Content
- What is paresthesia in neurology
- Causes of paresthesia
- Radiculopathy
- Neuropathy
- Development stages and symptoms
- Which nerves are most often affected
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Medicines
- Folk remedies
- Physiotherapy
- Massage
- Exercise therapy
- Neurosurgical methods
- Consequences and complications, prognosis
- Video about paresthesia
In neurology term paresthesia used to describe discomfort in the limbs, neck and other parts of the body.
What is paresthesia in neurology
Paresthesia in neurology is a violation of the sensitivity of parts of the body (mainly limbs), in which signs of numbness develop.
Paresthesia can occur in any person, the duration and severity of symptoms may be different. This type of violation can occur once due to a slight violation of blood circulation in limbs (for example, if you lie on your hand for a long time), but if symptoms occur frequently, then you need to contact to the doctor.
Causes of paresthesia
Paresthesia can affect the upper and lower extremities, lips and tongue, neck, and each localization has its own causes of occurrence: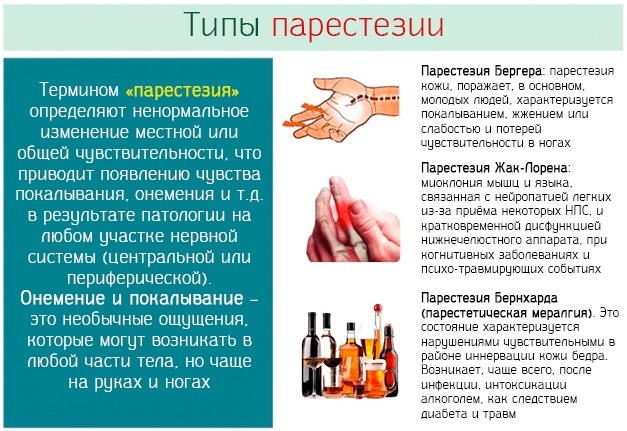
| Place of paresthesia | Causes |
| Face, lips and tongue |
|
| Upper limbs and neck | The main cause of impaired sensitivity of the neck and upper extremities is osteochondrosis or chondrosis of the cervical or thoracic spine. Also, the cause may be the presence of spinal injuries of these departments or damage to nearby muscles. Other causes of paresthesia include:
|
| Lower limbs | The reasons for impaired sensitivity of the lower extremities include:
|
The provoking factors for the development of paresthesia are: poisoning with toxic substances (medicinal or chemical, heavy metals) or their prolonged exposure, prolonged stress, as well as some degenerative-dystrophic disease.
Radiculopathy
Radiculopathy is a compression of the nerve roots due to a hernia or tumor of the intervertebral discs. The disease causes numbness of the limbs and the appearance of symptoms of paresthesia.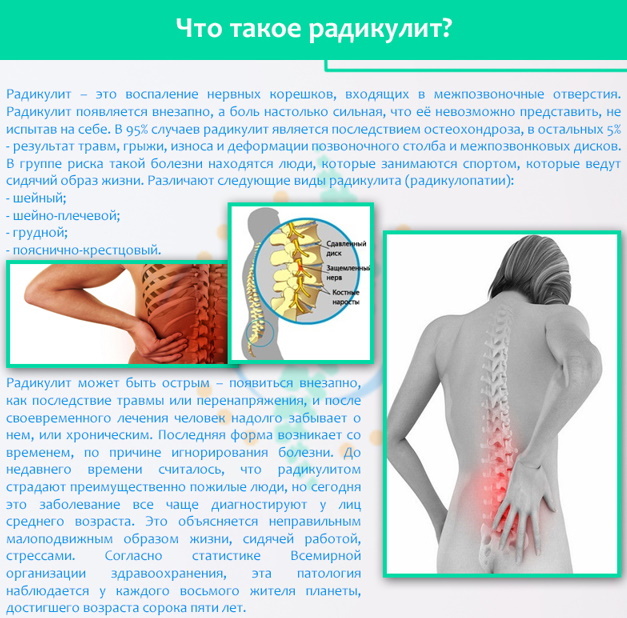
Depending on the level of the spine at which the nerve root is pinched, the following symptoms may occur:
- pain and numbness of the limbs;
- muscle weakness;
- stiffness in joints, muscles (especially in the morning, after sleep);
- pain in the affected area when coughing, sneezing.
With radiculopathy, painful sensations increase in the vertical position of the body and decrease in the horizontal one.
Neuropathy
Paresthesia is often a consequence of neuropathy - a pathology in which a nerve fiber is compressed or injured. With neuropathy, paresthesia occurs mainly in the lower extremities and, in the absence of diagnosis and therapy, leads to paresis (decreased muscle strength) of the legs. Less commonly, neuropathy manifests itself on the face or upper extremities.
The main causes of neuropathy are:
- diabetes;
- alcoholism (alcoholic neuropathy);
- neurological disorders:
- tumors of the brain or spinal cord and nearby nerves;
- connective tissue diseases;
- bone marrow lesions;
- deficiency of B vitamins and calcium;
- HIV, shingles, Lyme disease;
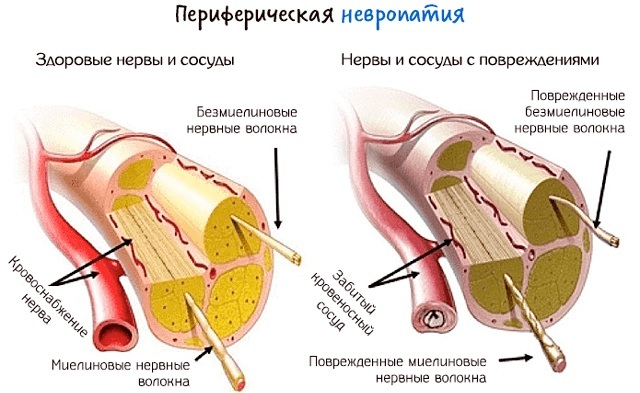
Peripheral neuropathy - an allergic reaction to drugs, food, insect bites.
Development stages and symptoms
Paresthesia is a pathology in neurology that has specific symptoms. In the early stages, periodic attacks occur, characterized by a feeling of numbness, tingling, or burning. They usually last a few seconds and go away on their own.
Later, attacks occur more often and have a longer duration, and the person begins to feel pain in the affected areas. Paresthesia can also develop at night, resulting in disturbed sleep.
At the most advanced stage, hair loss is observed in the affected area (due to a violation of blood supply and tissue nutrition). At night, the patient is disturbed by cramps, the fingers and toes are chilly and numb, in the morning it is possible to limit the mobility of the joints.
With cervical and facial paresthesias in a severe stage, headaches, dizziness, limitation of the mobility of the neck and shoulders are possible.
With a stroke, paresthesia in the upper extremities occurs suddenly and is characterized by the presence of symptoms on one side only. First, there is a burning sensation, then - limitation of the mobility of the hand. Also, with a stroke, the face and lips are often affected - burning and itching appear in the muscles.
Which nerves are most often affected
Hand paresthesia is most often associated with a pinched median nerve - this pathology is called Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. With paresthesia of the neck, back and legs, any nerves located in the zone of tissue nutritional disorders and squeezing of fibers by tumors or hernias can be damaged.
With paresthesia of the face and tongue, which develops as a result of the removal of wisdom teeth, more often than others, the mandibular and lingual nerves, which are connected, are damaged.
Diagnostics
With frequent symptoms of paresthesia, you need to consult a neurologist for diagnosis and treatment. The specialist talks with the patient and collects an anamnesis, which includes data on the general health of a person, chronic diseases, medication intake, lifestyle, professional activity. An examination and palpation of places where paresthesia occurs is also mandatory.
To diagnose the cause of paresthesia, a number of studies are used, including laboratory tests and instrumental methods.
If you suspect metabolic disorders that can cause paresthesia, the doctor prescribes a general and biochemical blood tests with the obligatory determination of the following indicators:
- urea;
- glucose;
- insulin;
- liver enzymes;
- glycated hemoglobin;
- calcium;
- vitamin B12;
- methylmalonic acid.
If there are signs of Raynaud's syndrome, a blood test for rheumatoid factor, specific antibodies and immunoglobulins is prescribed.
If the patient lives in an ecologically unfavorable area, works with heavy metals or work is associated with harmful working conditions, then it is necessary to donate blood to determine the concentration of toxic substances.
Instrumental diagnostic methods are used for suspected degenerative diseases of the spine, tumors of the brain and spinal cord, and stroke.
In this case, one or more of the studies may be prescribed:
- X-ray of a specific part of the spine;
- MRI of the spine and spinal cord;
- MRI of the brain.
Also, dopplerography of the vessels of the affected area is necessarily prescribed in order to assess the condition of the blood vessels of the limbs or neck.
Treatment
Paresthesia is often a consequence of a certain disease in neurology. When the cause is eliminated, paresthesia can be cured, in other cases (if it is impossible to cure or determine the cause of the pathology), the severity of symptoms can be reduced.
Medicines
Drug therapy for paresthesia depends on the specific disease. For example, diabetes mellitus requires drugs to regulate blood sugar levels, and osteochondrosis of the spine - chondroprotectors (drugs that strengthen the joints and protect them from destruction).
Almost all patients, regardless of the cause, have a deficiency of B vitamins. Therefore, they are prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes or drugs of group B to fill the deficit.
With severe paresthesia, pain relievers are prescribed (Diclofenac, Nimesil). To improve blood circulation, vasodilating drugs ("Cavinton", "Piracetam") are used. If the blood is thick, antiplatelet drugs are required (Aspirin, Clopidogrel).
Folk remedies
With the help of folk remedies, you can reduce the frequency and severity of attacks of paresthesia, improve blood circulation in the vessels and tissue nutrition.
Often, for paresthesias, therapeutic baths are used with the addition of fir essential oil (4-5 drops). The oil has an analgesic effect, relieves the manifestations of rheumatism, improves blood circulation in blood vessels and metabolism in tissues. The duration of the bath is 10-15 minutes, take every other day. Course - 10 procedures.
You can also prepare an ointment from 2 tbsp. l. camphor oil (you can take camphor ointment), 3 drops of eucalyptus oil and 1 tsp. l. honey.
Cooking process and method of application:
- Add eucalyptus oil to camphor oil, stir with a wooden stick or toothpick.
- Next, you need to add honey, mix everything again and place in a clean sealed container (preferably made of dark glass).
- The ointment must be insisted in a dark place for 24 hours, then stored in the refrigerator.
- The product should be applied in a thin layer to the places where paresthesia occurs, then wrap them with a cotton cloth. The compress must be kept on the skin for 30 minutes, then it must be washed off with cool water.
With osteochondrosis, rubbing with lilac tincture helps well. To prepare the product, it is required to place 200 g of lilac flowers in a container of dark glass, pour 500 ml of vodka and insist for 7 days in a dark cool place. After that, the tincture must be filtered and rubbed into the affected areas 2-3 times a day. The procedure helps to improve the mobility of joints and blood supply to tissues, thereby reducing the severity of the manifestations of paresthesia.
Contrast baths are also useful to improve vascular and skin permeability.

They are prepared as follows:
- You will need 2 bowls. One should be filled with hot water (but not boiling water, the temperature should be in the range of 60-70 ° C). It is required to pour cold (but not ice-cold) water into another container.
- Next, you need to alternately lower your hands in cold or hot water. You need to start with hot water. In each bowl, hands should be held for 5-7 seconds.
- The duration of the procedure must be increased each time. You need to start with 1 minute, and at the end of the course, bring the duration to 5 minutes. The course is 10-12 procedures.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods have analgesic, antispasmodic and vasodilating effects. With their help, you can eliminate the symptoms of paresthesia and prevent their further occurrence.
The choice of a specific method of physiotherapy depends on the cause of the appearance of paresthesia:
| Disease | Method |
| Diabetes | Electrophoresis with zinc for the iliac region, with calcium for the collar area. |
| Osteochondrosis | Electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, mud therapy, paraffin applications, diadynamic therapy (DDT), acupuncture. |
| Raynaud's syndrome | Paraffin, mud, ozokerite applications, DDT, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis with antispasmodics, acupuncture. |
| Tunnel Syndrome | Paraffin baths, electrophoresis, magnetotherapy. |
| Multiple sclerosis | Magnetotherapy, laser therapy, electrosleep, acupuncture. |
Additionally, therapeutic baths are shown with the addition of mineral complexes or medicinal substances. They have a tonic or relaxing effect (depending on the type of bath), dilate blood vessels and improve blood circulation, and have a general strengthening effect.
Physiotherapy is prescribed in a course of 10-20 procedures, the duration of the procedures depends on the specific method. Chronic paresthesia requires 1 to 3 courses of treatment per year. With a stroke, physiotherapy is contraindicated in the acute phase of the disease and for several weeks after the onset of symptoms - therapy is allowed only during the rehabilitation period.
Massage
Massage helps to relieve muscle tension, improve blood flow to tissues. It is recommended to take medical massage courses 1-2 times a year.
For osteochondrosis and other degenerative diseases of the spinal column, massage of the back and collar zone is prescribed. If a burning sensation and tingling sensation occurs in the upper extremities, massage of the collar zone, back and hands is prescribed; in the lower extremities - the lumbar region, legs and feet.
With paresthesia of the lips, tongue, massage of the face, head and collar zone is prescribed.
With periodic attacks, you can perform light self-massage of the affected area. It is recommended to use olive oil heated in a water bath. It is required to apply it to the affected area and massage this place with gentle circular movements for 5 minutes.
Exercise therapy
Physiotherapy is aimed at strengthening muscles and relieving tension from them, improving the mobility of joints and vertebrae, increasing blood circulation in tissues and eliminating pain.
For different forms of paresthesia, certain types of exercise therapy are used. Patients do the exercises either in the hospital under the supervision of an instructor or at home. Gymnastics can be performed both in courses and daily.
Neurosurgical methods
Paresthesia is a pathology in neurology that is treated mainly by the conservative methods indicated above.
In some situations, surgical intervention is necessary:
- ineffectiveness of conservative therapy;
- strong compression of nerve roots or fibers by tumors;
- progression of a tumor of the spinal cord or brain;
- the last stages of an intervertebral hernia.
Surgical treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of paresthesia, restoring normal tissue blood supply.
Consequences and complications, prognosis
Paresthesia is both temporary and permanent pathology in neurology. Temporary paresthesia resulting from a single deterioration in the blood supply to the tissues disappears on its own in a few minutes.
The success of the treatment of frequently occurring paresthesias depends on the cause of the pathology and its severity. In some diseases, it is possible to completely eliminate paresthesias, in some, only to reduce the frequency and strength of their occurrence.
If paresthesia is a consequence of a stroke, then the chance of complete restoration of limb mobility is about 20%. With multiple sclerosis, the most favorable outcome is possible in female patients, with a small number of body lesions and with the onset of morbidity up to 25 years.
Periodic paresthesias in the absence of therapy can lead to paralysis, numbness and atrophy of the limbs due to impaired blood supply to the tissues.
Paresthesia is a dangerous neurological symptom that is most often the result of another serious illness. With frequent numbness of body parts, a visit to a neurologist is required.
Video about paresthesia
Numbness and paresthesia of the legs:



