotations are possible;
- a sufficiently mobile part connects 2 relatively immobile: chest and sacral;
- massive vertebrae and the presence of intervertebral discs cushion movements when running, walking, jumping;
- the department withstands additional (over) loads due to strong muscles.
Sacral region
The section is represented by 5 vertebrae, which by adulthood (25 years) exist in the form of a single fused bone. After fusion, the bone looks like a pyramid, the top of which is directed downward. The inner surface (front) bears traces of fusion of the vertebrae in the form of transverse lines. The outer side (back) has longitudinal ridges - traces of the connection of the rudiments of the vertebrae.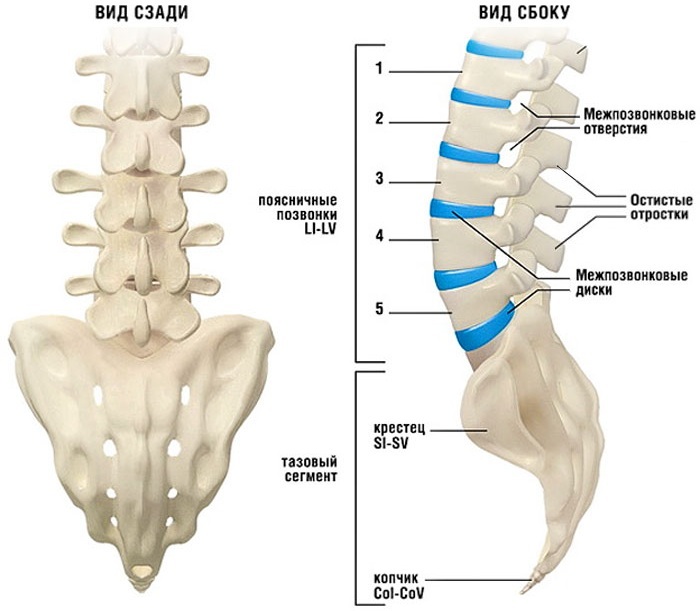
Sacral foramen are located on the sides of the bone. Spinal nerves pass through them, which innervate the lower extremities, the organs of the urinary and, in part, the digestive systems.
The sacrum, like the lumbar region, takes up most of the load on the body. Its anterior surface is involved in the formation of the inner wall of the pelvic cavity. This part of the spine is motionless and fixed by a powerful ligamentous apparatus.
Department functions:
- provides uniform load distribution;
- firmly fixed in its position due to fusion with the pelvic bones;
- structural features of the vertebrae make it possible to well protect the spinal cord, blood vessels and nerve endings;
- adjusts the stability of the upright posture.
Coccygeal department
At the developmental stage and in childhood, the coccyx is relatively mobile, however, at an older age, the vertebrae grow together and form one bone. The tailbone is considered a vestigial organ. With its development, variations from three and five vertebrae or four, six are possible.
Department functions:
- the attachment of the gluteal muscles to the bone regulates the movement of the hips while walking, running, squatting;
- participates in labor, deviating to the back and facilitating the passage of the fetus;
- takes heavy loads;
- controls the extension and flexion of the body, excluding cracks and fractures of the vertebrae of this section;
- ligaments and muscles of the tailbone ensure the work of the genitourinary organs, the lower parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
What does each vertebra in the spinal column affect?
The vertebrae in the human spine are numbered from top to bottom. Each vertebra, according to its structure and location, performs an important function for the body.
Cervical canal:
- C1 (1st vertebra of the cervical spine) has a direct effect on the work of the pituitary gland, the hearing aid. It regulates blood pressure, the work of the cardiovascular system, is responsible for the duration of sleep and the uniformity of breathing. Injuries to the vertebrae can lead to significant fluctuations in pressure, headaches, hearing impairment (inner ear) and impairment of attention and memory.
- C2 regulates the work of the visual and auditory centers in the brain. Damage to the vertebrae contributes to the development of migraines, the appearance of flies before the eyes, as well as fainting and an acute immune response to stimuli.
- C3 responsible for the work of facial muscles. Nerve fibers passing through the segment innervate the jaw, buccal, ear, and also regulate the work of facial nerve fibers. The lesion of the segment causes inflammation of the facial nerves, laryngitis, hearing impairment, discoordinated innervation of the maxillofacial region, and skin rashes.
- C4 regulates the work of the circular muscle of the mouth, nasal region and neck area. Its damage leads to neuralgia, myalgia, impairment of hearing and thyroid function. Possible diseases of the nasopharynx, cracks on the lips, in the corners of the mouth.
- C5, C6 regulate the muscles of the shoulder girdle and vocal cords. If the C5 segment is damaged, inflammatory processes occur in the pharynx, ligaments, trachea, bronchi (tracheitis, bronchitis). Muscle clamps, pain in the forearm, shoulders are the consequences of C6 injury.
- C7 coordinates the activity of the thyroid gland. Segment lesion causes muscle spasms of the upper extremities, thyroid dysfunction, decreased hormone synthesis, and psychoemotional imbalance.
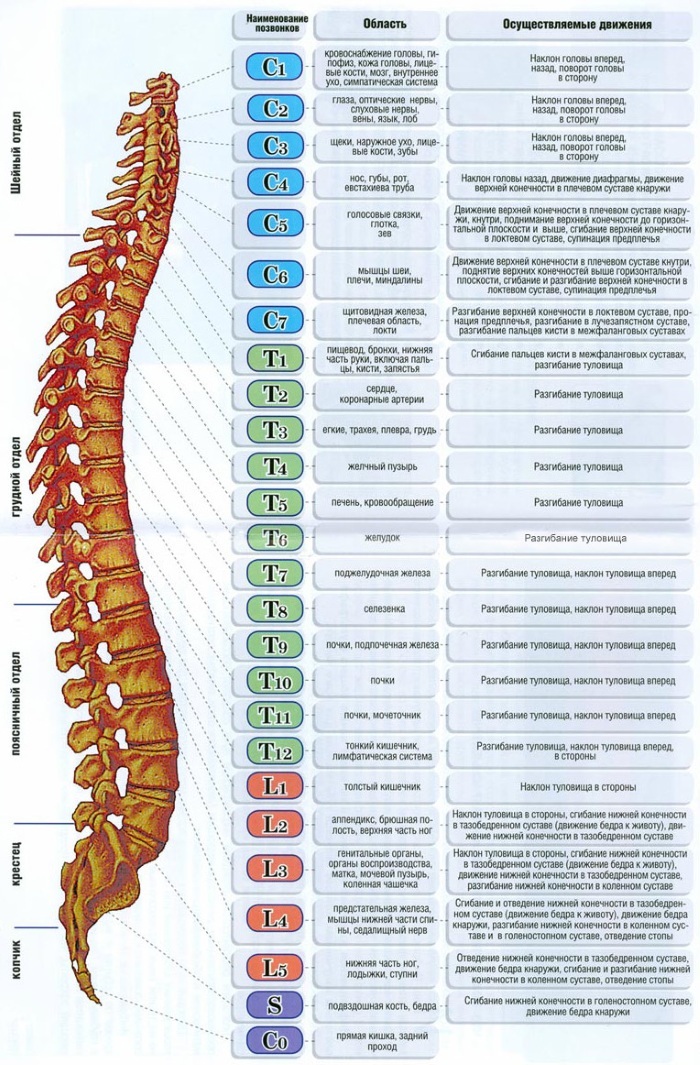
Thoracic department:
High mobility section:
- T1, T2 responsible for the work of the respiratory system: trachea, bronchi, lungs. Their displacement causes diseases of the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system: bronchitis, bronchial asthma, tachycardia, arrhythmia, ischemia of the heart muscle. Violations can also affect the work of the esophagus (reflux - gastritis).
- T3 regulates the respiratory system, the condition of the skin of the chest and nipples. Damage contributes to the development of pathological conditions in the bronchi, lung tissue and pleura. Failure to treat the underlying condition can lead to pneumonia or respiratory failure.
- T4 responsible for the activity of the gallbladder and the patency of its ducts. The pathological process of the vertebra or displacement causes cholecystitis, the formation of stones in the bladder and ducts, and liver pathology.
- T5 controls the liver. Violations can lead to cirrhosis or hepatitis. Additionally, with dysfunction of the liver and its ducts, blood pathology develops.
- T6 participates in the normalization of the gastrointestinal tract. Displacement or destruction causes ulcers, gastritis.
- T7 affects the work of the pancreas and duodenum. Infringement of the nerve endings can cause pancreatitis with a rapid transition to a chronic form, ulcers, diabetes mellitus.
- T8 provides regulation of the diaphragm. Segment problems lead to spleen abnormalities, respiratory failure and severe shortness of breath.
- T9 when nerve fibers are damaged, it causes a decrease in immunity, adrenal diseases with a decrease in hormone production, and delayed-type allergic reactions. With diseases, often, severe intoxication develops.
- T10, T11 due to infringement lead to nephritis, pyelonephritis, cystitis. Chronic fatigue and weakness are added to the symptoms of renal pathologies.
- T12 is responsible for the activity of the lower parts of the digestive tract, inguinal rings, the female genital area (fallopian tubes). Displacement can contribute to the development of pathologies of the small and large intestines, infertility.
Lumbar department:
- L1 if the element is damaged, it leads to the formation of pathologies of the intestinal tract, nerves, joints, vessels. Development of inguinal hernias, enterocolitis, intestinal obstruction is possible.
- L2 affects the work of the muscles of the thigh, lower intestine. Destruction or displacement causes appendicitis, colic in the intestines, pain in the groin, thigh.
- L3 regulates the work of the genitourinary system, is responsible for the innervation of the limbs. The damage can lead to diseases in the knee, hip joints, infertility, impotence and urinary disorders.
- L4 affects the work of the feet, legs, prostate gland. Infringement contributes to the development of sciatica, lyubmalgia, disorders of the urethra, pain in the knees.
- L5 responsible for the innervation of the legs. Damage to the nerve endings leads to swelling, pain in the legs, ankles. Flat feet is a formidable complication.
The sacral region is involved in the innervation of the buttocks, femoral area and lower extremities. The tailbone regulates the activity of the muscular part of the anus, as well as the work of the rectum.
In case of damage to the bone base of the sacrococcygeal section, back pain develops, work is impaired genitourinary system, lower digestive tract, hemorrhoids, focal femoral lesions bones. On the part of the genital area, there is a decrease in libido, an imbalance in the production of sex hormones, rapid weight gain, and inability to conceive.
The numbering of the vertebrae in the human spine in the region of the sacrococcygeal section is different depending on the number of fused bone bases.
The vertebral frame is an important component for the overall functioning of the body. If segments or nerve endings are damaged, it is extremely important to know the peculiarities of the functioning and numbering of the vertebrae in the spine. This allows you to correctly and timely identify pathologies of the spinal cord and the spinal column of a person.
Author: Didukh Tatiana
Spine Anatomy Videos
Spine anatomy:
