Content
- General characteristics, advantages of the group of fluoroquinolones
- Mechanism of action
- Classification of fluoroquinolones
- Basic properties
- Groups of drugs, generations
- Spectrum of action
- Indications for use
- Interaction
- Possible side effects
- Special instructions for admission
- Video about fluoroquinolones
Fluoroquinolones are a group drugs that have high antimicrobial activity. These funds are of synthetic origin. During their existence, an extensive list of effective antibiotics has been created.
General characteristics, advantages of the group of fluoroquinolones
More than 60 years ago, scientists discovered that nalidixic acid is capable of destroying microbial cells. This served as the impetus for further study of the compound, and soon oxolinic acid, known to many, was synthesized from it. Its antimicrobial activity was 3 times stronger than that of its predecessor.
The experiments were not over at this point. Soon, scientists were able to discover compounds that, by chemical nature, were derivatives of 4-quinolone, containing a fluorine atom. Now they are known to mankind as fluoroquinolones. As it turned out, these compounds do not occur in nature, so they are all exclusively of synthetic origin.
Fluoroquinolones are actively used to treat many infectious diseases. In addition, these drugs have a number of advantages over other groups of antibiotics.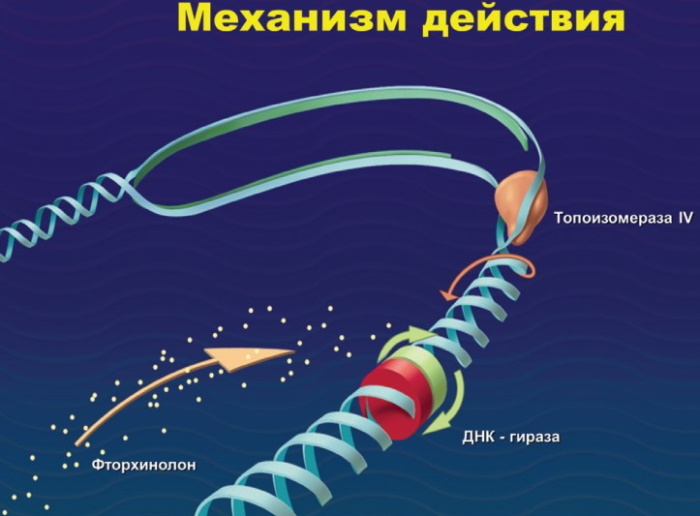
For example:
- A wide range of actions. Fluoroquinolones are capable of destroying both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, including multi-resistant strains of microorganisms. Thus, fluoroquinolones are effective even where many antibiotics are ineffective. The fact is that microbes are often able to develop resistance (immunity).
- A large list of drugs. At the moment, more than one generation of fluoroquinolones has been created. Each new class has improved characteristics than the previous one. The chemical structure of quinolones allows you to create more and more new variations of compounds, releasing more effective drugs on the pharmaceutical market.
- Extensive application experience. Since the use of drugs is counted for tens of years, mankind has significant experience in their use. More than one generation of people have been cured of bacterial infections by them, so doctors know a lot about the side effects and safety profile of fluoroquinolones.
- Lack of resistance in bacteria. A bacterial cell is capable of altering its genome in order to be immune to certain drugs. This is a natural process, and this is how the microbe tries to maintain its existence. Resistance most often develops in relation to tetracyclines, penicillins, and so on. Fluoroquinolones are less likely to cause resistance in microorganisms.
- Long period of elimination. Antibiotics of this group are excreted from the body for a long time (from 7 to 24 hours). This provides a higher therapeutic effect with minimal risk of side effects. Indeed, most fluoroquinolones have a therapeutic effect when dosed 1-2 times a day.
- Fluoroquinolones can be combined with most other drugs. It is very convenient when it is necessary to prescribe a complex treatment.
- The ability to penetrate into all organs and tissues of the body, which is important in the treatment of severe infections.
- Low risk of developing unwanted adverse reactions.
Mechanism of action
Fluoroquinolones, drugs and the list of antibiotics, on the basis of which is currently quite extensive, has 1 main mechanism of action.
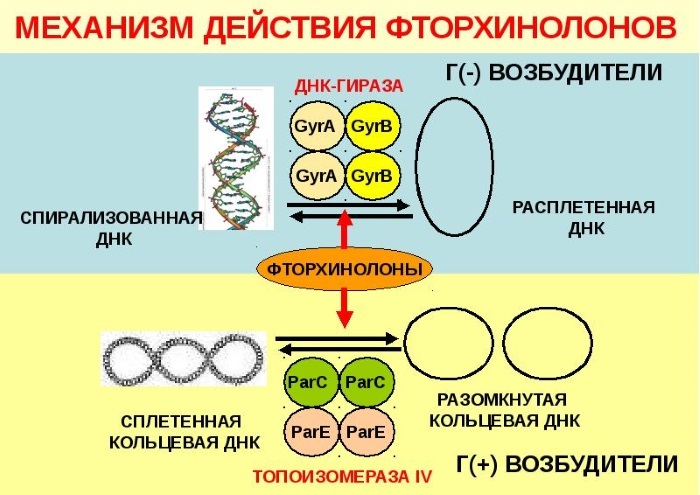
The antibiotic interferes with the production of 2 enzymes that are necessary for the existence of a bacterial cell.
These enzymes include:
- DNA gyrase;
- topoisomerase-4.
Thus, fluoroquinolones disrupt the process of bacterial DNA synthesis.
In addition, the mechanism of action of these drugs is due to the following effects:
- violation of the stability of the cell membrane;
- destruction of the RNA chain inside the microbial cell.
Thanks to this mechanism, drugs are able to destroy most pathogenic cells.
Classification of fluoroquinolones
This group of drugs has dozens of representatives. For this reason, there are as many as two classifications of fluoroquinolones.
By chemical structure (by the content of fluorine atoms):
- monofluoroquinolones;
- difluoroquinolones;
- trifluoroquinolones.
However, this system describes only those compounds that contain fluorine in their molecules.
Preparations of the fluoroquinolone group are also classified by generation. It is more complete and distributes funds to the groups to which they belong. It includes the entire list of antibiotics, regardless of the presence or absence of a fluorine atom in the molecule.

| Generation | Representatives |
| 1st | Nalidixic acid, oxolinic acid. |
| 2nd | Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin, Lomefloxacin, Ofloxacin, Pefloxacin. |
| 3rd | Sparfloxacin, Levofloxacin. |
| 4th | Moxifloxacin, Delafloxacin, Gemifloxacin. |
Basic properties
Fluoroquinolones have a number of characteristics:
- A wide range of antibacterial action.
- Bactericidal type of action.
- Beta-lactamase resistance.
- High antimicrobial activity.
- Slow habituation of microorganisms.
- High oral bioavailability.
- Duration of action is more than 12 hours.
- Low toxicity, good tolerance.
Groups of drugs, generations
Representatives of the 1st group served as the basis for the creation of all fluoroquinolones. Currently, they are practically not used. An exception is oxolinic ointment, which can be applied topically to prevent bacterial infections.
2nd generation is conventionally called gram-negative drugs. For the reason that they are mainly active against those microorganisms that have a negative Gram stain. However, representatives of this category can also be used against some gram-positive bacteria (staphylococcus, corynebacterium, Koch's bacillus).
2nd generation fluoroquinolones can be divided into 2 main groups.
Depending on their area of application:
- Systemic antibiotics. Can be used to treat infections of the respiratory tract, eyes, digestive system organs, skin and bone tissue. These include ciprofloxacin (Ciprolet), lomefloxacin (Lomflox), ofloxacin (in the form of tablets is produced under the name Ofloxacin, in the form of eye drops and eye ointment is called Floxal).
- Uroseptics. They are used to treat bacterial infections of the genitourinary system. Among them, Norfloxacin (the trade name of tablets for oral administration is Nolitsin, eye and ear drops are called Normax) and Pefloxacin (Abaktal) should be distinguished.
3rd generation drugs are actively used for respiratory infections (diseases of the upper respiratory tract). Unlike their predecessors, they are active against pneumococcus, chlamydia and mycoplasmosis. The main representatives of this class are sparfloxacin (Sparflo) and levofloxacin (Tavanic).
4th generation fluoroquinolones are the only representatives of which are active against anaerobic bacteria. These are the microorganisms that can exist in conditions without oxygen. As a rule, they are highly aggressive and cause severe disease (peritonitis, sepsis, osteomyelitis). These pathogens include the causative agent of tetanus, botulism, gas gangrene. The most popular representative of the 4th generation is Moxifloxacin (presented in the pharmacy as Avelox).
Spectrum of action
Fluoroquinolones, drugs and the list of antibiotics of which are numbered in dozens, have a very wide spectrum of action. A characteristic feature is that with each new generation this characteristic becomes even more extensive.
Preparations that do not contain a fluorine atom in their molecule are active mainly against gram-negative bacteria.
Such as:
- colibacillus;
- klebsiella;
- shigella;
- salmonella;
- enterobacteria;
- proteas;
- haemophilus influenzae;
- neisseria.
The spectrum of action of representatives of more modern generations (2,3,4) is significantly expanding.
For example, they become active against microorganisms such as:
- pseudomonas;
- pathogens of brucellosis, lyogenellosis and listeriosis;
- Pneumococcus;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma;
- tubercle bacillus.
It is worth highlighting moxifloxacin, which is active even against aggressive anaerobic bacteria.
Another feature of fluoroquinolones is that each generation is highly effective against those microbes that are resistant to the previous groups of drugs. For example, 3rd generation can cure infections that 2nd generation cannot cope with.
Indications for use
The most important use of these drugs in the treatment of nosocomial infections, as well as for the treatment of bacterial inflammation of the respiratory system and the genitourinary system during their severe treatment.
Often doctors prescribe drugs of the fluoroquinolone group for diagnoses such as:
- sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, gonorrhea, bacterial prostatitis);
- cystitis,
- pyelonephritis;
- pneumonia;
- bronchitis;
- typhoid fever;
- dysentery;
- salmonellosis;
- bacterial infections of the eyes and ears.
These drugs have proven their effectiveness in the treatment of more serious diseases, which have a high percentage of lethal outcomes. Such diseases include tuberculosis and anthrax.
It is worth noting that the choice of a drug can only be made by a doctor after a thorough examination and an accurate diagnosis. Self-administration and treatment with fluoroquinolones is strictly prohibited and can lead to complications of the patient's condition. The fact is that the definition of the treatment regimen depends on the characteristics of the patient (gender, age, chronic diseases), his diagnosis and the severity of the course of the disease.
Each drug of the fluoroquinolone group has its own characteristics and advantages:
- So, ciprofloxacin is active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, therefore, it is most often used in the complex treatment of tuberculosis.
- Ofloxacin is the most active drug among other representatives of the 2nd generation. But do not forget that generations 3 and 4 still have higher efficiency.
- Norfloxacin is often the drug of choice for the treatment of cystitis, pyelonephritis, and glomerulonephritis.
- Pefloxacin has the highest ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Therefore, in the form of injections, the drug can be used in the treatment of meningitis of bacterial etiology.
- Sparfloxacin has the longest half-life, therefore it is used only once a day, which is very convenient and reduces the
- Moxifloxacin is used more successfully than others for severe forms of bacterial infections, as well as for diseases of unknown etiology (when there is no culture analysis).
Interaction
Fluoroquinolones, drugs and the list of antibiotics of which include many representatives, are compatible with most other drugs. However, there are exceptions that you need to pay attention to before using these substances.
- Fluoroquinolones form chelate complexes that reduce their bioavailability with drugs such as antacids, medicines containing ions of magnesium, zinc, iron and bismuth, as well as vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and pefloxacin prevent the elimination of theophylline and caffeine, and increase their unwanted side reactions.
- With simultaneous use with NSAIDs, metronidazole and theobromine, the risk of developing adverse reactions from the central nervous system increases.
- Joint use with nitrofuran derivatives (furacillin, furazolidone) causes a decrease in the therapeutic effect of the latter.
- Fluoroquinolones of the 1st and 2nd generation, together with anticoagulants, increase the risk of bleeding. Therefore, if it is necessary to use blood-thinning drugs, their dosage should be adjusted in conjunction with the attending physician.
- Glucocorticosteroids, together with fluoroquinolones, can lead to tendon rupture. Especially in the elderly.
- The risk of kidney damage increases with the use of ciprofloxacin or norfloxacin with sodium bicarbonate, citrates and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (Brinzolamide, Dorzolamide, acetazolamide).
- The concentration of fluoroquinolones in the patient's blood may increase while taking cimetidine or azlocillin.
Possible side effects
Fluoroquinolones, drugs on the antibiotic list with minimal risk of side effects, can still cause them. In general, any antibacterial agents to one degree or another lead to the development of side symptoms from different body systems.
If we talk about fluoroquinolones, then most often they cause such undesirable effects as:
- pain, colic, heaviness in the abdomen;
- heartburn, nausea, vomiting;
- headaches, dizziness;
- insomnia;
- cramps in the calf muscles;
- myalgia (muscle pain);
- in people with epilepsy, an exacerbation of the condition and an increase in seizures are possible;
- heart palpitations (the fact is that fluoroquinolones cause prolongation of the QT interval on the electrokaryogram);
- dysfunction of the liver and kidneys (as there is an increase in hepatic transaminases, which indicates damage to hepatocytes). For this reason, doctors often prescribe an additional intake of hepatoprotectors to fluoroquinolones to protect the liver;
- fungal lesions on the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes, oral cavity.
- an increase in the degree of sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation. The fact is that ultraviolet light destroys fluoroquinolones, resulting in the formation of free radicals and damage to the skin. Therefore, during treatment with these drugs, it is important to avoid exposure to the sun or to use sunscreen. This is especially true for lomefloxacin and sparfloxacin;
- allergic reactions;
- increased risk of tendon rupture. Since the drugs suppress enzymes that are responsible for collagen synthesis. Elderly people over 65 are at risk.

However, despite the rather extensive list of side effects, fluoroquinolones are considered one of the safest classes of antibiotics.
Special instructions for admission
Fluoroquinolones, the drugs on the list of antibiotics with the highest safety profile, still have a list of special indications that you should pay attention to before starting treatment.
Although drugs are widely used in medical practice, there are still patients who cannot be prescribed them.
Fluoroquinolones are prohibited for use in the following cases:
- Children under 2 years of age. There are drugs contraindicated for up to 3 years. However, in pediatric practice, there are cases when it is necessary to use an antibiotic, despite contraindications. This can be done only in consultation with the doctor and under his strict supervision. It is the specialist who sets the dosage regimen individually for each child.
- Pregnancy at any time. There is no reliable data on the toxic effect of drugs on the fetus. However, nalidixic acid, which was used by expectant mothers, caused an increase in intracranial pressure in newborns.
- Lactation period. Small amounts of fluoroquinolones penetrate into breast milk, but there is evidence of the development of anemia in children whose mothers used antibiotics of this group during breastfeeding.
- The drugs are not recommended for adolescent children. This can presumably lead to damage to the musculoskeletal system. However, in exceptional cases, treatment with fluoroquinolones of this category of patients is permissible.
- Elderly people are prescribed drugs with extreme caution because of the risk of tendon rupture.
- Fluoroquinolones are also contraindicated in the presence of atherosclerotic plaques in the vessels of the brain.
- With diseases of the central nervous system, the risk of complications increases. The fact is that fluoroquinolones excite nerve endings, which can lead to a worsening of the course of Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, and cerebrovascular accidents.
- In the presence of intolerance to one or more of the components that make up the drug. Otherwise, an allergic reaction may develop. Each representative of this group of antibiotics has its own unique composition, you can get acquainted with it in detail in the instructions for use.
Fluoroquinolones are drugs that constitute an important component of modern antibiotic therapy. With each new generation, the list of indications for use is expanding, which confirms the relevance of this category of drugs. Do not forget about a number of contraindications and undesirable side reactions, so it is important to consult a doctor before using it.
Author: Olga Orlova
Video about fluoroquinolones
Basic pharmacology of fluoroquinolones: