Content
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Possible complications
- Training
- Procedure step by step
- Care procedures after
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Intravenous catheter placement video
Intravenous a catheter is a medical procedure, which provides for the introduction of a needle with special hoses and connectors into the cavity of the patient's peripheral vein. Catheterization of venous vessels makes it possible to get unhindered access to the general blood flow of the patient, saturate it with drugs and solutions necessary to maintain the stable vital activity of it organism.
This procedure is performed under sterile conditions in an inpatient department of a medical institution, and the procedure for its implementation is strictly regulated by the approved algorithm of actions of medical personnel.
All types of intravenous catheters connected to the patient's circulatory system require compliance with the rules of sanitary and hygienic care. There is no charge for venous catheterization in public hospitals. In private clinics, the cost of these manipulations is included in the total cost of the treatment process. The placement of an intravenous catheter requires high professional qualifications and extensive practical experience from medical personnel.
The incidence of complications from intravenous catheterization is about 15%. At the same time, 5% of patients experience mechanical damage to the blood vessels, 10% of patients develop infectious and inflammatory processes, and another 5% of patients are faced with various kinds of thrombotic complications.
In most clinical cases, the placement of an intravenous catheter is aimed at organizing unimpeded access to the general blood flow through the connection to the peripheral veins.
Indications
The algorithm of actions aimed at setting an intravenous catheter provides for strict adherence to the standards of absolute sterility.
Blood vessel catheterization is indicated in the following cases:
- the introduction of infusion drugs to patients who are not able to carry out their independent intake in tablet form;
- the therapeutic need for frequent intravenous administration of medications to patients with severe chronic diseases (for example, renal or hepatic failure, the presence of malignant neoplasms in the body);
- the urgent need for the implementation of the jet injection of antibacterial drugs with their instant delivery into the general bloodstream of the patient;
- taking venous blood for its laboratory examination for various parameters;
- ensuring unhindered access to the bloodstream in patients who are in severe condition, in need of urgent resuscitation measures using potent drugs;
- rehydration of the body after severe dehydration; electrolyte imbalance;
- fast organization of parenteral nutrition in relation to patients who are not able to carry out independent food intake.
Venous catheterization is indicated for patients who are scheduled for diagnostic examination by administering contrast agents with radiological properties. For example, to obtain more objective information during magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography.
Contraindications
Intravenous catheterization is contraindicated in the presence of the following health problems:
- damage to the skin, as well as subcutaneous fat in the area of the proposed puncture of the venous vessel;
- atrophic damage to muscle tissue;
- phlebitis of a vein, which must be catheterized.
Before deciding to use the intravenous catheterization method, the attending physician examines the patient's venous vessels for possible medical contraindications.
Possible complications
Insertion of an intravenous catheter (the algorithm of actions for installing this device is aimed at minimizing trauma to the blood vessel) can cause the following complications and negative consequences for the patient's body:
- infectious infection of the walls of the venous vessel, as well as the ingress of bacterial, viral or fungal microorganisms into the general bloodstream (a similar outcome is possible if the medical staff does not comply with the established norms sterility);

- perforation of a blood vessel and mechanical damage to its inner layer;
- the formation of thrombosis with further circulatory disorders;
- inflammation of the walls of the venous vessel;
- the development of side effects from drugs that are administered through an intravenous catheter.
Redness of the skin, swelling of epithelial tissues, swelling of the venous vessel, a burning sensation or acute pain in the puncture area indicates the development of complications of intravenous catheterization. In this case, the medical device must be removed from the cavity of the venous vessel, and the patient must be examined in detail.
Training
Intravenous catheter placement (manipulation algorithm established by the therapeutic protocol, is mandatory for the medical staff of the medical institution) requires the implementation of preparatory action. Before proceeding to the stage of catheterization, measures are taken to select a vein through which access to the general blood flow will be open.
In this case, the following criteria apply:
- it is preferable to use venous vessels that are more voluminous, elastic and as soft as possible to the touch, do not show signs of damage;
- first, a puncture of the distal vessels is performed;
- the introduction of the system's needle is best done inside the straight veins, which correspond to the length of the catheter itself.
Peripheral intravascular puncture catheters have different color shades due to differences in their length and lumen diameter. Correctly selected access to the vein is a guarantee of the success of the overall course of treatment.
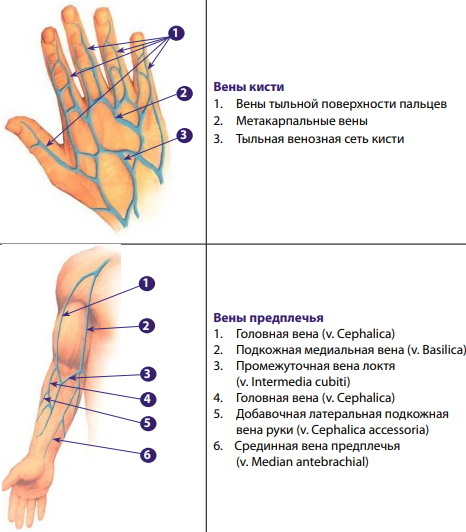
In the process of preparing a patient for intravenous catheterization, the opinion of the patient himself and the suitability of the venous vessel for its puncture should be taken into account. The room in which this type of therapeutic manipulation is carried out must be sterile. If necessary, before starting the intravenous catheterization procedure, the room is cleaned with disinfectants.
When preparing for intravenous catheterization, it is very important to select the correct catheter.
In this case, the doctor must be guided by the following criteria:
- the diameter of the inner lumen of the venous vessel;
- the required rate of supply of the therapeutic solution to the general circulatory system of the patient;
- the approximate period of time during which the catheter will be inside the patient's vein;
- biochemical properties of a medicinal solution introduced through an installed catheter.
Of great importance is the fact from which components the intravenous catheter is made. During preparation for the intravenous catheterization procedure, preference should be given to medical devices made on a polyurethane or Teflon base.
The use of catheters made from these materials reduces the risk of complications for the patient's body. With proper care, Teflon and polyurethane intravascular catheterization devices have a significantly longer service life.
Procedure step by step
The algorithm of actions for the installation of an intravenous catheter provides for the observance of the following rules of the instruction, which are mandatory for a medical worker of a medical institution:
- Wash your hands using warm water and soap.
- Collect a standard set of consumables required for intravenous catheterization:
- sterile cotton wool;
- ethanol;
- medical adhesive plaster;
- antiseptic wipes;
- trash tray;
- a syringe, inside which 10 ml of heparinized solution is collected;
- adhesive bandage;
- intravenous catheter complete with connecting tube;
- disposable sterile gloves;
- tourniquet for compression of blood vessels;
- sterile bandage;
- hydrogen peroxide with a concentration of 3%.

Preparation of the above consumables is carried out immediately before the intravenous catheterization procedure.
- Check the tightness and integrity of the package in which the intravenous catheter is stored.
- Make sure that a particular patient really needs an intravenous catheterization procedure.
- Provide quality lighting to the room.
- Help the patient to take the most comfortable position.
- Explain to the patient the essence of the procedure being performed, as well as its intended purpose.
- Prepare a container for disposal of consumables that will be used during the installation of an intravenous catheter.
- Select a healthy vessel for puncture.
- Apply a tourniquet 10-15 cm higher from the puncture site.

- Ask the patient to rhythmically squeeze and unclench his fingers to improve the filling of the venous vessel with blood.
- Select a suitable vein by palpation.
- Remove the harness.
- Choose the smallest IV catheter.
- Treat the surface of the hands with an antiseptic solution.
- Wear disposable sterile gloves.
- Reapply the tourniquet 10-15 cm higher from the intended catheter insertion site.
- Within 1 min. to treat the skin in the puncture area with an antiseptic.
- Wait for the skin surface to dry.
- Press on the vein with a finger of the upper limb 2-3 cm below the puncture site with a catheter needle.
- Remove the protective sheath from the IV device.
- The catheter, connected to the needle, is inserted into the cavity of the venous vessel at an angle of 15 degrees.
- Watch for the appearance of venous blood inside the indicator chamber.
- After the appearance of venous blood in the cavity of the indicator chamber, reduce the angle of inclination, and then insert the needle 2 mm deep into the vein.
- Fix the position of the stylet needle.
- The cannula is slowly moved to the very end from the needle into the vein cavity.
- Remove the harness.
- Pinch the vein to prevent blood loss.
- Remove the needle from the intravascular catheter.
- Remove the plug from the surface of the protective cover.
- Connect the fluid therapy system to the catheter.
- Secure the device with an adhesive bandage.
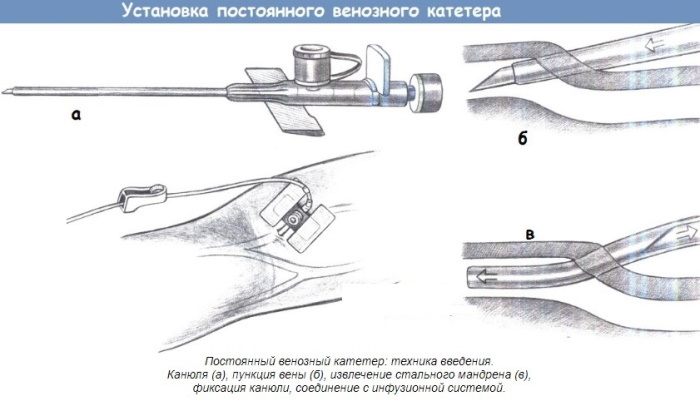
Intravenous catheter placement
The final stage of intravenous catheterization is the registration of the performed procedure in the patient's medical record and nursing journal. All consumables must be disposed of in a hygienic manner.
Care procedures after
The placement of an intravenous catheter (the algorithm of actions for puncture of the vessel is not violated under any circumstances) is only the first stage of infusion therapy. In order for the patient to be treated using the intravenous catheterization method without complications, it is necessary to follow the rules of sanitary and hygienic care, which are described in detail in the table below.
| Rule name | How to Perform Care After IV Catheterization |
| Prevention of infection | Each connector of the catheter is an open gate for the entry of infectious microorganisms. Contact with this device should be minimized. The intravenous catheter can only be touched with sterile disposable gloves, and all aseptic rules are followed. Otherwise, there is a high probability of infection of the venous vessel. |
| Replacing the plugs | Sterile IV catheter plugs should be changed as often as possible. It is strictly forbidden to use this element of the medical device, which was in non-sterile conditions. |
| Flushing the catheter | The intravenous catheter should be flushed with saline immediately after the next injection antibacterial agents, concentrated glucose-based medicines, preparations that contain blood components. |
| Prevention of thrombosis | In order to prevent the development of thrombosis, as well as prolong the service of the catheter itself, it is necessary to carry out additional washing during the daytime. These steps are performed between intravenous infusions. Saline is used as a flushing agent. After its introduction, a heparin solution is used in compliance with the percentage of 2500 IU of the chemical compound sodium heparin per 100 ml of saline.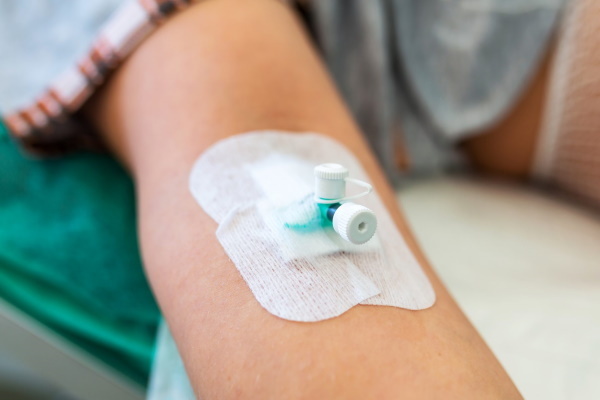
|
| Control over the condition of the fixation bandage | The medical staff caring for the patient should monitor the condition of the dressing, which acts as an additional fixator for the intravenous catheter. This consumable must be replaced in a timely manner before it becomes dirty. |
| Venous vessel monitoring | The puncture site of the blood vessel to which the intravenous catheter was connected should be regularly and thoroughly examined. This will allow early diagnosis of possible complications. In case of edema, redness of the skin surface, itching, painful sensations, changes in local temperature, it is necessary to remove the catheter from the cavity of the venous vessel. |
| Carrying out the correct replacement of the adhesive plaster | During a planned change of the fixing tape that holds the catheter, it is forbidden to use scissors. Compliance with this rule is aimed at preventing accidental cutting of the catheter, which then enters the vein. |
| Thrombophlebitis prevention | To ensure the prevention of the development of thrombophlebitis, a uniform layer of thrombolytic ointment is applied to the surface of the vein above the site of its puncture. The best drugs are Troxevasin, Lioton-1000 gel, as well as heparin-based medicines. |
| Control over unauthorized removal of the bandage | For pediatric patients and people who are in an inadequate condition, you need to pay more attention. Patients in this category can remove the fixation dressing, disrupting the position of the intravenous catheter. |
| Timely detection of side effects | Drugs that are injected into the patient's body through an intravenous catheter can cause adverse reactions in in the form of nausea, loss of consciousness, vomiting, fever, heart rhythm disturbances and frequency breathing. This symptomatology must be detected by a medical professional in a timely manner. A physician should be called for patients with signs of side effects. |
The patient's medical record records all the information regarding the volume of drugs that were introduced into his body through an intravenous catheter. The site of the catheterization should be changed every 2-3 days. This will minimize the risk of developing an infectious process.
Advantages and disadvantages
The placement of an intravenous catheter (the algorithm of actions for catheterization of patients should not be violated by junior medical personnel and doctors) has certain advantages and disadvantages.
The following advantages of this procedure are distinguished:
- significantly lower risk of pathogenic microorganisms entering the patient's general circulatory system;
- the possibility of prompt administration of drugs and infusion solutions necessary to stabilize the patient's condition;
- providing nutritional support for the patient's body;
- carrying out combination saturation of the patient's general blood flow with drugs with different pharmacological properties;
- round-the-clock monitoring of the patient's venous pressure indicators;
- saturation of the patient's body with all the necessary nutrients, minerals and vitamins in conditions where a person is not able to eat independently, is in a severe unconscious or comatose state.
Intravenous catheterization facilitates the work of the medical staff and also reduces the amount of pain for the patient. After installing a venous catheter, all injectable drugs enter the patient's body through this device. The nurse does not need to pierce the patient's vein every time with a disposable sterile syringe, which speeds up the therapeutic process and increases the level of comfort for the patient himself.
The disadvantages of venous catheterization include the following disadvantages of this procedure:
- during puncture of a blood vessel with a needle, mechanical damage to its walls in the form of perforation or rupture is possible;
- an installed venous catheter requires regular compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules for caring for its general condition;
- intravenous catheterization can only be performed by medical personnel who have undergone appropriate training courses, understands the complexity of this procedure, and also understands the risk of developing complications;
- there is always a risk of contamination of the venous vessel with a bacterial infection (even if the strict rules of sterility in medical practice periodically there are cases of the development of an infectious and inflammatory process that occurs after performing venous catheterization);
- inside the vein to which the catheter was connected, a blood clot may form, which can disrupt the general blood circulation in the body, cause ischemia of the vessel, as well as provoke a sudden onset of lethal outcome.
Venous catheterization is an important therapeutic procedure that can save the lives of critically ill patients. At the same time, this stage of the treatment process requires employees of the health care institution to perform adequate assessing all potential risks and complications that may develop after connecting the catheter to the general bloodstream sick.
Placement of a venous catheter is a complex and demanding medical procedure that involves strict adherence to the algorithm of actions to ensure unhindered access to the circulatory system sick.
The advantage of using this therapeutic technique is the ability to quickly administer a large amount of drugs with various therapeutic properties, stabilization of the general condition of severe sick. Intravenous catheterization is always accompanied by the risk of complications, most of which are associated with infectious invasion, mechanical damage to the vessel at the time of its puncture, as well as the formation blood clots.
Intravenous catheter placement video
Puncture and catheterization of a peripheral vein: