Content
- Classification of deformities of the gallbladder
- Causes of the disease in an adult
- Symptoms
- What is the danger of the disease, complications
- Diagnostics
- Drug treatment
- Folk remedies
- Diet for deformation of the gallbladder
- Surgery
- Forecast
- Video about deformity of the gallbladder
Pathology of the gallbladder in an adult, changes in the normal form of an organ are called. They can be congenital or acquired, arising from various reasons. Many deformities can be cured - with medication, surgery. Additionally, you must adhere to a diet. In the absence of complications, the prognosis is most often favorable.
Classification of deformities of the gallbladder
Anatomically, the gallbladder is divided into 3 parts - the body, the fundus and the cervical region.
Deformation can affect only one area or several at once:
- Multiple. In this case, there is a deformation of the organ in several places at once.
- Labile. These are temporary changes that go away on their own and do not require treatment.
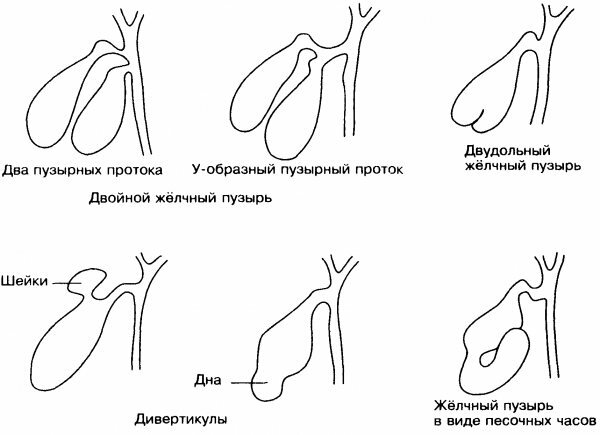
- Folded bladder (with constrictions and kinks). The organ takes on the appearance of a cone-shaped (Phrygian) cap and a tilted or curved apex. The deformation is divided into two types of bending - between the bottom and the body (retroserous) and between the funnel and the body (serous).
- "Hourglass". This is a type of "Phrygian cap" of the serous type, but in a more pronounced version. However, it is rarely acquired, more often it refers to congenital.
- Deformation of the neck. It often occurs against the background of a sluggish inflammation.
- S-shaped. In this case, a double bend of the organ is observed. But in adults it is rarely diagnosed.
- Deformation of the walls of the bubble. It develops due to chronic cholecystitis or adhesions.
- Contour. The outline of the organ changes due to impaired excretion of bile or chronic inflammation.
- Deformation of the cystic duct and artery (annular, short).
- Sinuses of Rokitansky-Ashoff. These are hernia-like protrusions of the bladder membrane with an increase in pressure in the organ.
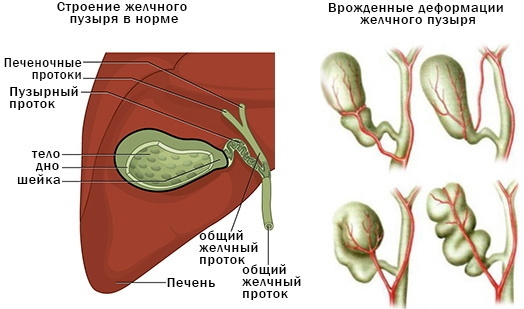
Position classification:
- Intrahepatic. The organ is in the hepatic parenchyma or is located on the right in the iliac region.
- Inversion. The organ is located in the middle of the body or on the left under the ribs.
- Rotation or rotation.
- Interposition. The organ does not have a common duct with the liver.
- Projection of the hepatic gate. At this point, the bladder passes into the main bile duct.
Classification of the rarest anomalies:
- Extra bubble. He is rarely diagnosed. It forms in the pocket of the main bile duct and becomes an independent organ.
- Agenesis. In this case, the bubble is absent, and bile accumulates in the common channel.
- Congenital diverticulum. The disease manifests itself with age. The muscle layer is deformed, the walls bulge. Bile stagnation gradually develops, which provokes inflammation, the formation of calculi and leads to calculous cholecystitis.
- Bipartite bubble. Two organs appear with a common duct.
Deformation of the gallbladder
Deformation of the gallbladder can be mild, mild or pronounced, complicated and uncomplicated. Classification by organ size - giant or underdevelopment.
Causes of the disease in an adult
Deformation of the gallbladder in an adult is a change in the normal shape of an organ. Most often, kinks, partitions are diagnosed. The bladder can be S-shaped, hook-shaped, rotor-shaped. Sometimes there is an organ in the form of a bull's horn or a Phrygian cap.
The cause of congenital deformities is trauma, smoking, drinking alcohol while carrying a child. Sometimes pathology is formed due to excessive physical activity or a hereditary predisposition.
The causes of organ deformities that occur in adults are:
- dyskinesia of the bile ducts;
- adhesions;
- chronic inflammation of the biliary tract;
- neoplasms (benign, cancerous);
- calculi in the ducts or gallbladder;
- weakening of the diaphragm;
- alternation of rigid, strict diets with gluttony;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- frequent overeating;
- age-related changes when organ prolapse, surgery, abdominal hernia are detected;
- labile changes (short-term) occurs due to wearing weights, heavy physical exertion;
- cholecystitis causes changes in the bladder neck;
- prolapse of organs;
- sclerotic changes;
- internal inflammation.
Deformation of the gallbladder appears due to Botkin's disease, due to malignant processes in adults.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the speed and stage of the pathological process. If changes occur suddenly, then this is accompanied by severe pain in the right hypochondrium.
Additionally, other symptoms appear:
- an increase in temperature;
- bouts of nausea;
- heartburn;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- yellowness of mucous membranes and skin;
- flatulence;
- decreased appetite or it completely disappears;
- pain on palpation;

- violation of the stool;
- yellow coating on the tongue;
- discoloration of feces;
- decrease in body weight.
With a gradual deformation of the gallbladder, there is a constant severity in the right hypochondrium, dyspeptic disorders, burning pain in the small intestine. Appetite disappears, feces become discolored. Fat fragments appear in it.
Symptoms also depend on pathological changes:
- The kink located between the bottom and the body of the organ. This is accompanied by nausea, severe sweating, acute pain in the right hypochondrium, which radiates under the shoulder blades. Sometimes there is weight loss, discoloration of the skin of the face.
- Multiple bends, when the shape of the organ is violated in several areas at once. This deformation is rare. The size of the bladder increases, the adhesion process develops, calculous cholecystitis, the blood flow in the liver is disturbed. All this is accompanied by severe pain, dyspepsia.
- With deformation of the neck, inflammation affects the outer walls of the organ. As a result, adhesions appear, which cause changes in the organ, indigestion.
A temporary change (labile deformity) is asymptomatic. Sometimes there is an unpleasant belching, headaches, severe fatigue. Soreness in the right hypochondrium appears after fatty, spicy food.
What is the danger of the disease, complications
Deformation of the gallbladder in an adult can have serious consequences. If, due to changes, bile does not come out completely, part of it accumulates in the organ. This is fraught with the development of inflammation and the subsequent formation of stones. Congestion causes folds and folds in the organ.
Twisting or bending completely provokes circulatory disorders. Gradually, it turns into tissue necrosis, a breakthrough of the walls of the organ, the exit of bile into the peritoneum. In the worst case, when it cannot leave the bladder due to the kink of the neck, an organ rupture may occur. Then bile will enter the abdominal cavity, intoxication will begin, the patient dies.
The most serious complication is necrosis of the bladder neck due to prolonged deformation. The result is tissue decomposition. Bile enters the abdominal cavity. After that, peritonitis develops, and without urgent medical care, the patient will die.
Diagnostics
The main method for diagnosing bladder deformation is ultrasound. Since the method is safe, pregnant women can also be examined using ultrasound. When detecting deformities, ultrasound is more informative than computed tomography. Most pathological changes cannot be detected using CT.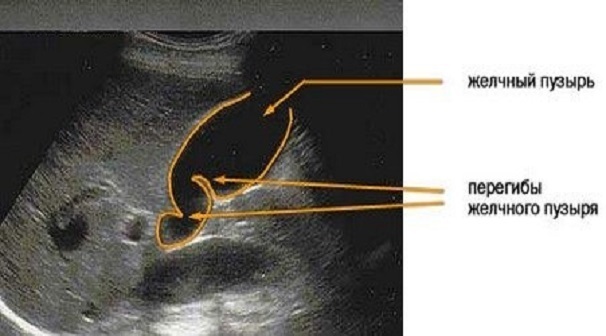
The ultrasound is performed in different projections to detect all the folds. During the examination, the liver and its ducts are additionally evaluated. If abnormalities are found, then the patient is sent for dynamic cholecystography.
Drug treatment
Deformation of the gallbladder in an adult in most cases requires drug treatment, especially if the disease is accompanied by painful symptoms. Often one course of therapy is not enough, and another 2-3 are prescribed for an additional 10-14 days. Treatment is aimed at restoring normal bile flow, relieving pain and inflammation. Complex therapy, several drugs are prescribed at once.
| Drug category | Examples of medicines | Therapeutic action |
| Analgesics and antispasmodics |
|
Relieve spasms and pain or reduce the severity of symptoms. With an exacerbation, drugs are administered intramuscularly. If stones are found in the gallbladder or with colic, an injection of "Atropine sulfate" 0.1% is given, patients in serious condition are prescribed Tramadol. |
| Antibacterial |
|
They use drugs of a wide spectrum of action that act immediately on many pathogenic bacteria |
| Probiotics |
|
Necessary to restore the microflora of the stomach, normal functioning of the digestive system. Probiotics are prescribed both separately and necessarily in conjunction with antibiotics. |
| Choleretic |
|
The drugs improve the excretion of bile. They are given after the stage of exacerbation and treatment with antibiotics, but in the absence of calculi in the gallbladder. |
| Vitamin complexes |
|
Replenish the lack of vitamins and minerals, strengthen the immune system. As a result, the body copes with the disease faster and more efficiently. |
If poisoning of the body has begun, detoxification therapy is performed. Additionally, physiotherapy procedures can be prescribed to alleviate the patient's condition. Severe pain is relieved by electrophoresis with novocaine. Ultrasound, exercise therapy, abdominal massage can also be prescribed. This helps to reduce the risk of stone formation and makes it easier for bile to flow out.
Folk remedies
Sometimes deformities can be treated with folk remedies. But before that, you need to consult a doctor. Perhaps traditional methods need to be supplemented with medication. Mostly herbs are used, which have a calming, choleretic, anti-inflammatory effect.
Folk recipes:
- Take 3 hours. l. chopped buckthorn, sage, mint and marshmallow. Add 1 tsp. l. cumin and the mixture are poured into a thermos. Pour 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 2-3 hours. Drink after dinner, 300 ml each.
- Take 3 hours. l. chamomile, mint and lemon balm. Pour the mixture into a thermos, pour 1 liter of boiling water. Insist for an hour, then drink 3 times during the day.
- Take 3 tsp. l. St. John's wort, 1.5 tsp l. chopped celandine and 2 tsp. l. mint and buckthorn. The mixture is poured into a thermos and brewed as in the previous version, and the scheme of use is similar.
- If, in addition to deformation, stones are found or indigestion is observed, then a collection of chamomile, fennel, buckthorn is prepared (all 1 tsp. L.) and bitter wormwood, mint, immortelle, yarrow (all 2 tsp. l.). Pour a mixture of 1 liter of boiling water, insist 2 hours. Then they drink 2 times a day, for 30 minutes. before meals.
- With acute cholecystitis, you can daily drink tea with mint, madder or dandelion root, crushed buckthorn bark.
- A drink made from mint with celandine or St. John's wort with tansy helps soothe irritation in the gallbladder and reduce pain.

Folk remedies do not give a quick result. The minimum course of such treatment is 2 months. It should be without gaps, therapy cannot be interrupted.
Diet for deformation of the gallbladder
In case of deformation of the gallbladder, it is necessary to follow a therapeutic diet - usually this is table number 5. From bread, you can only eat rye and whole grain, in small quantities. It is better to exclude pasta, as a last resort, choose from durum wheat. Any fresh baked goods and pastries are prohibited.
All fatty, fried and spicy foods are excluded from the diet. Salt addition is reduced to a minimum, sugar can be replaced with honey. Soups are prepared in a weak, low-fat broth with cereals, without meat. Onions, garlic, horseradish, radishes, turnips and egg yolks should not be added to dishes. Pureed soups are preferred, and porridge should be well boiled.
From the second courses you can prepare vegetable and fruit salads, vinaigrette, stewed vegetables. Low-fat dietary meat and fish, unsalted and low-fat cheese are allowed. Any canned food, pickles, smoked meats are prohibited. By-products and caviar are also excluded. If you cook meat or fish, they are finely chopped, but it is preferable to use it in the form of minced meat - for meatballs, cutlets, cabbage rolls, stuffed peppers.
Of eggs, only proteins are allowed - boiled or in the form of an omelet. Fermented milk products should be included in the diet daily. Lentils, peas, and beans are excluded from legumes. Fruits and berries are chosen sweet, sour - not. It will be useful to drink a glass of dried fruit compote daily. Season salads only with vegetable oil or low-fat sour cream, and mayonnaise, ketchups and sauces are prohibited.
Food can only be baked in the oven, stewed, boiled or steamed. All carbonated drinks, alcohol, coffee, kvass are excluded from the menu. You need to eat 5-6 times a day, in small portions (3 main and 2 snacks). The last time they eat is 3-4 hours before bedtime, no later than 21:00. Every day you need to drink 2.5 liters of still water. You can not overeat or starve - this negatively affects the gallbladder.
Surgery
Deformation of the gallbladder in an adult is first treated with medication. In the absence of the effectiveness of conservative therapy, a surgical operation is prescribed. In this case, the gallbladder is completely removed. There are two types of operations. The cavity is performed less often, since it is characterized by high tissue trauma, long-term recovery.
Most often, the gallbladder is removed using laparoscopy. It is safe, low-traumatic and highly effective. Instead of large incisions, multiple punctures are made in the abdomen. Instruments are introduced into them, one of which has a mini-camera. As a result, the doctor sees what manipulations he is performing.
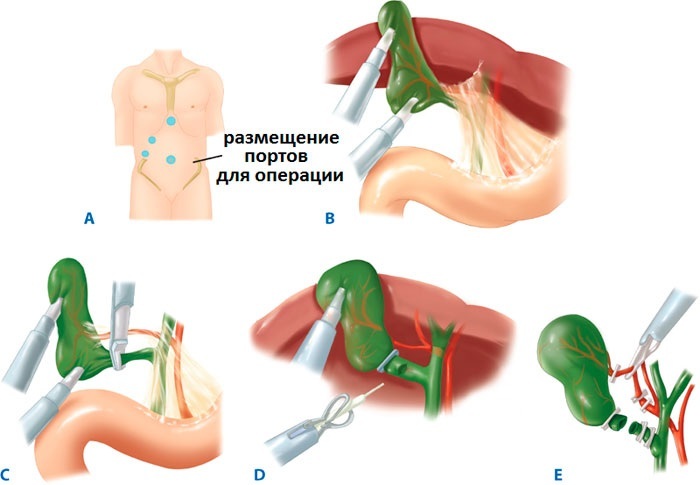
The gallbladder is removed, the bleeding of damaged tissues is immediately stopped. Then the instruments are removed and the punctures are sutured. The operation is performed under anesthesia and takes much less time than an abdominal one. After laparoscopy, the patient remains in the hospital for 3-5 days.
This is necessary for safety net - in case of complications, especially in patients with diabetes mellitus, as their wounds heal longer and with difficulty. Then the operated person must strictly adhere to the diet for at least 3 months. After that, they gradually switch to normal food. But doctors still recommend eliminating fatty, fried and spicy foods from the diet.
Forecast
Most of the detected deformities of the gallbladder can be successfully treated. This helps to restore the normal functioning of the organ, to prevent the development of complications and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. If pathological changes are detected on time, and the patient follows a diet, then complete recovery occurs in 95 percent of cases - after 3-6 months of course treatment.
An unfavorable prognosis only with complete stagnation of bile. Then the risk of bladder rupture increases. As a result, bile flows into the abdominal cavity, inflammation, infection begins, which can be fatal. Only an urgent operation can save a person. Open perforations result in death of the patient in 30% of cases.
Deformities of the gallbladder do not always require treatment. Without exacerbations and when this does not negatively affect the work of the organ or the health of an adult patient, he is under regular observation under the control of ultrasound, must follow a diet. Some deformations disappear on their own. At the slightest change for the worse, treatment is prescribed.
Video about deformity of the gallbladder
Deformation, kink of the gallbladder: