Content
- When is vaccination needed?
- Vaccination calendar
- Revaccination against diphtheria, tetanus
- Funds
- Procedure step by step
- Contraindications
- Possible complications
- Vaccination against viral hepatitis B
- Funds
- Procedure step by step
- Contraindications
- Possible complications
- Rubella
- Funds
- Procedure step by step
- Contraindications
- Possible complications
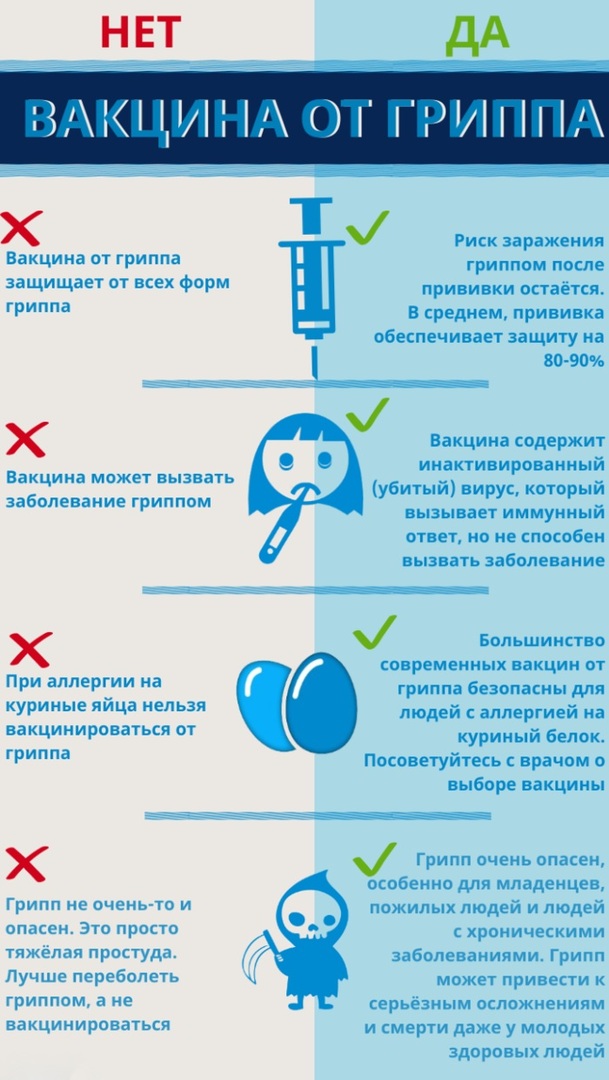
- Against the flu
- Funds
- Procedure step by step
- Contraindications
- Possible complications
- Measles
- Funds
- Procedure step by step
- Contraindications
- Possible complications
- Vaccination video
Vaccination is a must maintaining immunity for adults throughout life. The timing of their fulfillment by age in tabular form can be found on the net. Vaccinations need to be done not only when traveling abroad, but also to maintain the desired immunity during the period exacerbation of infectious diseases, which cannot be dealt with only by observing sanitary requirements.
Many diseases, immunity from which is created in childhood through routine vaccination, are gradually losing strength. During this period, an adult can catch an infection and get sick with a number of health complications that can be easily avoided with routine vaccinations.
When is vaccination needed?
Vaccinations by age (table of adult injections for which it is grouped by age intervals) must be done after the average the duration of immunity vaccinated by a previous vaccination or after revealing the absence of vaccination against a particular species virus. At the same time, an adult can tolerate the vaccination itself more easily or, on the contrary, more difficult, depending on the state of health.
Vaccination for adults is not considered mandatory. At the same time, there is a range of standard diseases, from which you can get vaccinated free of charge in the corresponding periods of life at the polyclinic at your place of residence. Such vaccinations are most often carried out by people with a specific profession. For example, employees of medical and educational institutions, employees of social services for the population and government officials.
Vaccinations for these categories of people are mandatory and help protect a person from possible infection with complex infectious diseases. A complete list of vaccinations, depending on age and type of disease, is specified in the order "On the approval of the national the calendar of preventive vaccinations and the calendar of preventive vaccinations for epidemic indications "of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation from 03/21/2014 No. 125n.
When traveling to the territory of some other states, to places with an increased risk of developing outbreaks of infection of the population, it is required make a number of additional vaccinations (against malaria, encephalitis), which will help keep a person healthy in a different climate and vegetation. At the same time, in the absence of vaccination, an adult may be denied a visa.
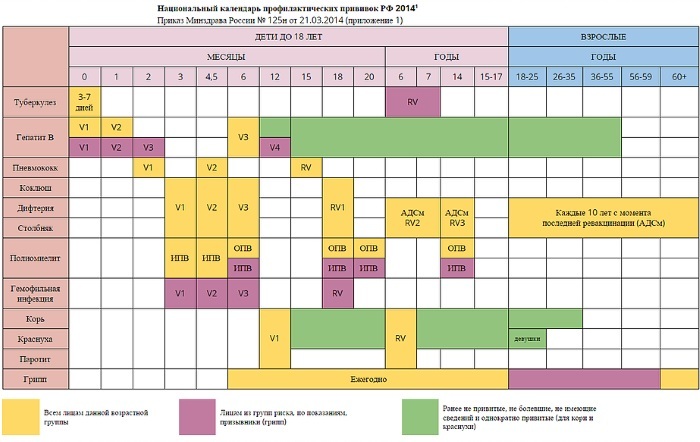
Vaccination calendar
Vaccinations by age (a table of adult drugs for which is grouped by the type of disease) are carried out depending on the state of health in the following order:
| Age or category of people | Disease against which vaccination is performed |
| after the age of majority and then after 10 liters. | diphtheria |
| From 19 y.o. and then every 10 liters. | tetanus |
| adults 19-55 years old, not previously vaccinated | viral hepatitis B |
| women 18-25 years old who have not previously received the vaccine or with a single vaccination | rubella |
| adults 19-35 yrs. | measles, including by way of revaccination |
| workers in social welfare and education, persons over 60 years of age. and those with chronic diseases, civil servants and medical workers, conscripts | flu |
There are separate groups of people who must be shown additional vaccinations against rare infectious diseases.
These include:
| Category of people | Disease against which vaccination is carried out |
| persons performing geological, agricultural and irrigation, disinsection and logging operations in areas prone to disease | tularemia |
| workers for the slaughter of large and small livestock and their processing, zoological and veterinary staff, persons working in the focal area for the disease | anthrax |
| adults traveling to countries prone to outbreaks | yellow fever |
| persons permanently residing in areas prone to outbreaks | plague |
| people who have received an animal bite, hunters, as well as employees of organizations performing work on the capture and maintenance of stray animals, gamekeepers, foresters, | rabies |
| persons 61 and older or persons with chronic diseases | pneumococcal infection |
| people working with sheep, storing livestock products, slaughtering livestock, veterinarians, livestock specialists. | brucellosis |
| employees working with livestock and live crops that cause these diseases | leptospirosis |
| persons traveling or working in an area prone to outbreaks | tick-borne viral encephalitis |
| employees working with livestock raw materials, as well as in areas where an outbreak of the disease has occurred | Q fever |
| citizens traveling to disadvantaged areas | cholera |
| public utilities workers, persons in contact with the sick, as well as all adults in the presence of a threat of an epidemic | typhoid fever |
| persons living or traveling to unfavorable territories, and contact with sick persons | viral hepatitis A |
| medical workers, employees of organizations in the field of catering, preschool and school education | shigellosis |
| living or arriving in regions with an epidemic of the disease | meningococcal infection |
| unvaccinated persons in contact with the patient | measles |
| not sick people in contact with the sick person | viral hepatitis B |
| people at the epicenter of morbidity | diphtheria |
| unvaccinated people in contact with the sick | mumps |
| persons in contact with patients with this disease, over 18 y. | polio |
| for preventive purposes | rotavirus infection |
| military conscripts | chicken pox |
| people with chronic illnesses, health care workers and employees of educational institutions, social welfare workers, border guards, volunteers, military personnel, civil servants | coronavirus infection caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus |
Revaccination against diphtheria, tetanus
Vaccinations by age (a table of adult drugs for which can be found as a comparison) against diphtheria and tetanus are carried out systematically. The duration of immunity after vaccination is maintained for the next 10 liters.
Moreover, in the case of the presence of concomitant factors (features of work, place of residence), the vaccination against diphtheria and tetanus is mandatory in 18 liters. Most often, adults aged 22-26 years are vaccinated. Then, every 10 years, each person must be re-vaccinated against these diseases.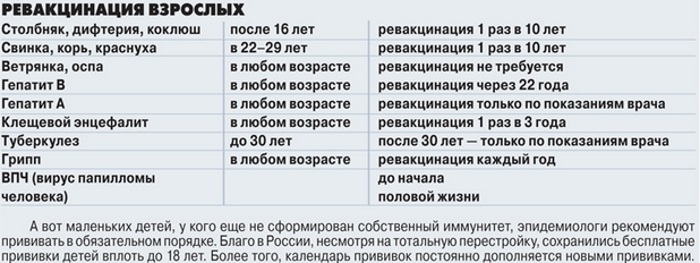
Vaccinations against tetanus and diphtheria are carried out after contacting the polyclinic at the place of residence and undergoing a general examination by a therapist. The vaccine itself does not cause side effects, especially when re-administered, and does not require preparation.
Funds
The main drugs for vaccination against diphtheria and tetanus contain human antibodies to the causative agents of these types of diseases. Bubo-kok, DTP-Hep B vaccine are used as the main drugs. These drugs are intended for intramuscular administration during routine vaccination.
Procedure step by step
Tetanus and diphtheria vaccinations do not require special training. To pass them, an adult needs to be healthy and not feel unwell on the day of vaccination. Only after a general examination and obtaining written consent for vaccination, the patient can be referred to the treatment room.
Vaccinations are administered by a healthcare professional who has special training in working with vaccines. The person skilled in the art knows the dosage, the method of vaccination and the rate of administration of the drug.
The patient is vaccinated as follows:
- The patient sits down or fits into the position indicated by the laboratory assistant and exposes the injection site.
- The vaccine is drawn into a syringe suitable for administration.
- Then the puncture site is treated with alcohol-containing drugs.
- The laboratory assistant makes a puncture and injects the vaccine into the muscle (thigh, buttock).
- Then the needle is removed and a swab soaked in alcohol is placed over the injection site.
- After a few seconds, the swab changes to a piece of clean cotton wool.
- The vaccine injection site should be clamped with your hand for 1-2 minutes. and the procedure is considered complete.
It is important to closely monitor the patient's condition after the vaccine has been administered. The vaccine itself takes root without complications, it is enough just not to wet the injection site during the day.
Contraindications
Vaccinations by age (a table of adult injections of which depends on the set of previously available vaccinations) against diphtheria and tetanus are not produced for all categories of people. All patients are examined prior to vaccination. During the examination, the doctor determines whether the patient is healthy and excludes possible contraindications.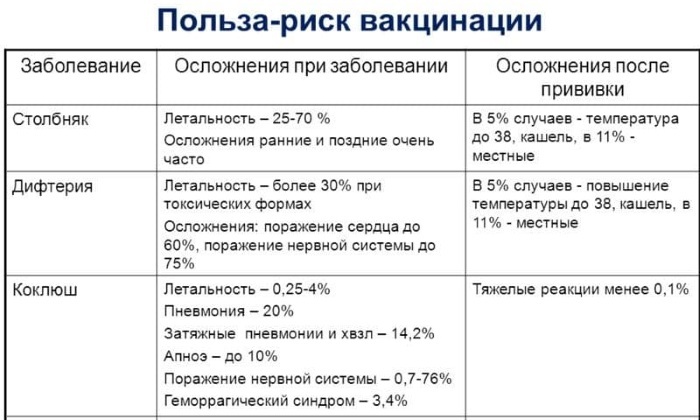
These include:
- allergic and anaphylactic reactions to protein;
- high fever;
- swelling at the site where the vaccine is to be injected;
- complications after a previous vaccination (fever, convulsions, collapse);
- allergy to the components of the drug;
- the presence of pronounced symptoms of the acute course of the disease;
- decreased immunity;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- neoplasms.
Possible complications
Vaccination against tetanus and diphtheria in adults by age, which is done in accordance with the vaccination table, can in rare cases manifest complications. The reaction to the vaccine can appear immediately or gradually progress over several days.
As complications after vaccinations against tetanus and diphtheria, there are:
- drop in immunity;
- redness or blue skin and swelling around the puncture;
- increased body temperature without additional symptoms;
- allergic reactions (rash, itching, ulcers);
- Quincke's edema;
- hives.
Vaccination against viral hepatitis B
Vaccination against viral hepatitis B is carried out once in childhood. If the patient has not been vaccinated earlier, vaccination can be carried out at the age of 18-55 years. Persons over 55 years old should not receive the vaccine due to the development of possible complications.
Funds
As a vaccine for vaccination against viral hepatitis B in Russia, antibodies are used from a person who has recovered from this disease. Currently used for injections: antihep, hepatect and bubo-kok.  The first 2 drugs are administered intravenously, and the last one is administered intramuscularly.
The first 2 drugs are administered intravenously, and the last one is administered intramuscularly.
Procedure step by step
Before vaccination, the patient undergoes a general examination and agrees to the procedure:
- The patient then sits down and exposes the arm above the elbow or thigh.
- The laboratory assistant uses a tourniquet to bandage the arm above the elbow, creating the desired level of blood pressure. In the case of intramuscular injection, the tourniquet is not applied.
- Then the site of the vaccine is moistened with alcohol and a puncture is made into a vein or muscle.
- The vaccine is introduced gradually.
- Then the syringe is removed, a cotton swab soaked in alcohol solution is simultaneously placed on the puncture site.
- After vaccination with intravenous drugs, the hand must be clamped in the elbow and held in this position for several minutes.
Contraindications
All categories of people can be vaccinated against viral hepatitis B, with the exception of adults:
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- having hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
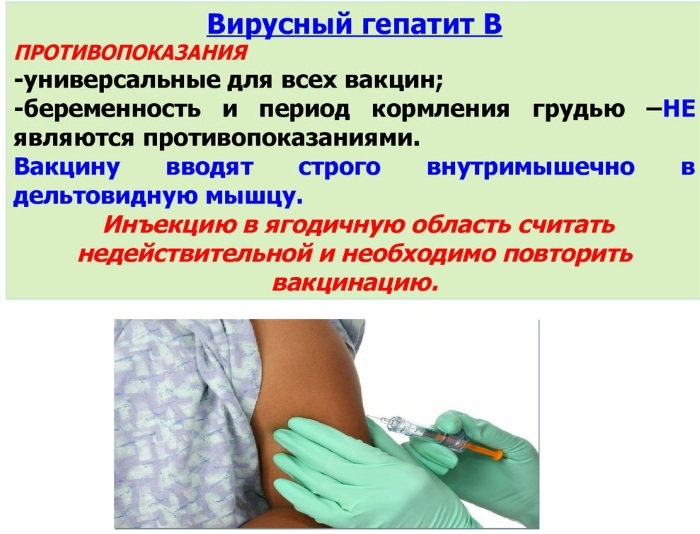
- with infectious and chronic diseases;
- with complications after a previous vaccination.
Possible complications
After the vaccine is given, redness and slight swelling may appear at the injection site.
In rare cases, patients develop:
- temperature increase;
- skin rash;
- cough, pneumonia.
Only with prolonged persistence of symptoms after vaccination against viral hepatitis B does the patient require treatment.
Rubella
Rubella is a complex disease with a number of complications. The rubella vaccine is given to children at 1 year old, and then repeated at 6 years old. With this introduction, the vaccine maintains immunity in a person to the disease throughout his life. Adults who have not been previously vaccinated or vaccinated 1 time, the vaccine is administered in the period of 18-25 years.
Funds
As preparations for the rubella vaccine, lyophilisate, rudivax, ervevax are used. The preparations contain the rubella virus alive in a weakened state, which allows the body to develop a sufficiently stable immunity to the disease.
The preparations contain the rubella virus alive in a weakened state, which allows the body to develop a sufficiently stable immunity to the disease.
Procedure step by step
Before the introduction of the vaccine, the state of human health must be checked.
After that, in the treatment room, the vaccination is done in the following order:
- First, the patient sits down and exposes the shoulder.
- The specialist dilutes the drug for injection and treats the injection site with an antiseptic.
- The vaccine is injected into the shoulder under the skin.
- Then the injection site is clamped with an alcohol-containing swab for several minutes.
Contraindications
The main contraindications for rubella vaccination include:
- allergies;
- infectious diseases;
- reduced immunity or infectious diseases that are difficult to carry before vaccination;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- malignant formations.
Possible complications
Rubella vaccines are generally well adapted by the human body.
After the administration of the vaccine, in some cases, patients observe:
- seals and redness at the puncture site;
- skin rash;
- arthralgia;
- arthritis or its exacerbation.
Against the flu
To create temporary immunity during the period of seasonal respiratory illness, patients are advised to use the influenza vaccine. After its introduction, adults do not get sick, or in case of infection, the disease passes quickly and gently, without complications.
Funds
Influvir, Sovigripp, Ultravac are used as drugs for influenza vaccination. The drugs contain a group of different types of influenza viruses, which are selected in the right combination, which helps to increase immunity to infections.
Procedure step by step
Flu drugs are given intramuscularly, most often in the thigh.
The procedure includes the following steps:
- preparation of the vaccine for administration (its dilution and set);
- patient preparation, skin treatment;
- drug administration.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to administer the vaccine only if:
- allergic reactions or strong post-vaccination reactions of the body to a similar drug;
- carrying a child;
- breastfeeding the baby.
Possible complications
Flu vaccines have almost no side effects.
However, in rare cases, they provoke:
- elevated temperature;
- sore throat and runny nose;
- headache;
- allergic reactions up to anaphylactic shock.
Measles
Measles is considered a childhood disease that is vaccinated at 6 months and then at 6 years of age. If a person has not been re-vaccinated or has not been vaccinated at all, the vaccine is given at the age of 18-35 years.
Funds
The drugs used for vaccination against measles are Ruvax, a live attenuated measles vaccine. The drugs include weakened strains of the virus that help build strong antibodies in the human body.
Procedure step by step
The measles drug should be diluted immediately before the procedure:
- Then the patient exposes the shoulder and the technician treats the skin with antiseptic agents.
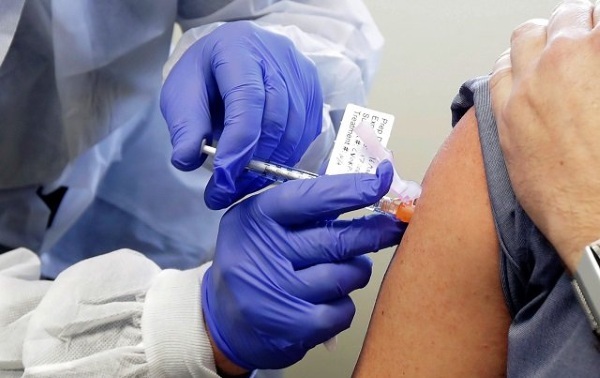
- The vaccine is then injected under the skin.
- The needle is removed and a cotton swab is placed in place of the vaccine.
Contraindications
The measles vaccine should not be administered in some cases:
- in the presence of chronic renal dysfunction;
- immunodeficiency;
- exacerbation of heart disease;
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Possible complications
Once administered, the measles vaccine is generally non-morbid.
In some patients, a few hours after vaccination, the following appears:
- increased body temperature;
- skin rashes on the body;
- compaction at the injection site.
Vaccinations by age against measles for adults, according to the approved vaccination table, are easily absorbed and do not require special treatment in case of complications. Any manifestations of vaccination go away on their own. During any course of the vaccination process, the patient develops persistent antibodies that will protect the body in the event of a possible outbreak of the disease.
Vaccination video
Komarovsky about vaccinations:
