Content
- Views
- Stages and degrees
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
- Drug therapy
- Nutrition for children with anemia
- Potential consequences and complications
- Video about anemia in children
Decrease in the total concentration of red blood cells in the blood due to low iron content causes anemia. A deficiency of a trace element leads to oxygen starvation of systems and organs in a child under 1 year old. This adversely affects health, can cause mental retardation, movement and activities such as crawling, walking.
Anemia is a term that refers to a reduced amount of hemoglobin in the blood, a red blood cell dye that has the ability to bind oxygen and release it into the cells of the body. The vital function of transporting oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the body depends on hemoglobin. Since the amount of iron-containing protein decreases with anemia, the supply of oxygen to the body is also impaired.
The amount of hemoglobin in the body can be reduced, on the one hand, due to an insufficient amount of it in erythrocytes or, on the other hand, due to an insufficient number of erythrocytes themselves.
Iron is the main building block of hemoglobin. Iron deficiency in the body lowers the level of hemoglobin, leading to iron deficiency anemia.
Infants and young children are at a higher risk of iron deficiency anemia due to the rapid growth of the body during this period.
The high-risk group includes:
- premature babies;
- children under 1 year old who are given cow's milk;
- breastfed infants over 6 months of age who are not fed iron-fortified cereals or other foods;
- formula-fed children who do not have iron supplements.
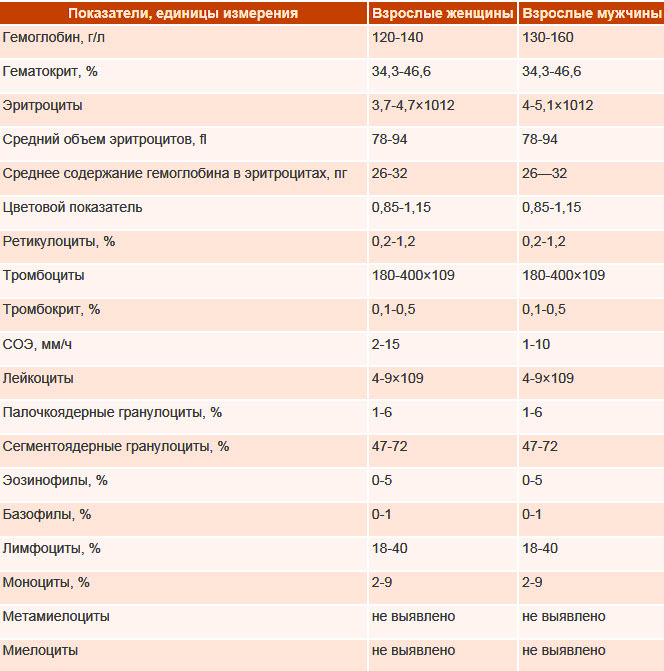
When determining anemia in children, laboratory criteria are applied.
The hemoglobin level, depending on the age of the children, is: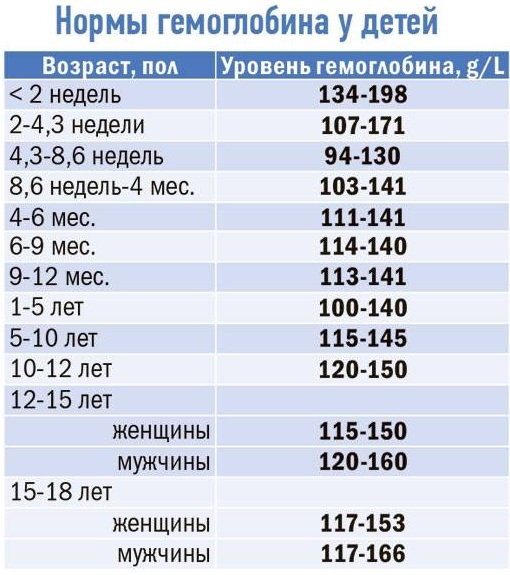
| 0-1 day of life | <144-150 g / l |
| 14 days of life | <125-130 g / l |
| 14-28 days of life | <120 g / l |
| 1 month - 6 years | <110 g / l |
Almost 10% of toddlers between 0.5 and 3 years old are iron deficient, but only about 30% of them are anemic.
Views
Anemia is classified according to various criteria. The congenital and acquired forms are more often distinguished. In the first case, there are pathological changes in genes that play an important role in hematopoiesis. These genetic defects occur in sickle cell anemia, one of the most common inherited diseases worldwide.
| Acquired anemia | Congenital anemia |
| Anemia in Chronic Diseases | Diamond-Blackfan anemia. Diserythropoietic anemia |
| Fanconi anemia | |
| Autoimmune hemolytic anemia | Sickle cell anemia |
| Thalassemia | |
| Iron-deficiency anemia |
The most common forms of anemia are iron deficiency and anemia associated with infectious disease. Infection with bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens often leads to anemia, which disappears after the infection has gone away.
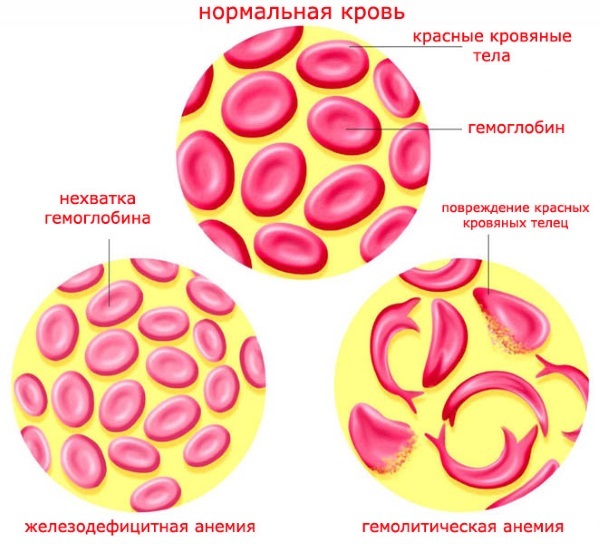
To find out the reasons, the size of the red blood cell is determined. For this, certain laboratory parameters, erythrocyte indices are used.
Red blood cell size classification:
| Microcytic anemia (too small red blood cells) | Microcytic hypochromic anemias are typical when:
|
| Macrocytic anemia (too large blood cells) | Macrocytic hyperchromic anemia can be caused by:
|
| Normocytic anemia (normal sized blood cells) | Normocytic, normochromic anemia occurs when:
|
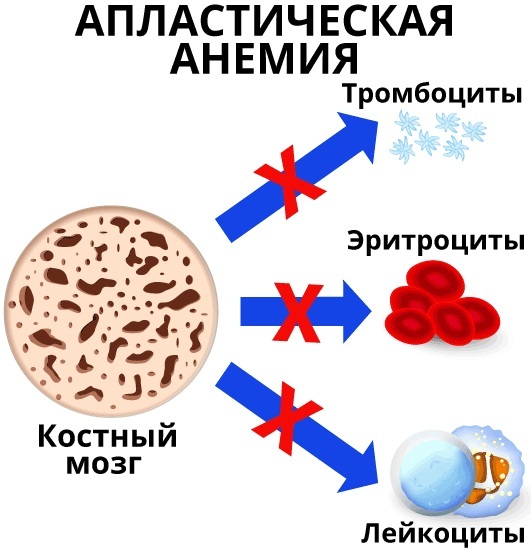
Each blood cell is made in the bone marrow and then released into the bloodstream. After a certain period of life, individual blood cells are destroyed again.
Based on this, anemia is classified according to the type of specific functional disorders of erythrocytes:
- Hematopoietic disorders.
- Increased breakdown of red blood cells (hemolysis).
- Bleeding (loss of red blood cells).
Stages and degrees
Anemia in a 1-year-old child develops with a deficiency of iron, B vitamins or folic acid.
The disorder is categorized by severity into 3 groups:
- Latent (hidden) deficiency. The need for iron exceeds the intake. Hemoglobin levels are still normal, but organ and transport iron stores are already depleted. The most important indicator is a drop in serum ferritin (a protein in the form of which the body stores iron).
- Functional deficiency. The increased requirements for iron outweigh the availability of its consumption. The amount of hemoglobin can only be maintained by regulatory mechanisms. The iron-binding capacity of the serum decreases.
- A clear deficit. The condition is characterized by a decrease in the number of erythrocytes and hematocrit per unit volume of blood, a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin.
Symptoms and Signs
With the slow development of anemia, the child gradually loses stability, productivity, quickly depletes, difficulties arise in the learning process, concentration of attention.
Typical symptoms:
- pale or yellowish skin;
- inflammation and cracks in the corners of the mouth;
- very smooth surface of the tongue;
- increased irritability.
With severe anemia, the child develops difficulty breathing (due to a lack of oxygen), and the heartbeat noticeably increases.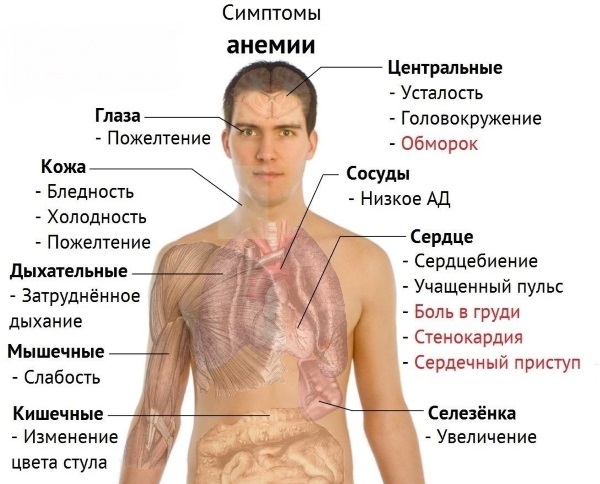
With the rapid development of anemia, in the case of large blood loss due to trauma or internal bleeding, the child develops symptoms:
- severe shortness of breath;
- decreased heart rate;
- drop in blood pressure;
- drowsiness;
- loss of consciousness.
Causes
There are 3 reasons or not enough red blood cells:
- decreased production of red blood cells in the bone marrow;
- loss of blood or red blood cells;
- increased destruction of red blood cells.
Red blood cells cannot be formed sufficiently if the necessary substances (iron) are not available in the required amount or the bone marrow cannot function. If red blood cells become deformed during a blood disease, the body breaks them down very quickly. Anemia is common when a person develops an infection, chronic illness, or cancer.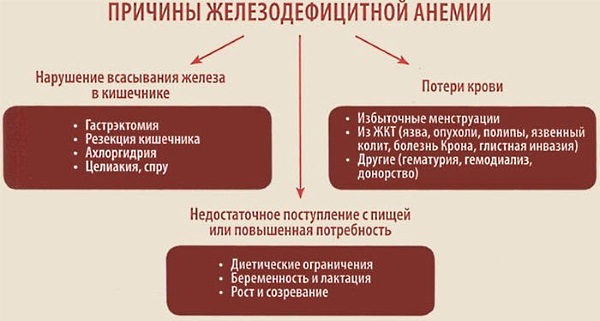
Anemia in a 1-year-old child is more often caused by poor nutrition. Iron deficiency can occur with a vegetarian or vegan diet. In children under 1 year of age who are fully breastfed, the mother's diet is critical. If their iron stores are depleted due to an unbalanced diet, the child is not getting enough the amount of iron from breast milk, vitamins B12, folic acid, which are also important for hematopoiesis.
Infants and young children grow at a rapid rate during the first few years of life, so their iron needs are higher than those of older children.
- Low birth weight increases the risk of anemia in infants and young children.
- Kidney weakness can be a cause of anemia in children and very rarely is hemolytic uremic syndrome due to kidney disease. This condition is characterized by bloody diarrhea.
- Cancer and many other diseases (liver dysfunction, blood diseases or congenital anemia, rheumatic diseases) can also cause anemia in children. Such causes are very rare, but when investigating, doctors always keep them in mind if they cannot find another obvious cause of anemia.
- The cause may be rare genetic diseases, hereditary blood diseases that cause anemia, thalassemia.
Diagnostics
Anemia in a child is usually diagnosed with blood tests. Regular screening is necessary because asymptomatic anemia is common in children 1 year of age and younger.
Blood hemoglobin screening is recommended for all infants 12 months of age. Screening should also include a risk assessment, which factors include feeding problems, poor growth and special medical needs. If your hemoglobin level is low, additional blood tests are done.
Basic diagnostic tests:
- Hemoglobin and hematocrit. The most common screening test, which gives a complete picture of the condition of the blood. With its help, the amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood is measured (cost from 400 rubles).
-
General blood analysis. Red and white blood cells, platelets and sometimes young red blood cells (reticulocytes) are checked (cost from 250 rubles).
- Blood smear microscopy. A small sample of blood is examined under a microscope to determine the cell morphology (shape, color, presence of various inclusions). Analysis cost from 150 rubles.
- Serum iron test. The concentration of iron in the serum is determined. The cost of the analysis is from 500 rubles.
Treatment methods
Anemia in a child 1 year old or younger is treated comprehensively, and therapy is based on 4 principles:
- Correction of the causes of iron deficiency.
- Normalization of food and regime.
- Prescription of preparations containing iron
- Concomitant therapy.
Most premature babies have mild anemia that does not require treatment. Although anemia is harmless and quickly treats, it can indicate another medical condition. To make sure that there are no concomitant diseases, you should consult a doctor.
Drug therapy
Before starting oral iron therapy, priority is given to addressing the underlying nutritional problem: the introduction of solid food at 6 months of age in breastfed babies and reducing cow's milk intake in older children age.
Drugs prescribed for children:
| Iron compounds with oxidation state | Medicines |
| Fe3 (ferric compounds) | Maltofer, Ferrum Lek. |
| Fe2 (ferrous compounds) | Totem, Ferronat, Hemofer, Ferroplex, Tardiferon. |
| Iron protein succinylate | Ferlatum. |
Children with iron deficiency anemia quickly restore hemoglobin after consuming enough iron.
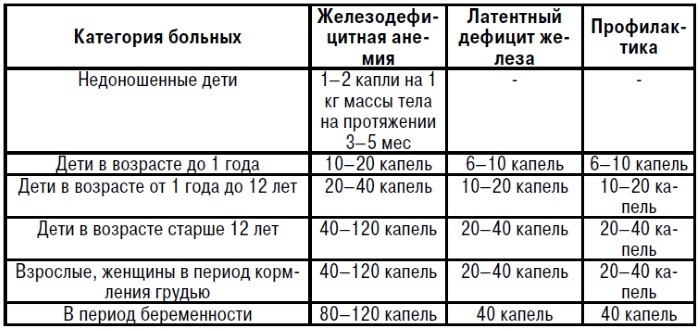
Method of administration and dosage of Fe2 + and Fe3 + preparations:
- The oral food supplement Fe2 + is: 2-3 mg / kg iron in one or two doses per day half an hour before or half an hour after a meal. Juice or water can be used to enhance the taste.
- Food supplement Fe3 + for oral administration: 3-5 mg / kg elemental iron in one or two doses daily with meals (preferably with juice or water).
The recommended duration of taking medications is 2-4 months (Fe3 + preparations are usually taken longer than this period). The duration of admission is adjusted by the doctor to normalize hemoglobin, as well as iron stores.
The doctor monitors the body's response to treatment only in cases of severe anemia, persistent iron loss, or suspected non-adherence to therapy.
Taking glandular drugs is associated with side effects that pediatricians always take into account in advance. Therefore, at the beginning of Fe therapy, fluid intake should be increased. If there are side effects, switching from Fe 2+ to Fe 3+ can help.
In the case of using Fe3 + preparations, the possibility of switching from drops to tablets or vice versa is considered. When prescribing iron-containing agents, the individual need is calculated based on the daily dose of elemental iron, which is 4–6 mg / kg. Large doses should not be given, since the amount of absorption of the trace element by the body is limited.
The transition to intravenous iron is considered in cases of severe anemia, an underlying systemic disease with an indication for intravenous iron. If it is necessary to make a quick correction of iron in the body, then drugs for parenteral administration should be used.
This is usually done for severe anemia. To date, infants have only 1 drug available for intravenous infusion: Venofer. In the case of intramuscular injection, Ferrum Lek is used.
Intravenous iron is the only alternative to oral administration. The main advantages of intravenous iron therapy are prevention of gastrointestinal problems, taste effects, and bypassing the intestinal mucosa barrier. In addition, the sensitivity of hemoglobin after intravenous iron infusion is better compared to oral iron.
Along the way, with iron deficiency, such children experience a lack of folic acid, vitamins C, B 12, PP, B6, A, E, copper and zinc. This is due to the fact that the impaired absorption of iron has a negative effect on the absorption of other trace elements. Consequently, complex therapy includes, in addition to iron-containing elements, the intake of multivitamin complexes.
In total, treatment with glandular drugs should be continued for at least 3 months, in sufficient doses, despite the normalization of hemoglobin levels. This is necessary to replenish iron stores in the depot.
Anemia in a 1 year old child sometimes does not respond immediately to treatment.
The most common reasons that do not allow an increase in hemoglobin:
- incorrectly calculated doses of the drug;
- the presence of chronic inflammatory diseases or neoplasms;
- worm infestations and other parasitic infections;
- vitamin B12 deficiency;
- unidentified causes of blood loss.
The successful outcome of treatment also depends on the symptoms, age and general condition of the child.
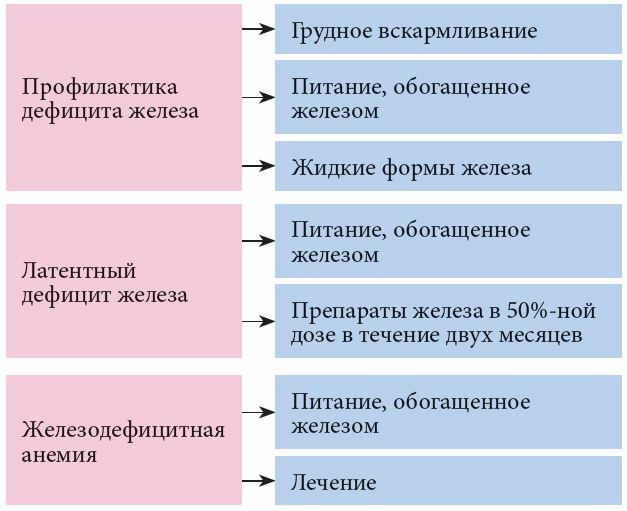
To prevent iron deficiency anemia, you should follow simple rules:
- From 4 months of age, babies who are only breastfed or partially breastfed should receive a daily iron supplement until foods rich in microelement.
- Infants who are bottle-fed do not need iron supplements, since all the necessary micronutrients are always present in the diet for children. Whole milk should not be given to infants under 12 months of age.
- Infants and toddlers 1 to 3 years old should eat iron-rich foods. These include iron-added cereals, red meat, and vegetables. Also important are fruits with vitamin C, which helps the body absorb iron.
Nutrition for children with anemia
In milder forms of anemia, the micronutrient deficiency should first be replenished with the help of a diet. The best source of iron in food is heme iron of animal origin.
An alternative to it are products:
- legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, soybeans, and white beans;
- wheat bran or nuts.
Iron absorption can be improved by adding various acids to the diet, which contain:
- orange juice;
- lemon juice;
- apples;
- grapes;
- pears;
- raspberry juice.

The following ingredients provide extra iron:
- Red meat (beef, lamb) contains iron in a form that is very easy to digest.
- Dark green leafy vegetables: spinach, zucchini, fennel, broccoli.
- Whole grain bread is rich in vitamins B, E, fiber and iron.
Severe cases of anemia affect other illnesses such as asthma or respiratory problems. In these cases, a blood transfusion is required for proper treatment.
Potential consequences and complications
Long-term effects are usually rare. They mainly affect children suffering from severe and long-term iron deficiency at a vulnerable stage of development. Iron deficiency can impair brain development, especially during infancy and early childhood, and lead to tangible and irreversible mental impairment. During pregnancy, it should also be assumed that severe iron deficiency seriously affects the development of the unborn child.
If an iron deficiency is detected and successfully treated, then the blood test is normalized within a few weeks. If the cause of the deficiency can be corrected, relapse should not be expected.
The most important thing that needs to be corrected in case of anemia in a child detected at 1 year old is iron deficiency, since it jeopardizes his intellectual development in the present and in the future. If a deficiency of a trace element is detected at an early age, treatment should be started in a timely manner, the diet and the child's regimen should be adjusted.
Video about anemia in children
Doctor about anemia in children: